The More You Eat, The Less Your Weight- Nutritional Basis for Treatment of Obesity
Emil Mukhamejanov*, Marina Balabekova and Gulgul Kairanbayeva
JSC National Medical University named after S.Asfendiarov, Kazakhstan
Submission: July 21, 2019; Published: August 21, 2019
*Corresponding author: Emil Mukhamejanov, JSC National Medical University named after S.Asfendiarov, Almaty 050000 st Tole Bi 88, Kazakhstan
How to cite this article: Emil M, Marina B, Gulgul K. The More You Eat, The Less Your Weight-Nutritional Basis for Treatment of Obesity. Nutri Food Sci Int J. 2019. 9(2): 555760. DOI:10.19080/NFSIJ.2019.09.555760.
Review
Obesity is an energy imbalance, which can be associated not only with a simple imbalance between consumption of calories and their burning on physical activity, but also as a result of an imbalance in the processes of energy production and utilization. Body weight is an important element of our health, therefore both regulatory (neuro-hormonal) and metabolic systems are involved in the regulation of its homeostasis. In the present report discusses the metabolic systems of energy homeostasis regulating protein synthesis process, heat production and gluconeogenesis process. They are involved in energy balance maintaining which allow body weight saving on a wide range of incoming calories. 3 ATP molecules are consumed for the synthesis of a peptide bond, and when it is hydrolyzed, only 1 ATP is recovered (a deficiency of 2 ATP for each peptide bond). Heat production is just the energy dispersion in the heat form and the more active it is, the more there is a blank combustion of food calories. With gluconeogenesis, 6 ATP molecules are expended on one glucose molecule synthesis, by glycolysis (the inverse conversion of glucose to pyruvate), only 2 ATP is released (4 ATP deficiency). Therefore, the more intensively these processes, the higher the energy deficiency and the less stored food calories. In other words, the better ensure the operation of these systems with substrates and co-factors for its activity, the higher the energy deficiency, the other way the more you eat, the less your weight.
All technology for the treatment of obesity are aimed at reducing intake of calories and increasing their outtake. But such a simple and clear principle stalled the problem. Man is a weak creature and wants to eat and lie down on the sofa, and therefore the number of obese people is constantly increasing, despite the number of new technological developments that promise a solution to the problem, for now we are losing the battle with obesity [1]. It is necessary to look for other approaches.
Obesity refers to a metabolic disease and primarily energy homeostasis disorder. The main energy source is glucose. This is due to the fact that the brain and hemic cells exclusively use glucose as an energy source. Therefore, when the concentration of glucose (blood sugar) is twice lower than the norm, insufficient energy enters the brain and it is shut down (instant fainting), and after five minutes death of brain cells and then death, therefore maintaining glucose homeostasis is an essential aspect of life processes.
Based on carbon skeleton transportation of organic compounds and interconnection phases between the processes of formation and utilization of ATP energy at different body endowments in energy (the nutrition - fast cycle), we developed a metabolic model of the interrelation between protein, fat and carbohydrates (Figure 1).
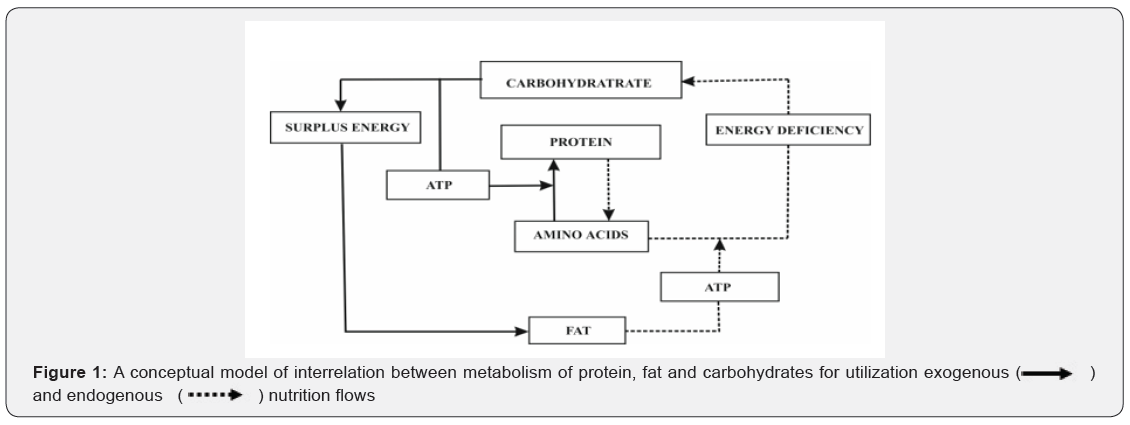
As can be seen from the model, with a decrease in the diet of carbohydrates and proteins, energy and substrate maintenance of the protein synthesis process is reduced, which contributes to the development of various functional disorders that are well studied in the prolonged fasting dynamics.
The intensity of the synthesis processes and protein degradation largely determines human health [2]. Regulation of protein homeostasis in the cell is the basis of the health of the whole body. Homeostasis is regulated at different levels and its violation leads to the development of cell dysfunction and, as a result, to diseases [2].
When the need for glucose increases, for example, during physical activity to maintain glucose homeostasis, the process of its endogenous synthesis (gluconeogenesis) increases to maintain glucose homeostasis, but functional proteins are used as a substrate, which leads to the development of various functional disorders. Therefore, all regimen technology and increasing physical activity lead to a decrease in protein synthesis or an increase in its catabolism, and therefore may lead to health impairment, especially in existing functional disorders. After of any reduce body weight technology cessation, the restoration of functional proteins is required, but this results in the return of lost body weight, and due to functional disorders, that have occurred, this return may be deplorable or the body weight will exceed the initial value. In this regard, it is necessary to develop technologies to prevent the loss of functional proteins and especially muscle proteins, which constitute half of all lean body weight [3].
An adequate intake of protein is needed in an amount of 1g/kg bw/d to muscle mass maintaining [4]. The years go by men decrease testosterone levels, and women have estrogen, which is largely responsible for the intensity of protein synthesis [5], but according to WHO recommendations, older people are recommended to reduce protein intake [6]. As a physical activity, it is better to use resistant physical activity, which exhibits a high anabolic effect and therefore contributes to a better preservation of muscle mass [7]. The use of anabolic amino acids, in particular leucine, should be recommended [8]. (B, D) Vitamins and (Ca, Mg) microelements improve protein synthesis [9], for this reason, it is advisable to use them in body weight control technology. In a pinch, the intake of testosterone and estrogen is recommended.
In the energy deficit phase, it is healthy to use musclemass technology. We have developed a specialized foodstuff, which included food compounds (Jerusalem artichoke, palm oil), which contributes to the maintenance of gluconeogenesis. This, on the one hand, prevents the use of muscle proteins for these purposes and, on the other hand, they do not release insulin hormone or decrease in performance capacity (British patent GB2496119 dated 01.22.2014).
Within this framework, the model we proposed allows for a new approach to the development of technologies based on the principle of preserving the soft lean mass in the nutrition /fasting cycle.
It is well known that with excessive consumption of food increases heat production [10]. This means that an organism tries to regulate the energy balance by “dropping” the excess energy flow by separating respiration from phosphorylation. At that, the energy of chemical bonds of organic compounds is not for ATP formation, but heat. Vegetable fat and cod liver oil increase the effect of dissociation, especially short-chain fatty acids [11], and there is a decrease in body weight when they are taken. In practice, the technologies for increasing heat production are widely used — thermo-belts, saunas. There are a number of pharmacological medicines that increase heat production (thyroxin, ephedrine). Although it is possible to simply burn organic compounds when they are taken, side effects occur, in particular, ATP deficiency state may occur in cardiac muscle function.
The one peptide bond formation (a compound of two amino acids) consumes 3 ATP (charge for accuracy and speed). The average protein contains about 100 peptide bonds, thousands of proteins are produced per day, so protein synthesis is the most energy-intensive process in the cell. However, when the peptide bond degradation, only 1 ATP molecule is recovered. Therefore, with an increase in the intake of food calories (especially protein), not only synthesis, but also protein degradation (protein circulation) is enhanced, which allows to maintain energy balance in a wide range of incoming food calories, therefore, protein intake are widely used in the dietary therapy [12]. All the technologies to improve the protein synthesis process listed above will help to increase the dietary therapy effectiveness accordingly.
The next system for the development of energy deficiency is the process of gluconeogenesis. If during glucose oxidation to pyruvic acid (PVA) 2 ATP molecules are released, then during the reverse synthesis of glucose from PVA, 6 ATP molecules are consumed [13]. Monosaccharides are usually considered as a source of energy for cell activity, however the only glucose monosaccharide is involved in this direction, while fructose monosaccharides and galactose can be used in the energy supply of life processes only after their transformation into glucose in the liver, but they are spending on gluconeogenesis 6 ATP molecules. Disappointingly, physicians and, in particular, nutritionists, do not know biochemistry well and believe that all monosaccharides have the same energy intensity (4kcal/g) and do not take into account the energy consumption associated with gluconeogenesis.
The better is the substrate maintenance of these energydependent processes, the higher the energy deficiency and the more efficient the reduction of body weight. This opens up prospects for the development of technology - the more you eat, the less your weight. it is necessary to use products containing compounds that improve the flow of these energydependent processes.
In the energy balance development, disruption of the energy production process at the aerobic stage of its formation can be of great importance, since at this stage 93% of the chemical bond’s energy of glucose and 100% of fat. Anaerobic oxidation of glucose, as previously indicated, produces PVA, which can later act as a substrate for oxidation in the citric acid cycle, but for this it should be carboxylated with the participation of pyruvate carboxylase in oxaloacetic acid and pyruvate dehydrogenase acetyl -CoA Magnesium ions, lipoic acid and vitamin B1 are involved as coenzymes in the activity of these enzymes; therefore, the deficiency in the nutrition of these cofactors reduces the efficiency of oxidation of PVA, therefore there is a correlation between the content in the diet of these co-factors with obesity [14]. This indicates of their reception expedience for the prevention and treatment of obesity.
When the possibility of aerobic oxidation of PVA is reduced, its recovery to lactic acid (lactate) increases, which stimulates lipogenesis, therefore, in people with obesity, the blood lactate level is higher [15] and a correlation is found adipocytes [16]. The amount of aerobic oxidation of organic substances largely depends on the efficiency of the biological oxidation chain, in which electron carriers are an indispensable factor, coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in particular and cytochrome C. CoQ10 concentration depends on the size of its synthesis and on dietary intake. CoQ10 synthesis decreases with aging [17] and, consequently, energy production at the aerobic stage decreases, therefore the role of anaerobic glucose oxidation growing, and the process of lactate formation increases, which contributes to the activation of lipogenesis and to obesity. Indeed, in mice (KKAymice) with obesity, it was shown that taking CoQ10 against of a diet with increased fat concentration prevents a visceral fat increase [18].
Thus, the metabolic principles allow us to develop a “magic pill” for lazy people, which can significantly reduce the obesity epidemic and will contribute to the preservation of human health and efficiency.






























