Casualty Agent (Yersiniosis) Detection in Reared Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Kohgiluyeh-Va-Boyerahmad Province in Iran
Mohammedsaeed Ganjoor*
Genetic and Breeding Research Centre for Cold Water Fishes (Yasuj city), Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute, Agricultural Research Education and Extention Organization (AREEO), I.R, IRAN.
Submission: May 30, 2017; Published: August 01, 2017
*Corresponding author: Mohammedsaeed Ganjoor, Department of Health and Fish Disease, Genetic and breeding research center for cold water fishes shahid-motahari, Yasuj, PO Box: 75914-358, Iran, Email: msg_isrc@yahoo.com
How to cite this article: Mohammedsaeed G. Casualty Agent (Yersiniosis) Detection in Reared Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Kohgiluyeh-Va-Boyerahmad Province in Iran. Oceanogr Fish Open Access J. 2017; 4(2): 555633. DOI: 10.19080/OFOAJ.2017.04.555633
Abstract
From the June to the August 2013, Casualty happened in fish of some ponds of a farm in an area of Kohgiloye-&-BoyerAhmad province. It is a province in southwest of Iran. Three ponds from eight showed more mortality, they have 5 to 20 dead fish every day for 45 days. Afflicted fish have dark body they swimming near surface or at the bottom of the pond and swam unmatched by the flock. Some fish showed hemorrhages around eye and within the oral cavity and exophthalmia occasionally. 45 moribund rainbow trout sampled for dissection and bacteriological examination. Kidney, liver and spleen of moribund fish examined for the detection and identification of bacteria causative agent of disease in rainbow trout. They cultivated aseptically on different media (Blood Agar, Tryptic soy Agar, TCBS Agar and MacConkey Agar).
All fish have been infected and suffered septicemia. A type of gram's negative bacterium was responsible of infection and mix infection didn't confirmed. The bacteria were able to growth on MacConkey agar. Detection had done based on clinical finding biochemical tests and staining. Based on it, the bacteria was a bacterium very similar with Yersinia ruckeri which induced infection. Identification continued by PCR method, therefore above result confirmed. Frequency of infectious fish estimated at least 0.375 percent. Application of enrofloxacine for 7 days reduced mortality but could not eradicate the infection so antibiotic therapy repeated 7 days more to eradication.
Keywords: Yersinia ruckeri; Disease; Rainbow trout; Kohgiluyeh va Boyerahmad
Abbreviations: ERM: Enteric-Red-Mouth Disease; BA: Blood Agar; TSA: Tryptic Soy Agar; TCBS: Thiosulphate Citrate Bile Sucrosr Agar; TSI: Triple Sugar Iron; CU: Citrate Utilization; MR; Methyl Red; TSB: Trypticase Soy Broth
Introduction
Nowadays, Rainbow trout culturing has been developed in Kohgiloyeh-&-Boyer Ahmad province of Islamic Republic of Iran. It is a province in the southwest of Iran. There are many water resources in the province which originated from Zagross mountains so aquaculture is a lucrative profession in the province. Rainbow trout cultivated lonely. In 2013 AD about 13400 tons fish (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cultivate in the province. It cost is about 38 million dollars [1]. Infectious diseases are being emerged due to developing fish culture at artificial condition especially at intensive systems. On the other hand circulated water and intensive system increase disease incidence [2]. Fish are depressed by low water flow in warm seasons and infectious agents may release in ponds by recirculated water. Depression decrease immunity in fish and water recirculation spread pathogens in fish flock horizontally especially while circulated water wasn't treated properly.
Yersinia ruckeri causes Enteric-red-mouth disease (ERM) in rainbow trout. It is an important disease of salmonid fish and was first described by Ross et al. [3] and Rucker [4]. The disease has been called in other word such as: Yersiniosis, Yersinic septicemia, Hagerman-redmouth-disease, etc. ERM produces high mortalities and severe economic losses on fish farms [5].
Enteric red mouth disease (ERM) has been one of the most significant diseases in salmonid aquaculture. Even though the disease has been diagnosed more than 25 years ago and commercial vaccines are available [6,7]. ERM have reported from several countries such as turkey, USA, Romania and Iran [8-11]. ERM is being reported since last few years from some provinces (Tehran, Fars, Hamadan and Chaharmohalvabakhtiyari) in Iran [12-15].
Signs of ERM particularly in infected rainbow trout may include hemorrhages in various tissue and organs, particularly around the mouth, mouth cavity, in the gills, in the musculature, the peritoneum, the body fat, viscera and in intestine. Clinical infection can also be characterized by a yellow discharge from the vent. Furthermore, severe inflammations of the distal portion of intestine and vent are frequently observed [16,17].
Y. ruckeri has been isolated from different salmonids (Oncorhynchus spp.), Pike, eel, carp, perch, roach, sturgeon and turbot. Further, it has also been isolated from freshwater invertebrates [18,19]. It is probably persistent in the environment, and transmit horizontally [17].
Materials and Methods
Fish
Three ponds from eight ponds have more mortality. It estimated that each pond contained about 4000 fish. 45 moribund rainbow trout with abnormal signs such as skin darkness, bad swimming, hemorrhagic were sampled from the ponds and examined for the presence of the etiological agent of the disease by dissection and bacteriological procedures.
Bacteriological examination
Plate culture is commonly used to isolate Y. ruckeri, so it used to isolation, then identification done by biochemical tests and staining [20,21].
Kidneys, Livers and Spleen of fish were cultured aseptically by streaking a loop onto Blood Agar (BA), Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA), Thiosulphate Citrate Bile Sucrosr Agar (TCBS) and MacConkey Agar plates and incubated at 30 °C for 48 hours. Isolated colonies were subcultured onto TSA and identified using conventional biochemical tests [22]. Characteristics of our isolated bacterium were compared with the reported biochemical properties of the Yersinia ruckeri in the literature [2,6,21,22].
Isolated colonies have been identified by biochemical test contains Catalase, Oxidase, Growth on TSI medium (triple sugar iron), Citrate utilization, Methyl Red (MR), Motility, H2S production, Indole, Growth at %6.5 NaCl and OF-test [23].
PCR method
Isolated colonies of bacteria evaluated by PCR assay. The bacteria cultured on TSB (Trypticase soy broth) medium (Merck, Germany) and was incubated at 30 °C for 48 hours, Then DNA isolated and extracted from it. Therefore, One milliliter of culture was centrifuged for 5min at 12,000 x g, the pellet was resuspended in 50ml of distilled water, and cells were lysed by boiling for 10min. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation for 30s at 12,000 x g. Aliquots of 5 μl of supernatant were removed and was used as template DNA for the PCR assay. PCR conditions consists of: Annealing temperatures (60 °C), polymerase concentrations (1.5U), deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) concentrations (200 μM), MgCl2 concentrations (2mM). PCR was performed in 50μl reaction mixtures containing 15 μl of sample as template DNA. The forward and backward primers which used in the detection of Y. ruckeri was [24].
(YER3, 5' CGAGGAGGAAGGGTTAAGT 3')
(YER4, 5' AAGGCACCAAGGCATCTCT 3')
Thermal cycling was done with the following conditions: an initial denaturation cycle at 94 °C for 2min, followed by 35 cycles of amplification (denaturation at 94°C for 40s, annealing at 60 °C for 40s, and extension at 72 °C for 60s), and a final 5min elongation period at 72 °C. Finally, PCR product were analyzed by electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide [24].
Anti biogram test
Anti biogram test achieved based on disk diffusion method [23].
Results
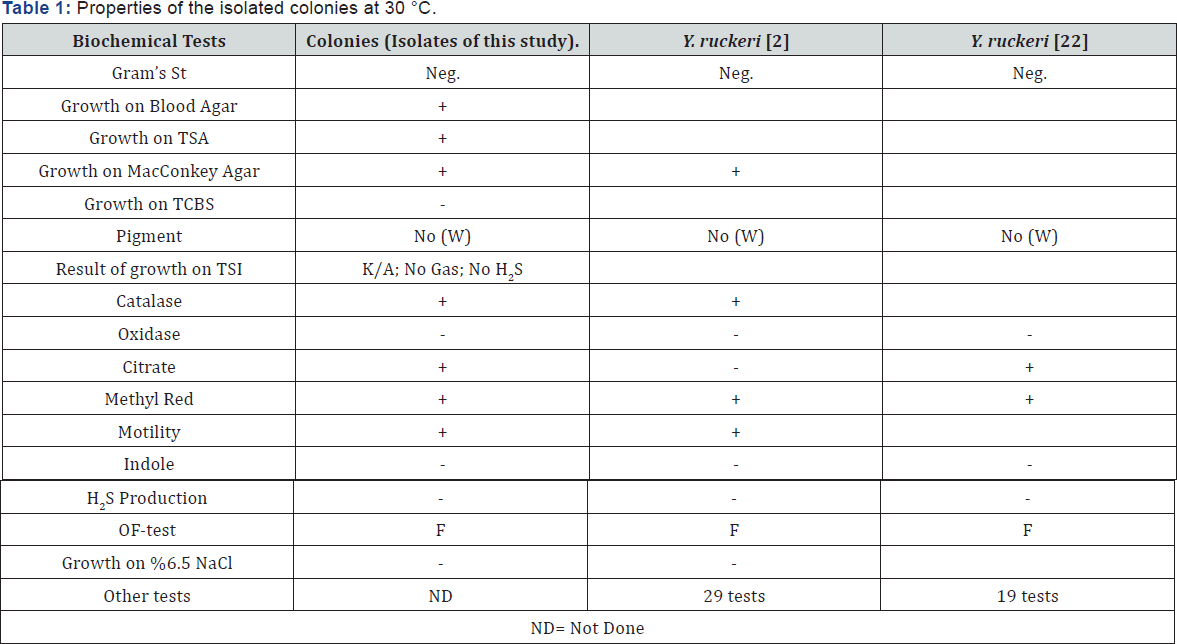
Gross clinical signs were characterized in infected fish by general lethargy, swimming difficulties and swimming close to the surface of the water or bottom of the pond. Often, hemorrhages were observed in the gills, around eye, around mouth, and in oral cavity. Dark pigmentation was commonly. Dissection shows some petechial hemorrhages on the surface of the liver. Furthermore, the peritoneum was occasionally filled with a yellowish fluid. Infected fish have lethargy and low appetite. Exophthalmos was sometimes accompanied by hemorrhages around the ocular cavity in some cases. The liver was slightly pale discoloration. A Gram's(-) negative bacterium isolated from all samples. All sampled fish have infected and a bacterium isolated from their livers, kidneys and spleens. So, the septicemia has been confirmed. Diagnosis of the causative agent of disease is important to specify a preventive strategy. Identity biochemical tests did to detection of the bacterium clearly so PCR-assay done. The bacterium did not growth on TCBS media therefore it was not member of Vibrio genus.It was a gram's negative bacteria which was able to growth on MacConkey agar medium. Its catalase test was positive while its oxidase test was negative. It wasn't Streptococcus bacteria based on catalase test. Other test which achieved to detection of the bacterium summarized in Table 1.
In the current study, some isolated colonies (10 colonies) were diagnosed from 45 moribund fish and compared with the reported results of biochemical characteristics of Y. ruckeri by Austin and Austin [22] and Akhlaghi [2]. The isolated bacteria in this study found to be very similar with Y. ruckeri. After biochemical tests some isolated colonies (10 colonies) evaluated by PCR assay. However, PCR procedure confirmed that the isolates are belong to the Yersinia genus as Yersinia ruckeri species.
Discussion
All samples were contaminated and a type of bacterium isolated from Liver, Kidney and spleen of all the moribund fish. Only a kind of colony has been grow on culture media, so mix infection didn't confirm. On the other hand, Gram's staining and growing on MacConkey agar show that the septicemia caused by a type of gram negative bacterium. The bacterium has been seen in form of cocco-rod shape. Therefore, according to the issue and also according to the examining results of catalase was inference such that mentioned bacterium couldn’t be Streptococcus and Lactococcus. Also, the lack of growing on Vibrios'-selective medium (TCBS agar) caused to was rejected the possibility of existence of vibriosis illness. It should be acknowledge that the separated bacterium was similar to Yersinia ruckeri from the view point of characteristic features, according to clinical signs and performed biochemical tests. It confirmed by PCR procedure.
It stated that yersiniosis was observed in rainbow trout at acute and chronic form and the bacteria may cause infection in all of ages of the fish [2]. Our observation also shows that some infected fish indicate clinical signs obviously, and the others have fewer signs with more activity and affected by pathogen later. Also, this matter is the reason of casualty's stairs. It founded that weaker fish become ill too early and stronger fish subsequently. The total mortality was about 1.87 to 7.5 percent in the 3 pounds.
Although 14 biochemical tests achieved but identification was not valid so there is need to a procedure to complete detection. Bacterial detection performed by PCR-assay. It confirmed the identity of the bacteria. PCR results shows that the bacteria were belong to the Yersina ruckeri species clearly.
Also, in current research both of fry fish and adult fish were infected and pathogen found in both of them. Therefore, the bacterium is able to cause infection in fish at different ages. But, we ought to mention that infection was acute in fry fish compare with adults. Guguianu also has been declared fry fish are more susceptible with the yersiniosis [9]. The application of Tetracycline or Enrofloxacine for 7 days as food additive show that both of the antibiotics are effective against this disease and cause to reduce mortalities but wasn’t enough to eradicate of the disease. So, it recommended that the length of therapy should select more than 7 days.
References
- ASRFI (2014) Annals statistical report of fisheries in IRAN. Iran Fisheries Organization, Iran.
- Akhlagi M, Sharifiyazdi H (2008) Detection and identification ofvirulent Yersinia ruckeri: the causative agent of enteric redmouth disease in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss) cultured in Fars province, Iran. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research, Shiraz University 9(4): 347352.
- Ross AJ, Rucker RR, Ewing WH (1966) Description of a bacterium associated with red mouth disease of rainbow trout (Salmogairdneri). Canadian Journal of Microbiology 12(4): 763-770.
- Rucker RR (1966) Remouth disease in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Bulletin of office International of Epizooties 65(5): 825-830.
- Ispir U, Gokhan HB, Ozcan M, Dorucu M, Saglam N (2008) Immune Response of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss) to Selected Antigens of Yersinia ruckeri. Acta Vet Brno 78(1): 145-150.
- Horne MT, Barnes AC (1999) Enteric redmouth disease (Yersinia ruckeri). In: Woo PTK, Bruno DW (Eds.), Fish diseases and disorders- viral, bacterial and fungal infections. (Vol 3) CABI Publishing, UK, pp. 455-477.
- Tebbit GL, Erickson JD, Van de Water RB (1980) Development and use of Yersinia ruckeri bacterins to control enteric redmouth disease. In: International symposium on fish biologies: serodiagnostics and vaccines. Dev Biol Stand 49: 395-401.
- Altinok I, Grizzle JM, Liu Z (2001) Detection of Yersinia ruckeri in rainbow trout blood by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Dis Aquat Org 44(1): 29-34.
- Guguianu E, Vulpe V, Lazar M, Rimbu C (2009) Yersiniosis outbreak in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) at a fish farm from northern Romania - Yersiniosis in rainbow trout. Cercetäri Agronomicein Moldova 43(3): 139.
- Çeker E, Karahan M, Ispir U, Çetinkaya B, Saglam N, Sarieyyupoglu M (2012) Investigation of Yersinia ruckeri Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum 1792) Farms by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Bacteriological Culture. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 18(6): 913-916.
- Tobback E, Decostere A, Hermans K, Haesebrouck F, Chiers K (2007) Yersinia ruckeri infections in salmonid fish. J Fish Dis 30(5): 257-268.
- Sedaghati V (1997) Study of enteric red mouth (ERM) in rainbow trout in north of Fars province. School of Veterinary Medicine DVM thesis No: 651. Veterinary School of Shiraz University, Iran.
- Soltani M, Fadaiifard , Mehrabi MR (1999) First report of a yersiniosis- like infection in farmed rainbow trout. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 19(4): 173-176.
- Soltani M, Tarahomi M (2002) Experimental infection of Yersinia ruckeri like bacterium isolated from rainbow trout farms in Tehran province. Third convention of Iranian Veterinary Clinicians. Mashhad, Iran, (29-31) pp. 37.
- Zorriehzahra MJ, Mohd Daud HH, Nazari A, Gholizadeh M (2012) Assessment of environmental factors effects on enteric redmouth disease occurrence in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss) farms in Hamedan province, Iran. J Comp Clin Path Res 1/3 pp: 79 -85.
- Willumsen B (1989) Birds and wild fish as potential vectors of Yersinia ruckeri. J Fish Dis 12(3): 275-277.
- Eiras JC, Segner H, Wahli T, Kapoor BG (2008) Fish Disease. (Vol 1,2) Science Publisher, USA, p. 612.
- Davis RL, Frerichs GN (1989) Morphological and biochemical differences among isolates of Yersinia ruckeri obtained from wide geographical area. Journal of Fish Diseases 12(4): 357-368.
- Dulin MP, Huddleston T, Larson RE, Klontz GW (1976) Enteric redmouth disease. Forest Wildlife and Range Experimental Station Bulletin, University of Idaho, Moscow 8: 15.
- Toranzo AE, Baya AM, Roberson BS, Barja JL, Grimes DJ, et al. (1987) Specificity of slide agglutination test for detecting bacterial fish pathogens. Aquaculture 61(2): 81-97.
- Romalde JL, Magarios B, Fouz B, Bandin I, Nunez S, et al. (1995) Evaluation of BIONOR Mono-kits for rapid detection of bacterial fish pathogens. Dis Aquat Org 21: 25-34.
- Austin B, Austin D A (1999) Bacterial fish pathogens. Diseases of farmed and wild fish. (2nd edn) Springer-Verlag, pp. 188-226.
- Forbes BA, Sahm DF, Weissfeld AS (2007) Bailey and Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology. (12th edn), Mosby, USA, p. 1056.
- Del Cerro A, Marquez I, Guijarro J (2002) Simultaneous Detection of Aeromonas salmonicida, Flavobacterium psychrophilum, and Yersinia ruckeri, Three Major Fish Pathogens, by Multiplex PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(10): 5177-5180.






























