Aggression among Annamalai University Students
Mohammad Ami N Wani*, R Sankar, R Raghavi and B Chinmaya
Annamalai University, India
Submission: March 17, 2017; Published: May 25, 2017
*Corresponding author : Mohammad Ami N Wani, Research scholar in Psychology Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu, India, Email: mypsyresearch@outlook.com
How to cite this article: Ami N Wani M, Sankar R, Raghavi R, Chinmaya B. Aggression among Annamalai University Students.Glob J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2017; 1(3): 555562. DOI: 10.19080/GJIDD.2017.01.555562
Abstract
The present study intends to elucidate the level of aggression among university students in Tamil Nadu. For this purpose 100 university students from different courses were randomly selected with equal number of boys and girls. Aggression Questionnaire constructed and standardized by Buss and Perry 1992 was used for the assessment of aggression level among students. Mean and t-test were applied for statistical analysis by using SPSS 16.0 version. The results demonstrated that boys show high level of aggression than girls. Findings also revealed that boys have higher levels of physical as well as verbal aggression than girls. Also anger and hostility was found more among boys than girl students. To sum up, on the basis of our results we conclude that there is significant gender difference in aggression and aggressive behavior
Keywords: Aggression; Anger; Hostility; Gender
Introduction
Aggression has dependably been a critical concern of mankind. Psychologists have constantly attempted to find out, what exactly aggression is. Different people define it in different ways. Some say it is a behavior that is intended to harm another person who does not want to be harmed. Some define it as the phenomenon in which an individual harms others to get joy and happiness.
In present days aggression is found to be one of the common problems among adolescents. It is found that throughout the most recent couple of years, aggression and violence levels have drastically increased among adolescents [1]. Aggression negatively affects student's academic achievement, emotional, mental as well as psychological development and academic performance, schools environment and if not controlled early, it may cause incidents of violence in the future too [2]. It also leads to violence and criminal activities while as in some cases it is closely associated with psychopathic behavior. Aggression can be shown physically as well as verbally. Physical aggression involves harming others by kicking, hitting, stabbing, or shooting them. And verbal aggression involves harming others verbally viz. name calling, yelling, swearing as well as screaming.
Aggression among students is a challengeable issue for researchers in these days, as it affects families, societies as well as nations too. Researchers have conducted many studies and highlighted various aspects of aggressive behavior among students. Researchers also found that responsively aggressive children are significantly more anxious than non-aggressive children [3]. Veiskarami et al. [4], Akhtar & Kushwaha [5] found that boys scored higher than girls in respect to aggression. Talukdar & Deka [6] also found that the male adolescents are significantly aggressive than female.
Simultaneously Sheikh et al. [7] reported that boys have high level of physical, direct as well as indirect aggression than girls. Datta & Firdoush [8] revealed that 66.5% children have physical aggressive tendency while as 56.8% have verbal aggressive tendencies. Kumar [9] found that students from science streams are more aggressive than arts students. Findings also revealed that students of private institutions are more aggressive than students of government institutions.
Methodology
Objectives
- To assess the level of aggression among boys and girls.
- To assess the level of physical and verbal aggression among boys and girls.
- To assess the level of anger and hostility among boys and girls.
Hypotheses
- Boys would have higher level of aggression than girls.
- Significant mean difference would be found between boys and girls in aggression scores.
- Boys would have higher level of physical and verbal aggression than girls.
- Significant mean difference would be found between boys and girls in physical and verbal aggression scores.
- Boys would have higher anger and hostility than girls.
- Significant mean difference would be found between boys and girls on anger and hostility scores.
Variables
In the present study aggression is the experimental variable and criterion variable is gender
Sample
The present study is based on sample of 100 students selected through random sampling method from Annamalai University Campus, Tamil Nadu and India. Further these subjects were equally divided into two groups on the basis of gender (Boys and Girls). Only those students, who met the following inclusion and exclusion criteria, were selected for the preset study
Inclusion criteria
- Students between the age group of 19-22 years old.
- Both boys and girl students were included.
Exclusion criteria (The following points are not so clear)
- Family pattern of students was excluded.
- Education level of the patient was not taken.
- Students were not selected on the basis of economical status.
Psychological tool
Aggression Questionnaire constructed and standardized by Buss & Perry [10] was used for the assessment of aggression level among students. This scale measures the 4 different types of aggressive behavior viz. Physical Aggression (PA), Verbal Aggression (VA), Anger (A), and Hostility (H). The scale consists of 29 items with five alternatives, Out of these items 27 items are positive items, scored as 1,2,3,4,5 while 2 items are negative scored as 5,4,3,2,1.
Procedure
The study was conducted in Annamalai University Campus Annamalai nagar Tamil Nadu India taking a sample of 100 students selected from different departments. Investigators personally met each subject, established rapport with them and obtained their consent for their participation in the study. After that aggression questionnaire was administrated to them. Before starting to fill the questionnaire, required instructions were given to each subject. After 10-15 minutes the students handed over the completed questionnaire to the investigator and were thanked for their cooperation. . In line with the objectives of the study, the data was analyzed using SPSS 16.0 version.
Results
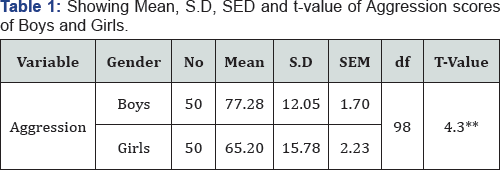
** Significant at 0.01 level.
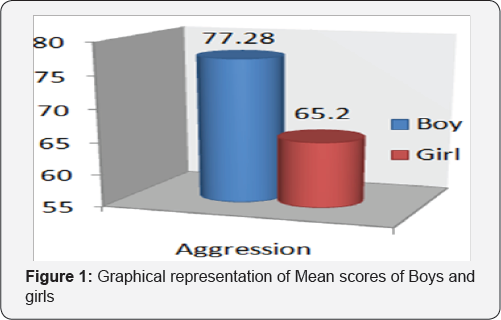
The main findings of the present study are shown in tables given underneath. From Table 1 above, it appears that the mean scores of Boys (M=77.28) in respect to aggression behavior is more than the mean scores of Girls (M=65.20). The table also shows S.D, SEM and obtained t-value of boys and girls [Boys, S.D=12.05, SEM=1.70, Girls, S.D=15.78, SEM=2.23) There is statistically significant difference (p<0.01) between the girls and boys (Figure 1).
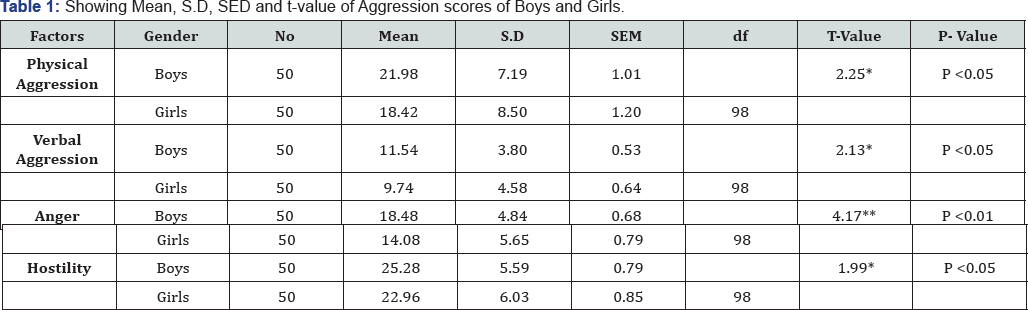
* Significant at 0.05 level, ** Significant at 0.01 level
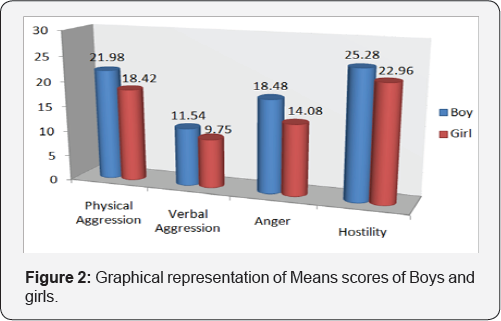
In Table 2, it is shown that Boys show higher level of Physical Aggression, Verbal Aggression, Anger, and Hostility than girls. The Mean, S.D, SEM and t-value of boys and girls was found [Physical Aggression, (Boys, M=21.98, S.D=7.19, SEM=1.01), (Girls, M = 18.42, S.D=8.50, SEM = 1.20), t-value=2.25, P<0.05], [Verbal Aggression, (Boys, M=11.54, S.D=3.80, SEM=.53), (Girls, M=9.74, S.D=4.58, SEM=.64), t-value=2.13, P<0.05], [Anger, (Boys, M = 18.48, S.D=4.84, SEM=.68), (Girls, M=14.08, S.D = 5.65, SEM=.79),t- value=4.17, P<0.01], [Hostility, (Boys, M=25.28, S.D = 5.59, SEM=.79), (Girls, M=22.96, S.D=6.03, SEM=.85) and t-value=1.99, P<0.05] respectively (Figure 2).
Discussion
The results of the present study demonstrated that boys are more aggressive than girls and boys show higher levels of physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger and hostility than girls. Considering the results on the basis of gender it was found that boys have higher level of aggression than girls. The obtained mean scores of boys (M=77.28) was found to be more than that of girl students (M=65.20). Therefore, our first hypothesis was accepted. Thus, we can say that boys are more aggressive than girls. Our finding is supported by Bettencourt & Miller [11] who found the same results in their research study that reported men are more aggressive than women. Similarly Malik & Katyal [12] also highlighted that males are more aggressive than females.
There was significant mean differences (p<0, 01) between aggression scores of boys and girl students, Therefore, the study's second hypothesis was accepted. Hence, our findings corroborate those of studies conducted by Talukdar & Deka [6] and Khatri [13] who found significant gender differences in aggression. They further reported that males are more aggressive than females.
Further findings divulge that mean scores of boys in physical and verbal aggression (M=21.98, M=11.54) is significantly more than the mean of girl students (M=18.42, M=9.74). Therefore our third hypothesis was also accepted. Hence we can say that boys are more physically and verbally aggressive than girls. Our findings are supported by Onukwufor [14] who reported significant difference between females and males in physical aggression. Results also revealed that males are more aggressive than girls.
We also found significant mean differences in physical and verbal Aggression of both groups, as obtained t-values of both Physical Aggression (T=2.25, df 98) and Verbal Aggression (T=2.13, df 98) are found significant at 0.05 level. Therefore our fourth hypothesis is also accepted. Our results are also supported by Jonathan [14] who found significant difference between male and female students physical aggression. Similarly Nakano [15] reported significant differences in verbal aggression among men and women. Results also show that men are more verbally aggressive than women. Owensa & MacMullin [16] also found boys have significantly high level of physical, verbal, direct as well as indirect aggression than girls. Our findings also show that boys have more anger and hostility than girls. The mean (M=18.48) of boys in respect to anger is found more than the mean (M=14.08) of girls, simultaneously boys have higher level of hostility than girls, and their mean (M=25.28) is more than the mean (M=22.96) of girls in respect to hostility, therefore our fifth hypothesis is also accepted. Research by Buss & Perry [10] supports our findings; they also found males are more hostile than females. We also found significant mean differences in anger and hostility among boys and girls. Obtained t-values of both anger (T=4.17, df 98) and hostility (T=1.99, df 98) are found significant at 0.01 and 0.05 level respectively, therefore our sixth hypothesis is also accepted.
Conclusion
To sum up, on the basis of our findings we conclude that there is significant gender difference in aggression. Boys are more aggressive than girls, simultaneously physical, verbal aggression, anger and hostility is found more among boys than girl students. In present days aggression is one of the common problems found among students of all age groups. Students from primary to university level show different level of aggression which is a challenge for growing world. If our students are aggressive, our future is in danger; they bodily affect the whole nation as they are the feature. Thus researchers should come forward to highlight the various aspects which cause this behavior. Therefore our student community would be helped from every stage from time to time by teachers, psychologists and counselors through different relaxation techniques and counselling process.
References
- Kevin JS, Carl EP, Cecilia S (2001) Quality of parent/adolescent attachment and aggression in young adolescents. Journal of Early Adolescence 21(2): 182-203.
- Jennifer LW, Terrie EM, Felton E, Lee R, Phil AS (1990) How early can we tell? Predictors of childhood conduct disorder and adolescent delinquency. Criminology 28(4): 507-533.
- Vitaro F, Brendgen M, Tremblay RE (2002) Reactively and proactively aggressive children: antecedent and subsequent characteristics. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 43(4): 495-505.
- Hassan AV, Masumeh Z, Seyyed AH, Hossein S, Karim J (2015) Comparative analysis of physical victimization among male and female high school students of Iran. International Journal of Life Sciences 9 (3): 9-12.
- Akhtar J, Kushwaha AKS (2015) Gender differences in aggressive behavior of adolescents. Indian J Applied Res 5(1): 525-527.
- Talukdar RR, Deka RS (2014) A study on aggression level among adolescents. International Journal of Social Scence and Humanities Research 2(4): 91-94.
- Shaikh F, Viveki RG, Halappanavar AB (2014) Physical and verbal aggressive behaviour pattern among school children in urban area of North Karnataka: A cross sectional study. JKIMSU 3(2): 55-62.
- Datta PP, Firdoush KA (2013) Association of aggression with socio-demographic characteristics: A cross sectional study among rural adolescents. National Journal of Medical research 2(4): 442-447.
- Kumar R (2012) Aggression among secondary school students in relation to their emotional competence. International Journal of Education and Allied Sciences 4(2): 97-102.
- Buss AH, Perry M (1992) The aggression questionnaire. J Pers Soc Psychol 63(3): 452-459.
- Bettencourt BA, Miller N (1996) Gender differences in aggression as a function of provocation: A meta- analysis. Psychol Bull 119(3): 422444.
- Malik A, Katyal S (1993) A comparative study of frustration in daughters of working and non-working mothers. Indian Psychological Review 40(1,2): 9-13.
- Khatri P (2003) Aggression, peer victimization, and social relationships among Indian youth. International Journal of Behavioral Development 27(1): 87-95.
- Onukwufor JN (2013) Physical and verbal aggression among adolescent secondary school students in rivers state of Nigeria. British Journal of Education 1(2): 62-73.
- Nakano K (2001) Psychometric evaluation of the Japanese adaptation of the aggression questionnaire. Behav Res Ther 39(7): 853-858.
- Owensa LD, MacMullin (1995) Gender differences in aggression in children and adolescents in South Australia schools. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth 6(1): 21-35.






























