Numerical Economy and New Industrial Firm Power
Paul Rosele Chim*
HDR Paris-Panthéon Sorbonne, Teacher-Reseacher, University of Guyane
Submission: July 24, 2018; Published: October 03, 2018
*Corresponding author: Paul Rosele Chim, HDR Paris 1-Pantheon Sorbonne, Teacher-Researcher, University of Guyane, Beta Minea EA 7485 University of Guyane, Email: Paul.roselle@univ-guyane.fr
How to cite this article: Paul R C. Numerical Economy and New Industrial Firm Power. Ann Soc Sci Manage Stud. 2018; 1(5): 555573. DOI: 10.19080/ASM.2018.01.555573
Abstract
Numerical economy put in a prominent place the fact that the digital revolution imposes a new model in consumption and production. The whole ecosystem is modified by the development of Internet, networks, big data, information flows, connected objects and applied services. The firms are adopting monopolistic and oligopolistic strategies that converge towards a new model.
Keywords: Numerical; Innovation; Organization; Model; Industries; Firms
Introduction
Using the expression « numerical economy », we want to speak about the New Technologies of Information and Communication (NTIC) and the firms with their activities in the framework of networks, connected things and electronic devices. These activities mobilize so much data’s and materials. With the computers, we organize a lot of knowledges, and for the treatment, the stocking and the communication processes and methods of information. The aim of this short paper is to open a discuss on the new industrial firms’ power and the emerging of a new model in the framework of industrial organization. Following future studies on this topic could provide other analyses [1]. Our purposes present two points: the industrial power and the new model (Figure 1).
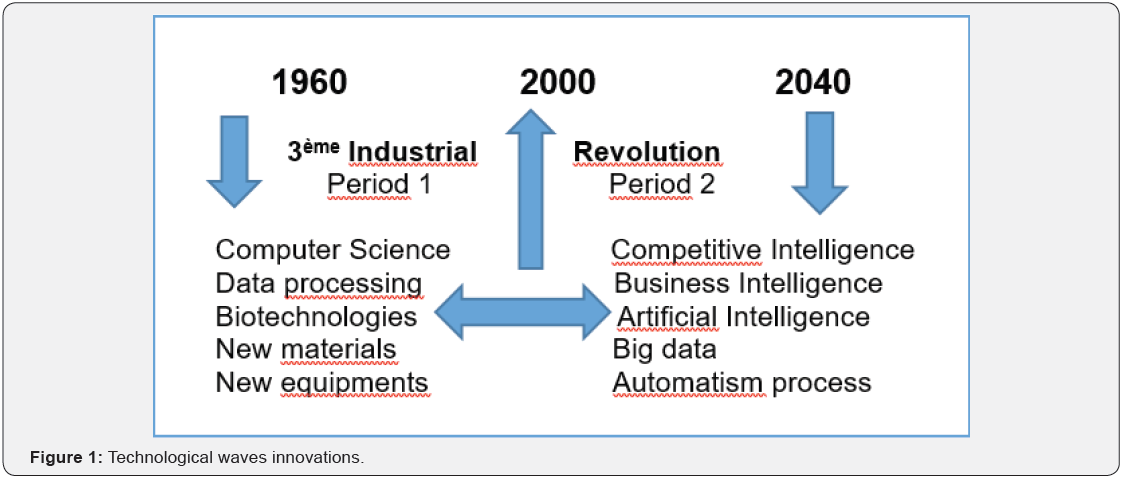
The new power of firms
Movie industry and Television networks in the United States [2], Europe and Asia-Pacific constitute the context where the firms are actives and illustrate permanently strategic alliances on technological of information and communication. Industrial crisis in the framework of cinema and television have launched technic and technological breakings because of the taking control of the technological firms. The years 1980, 1990 and 2000, are marked by concentration dynamics of the networks in Europe, the Majors in USA and Asia-Pacific [3-7].
Control on goods and markets presents various explanations:
- Technological evolution with numerical and digital system.
- Deregulation leading the end on natural monopolistic behaviors for network exploitations and televisions services.
- Transformation on the concurrence context and diversifying accentuated towards multimedia markets. We observe a movement of revival for the electronic industry.
- A great trend of adaptation for the firms because of an economic situation marked by the attention of the consumers on the multimedia markets.
In fact, the economic actors come from different sectors: network infrastructure, data processing, audiovisual, cinema, marketing distribution and advertising. The firms concerned control programs, network of diffusion like syndication, broadcasting and others. Phenomenon of globalization, expanding of culture consumption, information, advertising, communication, express the market power. Firms, the greatest are appeared by controlling equipment and new using of the web. On illustration in the music framework, that’s the case of iTunes, Apple Music, YouTube, YouTube Music, where the great firms of Internet are organizing market dynamics [7-10].
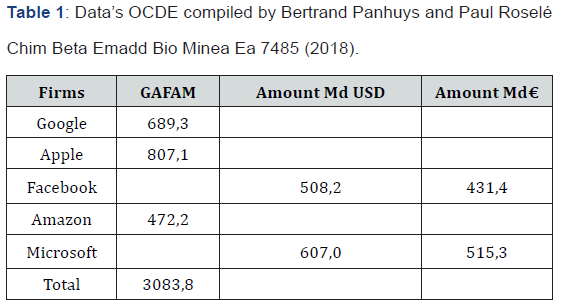
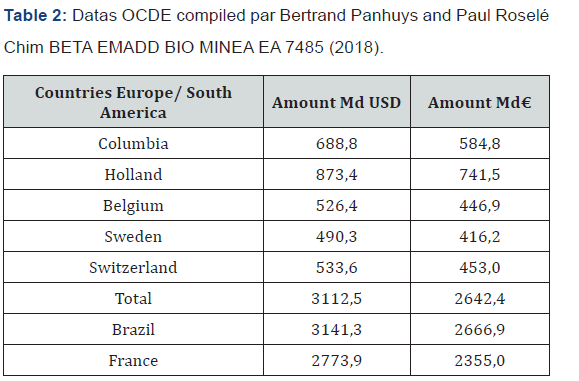
Success of these world leader firms come from their capacities for offering to the users’ applications and material equipment’s like computer hardware. The works of Kelly [8], Shapiro and Varian [11] show the fact that the consumers are situated in a system very different of this of classical economy. Electronic shopping and others are in the framework of great forces, they’re constraints. Users are sealed off within possibilities for changing technologies easy. World market is oligopolistic with firms, they have capacities to lead norms, standard functions constituting market power (Tables 1 & 2).
The New Model
Technology is a factor of breaking, destabilizing and changing movement [12,13]. In fact, these great industrial organization are very different in the world market because of their financial weight, numerous interests, the size of production site and distribution, website and political, economic, law sphere of influence in the states. During the year 2016, the sector of technologies exceeds this of finance when we examine the yearly classification PwC of the 100 first world quotation by stock exchange transactions. The value is appreciated by the NASDAQ. The GAFAM have the first places. The firms of the USA are overall the most dynamics with high values at the world level. It represents % of the 100 first firms before China and Hong Kong firms (11%), United Kingdom (7%), Germany (5%), Japan (4%) and France (4%) [14-19].
Observation
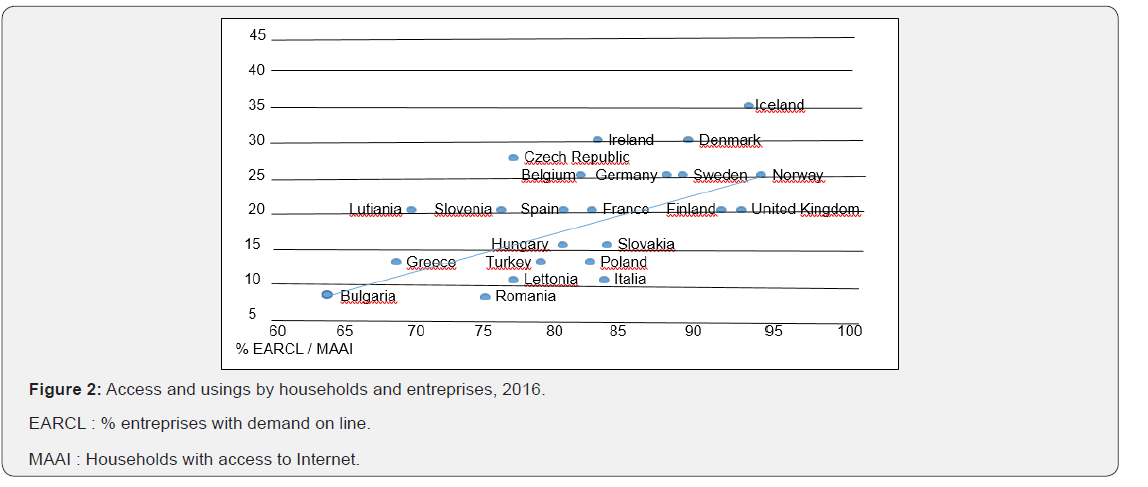
Apple stock exchange transactions and quotations are inferiors to the production of Holland, this of Microsoft is comparable with this of Columbia, and exceed this of Switzerland. The GAFAM financial weight exceed also richness created by France. It has the same level that this of a new industrial country like Brazil. In the Internet economy, USA cover 72% of the 50 first world sites of production, China represents 16%. The European firms have their intelligence competence in the technological and strategic market where numerical using are highs (Airbus, Safran, Thales, Rolls Royce, Zodiac, Launcher industry in French Guyana) [20]. The new rules of firms are competence, intelligence and competition. Transformation by innovation modifies the organization models and the new approaches of distribution. Numerical economy imposes some new methods of consumption based on the new giants of the Net (Figure 2).
Conclusion
Numerical economy and firms’ power are linked. The consumer behaviors for the products of the new technologies of information and communication modify dynamics of growth in the industrial countries. Firms are permanently developing technological strategic alliances. Great networks appear. That’s the case of the GAFAM enterprises with a new identity. We must remember the slogan of the Majors « That’s entertainment », a kind of industrial eternity, strategic technologic alliances forever. So, the states integrate numerical economy and the new industrial firms’ dynamics (Google, Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Airbnb, Microsoft, Samsung) with adaptations of long run.
References
- Amin A (1994) PostFordism, Blackwell Publishers, Oxford, United Kingdom.
- Baumol W, Panzar J, Willig R (1982) Contestable markets and the theory of industry structure, Harcourt Bras Janovich, New York, USA.
- Coase RH (1997) Firm, market and law, Diderot Multimedia Publishers, Paris, France.
- Galbraith JK (1967) (1989) The new industrial state. Third publisher, n° 143, Gallimard, Paris France.
- Ichbiah D (1995) Bill Gates and the Microsoft saga, Pocket Publishers, Paris, France.
- Ichbiah D (2010) How Google eats the world, Archipel Publishers, Paris, France.
- Isaacson W (2011) Steve Jobs The book pocket, Paris, France.
- Kelly K (1998) New rules for the New Economy, Viking Press, New York, USA.
- Panhuys B, Rosele Chim P (2018) Cyberspace economy and industrial strategies over the world economic poles, working papers, BETA EMADD BIO, University of French Guyane, France.
- Shapiro C, Varian HR (1999) Information rules: a strategic guide to the Network Economy, Harvard Business School Press, Boston, USA.
- Rosele Chim P (1989) Movie industry in the world crisis context, Doctorate in Economics, specialty Strategy and International Industrial Development, University of Paris X-Nanterre, Paris, France.
- Rosele Chim P (1999) Strategic alliances on technological network activities: the case of European multimedia, International Conference, Team-CNRS, CESSEFI, Central Planning Agency, Ministery of Economy, Finance and Industry, november, Paris, France.
- Rosele Chim P (2001) Economic revival and new technologies of information and communication Life and Economic Science Review, n° 157-158, special issue New Economy, Spring, Paris, France.
- Rosele Chim P (2003) Economy of cinema, television and communication, the Caribbean region and Hollywood, EPU Publishers, Paris, France.
- Rosele Chim P (2009) the New Technologies of Information and Communication and the tourism development territories, in Tourism Development EPU Publishers, Paris France.
- Rosele Chim P (2012) Management of Development in territories and business intelligence, HDR Works, University of Paris 1-Pantheon Sorbonne, Paris, France.
- Rosele Chim P (2016) The caribbean movie with french and creol identity: new economy and numerical revolution, CCEE Conference of European overseas regions, Basse-Terre, Guadeloupe.
- Rosele Chim P (2018) The caribbean and amazonian movie with french and creol identity: new economy and numerical revolution, Guadeloupean Journal of Studies, Jasor Publishers, Guadeloupe.
- Rosele Chim JA (1999) Theory of economic evolution Dalloz Publishers, translation of 1926, Paris, France.
- Stigler G T (1968) The organization of industry, Irwin Dorsay, New York, USA.






























