- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Key Opportunities and Challenges of Migrating IT Resources to Cloud Computing
Anam Nigar1*, Sadaf Saeed2 and Syed Nikbeen Hussaieni3
1School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun, China
2International Research Centre for Nano Handling and Manufacturing of China, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun, China
3School of Computer Science and Technology, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun, China
Submission: February 14, 2023; Published: March 07, 2023
*Corresponding author: Anam Nigar, School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun, China
How to cite this article: Anam Nigar, Sadaf Saeed and Syed Nikbeen Hussaieni. Key Opportunities and Challenges of Migrating IT Resources to Cloud Computing. Trends Tech Sci Res. 2023; 6(1): 555680. DOI: 10.19080/TTSR.2023.06.555680
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Abstract
This study identifies the main benefits and effects of moving data to the cloud, the opportunities and challenges when migrating IT resources to cloud computing, the security, compliance, and risks when migrating IT resource to cloud computing, the structure, services, and deployment models. And the concept of virtualization in the context of servers, storage, and network systems strategies for migration, as well as the benefits of cloud-based services for business applications.
Keywords: Cloud Computing; Software; Computer Services; Operational Expenditures; Capital Expenditures
Abbreviations: SMEs: Small and Medium Sized Enterprises; AWS: Amazon Web Services; GCP: Google Cloud Platform; IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service; EC2: Elastic Compute Cloud; PaaS: Platform as a Service; SaaS: Software as a Service; IT: Information Technology; OPEX: Operational Expenditures; CAPEX: Capital Expenditures; TCO: Total Cost of Ownership
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Introduction
Cloud computing refers to the distribution of computer services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, intelligence, and other services through the Internet. Cloud computing offers an alternative to maintaining a data center on the premises of a business. With an on-premises data center, it is our responsibility to manage everything, including the procurement and installation of hardware, virtualization, the installation of the operating system and any other necessary applications, the configuration of the network and the firewall, and the establishment of a storage area for data. After we have completed all of the initial setup, it is now our responsibility to manage it over its full existence the overall cloud computing process are shown in Figure 1.
We are elaborating the why businesses SMEs (small and medium sized enterprises) should adopt cloud technology. Moving information, localhost applications, services, and data to the distributed cloud computing infrastructure Several factors, including preparation and an examination of the impact on current corporate systems, will determine if this data transfer procedure is successful. Moving locally stored data in a public cloud computing environment is one of the most frequent activities.
The hotel sector may gain a lot from the idea of cloud computing [1,2]. The hotel industry’s management of information and computer resources will likely be significantly impacted by the shift to cloud computing [3,4]. Whether a company is a tiny, individual resort or a major, global hotel chain, technology investment must benefit the company. Since every firm will have a different approach, a thorough analysis must be done to pinpoint the key problems that need to be examined before moving to the cloud. The cloud is quite flexible in IT infrastructure that can be used by a wide range of end users in a variety of ways [5,6]. The cloud provider may instantly and dynamically allocate computing resources when new users join the system. In order to increase computing resources, cloud providers use a flexible cloud architecture that employs a very effective economies of scale technique [7].
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
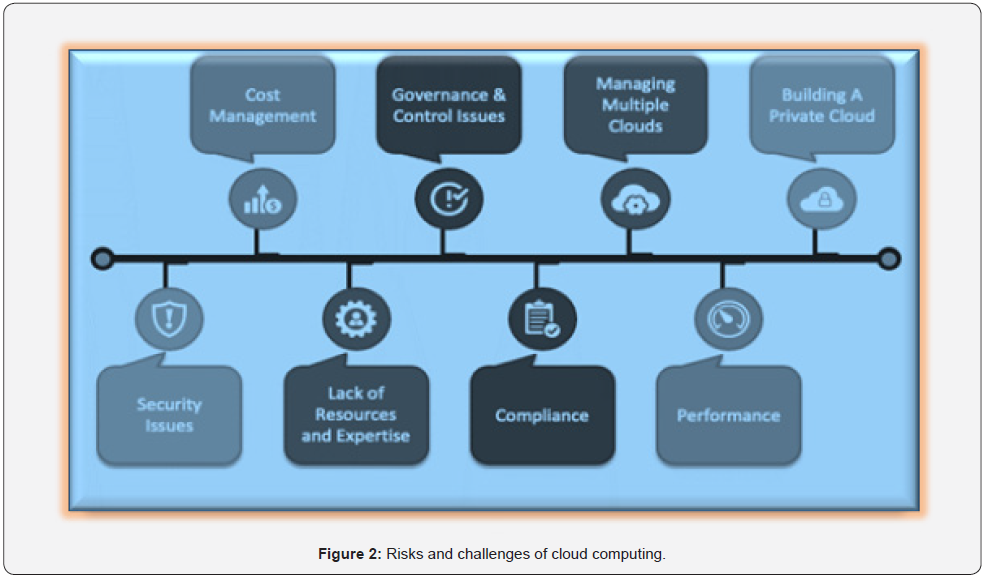
In order to migrating IT resources to cloud computing we have to face some challenges as show in Figure 2. The significant portion of the work that we do in cloud settings for a diverse variety of customers involves assisting those customers in overcoming obstacles caused by shifting workloads and fixing points that are not completely optimized. The most common difficulties associated with cloud migration are as follows.
• Lacking a clear strategy determined by business objectives
• Cloud sprawl caused by not having a clear understanding of the full scope of cloud environments
• Exceeding the planned budget
• Security weak points and failures of critical services
• Human error and a lack of skills required to operate the new infrastructure
Costs Management
Many companies migrate to the cloud without adequately assessing the work, which leads to an inaccurate cost prediction [8]. Additionally, because cloud environments are dynamic, expenses might unexpectedly increase if companies choose to expand their applications or incorporate new services [9]. Use an AWS calculator to prepare the budget appropriately since costs for AWS cloud migration vary based on the service used and the number of users [10]. As migrating data is a slower operation and where businesses may save money, experts advice starting with the least-used services in the application rather than the most-used ones [11].
Right Performance & Quality
The success of a smooth transfer may depend on the caliber, dependability, and performance of cloud apps [12]. Before making any plans for an AWS transfer, every feature, the least amount of downtime, and rapid access must be carefully taken into account. It is crucial to accurately predict how much downtime each migration step will cause and to have a plan in place to have as little of an impact as possible [1].
Lack of Resources or Expertise
Lack of Resources or expertise is one of the significant challenges in Cloud Computing [13]. Organizations are rapidly placing their workloads on the Cloud as Cloud Computing is significantly advanced [13]. Because of these factors, businesses face difficulties in keeping up the tools, and there is a need for expertise also increases. The following challenges can be minimized by providing extra training to the IT team.
Governance or Control
Governance or Control is also one of the challenges that users face in Cloud Computing. Proper IT governance ensures that the appropriate IT assets are implemented and utilized as mentioned in agreement policies [14]. Ensure that these assets are correctly working, and the maintenance has also been done; make sure that these assets support the organization’s planning and business goals [15]. Currently, in Cloud World, organizations do not have complete Control over infrastructure provisioning, DE-provisioning, and operations. The third-party cloud providers are providing governance support and best practices.
Compliance and Security
Various degrees of compliance validations and security requirements may be necessary for many different business types and the industries they operate in, regardless of where the systems and apps are housed-on-site or on the cloud [15]. “The cloud” is not a new technology, but rather a new method of providing computer resources. On the one hand, a vast concentration of resources and shared infrastructure may be more appealing to cybercriminals, particularly when combined with APIs for cloud administration that are open to the public. On the other side, however, security measures that are located in the cloud have the potential to be more resilient, scalable, and cost-effective. Numerous advantages, such as lower capital expenditures, agility, and resilience, make cloud computing appealing to enterprises. Yet, there may be both positive and negative effects on safety [16].
When implementing a cloud approach, a new model of shared responsibility emerges because of the presence of a third party (the cloud provider) who provides services on your behalf. The cloud service provider is responsible for cloud security, but you must take care of security within the cloud yourself. Instead of trusting your cloud service provider will handle security, you should take the time to learn exactly what falls under your purview [17].
Compliance and Security
Cloud Computing Services are entirely dependent on highspeed stable internet connection. So, the tiny enterprises might face connectivity problems and should invest a good amount in internet connections, so there is no downfall. Because if collapse takes place because of any issue, the business will face losses [18].
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform are the three largest public cloud providers, sometimes known as hyperscalers (GCP) [19]. The precipitous ascent of these three providers over the previous five years is a strong indication of cloud adoption’s rising trajectory. Regarding market share and quantity of services offered, AWS remains the industry leader. However, Azure has shown to be the undeniable number two. steadily narrowing the gap. Azure is the most popular cloud platform among corporations and huge platforms offered by Google Cloud for organizations is the most rapidly expanding of the big three and is widely regarded as an innovator. In general, public cloud companies provide three distinct cloud computing models.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
The best essential component of cloud computing is infrastructure as a service (IaaS), which offers a cloud-based, on-demand service. access to computer resources on one’s own, such as virtual resources (which are used in the operation of virtual machines), as well as dedicated resources in the areas of hardware, storage, and networking offers a cloud-based, on-demand service. Many clients are making their first foray into cloud computing with this. While these resources resemble certain familiar on-premises technologies, the underlying infrastructure is handled by the cloud platform provider rather than the end user, who just consumes the resources (such as virtual computers) on a payper- use basis [20]. Popular IaaS computing services include Specifically, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Cloud Platform (Compute Engine).
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS adapts the ideas behind IaaS. a step further. PaaS raises the level of abstraction of the. for end users up to foundational framework and including the operating system [21]. This implies that end users are not responsible for managing the virtual computers that are part of the underlying architecture of the operating systems that operate on them. Customers instead invest their time and effort into the deployment and maintenance of their applications, namely those that are constructed on top of the PaaS service. While this lowers infrastructure flexibility, it allows end users to access specific application services more rapidly, improving market speed while decreasing operational complexity [22]. Amazon Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure Web Apps are examples of services that fall within the PaaS.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
All SaaS solutions may be accessed using a web browser or an app and are typically cloud-based. Since the cloud provider takes care of all other aspects of the program, including the software itself, the end user only has to be concerned with the data that is stored on the application, not the underlying operating system, virtual operating system, or physical infrastructure. SaaS programmers such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce are just a few examples of popular applications [23].
All SaaS solutions are frequently located on the cloud and easily available through a web browser or a mobile application The end user just needs to worry about the data stored on the application since the cloud provider maintains everything else-from the software itself to the operating system that is running underneath it as well as the virtual and physical infrastructure. Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Google Workspace are examples of well-known software as a service projects.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Types of Computing Deployment Models
There are four basic types of cloud computing deployment methodologies now in use.
Private / On-Premises Cloud
An on-premises cloud, also known as a private cloud, is an extension of the on-premises IT architecture that incorporates certain features of public cloud computing. These qualities include Provisioning self-service and semi-automated and consumption of resources. It is often privately owned and managed by a single entity (i.e., an enterprise organization) for their internal consumption [24]. It is essential to keep in mind that a customer’s Private clouds can be hosted either on the customer’s premises, within the customer’s own data center, or on the customer’s premises of a third party, either in the form of a facility for co-location, or even at a local service provider. in the form of a managed service offering., or on the customer’s premises of a third party, either in the form of a co-location facility or even at a local service provider in the form of a managed service offering.
Both of these options have their advantages and disadvantages. Many enterprise customers have a preference to keep using private clouds that are run in their own data centers and are managed by their dedicated IT teams. These teams are responsible for the management of the infrastructure platform on a day-to-day basis, together with its procurement and provisioning. This model of deployment is typically associated with a high CAPEX (capital expenditures) cost, despite the fact that it provides advantages such as granular control, security, and flexibility.
Public Cloud
Large cloud service providers (also known as hyperscalers; see above) own and operate the public cloud as a globally dispersed, shared information technology (IT) infrastructure that features logical partitions to ensure the privacy and security of multiple tenants. In order for their clients to utilize these environments in a risk-free manner, cloud service providers develop and construct scalable platforms and assure the existence of logical security barriers. autonomously, and without human intervention. Importantly, users of the public cloud can switch from the conventional IT model of capital expenditures (CAPEX) to an operational expenditures (OPEX) model by paying only for the resources they actually use [25]. Multiple computing models (as described above) are made available to end users via the public cloud, which is an advantage over traditional deployment models due to the public cloud’s scalability, high reliability, availability, and cost efficiency.
Hybrid Cloud
There are two types of cloud deployment architecture: public and private/on-premises. When these two models are combined, customers gain access to the best features of both while also receiving an IT solution that is better suited to the needs of each department or LOB within the company. Hybrid cloud management is extremely adaptable, allowing consumers must fulfil demanding standards such as data sovereignty and security without giving up the advantages of the public cloud, such as innovation, cost efficiency, and scalability. However, the operational complexity associated with a hybrid cloud strategy may limit its applicability to only the most demanding of clients, such as large enterprises [26].
Hybrid architectures have a great deal more flexibility to fulfil both the established and the emerging needs of the business because they can access resources from both traditional data centers and public cloud computing environments. The increasing number of business clients who are starting to consume information technology solutions offered by public cloud providers is a major factor that is driving the rising popularity of the hybrid cloud architecture model. clouds while continuing to use their previous on-premises IT environments.
Multi-cloud
Although it is arguable that the multi- cloud the multi-cloud approach is predominantly oriented on the integration of a multitude of platforms hosted in the public cloud (at least two or more public cloud platforms), with or without the presence of private clouds. The implementation of this architecture is basically a specialized kind of hybrid cloud technology. It is possible to achieve this goal with or without the utilization of private clouds. An organization is given the by employing this strategy, it will be possible to deploy applications or information technology services across numerous cloud platforms that are controlled by employing a heterogeneous architecture and governance style across the board, several cloud service providers [27].
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Virtualization in Cloud Computing
The term “virtualization” refers to a technique that enables users to generate digital representations of actual devices such as servers, storage systems, and networks [28]. The ability to operate several virtual machines simultaneously on a single physical computer is made possible by virtual software that emulates the functionality of real hardware. Virtualization allows businesses to maximize the effectiveness of their utilization of their hardware resources and get higher returns on their investments. In addition to this, it powers cloud computing services that assist enterprises in more effectively managing their infrastructure [28].
If you use virtualization, you will have greater flexibility in how you interact with any hardware resource you choose. Physical servers require maintenance and upkeep, as well as consumption of electricity and storage space. If you want to access them, your options are frequently constrained by factors such as physical proximity and the design of the network. Virtualization is able to circumvent all of these restrictions because it abstracts the functionality of physical hardware into software. Your hardware infrastructure can be maintained, managed, and used just like an application when it’s connected to the web. Take for example a hotel that requires servers for the following three functions:
1. Safely storing emails related to business
2. Maintain an application that interacts with customers
3. Carry out operations on applications used within the company
Efficient Hardware Use
Using the technology known as virtualization, the hotel was able to generate three digital servers, also known as virtual machines, on a single physical server. It is capable of using the virtual machines in the same manner as the real servers and sets the operating system requirements for such machines. However, the business now has fewer pieces of gear, which has resulted in fewer associated costs.
Infrastructure as a Service
The hotel may take things take it one step further and make use of a cloud instance or virtual machine that is offered by a cloud computing provider such as Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS is in responsible of maintaining all of the underlying hardware, and the company may make requests for server resources in a variety of different configurations. These requests can be made using the AWS management console. On these virtual servers, every single software continues to work normally, and users are completely unaware of any modifications that have been made. The information technology staff of the organization will also profit from the streamlined management of the server.
How AWS with the Implementation of Computing in the Cloud and Virtualization?
By utilizing AWS, you have many options for rapidly developing, deploying, and launching cutting-edge technologies. For instance, you may profit from any of the following services:
• Use Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) to exert granular control over your infrastructure. Pick the central processing units, storage choices, and networking configurations that work best for your requirements.
• Utilize AWS Lambda for server-less computing to execute code without requiring servers.
• Amazon Light Sail may be used to construct affordable and predictable costs for virtual servers, storage, database management, and networking services.
Virtualization Has Many Advantages.
Virtualization offers many benefits to any business.
1. Efficient resource utilization
The use of hardware resources in your data center may be improved by virtualization. For instance, rather than running a single server on a single computer system, you might construct a virtual server pool on the same computer system by removing servers from the pool as needed and then returning them when they are no longer needed. Your data center will have more free space as a result of having fewer underlying physical servers, and you will spend less money on utilities like energy, generators, and cooling equipment.
2. IT Administration that is Fully Automated
Since actual computers may now be represented virtually, you can manage them with the help of various software applications. Administrators are the ones responsible for developing deployment and configuration scripts in order to construct virtual machine templates. You are able to replicate your infrastructure on a regular basis and maintain its integrity while avoiding manual settings that are prone to mistake.
3. Accelerated Catastrophe Recovery
When outside forces, such as natural catastrophes or cyberattacks, have a detrimental impact on the operations of a company, it may take many hours or even several days to recover access to the IT infrastructure and either replace or repair a physical server. With virtualized environments, on the other hand, the procedure just takes a few minutes. This fast reaction considerably enhances the resilience of the system and promotes the continuation of commercial activities, allowing operations to continue as scheduled.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
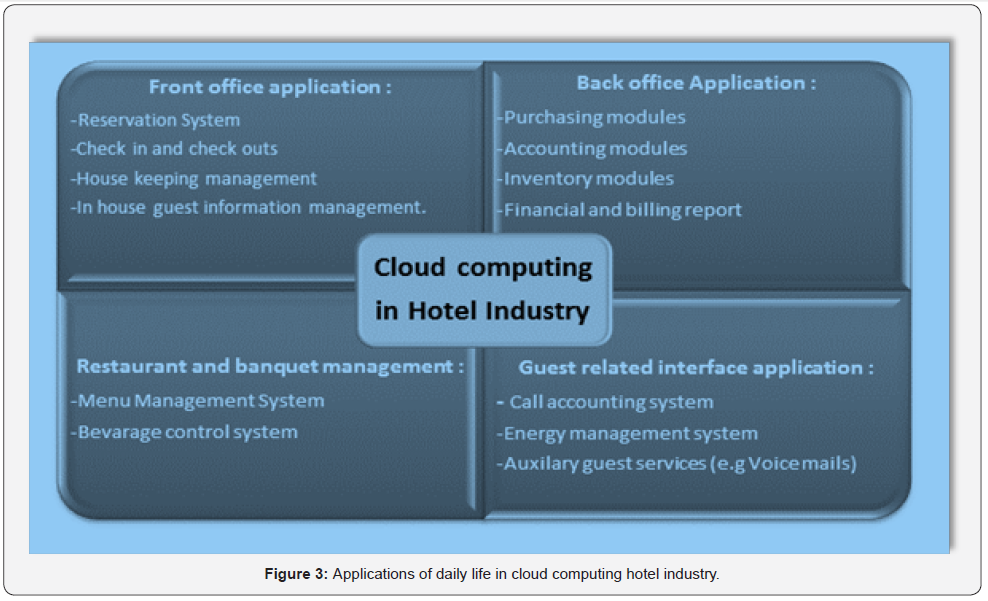
The total cost of ownership (TCO) is decreased, and delivery time is shortened, and possibilities for new innovations are expanded. The ability to quickly adapt to shifting market conditions and customer preferences is made possible by having data stored in the cloud. As a result of rising online demand and the popularity of remote work, many businesses have moved their services and data to the cloud in recent months. Companies that have already started transitioning to cloud computing are paving the path for future enterprises by expediting the cloud revolution Applications of daily life in cloud computing hotel industry as show in Figure 3. Benefits of migrating to the cloud are.
• Increased agility and flexibility
• Ability to innovate faster
• Easing of increasing resource demands
• Better managing of increased customer expectations
• Reduction in costs
• Deliver immediate business results
• Simplify IT
• Shift to everything as-a-service
• Better consumption management
• Cloud scalability
• Improved performance
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Migration Strategies
Cloud migration strategies No of the state of the IT environment at your place of business at the moment, it is imperative that your firm complete exhaustive preparation before beginning the migration process. Every cloud provider has its own unique set of cloud migration techniques, which are outlined in Table 1. These cloud migration tactics may be adapted to fit your cloud-migration strategy. Always keeping your customers and other end users in mind throughout each step of the migration process is the aspect of this process that is the most important.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Conclusion
In this review article, the disc implementing technology that runs in the cloud at a hotel should be done with the goal of either expanding earnings or reducing the amount of time spent on various activities. Computing in the cloud has the ability to give hotels IT and IS departments that are much simpler operations. Using a system that is hosted in the cloud may result in financial savings over the long run. Computing on the cloud offers numerous advantages over in-house server systems, including cost-effectiveness, efficiency, scalability, and environmental friendliness. These advantages may be found in cloud computing. Computing on the cloud, on the other hand, raises a number of questions that might prove to be problematic in terms of safety, legal accountability, dependability, and trustworthiness. Before opting to make the move to a cloud-based system, a hotel has to make an educated and extremely thorough choice to determine whether or not the advantages will exceed the difficulties.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
Acknowledgments
The authors are gratefully acknowledging the help of editors, reviewers and all his team.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Risk and Challenges for Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Developments Models and Architectures for SMEs
- Types of Computing Deployment Models
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Hotels Shifting their Focus to Cloud Computing
- Migration Strategies
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgments
- References
References
- Kim W (2009) Cloud Computing: Today and Tomorrow. Journal of Object Technology 8(1): 65-72.
- Ayoobkhan M, Kaldeen M (2020) An Empirical Study on Cloud Computing Technology on Hotel Industry in Sri Lanka. The Emerald Handbook of Ict in Tourism and Hospitality. Emerald Publishing Limited, Bingley, UK, pp. 425-440.
- Vella E, Yang L, Anwar N, Jin N (2018) Adoption of Cloud Computing in Hotel Industry as Emerging Services. International Conference on Information pp. 218-228.
- Schneider A (2012) The Adaptation of Cloud Computing by the Hotel Industry. University of Nevada, Las Vegas, USA.
- Schleier-Smith J, Sreekanti V, Khandelwal A, Carreira J, Yadwadkar NJ, et al. (2021) What Serverless Computing is and Should Become: The Next Phase of Cloud Computing. Communications of the ACM 64(5): 76-84.
- Shiau WL, Chau PYK (2016) Understanding Behavioral Intention to use a Cloud Computing Classroom: A Multiple Model Comparison Approach. Information & Management 53(3): 355-365.
- Buyya R, Yeo CS, Venugopal S, Broberg J, Brandic IJFGCS (2009) Cloud Computing and Emerging it Platforms: Vision, Hype, and Reality for Delivering Computing as the 5th Future Generation Computer Systems 25(6): 599-616.
- Khajeh Hosseini A, Sommerville I, Bogaerts J, Teregowda P (2011) Decision Support Tools for Cloud Migration in the Enterprise. 2011 Ieee 4th International Conference on Cloud Computing Ieee pp. 541-548.
- Chieu TC, Mohindra A, Karve AA, Segal A (2009) Dynamic Scaling of Web Applications in a Virtualized Cloud Computing Environment. 2009 Ieee International Conference On E-Business Engineering, Ieee pp. 281-286.
- Khajeh-Hosseini A, Sommerville I, Sriram I (2010) Research Challenges for Enterprise Cloud Computing.
- Qian L, Luo Z, Du Y, Guo L (2009) Cloud Computing: An Overview. IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing pp. 626-631.
- Dillon T, Wu C, Chang E (2010) Cloud Computing: Issues and Challenges. 2010 24th Ieee International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications. Ieee pp. 27-33.
- Tarhini A, Al Badi A, Almajali M, Alrabayaah SH (2017) Factors Influencing Employees¡ Intention to use Cloud Computing. Journal of Management and Strategy, Sciedu Press 8(2): 47-62.
- Takabi H, Joshi JB, Ahn GJ (2010) Security and Privacy Challenges in Cloud Computing Environments 8: 24-31.
- Ahmed HAS, Ali MH, Kadhum LM, Zolkipli MF, Alsariera YA (2017) A Review of Challenges and Security Risks of Cloud Computing 9: 87-91.
- Rana S, Joshi PK (2012) Risk Analysis in Web Applications by Using Cloud Computing. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research 2(1): 386-394.
- Pearson S, Benameur A (2010) Privacy, Security and Trust Issues Arising from Cloud Computing. 2010 Ieee Second International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science. Ieee pp. 693-702.
- Yang JN, Yang JK, Lin K (2015) The Cloud Computing and the Application of Cloud Computing in the Telecommunication Enterprise. Applied Mechanics and Materials. Trans Tech Publ 729: 195-198.
- Ucuz D (2020) Comparison of the IOT Platform Vendors, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, And Google Cloud, from Users’ Perspectives. 2020 8th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (Isdfs). Ieee pp. 1-4.
- Manvi SS, Shyam GK (2014) Resource Management for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in Cloud Computing: A Survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 41: 424-440.
- Giessmann A, Stanoevska-Slabeva K (2012) Business Models of Platform as a Service (PaaS) Providers: Current State and Future Directions. Journal of information technology theory and application 13(4): 31-55.
- Devi T, Ganesan R (2015) Platform-As-A-Service (PaaS): Model and Security Issues. International Journal of Advances in Applied Sciences 4(1): 13-23.
- Tsai W, Bai X, Huang Y (2014) Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): Perspectives and Challenges. Science China Information Sciences 57: 1-15.
- Diaby T, Rad BB (2017) Cloud Computing: A Review of the Concepts and Deployment Models. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science 9(6): 50-58.
- Jansen WA, Grance T (2011) Guidelines on Security and Privacy in Public Cloud Computing. National Institute of Standards and Technology. Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
- Li Q, Wang ZY, Li WH, Li J, Wang C, et al. (2013) Applications Integration in a Hybrid Cloud Computing Environment: Modelling and Platform. Enterprise Information Systems 7(3): 237-271.
- Singh Y, Kandah F, Zhang WA (2011) Secured Cost-Effective Multi-Cloud Storage in Cloud Computing. 2011 Ieee Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (Infocom Wkshps). Ieee pp. 619-624.
- Xing Y, Zhan Y (2012) Virtualization and Cloud Computing. Future Wireless Networks and Information Systems 143: 305-312.






























