The Role of Genetic Mutations on Gene MAOA Polymorphism (rs2273505) in Hysteria Disorder
Seyyed Mohammad Reza Miremadi and Shahin Asadi*
Division of Medical Genetics and Molecular Pathology Research, Harvard University, Boston Children’s Hospital, USA
Submission: February 15, 2023; Published: February 24, 2023
*Corresponding author: Asadi, Medical Genetics-Harvard University. Director of the Division of Medical Genetics and Molecular Optogenetic Research, USA
How to cite this article: Seyyed Mohammad Reza Miremadi and Shahin Asadi*. The Role of Genetic Mutations on Gene MAOA Polymorphism (rs2273505) in Hysteria 002 Disorder. Psychol Behav Sci Int J. 2023; 20(2): 556035. DOI: 10.19080/PBSIJ.2023.20.556033.
Abstract
Hysteria disorder is in the category of neurological disorders with functional origin. The diagnosis of hysteria disorder is the responsibility of the psychologist and is done after counseling sessions. In this disorder, the person in question complains about symptoms and physical disabilities. It is interesting to know that there is no medical evidence for the existence of these symptoms. So, what is the reason? Scientists have not yet been able to identify the exact origin of hysteria, but there are several possibilities for it. Hysterical disorder can be caused by excessive anxiety in a way that affects a person’s sensory and motor neurons. Also, the person may have experienced severe trauma in the past.
Keywords: Hysteria Disorder; Genetic Mutation; MAOA Gene; Polymorphism; Anxiety
Introduction
Hysteria is a type of mental disorder in the category of anxiety disorders whose symptoms are all physical. In fact, the person appears to have a physical illness, but there is no medical reason for this patient disorder. You may also find it interesting that the affected person suddenly feels paralyzed and cannot walk. While there was no damage to his body. Hysteria is caused by psychological causes that are present in a person’s history. This disorder requires psychotherapy for treatment [1]. Hysteria is a word that is mainly used for women since ancient Greece. Hysteria is actually called a wandering uterus and it has been believed that hysteria is caused by specific movements of women’s uterus.
In fact, abnormal movements of the uterus have long been known to cause a series of special physical and mental symptoms. Hysteria is undoubtedly the first mental disorder attributed to women, accurately described in the second millennium BC, and until Freud considered it an exclusively female disease. Over 4000 years of history, this disease has been considered from both scientific and demonic perspectives [1].
This disease was treated with herbs, sex or abstinence. Because of its association with witchcraft, it was punished and purged with fire, and was eventually studied clinically as a disease and addressed with innovative treatments. However, even at the end of the 19th century, scientific innovation had not yet reached some places where the only known treatments were those proposed by Galen.
During the 20th century, several studies hypothesized a decline in hysteria among Western patients (both women and men) and an increase in the disorder in non-Western countries. The concept of hysterical neurosis was removed with the 1980 DSM-III. Hysteria is used among people to be nervous due to mental pressure. In fact, from the point of view of meaning and history, applied hysteria is inappropriate. For example, saying the word “hysterical laughter” means that a person laughs due to mental pressure in a situation that is inappropriate. But the meaning of nervous in hysterical disorder is the connection of the disease with the central or peripheral nervous system of the body [2].
Changes in the meaning of the word hysteria
Hysteria has undergone enormous changes throughout history. As mentioned, at the time of the ancient Greeks, it was believed that the woman’s womb caused such symptoms. During the Middle Ages, such symptoms were considered to be the result of being possessed by ghosts and demons, and all kinds of tortures were applied to the person so that these demons and spirits would leave his body [2]. Hysteria is a slang term used to mean uncontrollable emotional excess and can refer to a temporary state of mind or emotion. In the 19th century, when hysteria was considered a diagnosable physical disease in women, it was assumed that the diagnosis was based on the stereotyped belief that women were prone to such psychological and behavioral conditions. Indeed, an interpretation of gender-related differences in stress response. In the 20th century, it was considered a mental illness. Many influential people such as Sigmund Freud and Jean- Martin Charcot devoted their research to hysteria patients [2].
\A modern interpretation of hysteria
Currently, most medical practitioners do not accept hysteria as a medical diagnosis. The general diagnosis of hysteria is divided into countless medical categories such as epilepsy, histrionic personality disorder, conversion disorders, dissociative disorders, or other medical conditions. Furthermore, lifestyle choices, such as choosing not to marry, are no longer considered symptoms of mental disorders such as hysteria.3
After a long time and with the advancement of medical science, doctors realized that symptoms appear without any medical or biological justification. Finally, the American Psychiatric Association removed the term hysteria and instead provided a more accurate and clear classification and called it physical symptom disorder, and some similar symptoms were included in the category of psychosomatic disorders. Click to learn more about physical symptoms and psychosomatic disorders [3].3
Definition of hysteria
Conversion disorder, formerly called hysteria, is a mental disorder in which a wide range of sensory, motor, or mental disturbances may occur. It is traditionally classified as one of the neuropsychiatric disorders and is not associated with any known organic or structural pathology. The earlier term, hysteria, is derived from the Greek word hystra, meaning “womb,” and reflects the ancient notion that hysteria was a female-specific disorder caused by uterine dysfunction. But in fact, symptoms of conversion disorder can develop in both sexes and can occur in children and the elderly, although it is often seen in early adult life. Conversion disorder in its pure clinical form appears to occur more among psychologically and medically naïve individuals than among complex individuals.
Also, the incidence of conversion disorder is decreasing in many regions of the world. Probably due to cultural factors such as increased psychological and medical awareness among the general public. Cases of classical conversion disorder, such as those often described by 19th-century physicians, have become rare. Many of the neuroses encountered in actual clinical practice are “mixed” forms in which conversion disorder symptoms may be intermingled with other types of neurotic disorders. Individual conversion disorder symptoms may also occur with psychotic disorders [4].
In the course of this disease, a person shows certain symptoms for which there are apparently no clear physical causes. These symptoms are very broad, but they usually include sensoryneurological disorders. For example, a person shows numbness and touch of a body part, blindness, deafness, inability to walk and other things, while there is no reason for it. In fact, hysteria is a type of anxiety disorder and is related to anxiety [5]..
Causes of hysteria
The causes of this disease are very complex and arise from the situation and psychological conflicts. As mentioned, the person does not have any defect or disorder in the nervous system that would justify his paralysis or blindness. However, he keeps his symptoms and medical interventions do not change his condition [6]. Sufferers often have deep psychological conflicts. In fact, these people have difficulty experiencing their emotions deeply. Instead of being able to express their emotions, or experience their conflicts and anger, they show them in the form of physical symptoms. For example, they may not show any kind of discomfort or stress symptoms regarding a subject that is very painful for them, but they show excitement in the form of paralysis in their legs. They often suppress their anxiety and stress. Unlike anxiety disorder, the person shows symptoms of anxiety [6].
Outbreak of Hysteria
As it was said, hysteria was considered to be a disease specific to women, but gradually, with the precise criteria for it, cases were seen among men as well. But in fact, this disorder has been seen more among women than men [7].
Treatment of hysteria
The treatment of hysteria has undergone many changes throughout history. One of the first treatments used for it was hypnosis. But later this treatment changed. During the psychoanalytic treatment, the psychoanalyst examines the person’s past, and the signs and symptoms disappear in the meantime. Other treatments such as schema therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy are also used today to eliminate signs and symptoms. In fact, this disease is unconsciously related to stress and anxiety and is aggravated by mental tension [8,9].
Materials and Methods
In this study, blood samples were taken from 50 people suffering from hysteria disorder, 40 of whom were female and 10 of whom were male and 50 people Health, and with their written consent, molecular genetic testing was performed to check the changes in these genes. Individual information (such as age, gender, medical history) was recorded. The subjects were selected after final diagnosis by a child and adolescent psychiatrist according to DSM-V criteria, signed a written consent for blood sampling, and filled out an interview form designed to understand the contribution of genetic influence.
2 cc of blood was taken from each person and in Falcons
containing EDTA as an anticoagulant; It was poured and then
the falcons were gently shaken to mix to prevent blood clots
from forming. Finally, the samples were stored in a -20°C freezer
to extract DNA from blood. Saturated salt method was used to
extract genomic DNA from whole blood samples. After DNA
extraction, its concentration must be determined so that a certain
concentration of DNA is subjected to the PCR reaction. In this case,
the concentration of DNA used is constantly maintained. Two
methods are used to determine the concentration and quality of
the extracted DNA.
1- Spectrophotometric method
2- Electrophoresis method
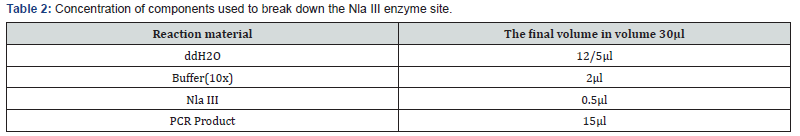
Spectrophotometry is a quantitative method and electrophoresis is a qualitative method. Molecular RFLP-PCR technique was used for this study. This technique is commonly used to examine different alleles of a gene in a population. The sequence diversity of the respective gene alleles creates different cleavage sites for the restriction enzymes, resulting in fragments of different lengths. Depending on the length of the DNA fragments obtained from the cut, the change in nucleotides can be detected. One of the advantages of this method is that it is fast and does not require a probe (Table 1).

Genotype determination: MAOA
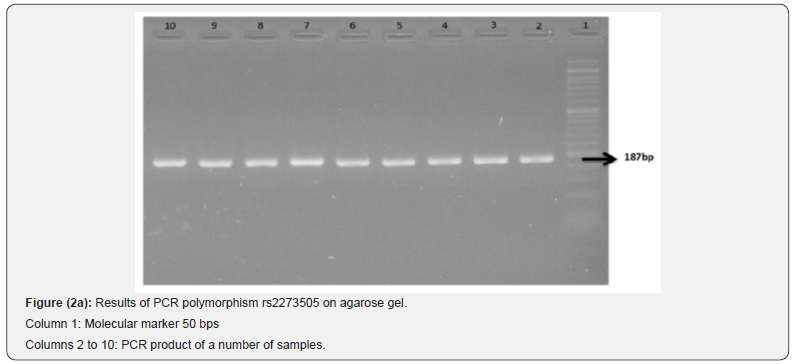
To determine the rs2273505 bi-allelic polymorphism, the intron 2 region was amplified by PCR. The characteristics of the primers are given in (Table 2-5), the PCR reaction concentration in (Table 2-6), and the PCR steps. PCR products were isolated on 2% agarose gel. Alleles were identified as 187 bp band after staining the gel with safe stain.


Investigation of MAOA polymorphism (rs2273505) by RFLP method
After PCR reaction using the mentioned primers according to the optimal PCR conditions, a fragment with a length of 187 bp was amplified. To ensure the performance of the PCR reaction for all samples, their PCR products were electrophoresed on 2% agarose gel and stained with Safe stain. PCR products were then cut using Nla III enzyme according to the following steps:
First, all the materials needed for the RFLP reaction, which include double ionized distilled water, a specific buffer of Nla III enzyme, Nla III enzyme, are poured into microtubes containing the PCR product. Then place the microtubes in a pan at 37°C for 16 hours. The concentrations of the materials used to break down the Nla III enzyme site are shown in (Table 2).
After this period, some of the product containing the enzyme was cut, loaded on agarose gel and electrophoresed. And in the last step, that photo was taken.
Nla III enzyme and its cleavage site
Nla III enzyme is a highly functional restriction enzyme and its
cleavage site is as follows:
5 ‘... C A T G ... 3’
3 ‘... G T A C ... 5’ (Figure 1)

Result
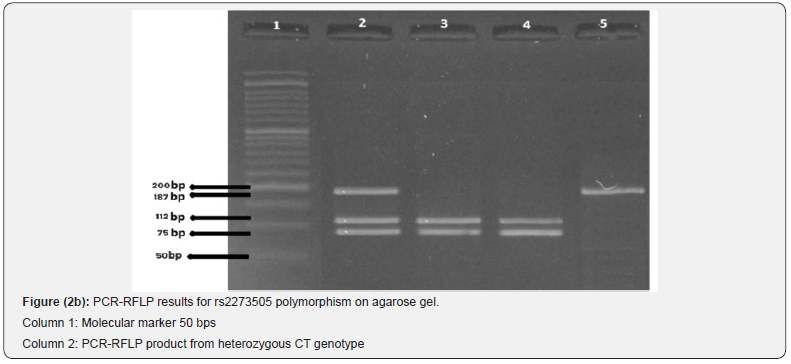
PCR-RFLP technique was used to investigate this polymorphism. The results of electrophoresis of PCR products related to amplification of rs2273505 polymorphism using appropriate specific primers and fragments of amplification of this polymorphism are shown. PCR fragments contain fragments of length 187bp (Figure 2a) and fragments from RFLP-PCR with the effect of Nla III restriction enzyme in the presence of T allele at the enzyme identification site located at the site of the relevant polymorphism; It is cut into two pieces with lengths of 112 and 75bp and in the presence of C allele it is cut into one piece 187bp and in the presence of CT allele it is cut into three pieces with lengths of 187, 112 and 75bp. (Figure 2 b).
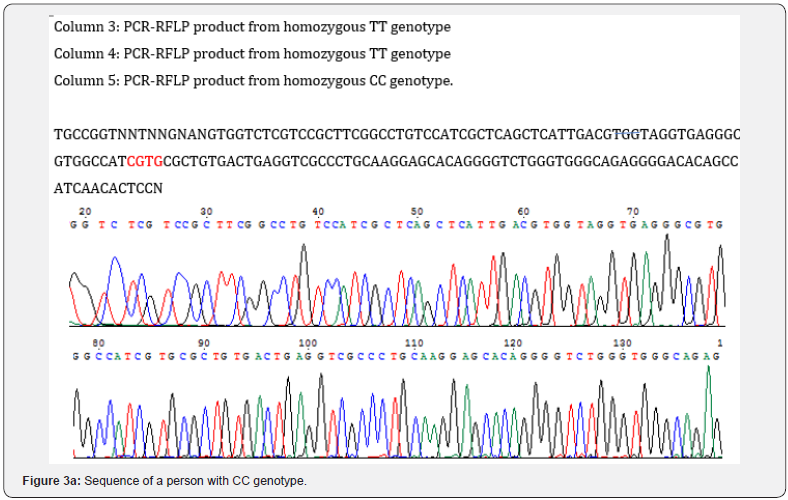
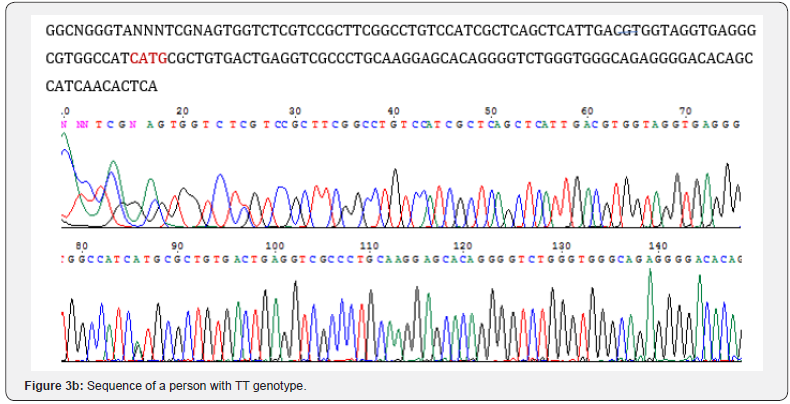
Sequencing of PCR polymorphism rs2273505 products: In addition to electrophoresis, PCR products were randomly sent to Fazapjoo to ensure sequencing, the results of which are shown in (Figure 3a & 3b).
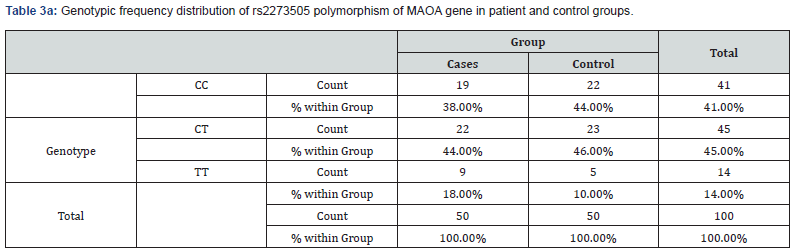
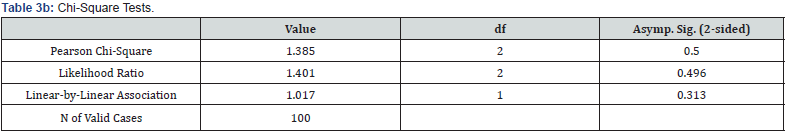
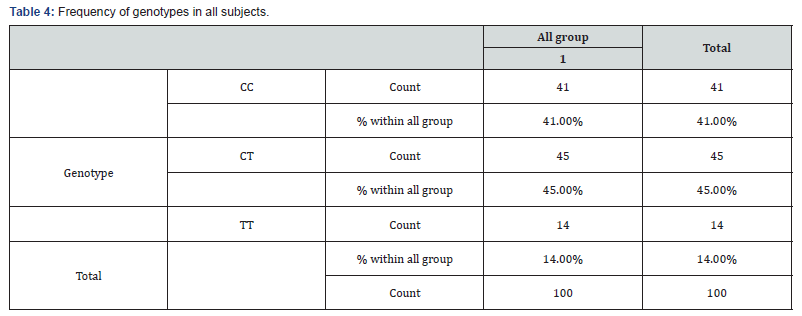
Based on statistical calculations and genotypic distribution between patients and controls, no correlation was found because the calculated P-value for different genotypes is greater than 0.05, which means that the hypothesis of the association of this polymorphism with Hysteria is rejected (0.5=P-value). The genotypic frequency distribution of rs2273505 polymorphism of MAOA gene was calculated in the whole patient and control groups (Table 4). In order to study the genotypes of this polymorphism in all subjects, Chi-square (X2) statistical method was used. P-value. Calculated for the genotypes of all individuals is less than 0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship in all subjects (P-value = 0.00).
Results of MAOA gene polymorphism rs2273505
In this study, the association of MAOA rs2273505 polymorphism with RFLP technique was investigated. In this regard, 50 people with Hysteria and 50 healthy people without a history of Hysteria as a control group in the northwestern region of Iran were studied. The characteristics of the sick and control subjects are given in (Tables 3a & 3b). The genotypic distribution of rs2273505 polymorphism was calculated for patients with Hysteria and the control group. The results of the study are given in (Table 3).
Frequency of CC, CT + TT genotypes between patients and control group
In addition to the frequency of CC, CT, TT genotypes, the dominant and recessive genotypes of this polymorphism were also examined between the patient and control groups (Table 5a & 5b). (Table 6a & 6b) lists the number of CC and CT + TT genotypes along with the frequency of each of them separately in the patient group and the control group. In order to investigate the relationship between CC genotypes and CT + TT in the patient and control groups, Chi-square method was used, which due to its significance level is 0.54, as a result between the genotypes of this polymorphism There was no significant difference between patient and control groups (P-value = 0.54).
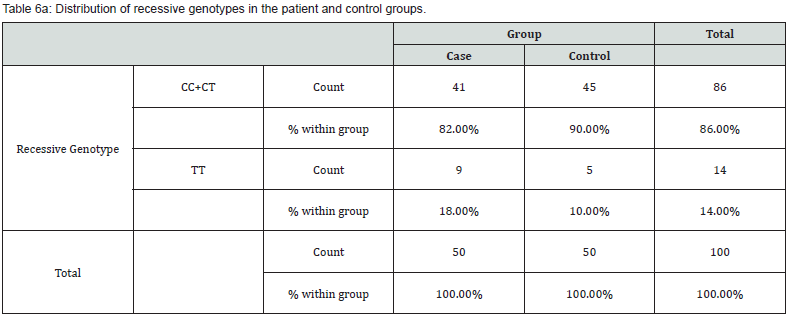
Frequency of CC + CT and TT genotypes between patients and control group
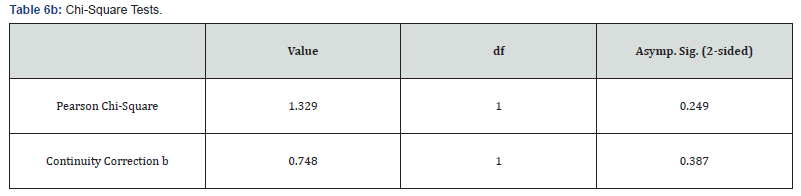
(Table 6a & 6b), lists the number of TT and CC + CT genotypes along with the frequency of each of them separately in the patient group and the control group. Chi-square statistical method was used to investigate the relationship between TT genotypes with CT + CC in both patient and control groups. Due to the fact that its significance level is equal to 0.24, as a result, there is no significant relationship between the genotypes of this polymorphism in the patient and control groups (P-value = 0.24).
Statistics Analysis
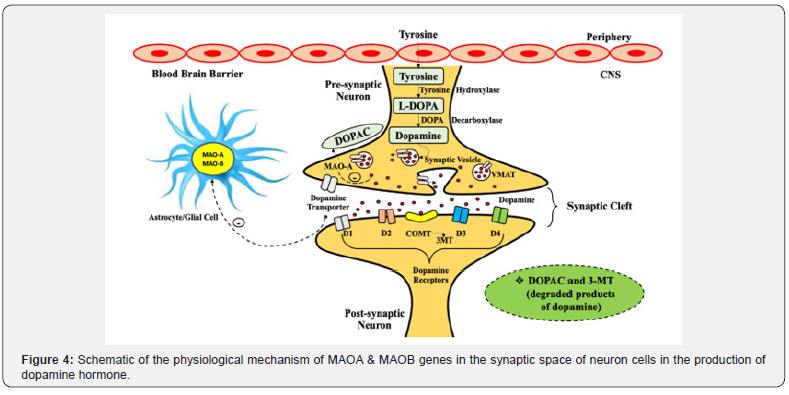
This study is a case-control study whose results have been statistically analyzed and compared between patients and controls and also between patient subgroups depending on the presence or absence of symptoms, by chi-square method. To take. In this study, a significant level of 0.05 is considered, in other words, P<0.05 indicates that the difference between control and patient is significant. While P<0.05 indicates that there is no significant difference between control and patient. In this study, CI confidence interval was used to investigate the relationship between patients and controls. If the CI overlaps, the data do not differ significantly (Figure 4).
Discussion
As it was said, hysteria is not a sign of physical and motor impairment. So it can be concluded that the existence of severe psychological conflicts is the cause of these symptoms. In people with this disorder, aggressive interventions do not have any positive results, and in fact, there is no evidence of the presence of relevant symptoms in his medical records. Environmental conditions play a major role in the severity of this disorder. The environment may be so stressful that the person cannot control and tolerate the situation. The result is that these people show a series of physical disabilities in response to those conditions. In fact, the emotional responses of this group of people are not normal. Because eventually it manifests as a physical defect. However, the treatment of hysteria is of great help to this group of people [10,11].
Imagine a war soldier claiming to be blind. The examinations performed on him do not prove such a thing. This statement may be caused by the stressful atmosphere of the war and may return to its normal state after leaving the atmosphere and treating hysteria. Hysterical disorder may also apply to the disability of other body parts [12].
Hypnotherapy
An effective hysteria treatment for conversion disorder is hypnotherapy or hypnotherapy. In fact, people with hysteria respond differently to hypnotherapy. They are more involuntary against hypnosis than any other person and do not show resistance. The greater the degree and severity of hysteria, the better the response to its treatment. Considering that the psychological reactions of these people are very different from other patients with psychiatric disorders, hypnotherapy is considered an excellent treatment for them. Of course, the basic and important point is that in order to improve the process of hypnotherapy, the person must cooperate with you. In fact, you cannot hypnotize them without their personal desire and cooperation. Of course, there is no doubt that this treatment is safe and effective. Because the mental weakness of hysterical people is so great that they respond positively to treatment [13].
Drug therapy or pharmacotherapy
Another available and approved treatment for hysteria is drug therapy or pharmacotherapy. Of course, the use of this hysteria treatment has its own conditions. For example, when a person does not respond positively to psychotherapy sessions, the second line of treatment is drug therapy. Of course, this is provided that the person in question suffers from other psychiatric disorders such as mania and major depression in addition to hysteria. In this case, the psychiatrist must prescribe the necessary anti-depressant and antipsychotic drugs to control and reduce the relevant symptoms. Remember that drug therapy only controls the relevant condition. In fact, the main treatment is psychotherapy sessions or CBT [14].
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is another method of treating hysteria. As mentioned, psychotherapy sessions should be considered for the hysterical person before any drug treatment. One of the effective methods in this treatment is for the person to gain insight into his disorder. When a person learns about his behaviors and movements and compares himself with other normal people in society, he has actually gained insight into his disorder. This treatment is more analytical and in fact the patient analyzes his behavior together with the psychologist. In order to find out more about his behavior, he is filmed during psychotherapy sessions. Along with psychotherapy, meditation and yoga can be used to relax the person as much as possible [15].
Relaxation and physical therapy
Relaxation and physical therapy in the treatment of hysteria reduce both stress and physical problems of the person. In fact, he kills two birds with one stone. Of course, physical therapy is recommended if a person is disabled or paralyzed in one or more of his limbs. Also, relaxation techniques significantly reduce the patient’s anxiety and stress. This has a significant effect on the symptoms of hysteria [16].
An important point about hysteria treatments
The use of each of these treatments largely depends on the individual’s condition and his response to the treatment. Finally, the psychologist considers one of these treatments for the individual according to the existing conditions. Know that until psychotherapy techniques are effective, there is no need to use drug treatments, unless the person is suffering from other psychiatric disorders. The main goal of treating people with this disorder is to minimize their stressful and crazy behaviors. Freud, who is the pioneer of psychotherapy in this type of disorder, believed that hysterical people have conversion-type defense mechanisms. He also finds the origin of this mechanism in the form of physical weakness, distress and excessive anxiety [17-20].
References
- Basavarajappa C, Dahale AB, Desai G (2020) Evolution of bodily distress disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 33(5): 447-450.
- Beattie M, Lenihan P (2018) Counselling Skills for Working with Gender Diversity and Identity. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers P: 83.
- Micale MS (2019) Approaching Hysteria: Disease and Its Interpretations. Princeton University Press, USA.
- Krasny E (2020) Hysteria Activism: Feminist Collectives for the Twenty-First Century, Performing Hysteria, Images and Imaginations of Hysteria. Braun Johanna (ed.) Leuven University Press Pp: 125-146.
- Abse DW (2013) Hysteria and Related Mental Disorders: An Approach to Psychological Medicine. Butterworth-Heinemann.
- (2020) Hysterical adjective - Definition, pictures, pronunciation and usage notes | Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary at Oxford Learners Dictionaries.com.
- Reynolds EH (2012) Hysteria, conversion and functional disorders: a neurological contribution to classification issues. Br J Psychiatry 201(4): 253-254.
- Hustvedt A (2011) Medical Muses: Hysteria in Nineteenth Century Paris. (W. W. Norton & Company). The Historian 74(2): 402-403.
- Evans M (2019) Fits and Starts: A Genealogy of Hysteria in Modern France. Cornell University Press, USA.
- Mota GM, Engelhardt E (2014) A neurological bias in the history of hysteria: from the womb to the nervous system and Charcot. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 72(12): 972-975.
- (2021) The History of Hysteria. Office for Science and Society.
- (2020) Female hysteria: The history of a controversial condition.
- Charcot JM (2013) Clinical Lectures on Diseases of the Nervous System (Psychology Revivals). Routledge.
- Macleod ADS (2018) Abrupt treatments of hysteria during World War I, 1914-18. Hist Psychiatry 29(2): 187-198.
- Jones A (2010) The Feminism and Visual Culture Reader. New York: Routledge Pp: 248-258.
- Rainey H (2020) Medical Vibrators for Treatment of Female Hysteria. The Embryo Project Encyclopedia.
- Coon M, Dennis J (2013) Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior. Cengage Learning Pp: 512-513.
- Costa DS Lang CE (2016) Hysteria Today, Why?. Psicologia USP 27(1): 115-124.
- (2021) Female hysteria: The history of a controversial condition.
- D Cecily (2014) Hysteria, Feminism, and Gender Revisited: The Case of the Second Wave. English Studies in Canada 40(1): 19-45.






























