- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Investigation of Nootropic Activity of Petnunia Hybrida Flower Extract
Ikram Khan*, Deepak Kumar Basedia and B K Dubey
Technocrats Institute of Technology-Pharmacy, India
Submission: January 18, 2022; Published: February 03, 2022
*Corresponding author: Ikram Khan, Technocrats Institute of Technology-Pharmacy, India
How to cite this article:Ikram K, Deepak Kumar B, B K Dubey. Investigation of Nootropic Activity of Petnunia Hybrida Flower Extract. Psychol Behav Sci Int J. 2022; 18(3): 555987. DOI: 10.19080/PBSIJ.2022.18.555987.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Abstract
The objective of the present work was to prepare the aqueous extract of Petunia hybrida flowers and evaluate its nootropic potential in rodent. The extraction yield of the flower of Petunia hybrida flowers in water by maceration was found to be 16.3% w/w. The preliminary phytochemical analysis suggests the presence of alkaloids, saponin glycosides, phenolics, terpenoids, sterols, and flavonoids in the flowers of the plant. The aqueous extract of Petunia hybrida flowers was evaluated for quantifying the total phenolic content. The total phenolic content was found to be 28.42±2.35 GAE mg/g.
The extract of Petunia hybrida flower was subjected to evaluation of nootropic potential using elevated plus maze test and Morris water maze test at dose levels of 200 and 400 mg/kg/p. o against scopolamine induced amnesia. AEPH (200 and 400 mg/kg, p.o.) were found to be significantly improving the open arms activity (both the parameters) compared to Scopolamine treated group in the elevated plus maze test. Results of MWM test in experimental animals confirmed a significant effect of Scopolamine-toxicity, AEPH (200 mg/kg) + SCOP, AEPH (400 mg/kg) + SCOP compared to control on latency to acquire hidden platform.
Keywords: Petunia hybrida; Nootropic; Morris water maze; Total phenolics; Extraction
Keywords: WHO: World Health Organization; GAE: Gallic Acid Equivalent; SD: Standard Deviation; MWM: Morris Water Maze; AEPH: Aqueous Extract Of Petunia Hybrida; AEAS: Aqueous Extract Of Annona Squamosa
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The ability of an individual to register the event, information and retains them over short or long periods of time is called as memory [1]. Nootropic agents such as aniracetam, piracetam, and pramiracetam and choline esterase inhibitors like donepezil, rivastigmine are being primarily used to improve memory, mood, and behaviour. According to the WHO more than 80% of the world’s population relies on traditional herbal medicine for their primary healthcare. In recent time there has been a marked shift towards herbal cures because of the pronounced cumulative and irreversible reactions of modern drugs [2].
Petunia hybrida is a hybrid of various species of petunia produced by hybridization P. axillaris and P. integrifolia [3]. The plant is known to contain some acylated anthocyanins which are cinnamic acid, coumaryl rutinoside glycosides and rutinoside glucosides acylated with caffeic acid. Anthocyanins are known to be associated with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-amnesic actions [4].
The literature reviewed led us to the conclusion that Petunia hyrbida has been investigated for its medicinal properties. In a previous study at our institute the leaf extract of the plant was found to be possessing estrogenic activity [5]. The literature also reveals the plant to contain 3-runitoside-5-glucosides which belong to class of flavanones. Thus, it was decided to explore other medicinal actions of the flowers of the plant. The objective of the present work was to perform solvent extraction of the flowers of Petunia hybrida and screen the crude extracts for nootropic potential in animal model.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Material and Methods
The flowers of Petunia hyrbida were collected from the local places of Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh in the month of January and authenticated appropriately. The flowers were rinsed with distilled water to remove impurities, dried under shade, and powdered using a blender at slow speed.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Extraction of Phytoconstituents
The powdered flowers were used for the extraction process by maceration method. 250 g of powder was evenly placed in jar filled with 1000 mL of distilled water for 2 days with intermittent shaking for the first 6 h and thereafter allowed to stand for the next 18 h. The extract was filtered through Whatman filter and concentrated using rotary vacuum evaporator. The resinous extract was collected and stored in desiccator to remove the excessive moisture. The dried extracts were stored in desiccators for further processing [6].
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
The extract was evaluated by qualitative phytochemical screening to identify the type of plant secondary metabolites present in it. The screening was performed for triterpenes/ steroids, alkaloids, glycosides, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, and phenolic acids. The color intensity or the precipitate formation was used as analytical responses to these tests [7].
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Total Phenolic Content
To determine the total phenolic content, 5 g dried powder was mixed with 80 mL of water and kept overnight. The suspension was filtered through a qualitative cellulose filter paper and the filtrate was diluted to 100 mL with water. The solution was stored at 4°C in amber bottles and served as the stock solution (50 mg/ mL) for subsequent analyses [8].
For total phenolic content determination, 200μL of sample was mixed with 1.4 mL purified water and 100μL of Folin- Ciocalteu reagent. After 3 min, 300μL of 20% aqueous Na2CO3 solution was added to it and the mixture was allowed to settle for 2h33. The absorbance was measured at 760nm with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Standard solutions of gallic acid (20-100 ppm) were treated similarly to obtain the calibration curve. The control solution contained 200μL of water and suitable reagents, and it was prepared and incubated under the same conditions as the rest of the samples. Results were expressed as milligrams of gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per 100g of the dry sample.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
Animal
The male/female wistar mice of amid 1 to 2 months of age weighing between 25-35g were used procured from approved suppliers from Bhopal. The rodents were allowed free access pallet diet (Lipton India Ltd, Mumbai, Ind.) and water ad libitum. All the laboratory conditions and animals were maintained as per CPCSEA guidelines throughout the experiments.
Acute Toxicity Study
The short-term and long-term toxic effects of both drugs and their extracts were performed within prescribed guideline set by OECD guideline no. 423. The albino rats of 150-200 g were employed for study and kept in 12 h day-night cycle with ad libitum access to water. The extract was suspended in 1% Tween 80, prepared in distilled water. Animals were fasted for 12 h with and extract was admistered orally with increasing doses to 2000 mg/kg considering as maximum weight. The observation made in first 4 h for any bizarre behavior like change in skin and fur, eye, hyperactivity, grooming, convulsions, sedation, hypothermia, salivation, tremor, coma, lethargy, body weight, and mortality. From the observations and study, 1/10th and 1/5th of the lethal dose was used as therapeutic dose & cut-off values were chosen as 200 & 400 mg/kg to evaluate dose dependent action for the assessment of nootropic activity [9] (Table 1).

Grouping of Animals for Treatment
The animals were divided in 6 groups with 6 animals in each
group. The grouping and treatment per group is presented below.
Group 1 control vehicle (0.9% NaCl)
Group 2 was injected with scopolamine (SCOP) 2mg/kg
intraperitoneally for 21 days
Group 3 and 4 were administered with aqueous extract
of Petunia hybrida (AEPH) at dose of 200 and 400 mg/kg/p. o
respectively and injected with SCOP (2 mg/kg) for 21 days. (For
Morris water maze study)
Group 5 and 6 were administered with aqueous extract
of Annona squamosa (AEAS) at dose of 200 and 400mg/kg/p. o
respectively and injected with SCOP (2 mg/kg) for 21 days. (For
elevated plus maze study)
Morris Water Maze Test [10,11]
Spatial learning and memory were assessed using the Morris water maze previously described. Briefly, the testing system was composed of a black circular pool (150cm in diameter and 30cm deep) filled with water (temperature 20±2 °C) and surrounded by extra maze distal visual cues of different shape, size, and color. The pool was divided in four quadrants.
A black circular hidden platform was placed in the northwest (NW) quadrant 2 cm under the water surface so that rat could escape from swimming. Experimental mice were screened for their swimming ability by recording the latency to reach the visible platform. Mice were trained to exit the water tank onto the platform by using the visual cues. Each mouse was placed inside the water tank facing the tank wall, at one of the four randomly selected entry points, once in every block of four trials.
The test was performed on four consecutive days (8 trials per day). The starting position was changed randomly for each trial and the animal was allowed to search for 60 s to find the hidden platform. Mice were guided to the platform, if failed to find the platform within 60 s. At the end of the trials, the rat was allowed to remain on the platform for 30 s. Morris water maze training was recorded using a web camera mounted to the ceiling. Recording was performed from 11:00AM to 2:00PM to exclude variations in performance resulting from circadian rhythmicity.
Elevated Plus Maze Test [12,13]
The Elevated plus-maze comprised of two open (50cm × 10cm) and two enclosed (50cm × 10 cm×40cm) arms that radiated from the central platform (10cm × 10cm) to form a plus sign. The maze was constructed of black acrylic sheet. The plus maze was elevated to a height of 50 cm above from the floor level by a single central support. All the four arms consist of infra-red beams fitted at regular distance. The experiment was conducted during the dark phase of the light cycle (9:00 - 14:00h).
The trial was started by placing an animal on the central platform of the maze facing an open arm. During the 5 min experiment, behavior of mice was recorded as (i) preference of the mice for its first entry into the open and closed arms, (ii) the numbers of entries into the open or closed arms, and (iii) time spent by the mice in each of the arms. The mice were considered to have entered an arm when and four paws were on the arm. The apparatus was cleaned thoroughly between trials with damp and dry towels. All behavioral recording were carried out with the observer unaware of the treatment of the mice had received.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Statistical Analysis
All analysis was performed using graph pad prism 5 for Windows. All statistical analysis was expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Results and Discussion
Extraction Yields
The extraction yield of the flower of Petunia hybrida flowers in water by maceration was found to be 16.3% w/w. The extract was resinous and black in color.
Phytochemical Screening
For detecting the occurrence of alkaloids, glycosides, tannins, saponins, flavonoids and terpenoids in the extracts, a small fraction of the dried extract was subjected to the phytochemical testing procedures by resuspending a small amount of each extract suitably into the sterile distilled water/ethanol. The findings of the phytochemical analysis suggest the presence of phenolics and tannins, proteins, and flavonoids in the aqueous extract of the flowers.
Total Phenolic Content
The aqueous extract of Petunia hybrida flowers was evaluated for quantifying the total phenolic content. Standard curve of gallic acid was plotted in distilled water. The result of the total phenolic content of the extract examined using Folin-Ciocalteu method. The total phenolic content of aqueous extract of Petunia hybrida was found to be 28.42±2.35 GAE mg/g.
Acute toxicity Study
There was no sign and symptoms or any toxic effects in rodents for both plants even at higher dose of 2000 mg/kg body weight. Thus, 1/10th of maximum dose was selected as effectual dose. The cut off value of 200 & 1/5th dose i.e., 400 mg/kg were chosen for evaluation of memory enhancing activity (Table 1).
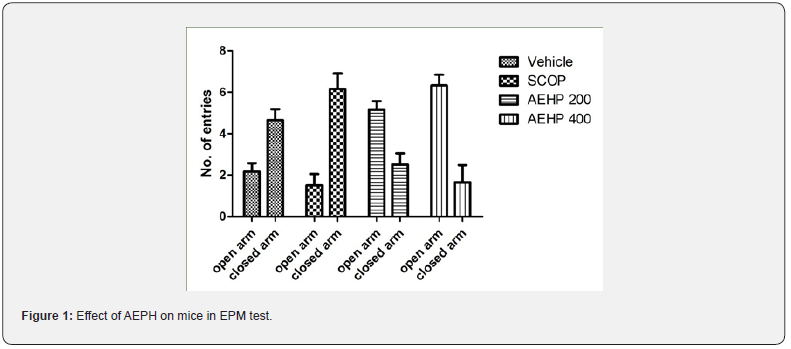
Nootropic Assessment in Elevated Plus Maze Paradigm
Scopolamine treated group significantly increased close arm entries and time spent. AEPH (200 and 400 mg/kg, p.o.) were found to be significantly improving the open arms activity (both the parameters) compared to SCOP treated group (Table 2). The time spent in open arm by the mice treated with vehicle was not significant while AEPH exhibited a significant result compared to SCOP (p<0.0001) in Two-way ANOVA. The number of movements in open arm on administration of AEPH (400 mg/kg) was found to be 6.33 ± 0.516 as compared to a meager movement of 1.5 ± 0.547 on Scopolamine treated mice (Table 2).
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
Exploration was originally validated as a predictive test of rodent, anxiety-like behavior wherein rodent prefers to remain in the closed arms than open arm. Effect of the aqueous extract of Petunia hybrida on scopolamine- induced learning and memory impairment in rodents showed positive response in elevated plusmaze (Figure 1).
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
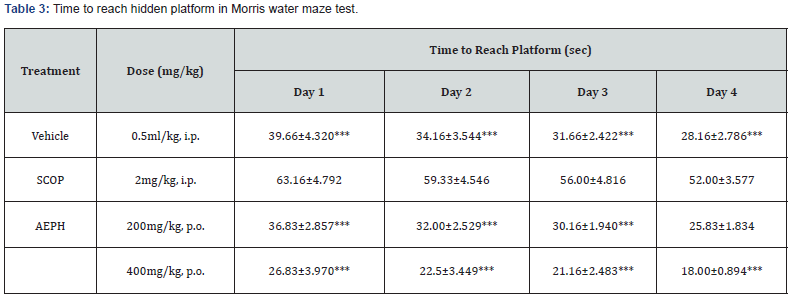
Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
MWM (Morris water maze) tests show that average latency to find the hidden platform by experimental rats. Our observations indicate that all experimental groups learned to find hidden platform in four experimental days. This implies that all experimental rats learn to escape swimming by searching hidden platform using visual cues. Results of MWM test in experimental animals confirmed a significant effect of Scopolamine-toxicity, AEPH (200mg/kg) + SCOP, AEPH (400mg/kg) + SCOP compared to control on latency to acquire hidden platform. In Two-way ANOVA confirmed a significant interaction between treatment (control vs. SCOP treated) × trial days (p<0.0001) and SCOP + AEPH treated × trial days (p<0.0001). (Figure 2).
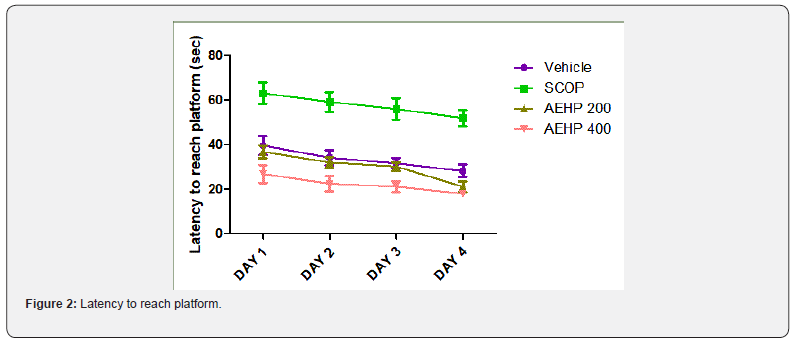
Water maze tasks were performed to evaluate effect of aqueous extract of Petunia hybrida flower treatment on the spatial memory abilities. Each data point represents the mean (±SD) latency of the trials for a minimum of six rats performed each day. The mice treated with 400 mg/kg AEPH required only 18.00 ± 0.894 seconds on the 4th day to find the hidden platform as compared to 52.00 ± 3.577 for the scopolamine treated mice (Table 3) (Figure 2).
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
Conclusion
The objective of the present study was to assess the nootropic potential of aqueous extract of flowers of Petunia hybrida using the animal models. The results obtained led to the conclusion that Petunia hybrida flowers are a good source of potential flavonoids and phenolic. The ability to reverse the scopolamine induced amnesia by the extract makes it a subject for further investigation to deduce the mechanism involved and optimize the nootropic potential of the plant.
- Research Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Material and Methods
- Extraction of Phytoconstituents
- Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- Total Phenolic Content
- Pharmacological Evaluation of the extract
- Statistical Analysis
- Results and Discussion
- Nootropic assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Nootropic Assessment in Morris Water Maze Method
- Conclusion
- References
References
- Vadthya J, Satyavati D, Pradeep Kumar C, Reddy M (2014) Evaluation of nootropic activity of Smrithi: a polyherbal formulation. The Pharma Innovation Journal 3(3): 33-41.
- Sreemantulu S, Nammi S, Kolanukonda R, Koppula S, Boini KM (2005) Adaptogenic and nootropic activities of aqueous extract of Vitis vinifera(grape seed): an experimental study in rat model. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 5: 1.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Petunia_%C3%97_atkinsiana
- Hidalgo M, Martin-Santamaria S, Recio I, Sanchez-Moreno C, de Pascual-Teresa B, et al. (2012) Potential anti-inflammatory, anti-adhesive, anti/estrogenic, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activities of anthocyanins and their gut metabolites. Genes Nutr 7(2): 259-306.
- Amreen R, Chaurey M (2021) Evaluation of estrogenic potential of ethanolic and aqueous extract of Pitunia hybrida. Journal of Pharmacology and Biomedicine 5(3): 312-318.
- Ojha P, Jain S (2021) Evaluation of wound healing action of Annona squamosa bark extract. J Pharmacol Biomed 5(4): 352-359.
- Khanna R, Chauhan P (2021) Formulation and evaluation of Annona squamosa hydroalcoholic extract loaded phytosomes. J Pharmacol Biomed 5(3): 342-351.
- Tiwari P, Joshi A, Dubey BK (2017) Total phenolic content, flavonoid concentration, antimicrobial and insecticidal screening of aqueous extracts of Annona squamosa (seeds), Azadirachta indica (leaves) and Lavandula angustifolia (flower). J Pharmacol Biomed 1(1): 30-43.
- OECD Guidelines (2001) “Guidance document on acute oral toxicity testing” Series on testing and assessment No. 23, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD Environment, health and safety publications, Paris, UK.
- Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J of Neurosci Methods 11(1): 47-60.
- Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nature Protocols 1: 848-858.
- Scheider P, Ho YJ, Spanagel R, Pawlak CR (2011) A novel elevated plus-maze procedure to avoid the one-trial tolerance problem. Front Behav Neurosci 5: 43.
- Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T (1990) Utility of an elevated plus-maze for the evaluation of memory in mice: effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacology 101(1): 27-33.






























