Every Man Needs Prostate Check up
Narmada P Gupta*
Department of Urology, Academic & Research, Chairman, India
Submission: June 09, 2016; Published: July 03, 2017
*Corresponding author: Chairman, Department of Urology, Academic & Research, Chairman, India, Email: narmadagupta@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Narmada P Gupta. Every Man Needs Prostate Check up. JOJ uro & nephron. 2017; 3(4): 555616. DOI: 10.19080/JOJUN.2017.3.555616
Keywords: Lower urinary tract symptoms; Prostate specific antigen; Transurethral resection of prostate; Laser prostatectomy; Light amplifications through stimulated emission of radiation; Transurethral incision of prostate; Transurethral resection of prostate; Transurethral e-nucleation of the prostate; Photoselective vaporization of the prostate; Robotic associated laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
Abbreviations: LUTS: Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms; PSA: Prostate Specific Antigen; TURP: Transurethral Resection of Prostate; LP: Laser Prostatectomy; LASER; Light Amplifications Through Stimulated Emission Of Radiation; TUIP: Transurethral Incision of Prostate; HOLREP: Transurethral Resection of Prostate; HOLEP: Transurethral e-Nucleation of the Prostate; PVP: Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate; RALP: Robotic Associated Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
Introduction
With the continuing improvement in the healthcare scenario in India, the longevity of life has increased from 31 years at the time of Independence to 67 years as per the last census. 11 percent of the Indian population will be more than 60 years of age in the coming decade. As a result, greater attention is needed for the care and health needs of our aging population.
Every man has some enlargement of prostate after the age of 50 years. Approximately, 17% of the men above 50 years and 35% of the men above 70 years suffer from Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS). The common causes of enlargement of Prostate include Benign (Non cancerous) enlargement or Cancer of the Prostate.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the lower urinary tract (LUTS) can be caused by the enlargement of the prostate gland and were previously also known as prostatism. Essentially, BPH causes two types of symptoms:
a. Storage symptoms: frequency (frequent passage of urine both day and night), urgency (inability to hold urine for a long time), urge incontinence (leakage of urine due to urgency) and
b. Voiding symptoms: hesitancy (delay in starting urination), decreased force of urinary stream, intermittency and post void dribbling. Associated urinary tract infection may also result in a burning sensation and some can have haematuria (blood in urine). Haematuria can also be due to cancer in the bladder and kidney (Figure 1). If diagnosed early, these problems can be treated by medication or surgery. If neglected, these problems may result in complications like retention of Urine, Urinary tract infection, blood in urine, Kidney failure, stones etc.
Diagnosis
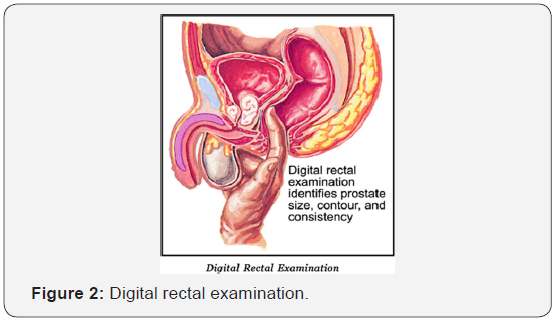
Diagnosis of BPH can be made by digital rectal examination (Figure 2). This simple procedure is performed by a physician who inserts a finger in the rectum to assess the size of the prostate and also diagnose different diseases of the prostate. It is advisable that all men over the age of 50 years should have a rectal examination. The other investigations are Transabdominal ultrasound (Figure 3), which is commonly performed everywhere, Uroflowmetry and Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) to distinguish with cancer Prostate.
Benign Enlargement of Prostate
Medical management
The rationale for medical management is based on the fact that BPH has both dynamic and static components. The dynamic component is due to increase in smooth muscle tone of prostate stroma, capsule and bladder neck due to alpha-receptors. The static component is due to stromal and epithelial growth that results in increase in size and volume of the prostate gland. 5 alpha reductase inhibitors play an important role of static component due to conversion of testosterone to DHT. The management of dynamic component is by alpha-blockers and static component by hormonal treatment.
Alpha-blockers are grouped according to their affinity for the receptors and duration of action. The adrenoreceptors can be alpha 1 and 2 types. The types 2 receptors are mainly present in blood vessels and give rise to lowering of blood pressure. There are 3 distinct alpha 1 receptors i.e. alpha 1a, alpha 1b and alpha 1d in the prostate. 70 % of alpha-receptors are alpha 1a and drugs blocking these receptors are known as uroselective aplha blockers.
The first generation aplha-blockers like phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine were non-specific and are not recommended for use due to their side effects. The second generation selective alpha-blockers are Prazosin, Terazosin and Dexazosin. Selective alpha-1 blockers cause a fall in blood pressure and therefore have to be used with caution and their dose has to be titrated. However, in-patients of BPH along with hypertension, selective alpha-1a blockers are preferred as they help both in relief of prostatic symptoms and hypertension. The third generation super selective alpha-1a blockers are Alfuzosin, Tamsuosin and Silodosin. They have minimum effect of blood pressure and are the drugs of choice. The short acting drugs like Prazosin has to be given 2-3 times a day but now slow release formulations are available which can be given once a day like other alpha-blockers.
The principal action of alpha-blockers is to decrease smooth muscle tone in the bladder neck, prostatic adenoma and prostatic capsule and also by direct effect on the bladder.
While efficacy of every aplha-blocker is the same, there is a difference in the duration of action and side effects. The common side effects are dizziness, asthenia, fatique and retrograde ejaculation and occur in 1 to 7% of cases. More often than not, these drugs induce symptomatic relief but there may not be significant improvement in the flow rate. The effect of alpha blockers last only as long as they are taken and once stopped, the symptoms may recur. In spite of alpha blockers, due to natural progression of the disease, size of the prostate may increase and the patient may go on to need surgical treatment.
For static component of BPH, the drugs of choice are 5 alpha reductase inhibitors. Finasteride, a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound, is a specific, inhibitor of type-2 alpha reductase, whereas Dutasteride has effect both on type 1 and 1 alpha reductase enzymes. After these drugs have been administered for some length of times, improvement in symptoms is noticed. In about 25% of cases, size of the prostate also reduces by 28%. They have minimal side effects and therefore there is no need for titration of the dose. These drugs also have the potential to alter the natural history and progression of disease and minimize risk of acute urinary retention. The results of this therapy are better if the volume of the prostate is more than 40ml and PSA is more than 1.4ng/ml. These drugs cause atrophy of the glandular epithelial tissue and serum levels of PSA decrease by 50%. In further evaluation of these patients, PSA should be multiplied by 2 for decision making in terms of prostate cancer detection. Other hormonal drugs like progestational agents, anti-androgens and flutamide are not recommended as they are not effective.
Combined medical management with selective alpha-1 blocker and alpha-5 reductase inhibitors is recommended for those who have large prostate along with symptoms as the mechanism of action of these two drugs is different and they work synergestically. Long term studies have found good effect of the combination therapy. The episodes of urinary retention and need for prostatic surgery may decrease. It is important for the patients who are on medical treatment to have regular check for PSA, ultrasound and uroflowmetry as in the long run; some of these patients may need surgical treatment.
Phytotherapeutic drugs
Phytotherapeutic drugs are derived from the plants and they are a group of herbal drugs. These drugs are popular in Europe and USA and are available over the counter. The mechanism of action of these drugs is not yet fully clear but they may give symptomatic relief temporarily. In india, various Ayurvedic and homeopathic drugs are being treated albeit without any scientific proof. Their use has reported reduction of congestion of the prostate gland and overlying mucosa but in the long term they may not be effective.
Transurethral resection of prostate (TURP) (Figure 4)
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) is the Gold standard in surgical management of BPH. TURP has stood the test of time during the last 70 years and became the most common surgical procedure in the hands of the Urologist. It is termed as gold standard because of effective long term out come and can be performed safely. During the last two decades, several advances have taken place to reduce the complications and morbidity of TURP. Eglesias continuous irrigation resectoscope is routinely used, which resects under low pressure and reduce absorption of the irrigating fluid. Advances in imaging like endovision camera and digital endoscopes, provides magnification and anatomy can be clearly delineated during the TURP. Saline is used for bipolar TURP which have advantages of minimum fluid absorption and hyponatremia. Thick loop resection provides better coagulation along with resection of the tissue, as a result bleeding is less. The thick loop can be used with monopolar as well as bipolar cautery. Due to use of saline, there is no limitation of time of resection and large prostate can be resected. The patient has better post operative recovery, less irrigation and shorter hospital stay.

In comparison to any minimally invasive treatment, TURP is the most cost effective with better outcome and is useful in developing countries where affordability of the treatment by a patient is equally important.
Laser prostatectomy
In a little more than 15 years, laser Prostatectomy (LP) for the management of obstructive benign prostatic hyperplasia has evolved in to three principally different techniques - namely, coagulation, cutting or enucleation and vaporization.
Laser is an acronym for light amplifications through stimulated emission of radiation (LASER). The principle of laser is based on the quantum theory by Einstein, which included the concepts of absorption, spontaneous emission and stimulated emission of energy.
Holmium Laser is an ideal surgical tool in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Holmium laser can cut, vapourize and resect prostate tissue with minimal bleeding. It can be used for transurethral incision of prostate (TUIP), transurethral resection of prostate (HOLREP) and transurethral e-nucleation of the prostate (HOLEP). It creates a channel identical to the TURP with immediate removal by obstructive adenomatus prostatic tissue. The removed tissue is available for histopathological diagnosis. The advantage of holmium laser is that the bleeding is minimum because while cutting the prostate, the holmium laser also coagulates. Catheter can be removed early and patients can be discharged from the hospital in 24 hours. The holmium laser can also be used in patients with cardiac pace maker.
Photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) has gained global acceptance because of its safety, efficacy outcomes on a par with TURP, long term durability and applicability to high risk and coagulation-deficient patients. Currently, 120 watt 532- nm Lithium Triborate laser vaporization prostatectomy is more effective and fast and produces a nicely healed prostatic cavity. There is a less steep learning curve for this procedure. The cost of the machine and disposable fiber is prohibitive. If a prostate is very large, more than one fibre will be required.
Laser Prostatectomy can be an alternative to TURP. At present, there is no concenses on Enucleation/Vaporization of the prostate. Long term outcome are better with enucleation but there is steep learning curve. Vaporization is better in patients with bleeding disorder/on anticoagulants but there is high cost. Large size prostate are coming for surgical management, therefore, it is important to choose a procedure which gives long term and durable results. Cost and long term durability is an important factor in developing countries.
Cancer prostate (Figure 5)
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Males in USA. In India, the exact incidence is not known due to lack of awareness and unavailability of such information on a wide scale. At an early stage of prostate cancer, there are no specific symptoms and thus the patients are often diagnosed late when the disease is already advanced. Prostate cancer, if diagnosed early, can be completely cured, where as when diagnosed at an advanced stage, it can only be controlled for some time. If untreated, prostate cancer can be a cause for significant morbidity & mortality. In USA, 90- 95 percent of prostate cancer cases are diagnosed early, where as in India, 90-95 percent are diagnosed in advanced stage. This reverse scenario is primarily due to lack of awareness about this potentially curable disease. Changing the outlook of this disease in India is a big challenge for India.
Surgery - radical prostatectomy (Figure 6 & 7)
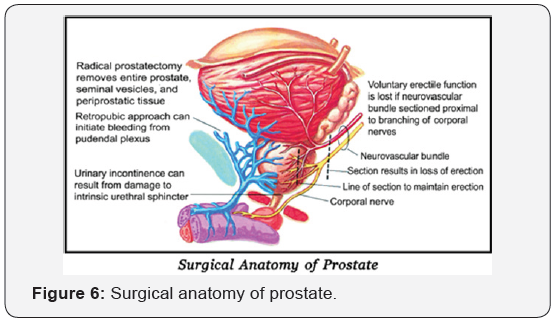
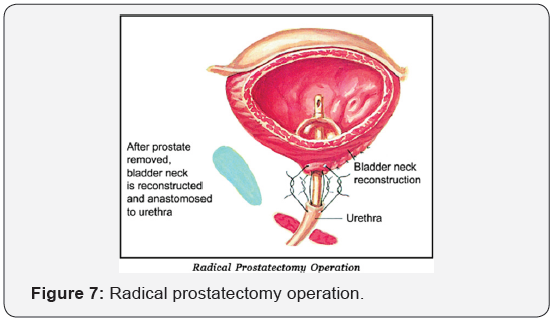
This is indicated in men who have life expectancy more than 10 years, no significant associated diseases, age less than 75 years the disease localized to the prostate gland. In this operation, the complete prostate gland is removed. The advantage of the operation is that as the disease is completely removed, patient can have a normal life span. However, the patient has to come for regular follow up.
Radical Prostatectomy can be done by open surgery by transpubic or perineal approach, laparoscopic (key hole surgery) or Robot assisted laparoscopic surgery.
Radical prostatectomy was traditionally done by open surgery which was associated with significant complications like blood loss, requiring blood transfusion, injury to rectum, urinary leak etc.
Robotic Associated Laparoscopic Radical prostatectomy (RALP) started around 2000 and today more than 80% radical prostatectomy in USA are done robotically. The advantages of Robotic Surgery are less blood loss, early recovery, less hospitalization. The functional and oncological outcome is as good as open surgery. The complications of surgery have significantly reduced and patients do not require any blood transfusion. The recovery is fast & patient can go home in 48hrs. The incontinence rate has significantly reduced and 90% patients become fully continent in 6-9 months. With nerve sparing technique, the incidence of erectile dysfunction has reduced and can be treated by drugs.
In India, we are routinely doing Robotic Radical Prostatectomy since 2006 and more than 250 such cases has been done with outcome as good as anywhere in the world and at Medanta at a fraction of cost in comparison to USA and Europe.






























