Lifestyle Management and Eating Disorder among College Going Students
Manavi Keshari, Sunita Mishra* and Madhavi Daniel
Department of Food and Nutrition, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University (A Central University), India
Submission: June 05, 2023; Published: July 21, 2023
*Corresponding author: Sunita Mishra, Assistant Professor Department of Food and nutrition, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University (A Central University), Vidya Vihar, Raebareli Road, Lucknow, U.P, 226025, India, Email: sunitabbau@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Manavi K, Sunita M, Madhavi D. Lifestyle Management and Eating Disorder among College Going Students. Curre Res Diabetes & Obes J 2023; 16(5): 555948.DOI: 10.19080/CRDOJ.2023.16.555948
Abstract
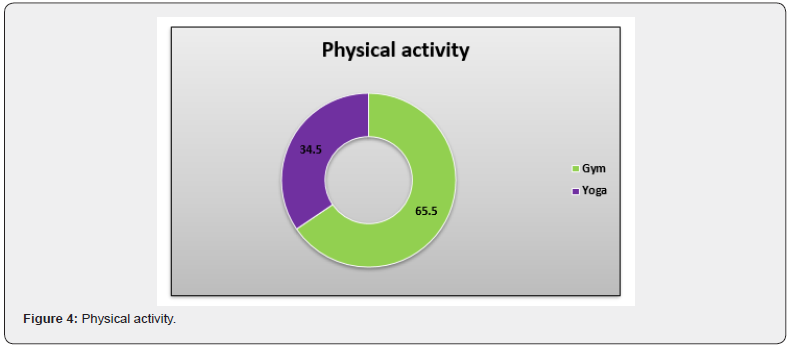
This study was grounded on the assessment of lifestyle management and eating disorders of fat people. Obesity is a multi-factorial disease that accumulates excess body fat and leads to negative effects on health. Obesity continues to accelerate resulting in an unprecedented epidemic that shows no significant signs of decelerating any time soon. The main cause of obesity is long-term energy imbalance between consumed calories and expended calories. Anthropometry is a screening tool that determine obesity in a general population. Obesity detection can be done by assessing BMI ranges. This survey represents the age of the participants ranged between 18-30 years. The age was grouped into the table between two categories i.e., 18-24 and 25-30 years.18-24 years participants population was greater than 25-30 years. Male participants were greater than female participants. Male were 41.7% and female were 58.3%. Most of the students stays in paying guest accommodation. Students stays in paying guest accommodation 37.5%, hostel 33.3% and home 29.2%. According to survey, the BMI range showed, many of respondents were overweight. About 44% respondents were overweight, 34% respondents were obese, 20% respondents were normal, and 2% respondents were underweight. Usually respondent’s consumes non-healthy foods which contains high fat content, according to survey report 75% respondent’s consumes healthy foods, 31.30% respondents daily consume beverages, 25% respondent’s consume high fat food, 43.80% respondent’s consume junk food and 37.50% respondent’s consume high saturated food as their meals which shows eating pattern of them. Respondents have a lifestyle with low physical activity and disordered eating habits, which promotes them to a risk of being overweight and obese. 65.5% of respondents go to gym and 34.5% do yoga to make themselves physically fit and healthy.
Keywords: Eating disorder; Gym; Yoga; Meditation; Depression; Lifestyle; College student
Introduction
Obesity is extending globally as a public health issue. Patients with obesity are at high risk for expanding a scale of coexisting conditions, which includes diseases like cardiovascular disease (CVD), gastrointestinal disorders, type 2 diabetes (T2D), joint and muscular disorders, respiratory problems, and psychological issues, which may seriously affect their daily lives as well as raising mortality risks. The World Health Organization (WHO) outlines obesity as unusual or extreme fat aggregation that presents a risk to health [1]. Obesity renders a significant expostulation to prone disease prohibition and health beyond the life strategy at the world. Usually obesity is defined thoroughly as spare body weight for height, but this simple definition misrepresents an etiologically complex phenotype essentially correlated with surplus adiposity, or body fatness, that can clear metabolically and not just in terms of body size [2].
Regardless of worldwide interest in body-weight control, the frequency of obesity carry on with rise worldwide. Prevalent public health counsel for obesity avoidance is clearly weakening. Prevention of obesity clearly states the relevance of everyday public health advice for body-weight control, i.e. to degrade utilization of fatty foods, to eliminate utilization of sugar and to evade snacking between meals. An excessive intake of carbohydrate : fat ratio should enhance body-weight control, as high-carbohydrate low-fat diets are less probable to steer overeating, and if overeating does happen, less of the surplus energy is probable to be stored as fat. However, it is endorsed that for the long-term prohibition of weight gain, suggested to increase the utilization of carbohydrate-rich foods may be more efficient than advice, which concentrates on reducing utilization of fatty food. Moreover, in view of the converse kinship between fat and sugar consumption, sugar may have an approval to play in body-weight regulator in assisting in expanding carbohydrate : fat ratio. Nibbling for most humans appears not to unfavorably influence body-weight control, and for some it may improve control. This condition may persist because frequent eating aids appetite control, thus avoiding overeating at meals, and as snacks generally incline to be higher in carbohydrate and lower in fat than meals, frequent eating may be a plan for expanding carbohydrate : fat ratio. It is also advised that eating ‘little and often’ may be a more cooperative condition of eating for a physically active legacy than eating large meals.
Perhaps the most suitable suggestion on food intake that would work mutually with synchronous advice to strengthen physical activity is to eat more carbohydrate, and to eat frequently [3]. Eating disorder symptoms are widespread among college students. Bearing eating disorder and unhealthy weight instruction methods turn out to have increased in this population during the last decade and involve even greater number of students. Subclinical indications are interrelated with meaningful discomfort and disability and carry on over time [4]. Eating disorders are one of the highly under-researched and complicated to identify psychiatric illness, with a greater mortality rate, particularly among the adolescent age group. Binge eating disorder, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa are set down to be the most prevalent forms of eating disorders, but in India they present in a less defined manner. Eating disorders are incredibly severe health issues that involve people of all ages but generally seen among adolescents and students. Eating disorders are primarily visualized by the mental effects of obsession with body weight, shape, and diet. There is a flock of factors that consequence these disorders, like socioeconomic status, stress, media, and so on. They can also be related to other psychiatric disorders, like depression and anxiety, making them more dangerous and probably destructive. To introduce to the load, the diagnosis of eating disorders can be inaccessible, and more than one-half of all cases go unrevealed [5].
Anorexia nervosa has the maximum mortality of any psychiatric disorder. It has a frequency of about 0.3% in young women. It rises than twice as usually in teenage girls, with an average age of onset of 15 years; 80-90%, most of the patients with anorexia nervosa are female. Anorexia is the most ordinary state of mind of weight loss in young women and of acknowledgement to child and adolescent hospital services. Generally primary care practitioners confronts few cases of severe anorexia nervosa, but these consider enormous distress and frustration in carers and professionals. The core psychological feature of anorexia nervosa is the excessive overestimate of shape and weight. People with anorexia also have the physical ability to endure excessive selfassessed weight loss. Food limitation is only one phase of the practices used to lose weight. Most of the people with anorexia use over exercise and over activity to burn calories. They generally choose to stand either sitting; develops chances to be physically active; and are dragged to sport, athletics, and dance. Purging patterns include self-induced vomiting, together with misapplication of laxatives, diuretics, and “slimming medicines” [6].
Bulimia nervosa is a disorder that is identified by binge eating and unsuitable offset action to control weight with probably dangerous sequelae. It is necessary to distinguish and assess this condition immediately and to treat the patient adequately while observing progression and potential medical complexities. This activity portray the assessment and handling of bulimia nervosa and emphasizes the role of the inter professional team in the care of patients with this disorder [7]. Regular physical activity is essential to maintain good health, well-being and to stay fit. As individuals become more aware of the benefits of engaging in physical activity, the prevalence of people going to the gym or fitness centers is on the rise. Regular physical activity is essential to maintain good health, well- being and to stay fit. As individuals become more aware of the benefits of engaging in physical activity, the prevalence of people going to the gym or fitness centers is on the rise. Regular physical activity is essential to maintain good health, well-being and to stay fit. As individuals become more aware of the benefits of engaging in physical activity, the prevalence of people going to the gym or fitness centers is on the rise. Regular physical activity is essential to maintain good health, well- being and to stay fit. As individuals become more aware of the benefits of engaging in physical activity, the prevalence of people going to the gym or fitness centers is on the rise.
Regular physical activity is essential to maintain good health, well- being and to stay fit. As individuals become more aware of the benefits of engaging in physical activity, the prevalence of people going to the gym or fitness centers is on the rise. Regular physical activity is necessary to build good health, happiness and to stay fit. As individuals become more conscious of the benefits of fascinating in physical activity, the occurrence of people prevailing to the gym or fitness centers is accelerating. The quick development in the market for fitness devices and apps poses the possibility of supplying calibrated perception into an individual’s exercise routine and facilitating personalized interventions [8]. Yoga is an ancient science, practicing yoga could make our brain retain activity and physical function delivering to symmetric unity, thus tempting our physical health and enhancing the emotion of happiness. The World Health Organization (WHO) states yoga as a complete physical, mental, and social welfare and not simply the absence of disease or ailment. Yoga has turned into one of the most sophisticated body building exercises and is very popular with youngsters [9]. Meditation and yoga is a merger of meditation and its surrounding which have achieved craze in concurrent scientific research and have been used for numerous mental health like stress, anxiety, depressive disorders, etc. and physical conditions like pain, etc. Worldwide, yoga and meditation are examined as a preference and reciprocal approach to the treatment for both psychological and physical disorders, and to achieve a better quality of life [10].
Individuals with obesity have high risk of depression: a 55% higher risk was recorded by a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies in which depression was evaluated several years after obesity was estimated among individuals with no depression at baseline. If obesity does predispose to depression and other signs of psychological distress, which includes anxiety and somatic complaints, the raising rates of obesity might deteriorate overall population mental health the same way it has been shown to reduce population physical health [11]. According to World Health Organization (WHO) nearly 800,000 people die due to depression every year. Depression haunts almost 350 million people in the world. It has recently been found that depression as a chronic psychological distress plays a significant role in the accelerating vogue of obesity throughout the world [12].
There are three major determinants for whether an individual remains healthy or develops illness: genetics, lifestyle and chance. Little if nothing can be done to influence genetics and chance but changes in lifestyle, both good and bad, can have substantial impact on health. Life sustaining activities include proper nutrition and exercise, healthy sleep patterns and adequate rest, healthy coping with stress and ability to use family and community supports and resources [13].
Objectives
a) To study associated factors like frequent eating, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, gym, yoga, meditation, depression in obese person
b) To study lifestyle management involving eating and obesity
Material and Methods
I. Research method: a cross-sectional method, Observation test
II. Locale of the study: the experiment was carried out in the BBAU campus of Lucknow
III. Period of the study: august 2022- May 2023
IV. Sampling method: probability systematic sampling method
V. Criteria of the study: study was carried out through survey in the google forms
VI. Sample: students of BBAU Lucknow city
VII. Sampling technique: The selection of sample will be done on the basis of random sampling
VIII. Anthropometry: Body Mass Index (BMI) has traditionally been used to identify individuals who are the most likely to be overweight or obese. It is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the height in m2. Generally, a high value indicates excessive body fat and consistently relates to increased health risk and mortality.
Calculation: Weight (kg) / Height m2
Underweight: it is the body weight which is too low for a normal healthy adult or child. It is caused by multiple factors like lake adequate nutrition in the body (Table 1).

Normal weight:
Overweight: it is the condition where the body weight is 10%-20% greater than the mean standard weight for age, height and sex.
Obesity: it is a complex chronic disease developing from interactive influences of numerous factors like social, behavioral, psychological, metabolic, cellular and molecular.
An etiology of Obesity:
Genetic factors: genetically there is a chance of 50-70% of a person becoming fat more than any other factor. The chances of becoming 80% obese when both the parents are obese while chances becomes 50% when only one of both the parents was obese.
Age and sex: it can take place at any age in any sex as long as the person is under positive energy balance. Nutrition Foundation of India studies shows that females are more overweight than males.
Eating habits: certain types of eating habits may lead to overweight and obesity like- excessive eating, continuously eat fast or junk foods, consumption of sugar added products, consumption of carbonated drinks, etc.
Physical activity: mostly obesity is seen under people living sedentary lives and give less time to physical activities. Physical activities plays an important role in day-to-day life through which person becomes fit and healthy.
Stress: having stress, depression, anxiety may lead to excess calorie intake. According to some studies people consumes more fatty foods as their lives grow stressful.
N of Terms
Lifestyle
Theoretical definition: The term “lifestyle” generally means a pattern of individual practices and personal behavioral choices that are related to elevated or reduced health risk (Health line dictionary, 2009). The WHO (1999) defined lifestyle as the way of living that lowers the risk of being seriously ill or dying early. It is also about physical, mental, and social wellbeing [14].
Operational definition: The self-reported responses of 1000 college students (who participated in this study) regarding 104 health habits in term under six lifestyle domains including physical activity, dietary, self-care and safety, stress, social and emotional wellness, and sleep patterns.
Risk behaviors
Theoretical definition: Behavioral pattern associated with a high risk of developing a chronic illness (Payne et al, 2007).
Operational definition: The self-reported unhealthy behavioral patterns by 1000 students who participated in this study with respect to physical activity, dietary, self-care and safety, stress, social and emotional wellness, and sleep patterns.
N of TERM
Lifestyle
Theoretical definition: The term “lifestyle” generally means a pattern of individual practices and personal behavioral choices that are related to elevated or reduced health risk (Health line dictionary, 2009). The WHO (1999) defined lifestyle as the way of living that lowers the risk of being seriously ill or dying early. It is also about physical, mental, and social wellbeing.
Operational definition: The self-reported responses of 1000 college students (who participated in this study) regarding 104 health habits in term under six lifestyle domains including physical activity, dietary, self-care and safety, stress, social and emotional wellness, and sleep patterns.
Risk behaviors
Theoretical definition
Behavioral pattern associated with a high risk of developing a chronic illness (Payne et al, 2007).
Operational definition: The self-reported unhealthy behavioral patterns by 1000 students who participated in this study with respect to physical activity, dietary, self-care and safety, stress, social and emotional wellness, and sleep patterns [15].
Lifestyle: defined as a pattern of people’s practices and personal behavioral choices that are related to elevated or reduced health risk.
Risk behaviors: associated with a high risk of developing a chronic illness. The self-reported unhealthy lifestyle pattern by 50 students at the college who participated in this study with respect to physical activity, dietary, self-care, stress, social and emotional wellness and sleeping pattern [16].
Participants and Procedure
People were emailed, WhatsApp, an invitation to complete an online survey invite connect to join the questionnaire was circulated in social media apps like WhatsApp. The study goal was to see the lifestyle management of obese people among the number of participants who fill this survey form. The survey was conducted in English language. Participants are from 18-24 and 25-30 age group from the BBAU campus itself. The participant’s identification was kept secret [17].
Demographics: participants were asked to self-report their name, age, gender, e-mail, address, phone number, qualification, living arrangements and anthropometry measurements like height and weight.
Lifestyle pattern: participants were asked a variety of questions related to their lifestyle like their eating pattern, physical activities (Figure 1).

Result and Discussion
(Table 2) Represents the demographic data of participants. The age of the participants ranged between 18-30 years. The age was grouped into the table between two categories i.e., 18-24 and 25-30 years. 18-24 years participants population is greater than 25-30 years. Male participants were greater than female participants. Male were 41.7% and female were 58.3%. Most of the students stays in paying for guest accommodation (PG). Students stays in paying guest accommodation 37.5%, hostel 33.3% and home 29.2% [18].

Statistical Analysis
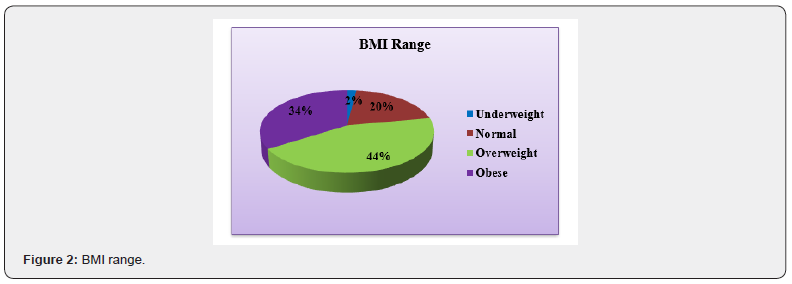
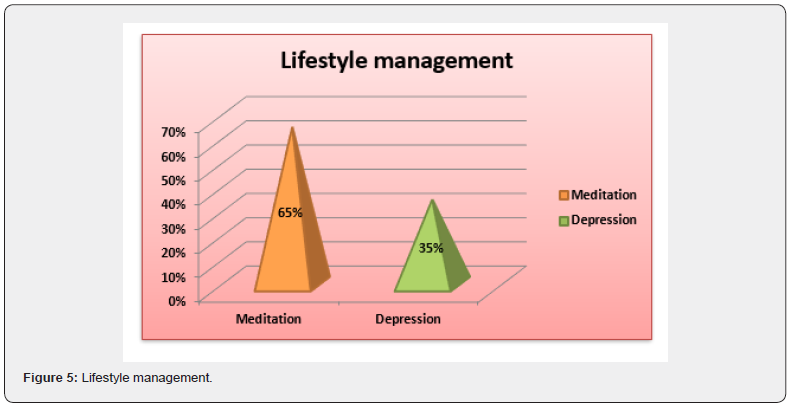
This chart shows that many of the respondents are overweight. As per the survey suggests that 44% of respondents are overweight, 34% respondents are obese, 20% respondents are normal, and 2% respondents are underweighting as per the BMI range [19] (Figure 2). This chart presents information about eating habits of the respondent’s 75% respondent’s fall into the category of consuming healthy foods, 31.30% respondent’s consumes beverages daily, 25% respondent’s falls on consuming High fat food, 43.80% respondent’s falls into the category of consuming junk food on daily basis and 37.50% respondents consumes more high saturated food to fulfil their daily need [20] (Figure 3). This chart gives information about the physical activity participated in by the respondents. About 65.5% of respondents do yoga to keep them physically fit and healthy. About 34.5% of respondents go to gym to look or feel better, lose weight and for body building (Figure 4). This chart shows the lifestyle management involving mental health and fitness of the respondents. 65% of respondents fall in the category of doing meditation while 35% respondent’s facing depression due to their hectic lifestyle management [21] (Figure 5). This chart shows the eating disorder among the respondents. 50.60% of respondent’s falls in the category of body weight dissatisfaction. 34% respondents are obese and 15% of respondents falls in the category of binge eating (Figure 6).
Conclusion
Obesity around the world is the most serious problem related to public health and it is continuously affecting people’s health because of their lifestyle. Excessive fat accumulation in the body are likely to stay obese in adulthood and also responsible for various diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc. [22]. This study suggests that most of the respondents of the college are overweight according to their BMI range. College students mostly didn’t take their meals on time because of their lazy time management. Generally students consumes fast food or junk food which contains high levels of fat, excessive accumulation of fat can promote a person to being overweight and obese. This is strengthening the need to encourage a healthy lifestyle, healthy food habits and physical activities to avoid being obese and overweight and their related complications [23]. This study shows that most of the respondents leading healthy lifestyle while being overweight and obese to maintain their fitness. Most of the respondents do gym and yoga to maintain their physical fitness and mental health.

Acknowledgement
I would warmly thank, and great credit goes to prof. Sunita Mishra, Dean and Head, for school of home science, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Lucknow for her immense support and encouragement during the research planning and also for all way showing the right path and enlightening students with her knowledge.

References
- Fruh MS (2017) Obesity: Risk factors, complications, and strategies for sustainable long‐term weight management. Journal of The American association of nurse Practitioners 29(S1): S3-S14.
- Hruby A, Hu FB (2015) The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 33(7): 673-689.
- Kirk TR (2007) Role of dietary carbohydrate and frequent eating in body-weight control. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 59(3): 349-358.
- Jones M, Darcy A, Colborn D, Srewart MC, Fitzpatrick (2012) Eating Disorders on College Campuses: Implications for Prevention and Treatment. Harvard Health Policy Review 13(2): 28-38.
- Iyer S, Shriraam V (2021) Prevalence of Eating Disorders and Its Associated Risk Factor in Students of a Medical College Hospital in South India. Cureus 13(1): e12926.
- Morris J, Twaddle S (2007) Anorexia nervosa. BMJ 334(7599): 894-898.
- Jain A, Yilani M (2022) Bulimia Nervosa. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Radhakrishnan M, Misra A, Balan RK, Lee Y (2020) Gym Usage Behavior & Desired Digital Interventions: An Empirical Study. International Journal of Novel Research and Development.
- Perur SD, Kenchannavar H (2019) The Study of Effect of Yoga and Meditation Using Current Technology. Journal of Yoga and Physiotherapy.
- Gupta S, Dhawan A (2022) Methodological issues in conducting yoga- and meditation-based research: A narrative review and research implications. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine 13(3): 100620.
- Jokela M, Laakasuo M (2023) Obesity as a casual risk factor for depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis of Mendelian Randomization studies and implications for population mental health. Journal of Psychiatric Research 163: 86-92.
- Rabiei S, Tabesh, MR, Jahromi SR Abolhasani M (2023) The association between depression, obesity and body composition Iranian women. Clinical Nutrition Open Science 47: 44-52.
- Ahmed H (2009) Lifestyle And Risk Behaviors Among College Students In Erbil City. Research Gate.
- Chauhan T, Mishra S (2017) Inherited Factor Related to Childhood Obesity and Its Prevention. International Journal of Research in Applied, Natural and Social Sciences 5: 2347-4580.
- Singh M, Mishra S (2012) Fast Food Consumption Pattern and Obesity among School Going (9-13 Years) in Lucknow District. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), pp. 2319-7064.
- Mishra S, Padhan S (2010) A study on perception, habits and knowledge systems about traditional food relating to health and nutrition among ADI women living in diverse socio-economic systems of Kalahandi district, Orissa. Food science research Journal 2(1).
- Verma R, Mishra S (2020) Nutritional and Consumers Behavior towards Street Foods. European Journal of Nutrition & Safety 12(12): 64-73.
- Arya G, Mishra S (2013) Effects of Junk Food & Beverages on Adolescent’s Health. IOSR Journal of Nursing and health Science.
- Agrawal R, Mishra S, Dixit VK, Rai S (2009) Association of Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disorder with obesity. Indian J. Prev Soc Med 40(4): 127-129.
- Mishra S, Wasir HS (1997) Obesity As a Risk Factor for Coronary Artery Disease. Journal of Association of Physicians of India 45(7): 555-558.
- Singh S, Verma P, Mishra S (2013/12). Potential of herbs in prevention of obesity: A review article. International Journal of Health Sciences and Research 3(1): 159-167.
- Srivastav, SK, Kumar S, Puranik B (2018) Prevalence of Obesity in Students of College Going Age. Global Journal for Research Analysis 4: 2277-8160.
- Makkawy E, Alrakha AM, Al-Mubarak AF, Alotaibi HT, Alotaibi NT, et al. (2021) Prevalence of overweight and obesity and their associated factors among health sciences college students, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care 10(2): 961-967.






























