Securing E-Learning System with Crypto-Biometric Multimedia
Afolabi AO1* and Adagunodo ER2
1Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Nigeria
2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Obafemi Awolowo University, Nigeria
Submission: March 19, 2018; Published: June 25, 2018
*Corresponding author: Afolabi AO, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Nigeria; Email: adefolabius@yahoo.com
How to cite this article: Afolabi A, Adagunodo E. Securing E-Learning System with Crypto-Biometric Multimedia. Biostat Biometrics Open Acc J. 2018; 7(2): 555710. DOI: 10.19080/BBOAJ.2018.07.555710
Abstract
The security mechanism used by most E-learning system is that of user-name and password which can be breached by mere guess-work or get lost particularly in order to conduct effective performance evaluation, therefore there is need for a more secured E-learning portal, with this background, this Paper focused on providing a better means of security for e-Learning system and this is a synergy of facial recognition and Data Encryption security scheme. This is not only an E-learning system, but a multimedia E-learning system that involves both audio and texts. It affords the learner of hearing the audible voice of the instructor which makes it very interactive and interesting. The facial recognition system is a computer application used for automatic or on the spot identification of a person through the digital image, video frame or video source and when there is a match then the user is granted access to the E-learning environment. The Data Encryption mechanism involved, further strengthens the security measure of the Elearning System. It will not allow any information stored in the database to be read for it appears in encrypted form that has to be decrypted before access to the information contained. This Paper therefore is about development of a multimedia E-learning system whose security mechanisms is based on both Facial Recognition and Data Encryption.
Keywords: Security mechanism; Data encryption; E-learning system; Facial recognition; Video frame; Video source; Multimedia; Stream; Bandwidth; Page-turning; Unreadable gibberish; Mathematical calculations; Algorithmic schemes; Cyphertext; Image-based algorithms; Interoperability; Mcrypt; Eigen faces; Covariance matrix; DES algorithm; Enciphering process
Review Article
Overview of Secured Multimedia E-Learning
With the introduction of streaming multimedia in the past few years, large multimedia files can now be delivered even over modem connections. Streaming multimedia is an Internet data transfer method that facilitates the transfer of audio and video files from computer to computer in a “stream.” Streamed media packets can be played as soon as the data starts arriving at the receiving computer—users do not have to wait until the full file has been downloaded. Streaming audio has been more successful than video, which has generally been limited to small picture sizes or low resolution (grainy) video Paperions, but as the bandwidth increases, higher quality, full-screen video becomes possible. When a sound file is to be prepared for streaming, it is compressed to reduce the overall size of the file. Streaming audio is currently being used as a supplement to classroom-based and online course delivery, usually in the form of pre-recorded lectures, interviews with guests, student Papers, samples of student classroom interaction, or sound bytes of content relevant to the course of study. When implemented wisely, video can alleviate the “page-turning” boredom of many online courses [1].
The multimedia based e-learning content of this site is protected by data encryption, as more users come to understand the internet’s open nature and the dangers of web surfing, Today’s web browsers automatically encrypt text when making a connection to a secure server. This prevents intruders from listening in on private communications. Even if they are able to capture the message, encryption allows them to only view scrambled text or what many call unreadable gibberish. Upon arrival, the data is decrypted, allowing the intended recipient to view. Without this security mechanism, information transferred over the internet can be easily captured and viewed by anyone listening. Data encryption refers to mathematical calculations and algorithmic schemes that transform plaintext into cyphertext, a form that is non-readable to unauthorized parties. The recipient of an encrypted message uses a key which triggers the algorithm mechanism to decrypt the data, transforming it to the original plaintext version. Another security mechanism implemented in this Paper is the Online face recognition which facilitates a user who is equipped with a display device. Our online single-image face recognition system is implemented using still image-based algorithms [2]. Principal Component Analysis based facial recognition algorithm was implemented. It Papers an image to a lower dimensional subspace defined by a set of orthonormal basis vectors that account for the maximum variance of the Papered images. The Papered images are represented by sets of principal components which are used for classification. In our work, the MPEG-7 face descriptor is used to extract the features and it differs from others in the way it generates the set of basis vectors using both an original and a flipped face images. In our method, the features of the images are extracted using the MPEG-7 face descriptor and two multi-class classifiers (one-against-one and one-against-all) are incorporated into the SVM method. The system is developed by the use of Macromedia MX Studio, ColdFusion MX and Flash Communication Server products, languages such as MATLAB, JAVA, PHP- Hypertext Pre-processor for the scripting language and MySQL for the database.
The service architecture
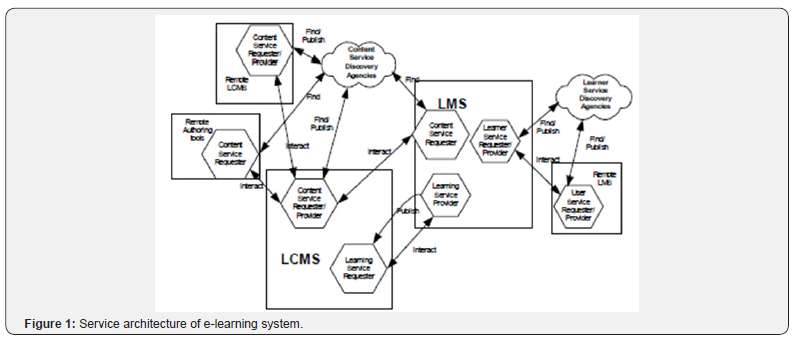
From the features of Web Services, we know that Web Services are perfectly feasible for implementing the interoperability of e-learning systems for three main reasons. Web Services provide a unified programming model for the development and usage of private Intranet as well as public Internet Services. As a result, the choice of network technology can be made entirely transparent to the developer and consumer of the service. Figure 1 shows how Web Services can be used in an E-learning environment. This architecture defines how different e-learning systems exchange messages through the interaction of Web service agents in each system. Service Provider is the platform that hosts access to the service. It has also been referred to as a service execution environment or a service container. Its role in the client-server message exchange patterns is that of a server. Service Requestor is the application that is looking for and invoking or initiating an interaction with a service [3]. Discovery Agency is a searchable set of service descriptions where service providers publish their service descriptions. The service discovery agency can be centralized or distributed. Standard compliant learning information presented by XML that is wrapped with the SOAP specification is exchanged between the requester and provider. The provider publishes a WSDL file that contains a description of the message and endpoint information to allow the requester to generate the SOAP message and send it to the correct destination.
Implementation
The implementation of this Paper was divided into three phases. The first phase consists of the facial recognition which was implemented with MATLAB. The second phase deals with the data encryption which we implemented with PHP using a publicly available library called Mcrypt. The third phase is the E -learning environment which we implemented with Microsoft power point for the multimedia and html codes for the scripting [4].
Phase One
This stage consist of the facial recognition system implemented with MATLAB. Figure 2 shows the home page of the whole system in MATLAB environment. In Figure 2, the user is given the options to select according to the operation he intends to perform. In the face recognition, the eigen vectors are often referred to as Eigen faces and the lower dimensions subspace is called face space-each Papered image in the set is then a linear combination of the eigen faces that associate with the largest eigen values. In our face recognition system, PCA incorporated in the MATLAB represents a facial image by a linear combination of a set of 48 basis vector from the eigen faces of the covariance matrix constructed by the training images. From a new image input the system compares it to data base image for it is recognition. The database contain only four images [4].
Database Index
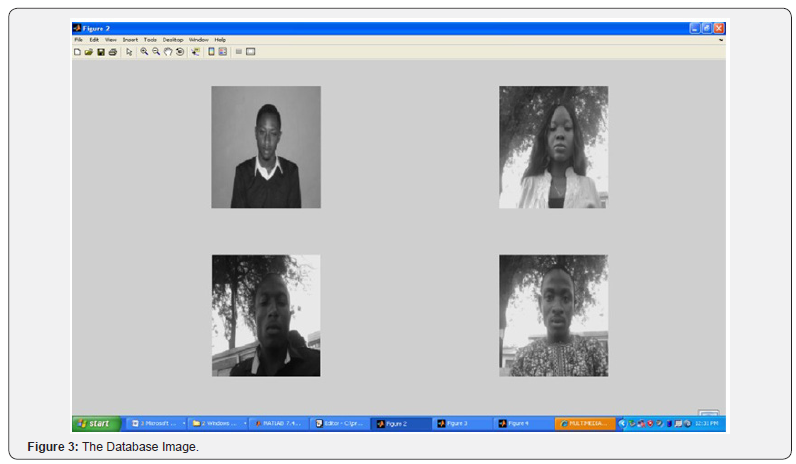
We used the grey scale FERET facial image database in this Paper because the Eigenfaces algorithm required manual selected land mark locations and a file with coordinates of the land mark was provided for all the images. Four images were stored in our database, the image were in jpg format and are contain in a folder as the whole Paper. Only four face images have been stored in our database so as to ensure high recognition accuracy (Figure 3).
Facial Recognition
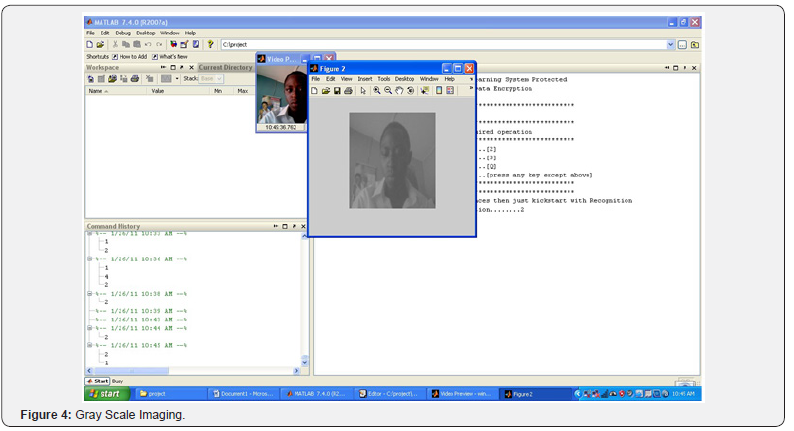
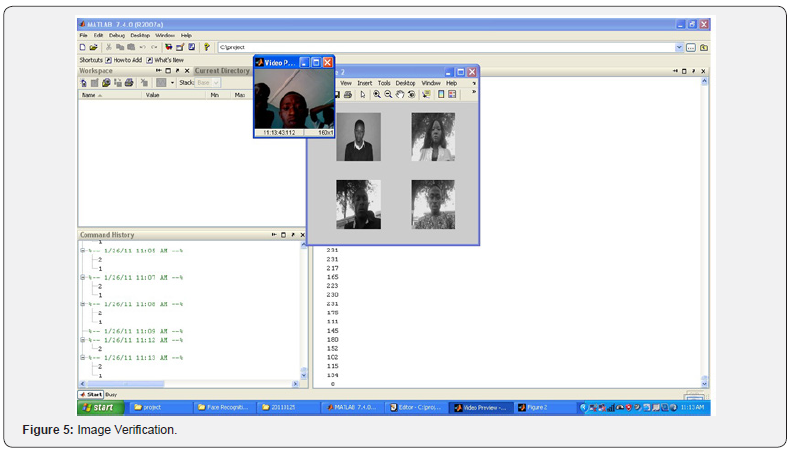
At the Home page when the second option is selected the software activates the webcam which captures the image adjacent to it and then converts it to the grey scale for recognition. The grey scale is used to remove all external inferences with the image such as light, gesture and other external interferences as seen in Figure 4. The system then compared the new image with the images stored in the database by scanning through the four images in the database as shown in Figure 5. If it is able to recognize it, It permits the user by allowing the user to move on to the next phase. If the phase recognition fail it allows the user to return to the main page and try again as shown in Figure 5 to implement the eigen face recognition, a new library was included in matlab [5].
Phase 2
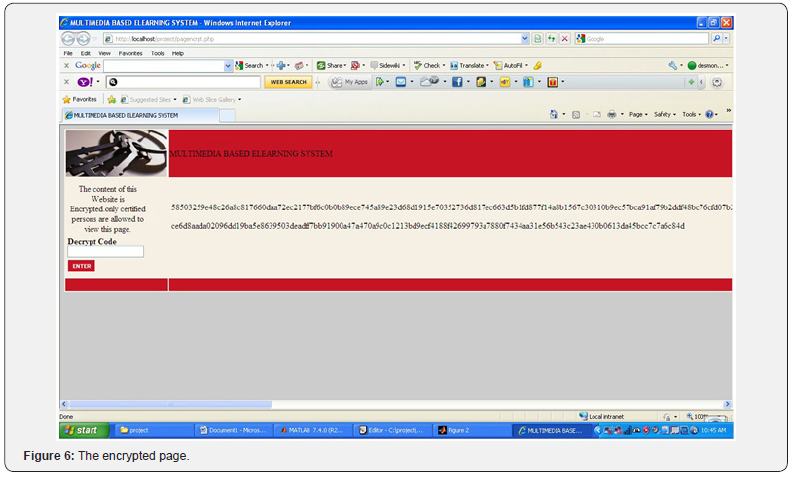
With success in the facial recognition begins the second phase of our implementation. In this phase the user sees an encrypted web page and the whole feature makes no sense at all. Unless the user has the decryption code he is unable to decode the content of the page. The encrypted page is shown in Figure 6.
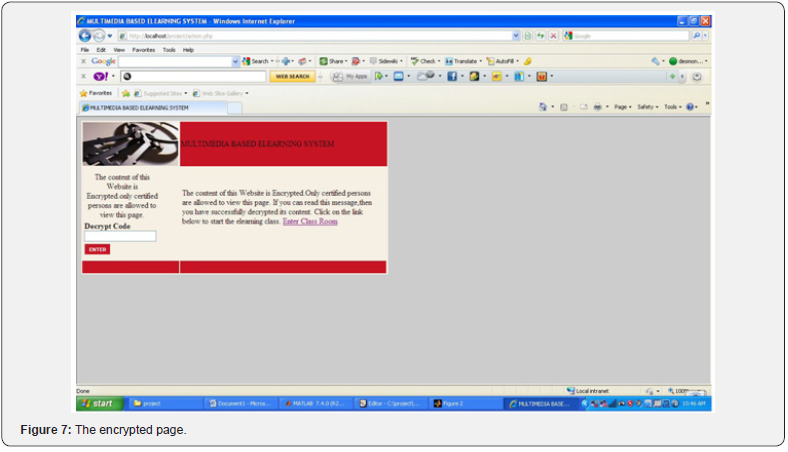
In Figure 6 encrypted text is displayed the system immediately decrypts the page and it becomes intelligible to the user and he can then proceed. In the event of failure to enter the correct code the system issues a new instruction directing unauthorized access To implement the encryption, we pass MCRYPT, Encrypt which is a function in PHP in the direction of the content or argument we intended to encrypt. MCRYPT offers a choice between a number of ciphers-different single key algorithm. To decrypt we pass MCRYPT DECRYPT function which return the encrypted pages to its readable content. The DES algorithm was used in this. It is designed to encipher and decipher blocks of data consisting of 64-bit key 1. Deciphering was accomplished by using the same key for enciphering, but with the is schedule of addressing the key bit altered so that the deciphering process is the reverse of the enciphering process. Figure 7 shows the decrypted page [6].
Phase Three
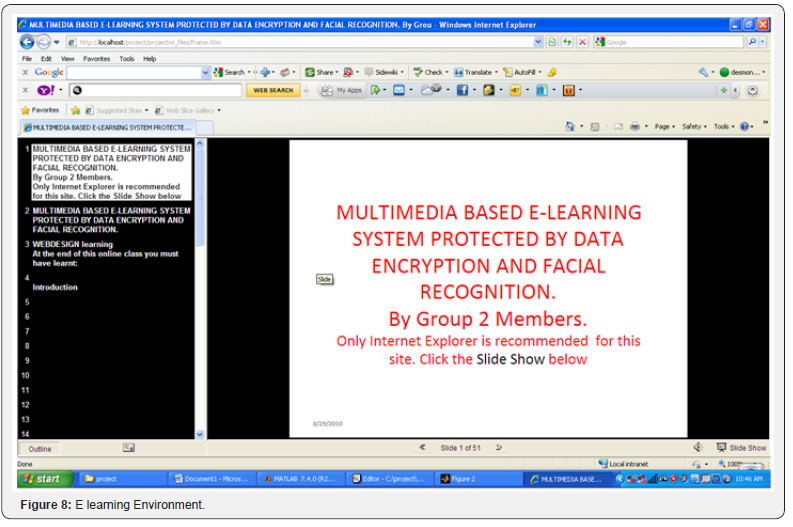
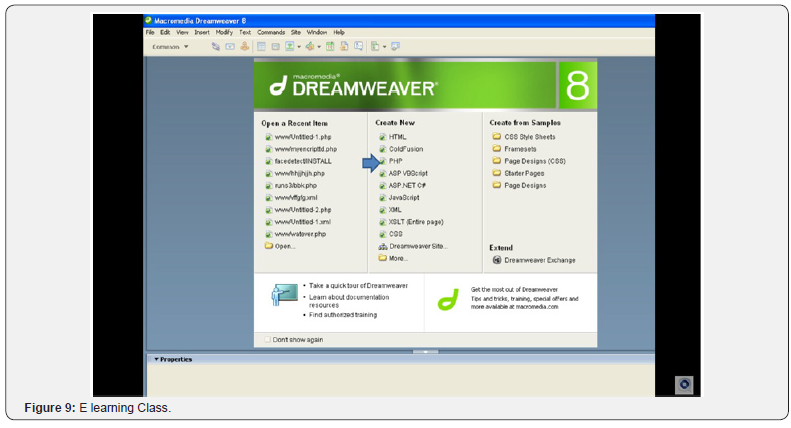
The third and final phase of implementation of this Paper is the implementation of the multimedia based learning environment. This Paper is web based, portable and platform independent with interactive and user friendly GUI. Microsoft PowerPoint was found to be appropriate to implement this phase. Figure 8 shows the Elearning environment which was implemented with Microsoft power point. It involves the creation of slides for each class and simultaneous recording of the audio tutor. In this Paper the idea was to create an Elearning environment to teach webdesign using Dreamweaver software. Microsoft power point 2007 was discovered to be appropriate for this implementation because of its wide features which includes the ability to create slides and record audio sounds. The design of the Elearning environment with PowerPoint was accomplishment by taking still images of the dreamweaver environment representing each stage of the course. Each image then placed on a slide with its corresponding audio tutor recorded. On entering the multimedia elearning environment the user sees in stage as in Figure 6. he can then click on the ‘slide show’ at the bottom right corner to begin the elearning class. The sequential display of page and its corresponding audio makes the whole system unique and enhance learning of the web design. Figure 9 shows the elearning class. Since the Paper is intended to be web based, we converted the Microsoft power point format of the Elearning environment into html format by choosing the html option in the save as menu. Saving it as a HTML code, we were able incorporate the whole system as a web based application.
Phases Integration
Thanks to the extensibility of PHP we were able to integrate the three phases into one single System. The system begins loading from the first Phase in the MATLAB environment, on successful image verification it proceeds to the web page implemented with PHP and on successful page decryption it goes to the final phase which is the e-learning environment (Figure 10).

Conclusion
A functional multimedia based e-learning system that is protected by data encryption and facial recognition. The development is a pilot Paper that guarantees an improvement in security of E-learning System. It is hoped that this system if implemented in a large scale will proffer solution to data insecurity. The infrastructure for virtual classroom could be improved by adopting the context employed in this development particularly the added multimedia facility.
References
- Horton W (2003) Evaluating e-learning. Alexandria, VA: ASTD
- McConnell D (2006) E-Learning Groups and Communities. Open University Press, London, Uk.
- Paulsen M, Vieira V (2006) State of the Art Report: E-learning Quality in European SMEs-an Analysis of Elearning.
- Kirkpatrick DL (1994) Evaluating Training Programs: The Four Levels. San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, USA.
- Rosenberg MJ (2006) Beyond e-Learning: approaches and technologies to enhance organizational knowledge, learning and performance. San Francisco, CA, USA.
- Bledsoe WW (1996) The model method in facial recognition. Panoramic Research Inc. Palo Alto, CA, USA.






























