Developing Positive Behavior in University Graduates
Muhammad Nasir Khan1*, Fareeda Yaseenzai2 and Amanullah3
1Department of Education, International Islamic University Islamabad, Pakistan
2PhD Scholar, International Islamic University Islamabad, Pakistan
3Lecturer, Federal College of Education, H - 9, Islamabad, Pakistan
Submission: July 14, 2022; Published: September 06, 2022
*Corresponding author: Muhammad Nasir Khan, Research Associate, Department of Education, International Islamic University Islamabad, Pakistan
How to cite this article:Muhammad Nasir K, Fareeda Y, Amanullah. Developing Positive Behavior in University Graduates. Ann Soc Sci Manage Stud. 2022; 7(4): 555720. DOI: 10.19080/ASM.2022.07.555720
Abstract
It’s important to analyze the behavior of youth particularly university graduates in view of the contributions of youth in developing peace and sustainable development. Many studies reflect the exisiting situation of violence among the youth and is the greater concern of parents and professionals (Alikaúifolu, 2016). It is necessary to understand behaviors that may occur because of a lack of understanding of the “other” and its culture. Purposive sampling is used in the selection of participants. Data are collected through interviews with 15 university graduates. Data that is collected through the personal visit provides the in depth understanding of the real (Mack, Woodsong, MacQueen, Guest, & Namey, 2005; Ospina, 2004). The qualitative research contributes to providing the vision of the existing realities (Patton, 2002; Watt, 2007). The questions in qualitative research are comprehensive and are for the examination of the central occurrence in a study [1]. Therefore, findings of the study determine the existing situation of violence and define the nature of violent incidents refer to student-on-student. The findings indicate the insufficient teacher training programs to address the violent behavior of the students.
Keywords: Violence; Youth; Experiences; Participants
Introduction
The psychology of behavioral support focuses on the utilization of the principles and techniques that are in favor to improve the satisfaction and performance of coaches, athletes and the teams. Collective objectives include to decrease the problems in the behavior, addressing the emotions and anxiety, focusing the confidence on the athletes and teaching the new techniques to improve the performance of the athletes and coaches in the different sports [2].
Analysis of the behavior looks to be effective and in practice when is addressing the various aspects of our lives particularly in the field of our behaviors and different aspect of our lives in almost all societies of the world. Various aspects and principles of behaviors can be analyzed with respect to sports [3].
A behavior assessment is a tool that is used in psychology to identify, examine, predict, and improve a person’s behavior. It is often used in education and in therapy settings when individuals are engaging in inappropriate behaviors. Behavior assessments can also be helpful in sports psychology. They can be used for the purpose of improving an athlete’s attitude, sportsmanship, or cooperation. They can also help an athlete learn specific skills and techniques they need to succeed at their sport.
(https://study.com/academy/lesson/).
Research in behavior analysis in early have a focused on the athletes and the determination of the feedback of the athletes. Komaki (1977) determined the impact of the nature of feedback of athletes in different fields of the sports in the world.
Behavioral Development
Various research studies indicate that contributions in co-curricular activities indicate direct assessment of the behavior. It’s important to ensure the contributions of youth in co-curricular activities for the behavior development. Different studies concludes that sports enhance the psychological health of youth that have good effect on the behavior of the youth (Martin & Thompson, 2011). Different studies concludes that challenging behavior in youth can be reduced with the participation of youth in the co-curricular activities (John, 2019). Contributions of youth belonging to different cultures enhances the vision of tolerance and peace in the.
Overview of Behavior Development in Cultural Context
Culture and behavior of the youth are interlinked with each other. Culture build and provides the dimensions to the youth for the development of behavior. Therefore, it’s important to evaluate the values of culture to assess the behavior of the youth (Khan, 2018). Cultural values vary from culture to culture. Its necerassy to teach the universal truth and educate the youth about the common values to the youth for developing the tolerance in the youth. Cultural values of youth should be in consideration while arranging the conversations and dialogues of the participants. Variations and intensity of behavior in youth needs to be assessed for further developing the policies to smooth the behavioral issues in the youth. Various studies elaborate that the intensity of behavioral issues should be addressed well in time to reduce the violence and crimes in the youth ( Geyer, 2017).
Causes of Challenging Behavior in Youth
According to Powell, Dunlap & Fox [4] elaborates the article about intervention and prevention for challenging behaviors of school children that challenging behavior in the children is commonly observed and exists in repeated forms that are leading to violence among the students. This phenomenon has been observed in many schools and would be addressed with modern techniques. Such challenging behavior patterns may be observed in the athletes. Challenging behavior mostly exist in the forms of disorders in the psychological health and in the form of aggression and anxiety. Burton [5] elaborates that a number of complications in the psychological health led to such kind of behavior. Teachers association (2007) determined that various climate situations lead to behavioral and emotional complications in the youth and athletes. Sutton (2000) mentions that various research studies in United Kingdom indicates that the prevalence of fourteen year old with behavioral and emotional problems [6-10].
The following are the major causes of differences in behavior:
i. Climate factors
ii. Psychological factors
iii. Individual differences
iv. Differences in family patterns
(UNESCO, February 2000, p-09)
Violence in Youth in View of Family Climate
Children living with domestic violence have been described as the ‘forgotten’ or ‘invisible’ victims. Causes of violent acts among students refer to students’ socio-economic positions of their parents (Kalogridi, 1995). Empirical evidence represents that lack of discipline in the parental climate and the poor supervision promotes the risk for the anto-social behavior in the adolescents and youth (Loeber et al., 1993; Yoshikawa, 1994). The social development of a child is dependent on the provision of available opportunities and skills that are provided in the family climate and the school climate. The patterns of behavior are dependent on the behavior of the parents and teachers towards the child. Unfavorable climate of the family has a negative impact on the psychological and behavioral adjustment of the children (Moreno et al., 2009; Jaureguizar and Ibabe, 2012). More violent behavior has been observed in the children with traditional families (Kennair and Mellor, 2007).
Cultural Impact on Youth Violence
Specific cultural factors have been found in promoting the violent attitude in the children. For example, Smith (2004) concluded in a study on correlation between deviant culture and school violence in rural areas in Sudan that culture of harsh attitude of parents towards their children was responsible of aggressive behavior in students at school (p.21). Similarly, Smith (2005) conducted a study on 37 high school students in rural areas of South Africa and concluded that culture of rape was major factor of sexual violent attitude in students (p.17) [11-16].
Discussion
Lack of understanding other and the nature of culture is widely affecting the behavior development of youth. The higher education institutions should consider particularly individual differences and the cultural contradictions in the teaching learning process. The new generation should be prepared to face the behavioral changes with tolerance and positive attitude. This is important in the sports and cultural events as well. Studies concluded that the behavioral differences and contradictions have been particularly observed and in the experiences while sports and cultural festivals (Buschesky, 2017). This should be in the consideration to develop the strategies and to create the climate of peace while arranging the sports and cultural festivals at national and international level. Creating the climate of peace for the individuals belong with different cultures should be the priority of the event’s organizers (Vaillancourt & Hymel, 2010, p. 38).Professional development for schools in the development of strategies used to stop student emotional violence including bullying.
Procedure of Data Analysis
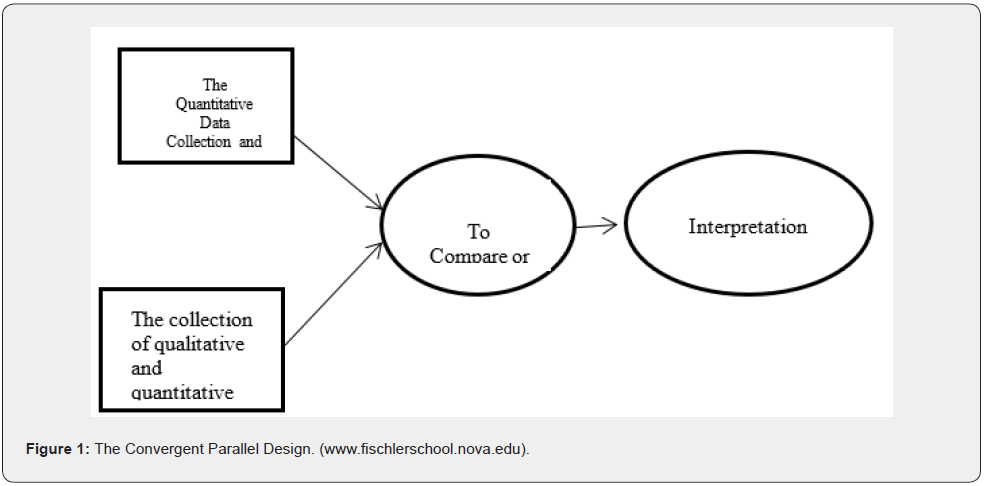
The tool of research for the study was convergent parallel design that is a type of mixed method. The researcher in the convergent parallel design is concerned with collection of quantitative and qualitative data,, analyzing the two data sets separately and mixes the two databases by merging the results during interpretation (Figure 1).
Population
The purpose of the study is to identify the behavior that may occur because of the lack of understanding others and culture of others. For this purpose, experts’ opinion was taken. Experts of behavior development were selected with convience sampling from the higher education institutions.
Instruments of the Study
Mixed method approach was used in the study. As a tool of research, interview and questionnaire was used in the study as a tool of research. Structured interview and questionnaires were used in collecting data.
Collection of Data
The researcher collected the data by personal visits of the participants. Privacy was confirmed to the participants and the objective of the study was determined by the participants. The questionnaire was five point likert scales (strongly agree, agree, undecided, disagree and strongly disagree).
Data Analysis

*Significance df= 4 Table value χ2 at 0.05 level=9.488
(Table 1) Table 4.608 indicates that the calculated χ2 value was found to be 69.82, which is greater than the table value at 0.05 level. Hence, the statement, is accepted.
(Table 2) Table 4.609 indicates that the calculated χ2 value was found to be 88, which is greater than the table value at 0.05 level. Hence, the statement is accepted.
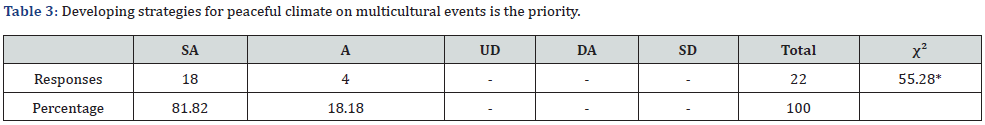
(Table 3) Table 4.610 indicates that the calculated χ2 value was found to be 55.28, which is greater than the table value at 0.05 level. Hence, the statement is accepted.
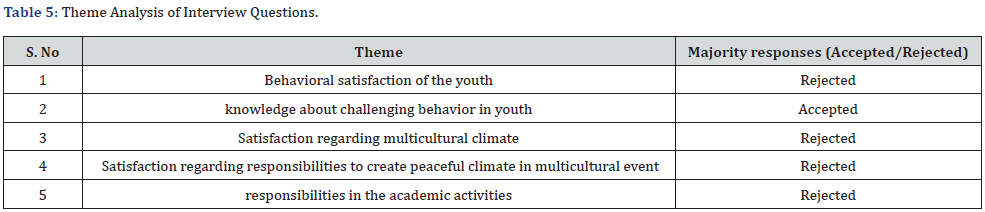
(Tables 4 & 5) Table 4.613 indicates that the calculated χ2 value was found to be 69.82, which is greater than the table value at 0.05 level. Hence, the statement is accepted.

*Significance df= 4 Table value χ2 at 0.05 level=9.488
*Significance df= 4 Table value χ2 at 0.05 level=9.488

*Significance df= 4 Table value χ2 at 0.05 level=9.488
Conclusion
The study concludes that strategies to control the behavior of youth is the fundamental responsibility of the teachers in the higher education institutions. It’s important to consider the behavior and nature of the cultures of the invited people for adopting the strategies and discipline for peaceful climate. The study concluded that lectures to follow the discipline would be part of the teachings in the higher education institutions. The study concluded that higher education institutions need to revise their policies to overcome the violent attitude in the students and to develop the positive behavior. The teacher training needs to revise in the context of developing the positive behavior.
Recommendations
i. Educate the youth about the behavior changes and the analytical approach in developing the behavior in university graduates.
ii. Concluded and authentic information about the analytical approach in behavior is urgent need of the day for the university graduates.
Provision of access to training resources for the positive behavior.
References
- Nicolai S (2009) ‘Chapter 1: The best and worst of times’, In Nicolai S (Ed.) Opportunities for change: education innovation and reform during and after conflict, UNESCO, International Institute for Educational Planning, Paris, France.
- Rushall BS, Siedentop D (1972) The developmental and control of behavior in sport and physical education. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, Pennsylvania.
- Martin G, Osborne JG (1989) Psychology, Adjustments, and Everyday Living. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, United States.
- Powell, Dunlop & Fox (2006) Prevention and Intervention for the Challenging Behaviors of Toddlers and Preschoolers: Infants & Young Children 19(1): 25-35.
- Burton M (2001) Understanding and responding to behavior challenges: An Investigative Approach. Manchester, England.
- Lindsley OR (1992) Precision teaching: Discoveries and effects. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 25(1): 51-57.
- Banta B (1993) Peaceful Peoples: An Annotated Bibliography. Metuchen, New Jersey: Scarecrow Press, United States.
- Bey TM, Turner GY (1996) Making School A Place Of Peace. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
- Fountain S (1999) Peace Education in UNICEF.
- Galtung J (1981) Social cosmology and the concept of peace. Journal of Peace Research 18(2): 183-199.
- John W Simon ( 2013) Understanding Peace Teachings in School Climate; New Comprehensive Publications, Romania.
- Jonson (2012) Peace Teachings in School; Brilliant Publications press.
- Kampel S (2017) Peace Practices: New Reflections, Green House Publications press.
- Irny SI, Rose AA (2005) Designing a Strategic Information Systems Planning Methodology for Malaysian Institutes of Higher Learning (isp- ipta), Issues in Information System, VI(1).
- Ilfiandara S, Riswanda ( 2019) Peace Education Pedagogy: A Strategy to Build Peaceful Schooling, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia.
- UNESCO (2005) Peace Education.






























