Work Related Stress: A Literature Review
Harshana PVS*
Department of Agriculture Economic, Ruhuna University of Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka
Submission: October 02, 2018;Published: November 19, 2018
*Corresponding author: Harshana PVS, Department of Agriculture Economic, Faculty of Agriculture, Ruhuna University of Sri Lanka, Mapalana, Kamburupitiya, Matara, Sri Lanka
How to cite this article: Harshana PVS. Work Related Stress: A Literature Review. Ann Soc Sci Manage Stud. 2018; 2(3): 555586. DOI: 10.19080/ASM.2018.02.555586
Abstract
Work related stress is an ordinary reaction that occurs when the work weight progress toward becoming excessive. Occupational wellbeing impact to soundness of representatives and strength of the association. Work related stress is a genuine and developing issue in the present world. It is imperative that this issue is tended to and that move is made to address the issues this may make both for people and the associations in which people work. This paper reviews the idea of work-related stress, work related stress models and demonstrating how it effect on effectiveness and performance of the organization. Be that as it may, since not all the job-related stress has negative effect it may act as a morale booster of the employees too. These should be taken into consideration by the top-level management in order to increase job performance while reducing the work-related stress.
Keywords: Work related stress; Strength
Definition of Occupational Stress
As per distinctive investigations the thought of stress has been anticipated and shown with various qualities. According to the definition from one scholastic from the long history, stress could be described as “the non-specific response of the body to any demand placed upon it” (Selye, 1987, p.17).Following the literature in the near histories; the term of stress has been recreated in the form of a term which could be used to describe a force that results in or else causing for the deformation and meanwhile the response to the stress now could be possibly described as the strain referring to the manifestation in a body Le Fevre et al. (2003). The concept of stress is always accompanied by several notions such as performance, motivation and as well as the employee wellbeing when referring to anorganization.
As described in many research articles on employee stress levels, it is obvious that the employers are keeping constant tracks in line with the optimal stress levels to boost the employee performance. Nevertheless, it was also mentioned that these sorts of would not much help to maintain fine line between stress levels, motivation and one’s wellbeing [1]. The notion of stress would not always act as a negative factor according to Papasolomou-Doukakis et al. (2004) to be eligible and fully engaged in the competitive environment within the prevailing organization the amount of pressure or the stress that would arise at time can also act as a motivator.
Stress Models
According to the publications by New Zealand government on work safety, there are seven models to be discussed in general with special references [2]. The very important thing to note on these models is that none of these models are perfectly describing any backgrounds for the various models for stress, yet some models are adding values while some are hiding certain values. The models can be named in sequence; “A traditional model”, “The bucket model”, “An Academic model”, “The demand, control, support model”, “The effort rewards imbalance model”, “The ‘status syndrome’ – the effect of hierarchy”, “An alternative model of stress”.All these models have some sort or the certain level of similarities in the theories that are discussing within the model.
For instance, the first model which is named above, A traditional model; this describes in simply the stress is a certain level of perception that leads the mind of the employee towards an end where he or she is going to think that he or she would not be able to cope with the work stuff and finally result in fatigue. The best example to precise that the models are describing a certain level of similarities is that the “Bucket model” is also describing the fatigue condition of an employee which leads for the employee to experience unpleasant experiences by linking the human body in to a bucket full of unpleasant experiences.
Key Concepts
Employee stress has been named in different ways over the years and it’s commonly called occupational stress or work place stress. Also, its meaning developed over the years, Initial days, it was identified as the pressure from the environment an employee gets. But later it was identified as it get an employee within him. Now it is identified as the relationship between a situation and employees’ reaction towards it. When an employee cannot fulfill the demand, she/he gets from the environment, he/she will get stress. This may be a mental or physical demand.Also, it’s an unwanted reaction people have on severe pressures or demand placed on them. Work environment and management support will greatly help employees to manage their work place stresses.
Selye (2006) says that stress is a nonspecific response of the body to a demand. If an employee gets a work load than they can handle, they will get stress. But the level of stress is differing from employee to employee. If the stress is continuing for a longer period it will lead to mental, physical and behavioral problems. Based on a research done in Sri Lanka (Opatha, 2011), addiction to smoking and drinking may be a result of stress.
Even though sometimes, stress has a positive effect for employees all the time when they extent their limit, they get negative results.Eachemployee will get stress at any point in their job. Malta [3] mentions that when a person gets a stressful situation frequently, he/she will not be able to cope with the situation. Work place pressure will help employees to keep motivated and learn. But individual differences and available resources will change the employee’s cope up level and make him/her stressful.
Various research shows that many stressful situations occur when employee face excessive work demand in his jobs. If the employee’s knowledge and abilities cannot fulfill the work demand, he trends to face work place stress. Also, when the employee doesn’t have any choice on his jobs, some time she/ she must perform his/her jobs without willingness. In such a situation, there is a big chance that employee get work place stress. If an employee is in a wrong job for his personality it also will lead to occupation stress.In this research study, employee stress, occupational stress organizational stress will be used as one word. As mentioned above occupational stress cause damage the physical, mental and behavioral aspect of an employee. Using all three aspects, we can identify employee stress level in work placeHFRS (2011).
Evidence on the occupational stress
Occupational stress occurs when the employees experience aversive or unpleasant emotional states in their work place. Kyriacou and Sutcliff defined stress as the unpleasant emotions like tension, frustration, anxiety, anger and depression[4]. Newton (2009) and Head and wearing (2002) also defined the work place stress like the above definition. Various psychological theories also provide definitions of stress. Specially Beehr and Newman, 1978, French et al.and Cooper, 1998 also contributed extensively for the research on occupational stress.Eg: If an introvert employee is placed as a marketing of officer, he will not be able to perform his job well and this will lead to stress.
When employee cannot cope with his day to job requirements, it easily lead to the occupational stress. By improperly manage work organizations, by not properly manage work designs, poor leadership and management, poor working conditions and competitive work cultures can be main courses of stress in today’s business word. (Mead, 2001). According to Mead (2001) workload is the main source of employees’ occupational stress. When the production rate high and work load is there is a negative relationship to the employee’s performance. When the performance low, he/she trend to get stress. Siegrist did a 5 years study using 1,100 factory workers in 1996. This research pointed out that when the workload increases workers stress level, blood pressure and cholesterol level increase. Rubina et al. (2008) did a similar research on work place stress and they found out that lack of resources, workload, lack of communication, discomfort with supervisors have contributed to increase the stress level of the employees[5,6].
Asifargue that (2009), technology suppose to shorten the working week and give more leisure time to the employees, but reverse is happening. People are working long hours and spend less hours with family. Due to less family time, employees get stress,Subha and Shakil (2010) mentioned that rapid work place changes have increase the work place stress[7]. Many people in various jobs are finding difficult to cope up with the rapid changes in technology. Another important fact here is, employees feel that they are a part of a machine and they don’t feel they are a human and they have an individual live. This lead to the work place isolation and stress. Gallespie et al.(2001), found out that introduction of new technology (Internet communication, web based on line teaching, software packages) have increased the workload and occupational stress. Since the university staff do not get adequate training and time allocation for their competency development, these new technological changes lead occupational stress.
Not only that Asif pointed out that shift works, deadlines, longer working hours, distance to work place and commuting to work place, unfavorable working conditions, work mates and colleagues, job security and boredom will lead to the occupational stress. Rubina et al. (2008), mentioned that distance to work place also course for the occupational health, Due to the modern congested roads, will increase the stress level of the employees. Now days, most of employees are working far away from their homes and those employees’ trend to get occupational stress easily. According to Elovainio et al.(2002), “Working in a job just for the money leads to a lack of self-value& lack of fulfillment”. Meneze (2005) mentioned that (2005) “most people don’t realize just how stressful this can be and they underestimate the longterm effects it can have on their health. According to Parikh et al.(2004) when an employee gets this kind of work place stress is the most difficult to spot and challenging to fix, since finding a rewarding job is not always easy[8].
Michie(2002) pointed out that working with people that an employee doesn’t like and don’t ‘get on with’ can be a huge source of workplace stress. According to Giga & Hoel (2003) “spending many hours each day with people you hate can be very bad for your long-term health, specially, if an employee gets angry or resentful regularly it will badly affect to the health of the employee. Employees always should try to find ways of improving relationships with colleagues at work and reduce the risk of getting work place stress.
According to Malta [3] mentioned that job for life is concept have gone now and losing a job is very stressful. Due to this worker are struggling to keep his jobs. Schultz (2002) says that “changing occupations is far more common now days - this can be one of the most stressful times in a person’s life”. Also, they highlight that “lack of funding, resources and support services, most workers identify diminishing resources as a primary barrier to carrying out their role efficiently and to an appropriate standard leading to stress”.
Further to Gillespie et al.(2001), lack of resources leads to the decline in staff numbers, and therefore no longer adequate staff to perform the work required. This causes more pressure on the few workers and creates unbearable workload for workers and therefore as a result occupational stress increase. One other factor that affects employee performance is technical training. According to Levey (2001), employees can bring skills to a position but there are likely to be internal, company- or industry-specific activities that will require additional training. For instance, if a process requires a new software package it’s unrealistic to expect employees to just figure it out; they should receive adequate training. Rubina et al.(2008) argue that proper technical training does not only improve employee performance but also improves their efficiency.
Through knowing how to use and handle specific tasks at work, makes employees accomplish the tasks much easier and efficiently. On the other hand, having no proper technical training hinders employees‟ performance in that they will need spend more time and consult experts which would even mean more costs to the organization. When the company provide proper technical training, he will work in the company without stress. But if the employee were not properly trained, he will get stress. According to Rebecca (2010), employees don’t perform in a vacuum. There are a variety of factors like
a) Personal
b) company-based and
c) external
Work place environment and culture are very important factors for employee’s performance in an organization. Deena (2009) says that some people are highly sensitive to the organization environment and culture while some are less. Workplace should be conducive for work and perform the given tasks effectively. Parikh at el emotions that organization environment should be modifies to help employees to perform. A favorable working environment will ensure that employees perform well.
In 2009, Asif indicates that employee’s qualification and job fitness will help employees to reduce job stress. When employees qualified for the job only, they will perform the job and meet the expectations. The knowledge, skills and attitude should match toward the jobs. According to Deena (2009) when an employee is in a wrong job, he will not be able to perform, and the company cannot achieve the expected results. Levey (2001), mentioned that knowledge and skills pays a vital role in organizational performance and if the employee is not perform his job due to lack of knowledge or skills, he will get stress. When an employee has required skills with proper attitude, he will exceed in his job without workplace stress.
According to Asif (2009) when the employees have clear goals and expectation they can perform well. When the employees do not get clear goals, since they cannot perform, they get further attributes good employee performance to clear goals and expectations. When everyone understands the targets and expected outcomes, it is easier to take steps to get there and measure performance along the way. Organizations without clear goals are more likely to spend time on tasks that do not impact results.
In addition, Rebecca (2010) argues that if organizations are to achieve clear goals and directions, support from superiors is very necessary. Superiors must understand the needs of the employees for the employee to work efficiently. Sometimes frequent fault finding of the employee’s work may also lead to deficiency in work. Employee effectiveness is also lost if there is no proper guidance or planning in an organization. Michie (2002) relates this situation to a tourist who has no guide. He notes that it would not be long before such a tourist loses his track or direction and so would be the case of an organization which has no good supervisoremployee relationship.
Mead (2000) mention that quality of tools and equipment can also affect performance of employees and reduce the stress level they get in the work place. Adding to that Malta [3]mention that as a driver needs a vehicle in operating condition, each employee need tools and equipment necessary for their specific jobs. Physical tools, supplies, software and information’s can be identified as the tools and equipment. Malta mentioned that today there are up to date software which do work and help to perform tasks in real time and much faster compared to manual systems or outdated software. As mentioned by Mead (2000) outdated equipment. Not happing proper equipment and tools effect to the performance of the employees and finally the result of the company. When proper equipment’s are not available for work employees cannot perform well and due to that they get occupational stress.
According to Rebecca (2010) company culture are affect to the tress level of the employees. When they have a competitive culture, they get more stress than in a cooperative culture. Also Rebecca mentions that poor work place moral, there will be more whining, complaining and people will do their job without commitment. On the positive end, the workplace is energized by a sense of purpose and teams that genuinely want to work together.
Empirical Evidences on the Stress and Organizations Performance
Stress mainly affect to the employee turnover (Mead, 2009). The rate of turnover varies from company to company. The highest level of turnover normally found in private sectors than public sectors. The levels of turnover also vary from region to region. The highest rates are found where unemployment rate is lower and where it is easy for people to get alternative employment. Sometimes employee turnover benefits organizations positively. This might happen when a poor performer is replaced by a more skilled employee and when a retired employee replaced by a younger one.
Employee turnover may be also costly as it requires different cost to take account such as administrative costs of recruitment, cost of covering during the period in which there is a vacancy, training cost for the new employee etc. (Dessler, 2000).Turnover occurs for many different reasons. Sometimes new job attracts employees and pull them to leave the old one. In contrary employee also pushed to leave job due to the dissatisfaction in their present workplace or by domestic circumstances when someone reallocates with their spouse or partner. A poor relationship with the management can be an important reason for the employees to leave their jobs. It is relatively rare for people to leave jobs in which they are happy even offered by higher salary elsewhere.
A lack of proper training and development is also major cause for voluntary turnover. Employees prefer security of their jobs. Turnover could be minimized through considering different preventive measures by the management. These may include providing training to the line managers for an effective supervision before appointing or upgrading them, providing security of jobs with good working environment etc. There may be an offer for retraining the existing managers who have a poor record at keeping their staff happily. Supervising managers could be accountable for employee turnover in their teams. Maximization of opportunities for individual employees such as accommodate individual preferences on working hours, regular appraisals, providing as much job security as possible can help to reduce turnover. Due to the factor motioned the above can lead to increase the stress level of the employees and then those employees will leave the organization. Employee’s high turnover rate will reduce the company’s profitability.
Occupational stress reduces the morale of the employees. Workplace events play a large part in changing employee morale, such as heavy layoffs, the cancellation of overtime, cancelling benefits programs, and the lack of union representation. Other events can also influence workplace morale, such as sick building syndrome, low wages, and employees being mistreated.Factors influencing morale within the workplace can be illustrated through the below given attributes:Job security, management style, staff feeling that their contribution is valued by their employer, realistic opportunities for merit-based promotion, the perceived social or economic value of the work being done by the organization as a whole, the perceived status of the work being done by the organization as a whole, team composition, the work culture.
When the above factors positively influence the stress, the employee get low morale and if it’s other way employee get high morale.To determine the impact of downsizing, the effects of job insecurity and economic need to work on employee attitudes was examined by Brucknerand his colleagues in 1992. In this study, Brockner decided to use work effort as a measure of job attitudes. The study found that high job insecurity coupled with high need to work, resulted in increased work effort following a layoff. High job insecurity coupled with low need to work resulted in no change in the level of work effort. This seems to indicate that when there are high levels of job insecurity, as would be expected during downsizing, employees with a high need to work will increase their work effort, while those with a low need to work will have no change in work effort.When an organization downsize its work force, there will be high stress level in the company.
All the time stress having undeniable effects on corporate performance, stress has been understood from the individual perspective. All the time researchers have done research on the effects of stress has been centered on individual performance. According to Newstroom (2007) there is an inverted U relationship is the most studied pattern of the stress and performance. The meaning of that is moderate level of stress stimulate the body to perform. It means too low or too high stress influence performance negatively.According to Robbins (2003), the inverted U pattern may also describe the reaction to stress overtime as well as to changes in stress intensity. “The notion that stress has detrimental effects on individuals, and subsequently affects the performance of organizations is shared by a several researchers[9,10].
According to Everly& Benson (1989) mention that “overtime stress response exerts a generalized wear and tear on the body” and unhealthy body will not help employees to perform in their jobs. But according to Welford [11] optimum level of stress at work will employees to work at their optimum level. When employees get adequate challenges, they get optimum level of stress. Therefore, according to Welford [11]and Jing [6] a certain number of employees stress beneficial to the organization and increase the organizational profits.
According to Lambert, Lambert &Ito [3] stress is a major contributing factor to corporate inefficiency, high staff turnover, absenteeism, decreased quality and quantity output and increased health care cost for staff. In 2007, Ngeno [10] conducted a research to examine the causes for burnout among the primary teachers in Kenya. In this research he found out that burnout has a negative impact on the performance of the teachers.Also, according to the research conducted by Munali in 2005, stress affect the performance of the hotel workers. For this research Munali collected data from 300 hotel employees and finally found out that stressful employees get absent from work due to physical illnesses.
According to Ivancevich et al. [12], while organization consequences are many and varied, they share one common feature. Stress cost organizations money. Ongori&Agolla[5] mention that greater the stress encounter by the employees in their life tend to reduce the performance of the employees. According to them the finally it negatively affects to the performance of the organization. According to Elovainio et al.(2002) occupational stress is challenge for employers and high level of occupational stress lead to low productivity and other employee problems. He further cited that employers should find a way to address the issues of occupational stress since it badly impacts to the performance of the employees[13-15].
Conceptual Model on Stress
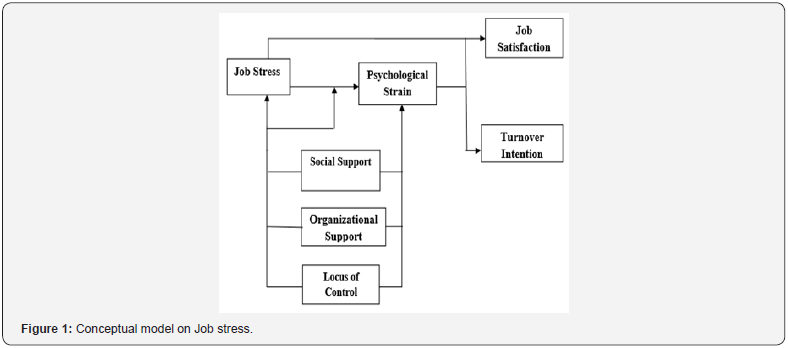
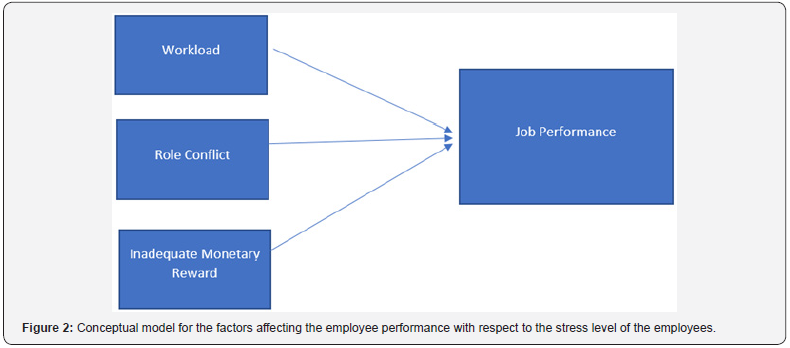
There exist various publications on the name of job or work stress and its relationships with several internal and external factors.According to Shrestha[16] he has examined that “there exists relationship with job stress and psychological strain and the moderating effects of locus of control social support and perceived organizational support in this relationship”(Figure 1). Models have been discussed in order to find the relationship of the job performance and the stress level of the employees of different organizations. According to Ali et al.[17] in the year 2014, their study was carried out in search of the factors affecting the job performance keeping the variable of job performance as the dependent variable and the stress factors as the independent variables (Figure 2).
Summary
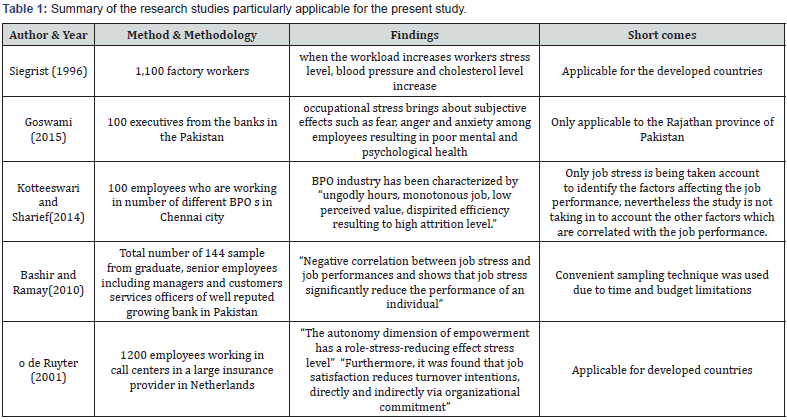
There are number of models which have been described throughout the stress literature. Out of all the stress models the models that described the linkages between the job performance and the impact from the stress levels have been taken in to account when conducting this research. Some basic research which is being used for the research could be summarized as shown in the (Table 1).
Conclusion
Job stress represents the most complex territories confronting the present manager with regards to dealing with their employees. Numerous investigations have shown an expansive effect at job stress on the job performance and job productivity of organization.
References
- Ahmed, A, Ramzam, M (2013) Effects of Job Stress on Employees Job Performance A Study on Banking Sector of Pakistan. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) 11(6): 61-68.
- Worksafe (2013) New Zealand Governement. Models of Stress.
- Lambert, C, Ito, M (2004) Workplace stressor, ways of coping and demographic characteristics as predictors of physical and mental health. International Journal of Nursing Studies 41(1): 85- 97.
- Ko de Ruyter (2001) Role stress in call centers: Its effects on employee performance and satisfaction. Article in Journal of Interactive Marketing 15(2): 23-25.
- Ongori, H, Agolla, JE (2008) Occupational stress in organizations and its effect on organizational performance. Journal of Management Research 8(3): 123-134.
- Jing, L (2008) Faculty’s job stress and performance in the undergraduate education assessment in China: A mixed method study. Educational Research and Review 3(9): 294–300.
- Bashir, U, Ramay, IM (2010) Impact of Stress on Employees Job Performance; A Study on Banking Sector of Pakistan. International Journal of Marketing Studies 2(1): 122.
- Munali, J (2005) Stress and individual performance of workers in hotels at the Kenyan coast. (Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation). Thesis. Andhra Pradesh Open University, Hyderabad State. India.
- Deshpande, A, Chopra, RK (2007) Fundamentals of organizational behavior. Sun India Publications, New Delhi, India.
- Ngeno, G (2007) Causes of burnout among primary school teachers within Kericho municipality, Kenya. Journal of Technology and Education in Nigeria 12(2): 9-18.
- Welford, A (1973) Stress and performance. Ergonometric 16(5): 567- 575.
- Ivancevich, Konapske, R, Matteson, M (2006) Organizational behavior and management. McGraw Hill, New York.
- Folkman, S, Lazarus, RS (1980) An analysis of coping in a middle-aged community sample. Journal of Health and Social Behavior 21(3): 219– 239.
- Goswami, TG (2015) Job stress and its effect on employee performance in banking sector. Indian Journal of Commerce & Management Studies EISSN: 2229-5674, ISSN: 2249-0310.
- Kotteeswari, M, Sharief, ST (2015) Job stress and its impact on employees’ performance a study with reference to employees working in BPOs. Research paper IJBARR ISSN No. 2347–856X.
- Shrestha, A (2013) Relationship of Job Stress, Locus of Control, Organizational Support, and Social Support to Psychological Strain. Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intentions: A Study in Nepali Commercial Banks.
- Ali, UW, Raheem, Nawaz, Imamuddin (2014) Impact of Stress on Job Performance: An Empirical study of the Employees of Private Sector Universities of Karachi, Pakistan. Research Journal of Management Sciences 3(7): 14-17.






























