Physical Education Teachers’ Practical Obligation to Legal Responsibilities and Liabilities (Case Study: Physical Education Teachers of Isfahan Province)
Mina Mostahfezian1*, Somayeh Rahbari1 and Masoud Raeei Dehaghi2
1Department of Physical Education and Sports Science, Islamic Azad University, Iran
2Department of Law, Islamic Azad University, Iran
Submission: August 10, 2018; Published: October 09, 2018
*Corresponding author: Mina Mostahfezian, Department of Physical Education and Sports Science, Najaf Abad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Najaf Abad, Iran, Tel: 00989133155039; Email: dr.mostahfezian@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Mina Mostahfezian. Physical Education Teachers’ Practical Obligation to Legal Responsibilities and Liabilities (Case Study: Physical Education Teachers of Isfahan Province). Ann Soc Sci Manage Stud. 2018; 2(1): 555578. DOI: 10.19080/ASM.2018.02.555578
Abstract
Background & Purpose: Sports law is a set of rules, regulations, norms and principles that creates certain context and specific guidelines on relations between people (coaches, referees, spectators, athletes, administrators, teachers, and others) in sports environments and in exercises, especially competitions with the aim of establishing the Justice, law and creating order. The purpose of this study was the evaluation of physical education teacher’s practical obligation to legal responsibilities and liabilities.
Methodology: The method of this research was survey research and fieldwork were done. For this purpose, 407 physical education teachers were selected with using random stratified sampling method. A researcher-made questionnaire was used for collecting the data; its reliability was confirmed by Cronbach’s alpha test= α) 0.84). The data were analyzed using T tests and analysis of variance.
Results: The findings indicated that the physical education teachers’ knowledge of sports law components was above average (μ>3). There was a significant difference between the service record, the level of education and the educational level regarding the practical obligation physical education teachers to legal responsibilities in the components of commitment and responsibilities, equipment standards, responsibilities of the manager and expert, and objectives and missions (P ≤ 0/05)
Conclusion: According to the results of the research, it is suggested that to be taken the necessary steps for further improve the legal and lawful awareness of the sports community, including the continuing education of physical education teachers in the form of in-service training courses, the formulation of new rules and regulations, etc.
Keywords: Practical obligation; Sports teacher; Sports law; Physical education
Introduction
In today’s world, sport is one of the effective educational and ethical ways, especially for young people, a tool that is becoming more and more scientific day to day. From a political point of view, victories in the sports events are also useful tools to announce and prove national credibility; consequently, large budgets and human resources are spent on sports development and success in the related fields [1]. Undoubtedly, with the increasing enthusiasm of young people in the country to learn a variety of sports fields and the encouraging successes that they have gained in international contexts, sports development has been considered something beyond the demand and as national and social demands. One of the ways through which this goal can be realized is the activities of teenagers and young adults in schools and their participation in sports competitions and sports mentors and coaches are of the important factors and components in line with reaching the above-mentioned foals.
In the wide field of sport, the connection between humans sometimes makes people, for various reasons, intentionally or unintentionally, damage each other, and this damage sometimes causes a person’s loss and sometimes criminal act of an individual, can be harmful to the whole society. Because in sports environments, most of the decisions are in the field of the authority and responsibilities of sports users, reveal their effects individually; hence, the most important responsibility of sports coaches is to take care of the physical, mental and prestigious integrity of the athletes. Whenever the instructors’ failure to accomplish the task is evident or the causal relationship between failure and injury is established, they will be responsible for compensation [2]. The results of numerous foreign and domestic researches that have been done on sports activities indicated that: athletes have been affected by many physical injuries and they sometimes paid treatment costs, and, in some cases, they were not able to continue their sports activities [3,4]. Security and efficiency components are among the most important components in all kinds of activities, especially in sports activities, security of sports places and environments where athletes are engaged in sports actives usually take less attention. Based on this fact, by means of certain activities and measures, risk factors of the sports spaces must be resolved, any incidents related to safety factors must be prevented and the number of injuries should be reduced [5].
On the other hand, since, athletes’ competitions and training accidents can be costly and unpleasant, in this regard, James & Nafziger [6]. proposed that providing appropriate solutions to create facilities and resolve existing barriers, such as: sports fields, sports equipment, platforms and sports space coverings, hygiene and sports realms are only possible by means of conducting researches and providing statistics and research data [6]. Sultan Hosseini [7], in their paper entitled “technical skills and abilities for sports managers” concluded that sports managers, in order to be effective in fulfilling their duties and be successful, need skills and abilities such as effective monitoring the implementation of sport calendar, facility management, ability to organize sports teams, manage sports events, manage sport camps and travels, and plan sports exercises [7]. Physical education teachers are responsible to do their best in maintaining the facilities and equipment of the school and using them optimally.
Nowadays, in different professions, compared to the past, human awareness of him or her rights and responsibilities and the consequences of negligence and indifference in performing duties have been developed exponentially. Along with this growing trend, physical education teachers move along with this movement and they do not consider themselves needless of civil rights and responsibilities knowledge, both to increase their knowledge and to increase awareness of the authority, liabilities, and responsibilities with high mental readiness to prevent irreparable losses and minimize the number and severity of accidents. Students’ happiness and enjoyment from physical education and sport, promoting students’ physical and mental health, preventing liabilities caused by negligence and indifference, insufficient training, inadequate monitoring, and knowledge, preventing the weakening of the image and credibility of physical education and sports schools and physical education teachers are among the main reasons for physical education teachers in line with the getting the right and proper awareness of their sports rights, duties and authorities. On the other hand, although, utilizing sports law and civil rights is at the beginning of its growth path, it has grown more than before.
An accurate and complete philosophy for physical education is necessary for the education system of the country and determines the direction of strategies, goals, and country physical education programs [8]. In other words, it is this philosophy and principals of physical education and its correct understanding that the Fundamental Reform Document of Education document focuses on the fundamental transformation in the field of physical education based on designing perspectives and formulating general and minor goals. Lack of knowledge and awareness in line with the existential philosophy of physical education for many physical education specialists (planners, managers, teachers, and instructors), willingly or unwillingly, maybe distort planned programs to reach the vision plane [9].
Talking about the teacher’s civil responsibility is based on two important principals: one is that the teacher is responsible for teaching and training, and another principle is that s/he must take care of students. Relying on these two true gives a distinct characteristic to the teachers’ civil responsibility [10]. Based on article 6 of the civil liability law, while students are supervised and controlled by teachers, they are responsible for the students’ harmful actions [11]. About 20-30% of children’s injuries happen in and around the school, Khosravi, Yaghmai (2010). Due to agerelated features and lack of experience; students are exposed to the risks of accidents at school. Since children spend nine months of their life at school, the share of events at the school in line with promoting education and health can be impressive. According to official statistics, from the beginning of the year 2008 to mid-May of 2010, 2941 students were injured in the schools of West Azerbaijan province, and they referred to the insurance organizations of the relevant province to get the costs of these damages and injuries, and they received a sum of 2548472275 Rls damages costs that most of these events happened in the school environment and more than half of them occurred in sports events and sports clubs [12].
Physical education is an applied science that by means of various sciences tries to make the favorable changes [13]. Physical education class via the physical skills training and the necessary requirements can increase physical activity throughout the life cycle [14]. In a lawful society, physical education teacher’s failure can expose him/her and the school to legal charges. Van der Symsen (1990) indicated that the highest number of charges against physical education teachers is due to insufficient protection. Enough protection is related to the ratio of students to teachers, teacher’s exercises, the distance between the student and the teacher at the time of the incident and the observing safety rules [15]. For many reasons, citizens in our country, unlike advanced countries, against the losses, rarely file a lawsuit against the organization, which, more than a legal problem, is a cultural problem due to people’s ignorance to their basic and civil rights Jabari & Shoariaan [16].
Young [17], believed that awareness of law principals is necessary for professional sports managers. Bases on the importance of the issue, he introduced the necessary legal issues for professional sports managers as, risk management, administrative laws, tort law, contract law, product liability, constitution, the judicial system, and legal researches. Since respondents believe that understanding appropriate risk management approaches reduce their liability, have identified risk management as the most important component [16]. Alla Joseph Babalola [18], in a paper entitled “Sources of Legal Liability among Physical Education Teachers” expressed the responsibility arising from physical education teachers’ negligence in four areas of supervision, equipment and facilities, injuries from sports participation and proper instruction [17]. Also, the National Intramural-Recreational Sports Association (2014) has announced legal liability and risk management as a part of eight core professional competencies of sports managers. Legal competencies are risk management - crisis management, damage liability, sports exceptions-consent, legal procedures, and insurance coverage and plan [19].
Partington’s [20], study results entitled “Modern sports coaching and the law: analyzing, clarifying and minimizing negligence liability” indicated that in coaching training and activities emphasis must be placed on developing coaches’ awareness and knowledge and understanding from developing legal areas [20]. Anu et al. [21], in their research inspected the injuries associated with participation in an adolescent physical activity in sports clubs, school sports activities and other leisuretime physical activities. This study disclosed that physical activity injuries in sports clubs are more than other physical activities in teenagers in different conditions. Since injuries during adolescence can have consequences for their participation in future physical activity also their future health, so it is important to introduce preventive measures more broadly and quickly to the sports club environment. This research also demonstrates that extents of injuries are associated with the number and intensity of adolescent sports participation, and due to the health benefits, it is recommended that adolescents participate in physical activity daily.
To reduce the risk of injury, the results of this research support the perspective that more preventive measures should be taken [21]. Soligard et al. [22] recommend that coaches and teachers play a vital role in injury prevention in sport club activities and school sports activities. Coaches, support staff, and teachers should apply the rules and exploit the way of using safety equipment such as hats and eye protection clothes. They should also evaluate environmental factors such as weather conditions and the conditions of using equipment such as gymnastics equipment [22].
Foroughi Pour [23] in a study that scrutinized the familiarity level of sports teachers, coaches and sports managers of Tehran with the athletic rights, concluded that a small percentage (17%) of sports coaches are familiar with sports law issues. Izadi et al. [24] in their research entitled “The Role of Risk Management Practices in Decrease of Lawsuits Concerning of Tehran’s Swimming Pools” concluded that there was no significant relationship between experience and risk management operations. Of course, a significant relationship was observed between the occurrence of incidents in swimming pools and lawsuit. The results also revealed that there is a significant relationship between the number of lawsuits and risk management measures in swimming pools. They concluded that using risk management measures could reduce the incidence of accidents and lawsuits in pools and provide a safe atmosphere for users of these places [24]. Yazdanian [25] in his research entitled “The plan of civil responsibility’s teachers arising from the practice of student in the Iran law with a comparative study in French law”, concluded that in the other countries law, the civil liability of teachers was particularly considered while this subject has not been mentioned in Iranian law [25]. Bonyan & Kashef [3] in a research entitled “The Different Legal Viewpoints between Male and Female Sport Coaches in the Sport Events” demonstrate that there is a significant difference between women’s and men’s views on legal liabilities, which means that female sports coaches had a greater awareness of legal liability than male coaches.
In terms of academic certificate, there was a significant difference between instructors with different certificate in line with awareness of sports law, this means that coaches with a master’s or degree higher were more aware than others, regarding service experience, there was a significant difference between coaches’ perspectives, which means that coaches with a medium to high (15 years or more) work experience were more aware of legal knowledge. Kashef [3] & Mostafapour Anzali [26], in their research entitled “Practical Obligation of Sports Coaches to the Legal Responsibility from Athletes Viewpoint” concluded that 73.28 % of sports coaches were aware of their legal liabilities. There was also a significant difference between the women’s and men’s perspectives, academic certificate and experience and skills regarding the level of commitment of sports instructors to legal responsibilities [26].
Nazarian [27] in a research assessed the determinants of the legal competencies of sport executive executives from the point of view of academic experts and sports managers, the results indicated that six determinant factors the necessary legal competencies of sport executive managers were the management of sport facilities and equipment, plans and programs to deal with emergencies, adherence to the law, organizational policies and procedures, risk management, and public relations. In addition, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups of women’s and men’s opinions about the priority of the legal competencies required by the executive directors [27].
In Article 7 of the civil liability law, only the responsibility of supervisor and caretaker of “minor” and “insane” ones have been discussed, while the teacher’s civil liability may also be indicated in line with the mature and wise students. According to Article 11 of the civil liability law, in case of a teacher’s mistake, the teacher himself is responsible. In Iranian law, in the current situation and in line with the Article 11 of the civil liability law, the government will not be liable for this mistake. As soon as the student becomes mature, on the one hand, he is excluded from the inclusion of Article 7 and, on the other hand, teacher’s civil liability because of student’s practice in Iranian law has not been mentioned and in accordance with Article 11, the government is not responsible. But, if the liability arising from the action of someone else is based on the teacher’s fault in line maintaining and taking care, is a guarantee for the injured party in order not face with lack compensation. Although this responsibility apparently is due to the action of someone else, in fact, it is a kind of responsibility arising from the act of the person. Consequently, it is expected that legislator drafts regulations in this regard. In jurisprudence, there are also tools to respond to the teacher’s liability because of the student’s practice, be means of jurisprudence and comparative law the desired issue will be reflected in the rules to achieve this goal [28].
Since there are approximately 13 million students in the country and the injuries that occur during sport activities during school hours for students [29], also increase in charges against physical education teachers and in accordance with article 59 of the Islamic Penal Code, which stipulates that “actions that parents and legal guardians and caregivers of the minors and wards that are executed to train or protect them, provided that the abovementioned measures are in the conventional range of training and protection will not be considered as a crime”, and the sports teacher and coach is also obliged to protect and train athletics based on the case; therefore, they will be a clear indication of the supervisors mentioned in the article [30], students’ physical health and reducing sport incidents are of the goals of the physical education classes curriculum in schools, and they will be realized by adequate and timely supervision and protection of teachers in the field of sports events and exercises, proper scientific and practical training and preparing students, basic primary aid and exercising special precautions, physical education teacher’s effective and consistent presence in the class, warnings and safety training, removing non-standard equipment, providing appropriate protective equipment and visiting, preserving and maintaining sports equipment. Preventing an incident requires an awareness of the causes of any incident. The proper and sound recognition of the causes of athletic accidents will decrease the incident and increase the students’ health and lack of teachers’ full and proper understanding of the legal duties and authorities cause liability for them.
In today’s changing and growing world, nobody is needless of training and education. Activities in school and learning have shaped a huge part of human life. Nowadays, the teacher needs other information and expertise in his specialized field [31]. The results of the conducted researches indicate that several factors will cause accidents and student injuries; hence, in the case of full awareness of legal issues, teachers will feel more responsibility and liability and incidence in the sports environment will be reduced; consequently, due to the lack of research in the field of sports law, especially teachers commitment in the country, the main aim of the current research is to investigate the level of commitment of physical education teachers in Isfahan province. In this way, while getting enough information from the level of commitment and the way teachers function in legal duties, weaknesses in this field will be identified and effective solutions will be provided to overcome the existing obstacles and problems.
Materials and Methods
This study was done by means of field survey method. The statistical population of the current study consisted of all physical education teachers in Isfahan province that based on statistics of the Isfahan province education department, they were 1740 people. Sampling was done by means of a stratified random method in accordance with sample size and based on Cochran and Sharp method 407 people were selected as samples. A researchermade questionnaire was used to collect desired data and it was designed according to theoretical foundations and valid sources in the field of sports law. To determine the questionnaire validity, 10 sports management professors were asked to indicate their comments and suggestions regarding the form and content of the questionnaire, the questionnaire items drafting, the completeness of the questions regarding information collection in the field of research variables, the coordination of the questions text with questions options, and deleting or adding question or questions. In the process of inspecting these comments, due to vagueness and heterogeneity with the aim of the research, some questions were deleted, and about repetition or overlapping, some of the questions were merged.
Also, several questions, which considered necessary for the questionnaire by experts, were added to the questions. In this research, a confirmatory factor analysis was used to determine the construct validity, and the results indicated that the relative chi-square index of the model has an acceptable value of 2.64 and signifies a good fit of the research model. Also, the P value was smaller than 0.01, since the P value for the mentioned pattern was greater than 0.05, it can be concluded that the relative chisquare index is acceptable for the pattern (AGFI = 0.84, df = 406, P = 0/01). To determine the reliability of the research, researcher distributed 30 questionnaires in the research community by means of a simple random method and after completion collected those questionnaires, by means of calculating the variance of this sample, a reliability of 0.84 was obtained through the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient.
Finally, the 39-item questionnaire was prepared in three sections and it was ready to be distributed among the statistical community. The first part contains the introduction of the questionnaire, in which explanations were given about the questionnaire. In the second part of the questionnaire, some of the demographic characteristics, such as gender, service record, and educational level were articulated and in the third part of the questionnaire, the main items of the study were designed based on seven dimensions (laws and regulations, rights and privileges, obligations and liabilities, equipment and facilities standards, field of training, responsibilities of department managers and expert, physical education goals in schools) were designed and by means of Likert scale they were determined based on scores 1 to 5. Each dimension and index were assessed based on the scores given by the participants to the related items (from 5 (so much) to 1 (very low)).
The average score of the items in each component determined the total score of that component and then the scores of each dimension or index were determined based on the average of the components for each dimension or index. In the current study, to analyze the statistical data, the statistical package of social science or SPSS version 21 at the error level of 0.05 was used. In order to analyze the research data, descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation, frequency, and percent) were used and at the inferential statistics level, one-sample t-tests were used to compare the mean of the research population with the average perspective of the participants in the study, and the mean value for each item was considered as 3, and t-test and variance analysis were used to examine the differences between legal components and respondents’ opinions.
Results
The research descriptive findings revealed that 52% of the participants were female and 48% were male. According to the collected data, it was found that 21.71% of the participants had an associate degree, 67.44% had a bachelor’s degree and 10.55% had a master’s degree. Investigating the work experience showed that 34.88% had a service record of fewer than 5 years, 17.55% between 5-10 years, 18.6% between 11-15 years, 13.69% between 16-20 years and 15.5% between 21-25 years. The obtained results showed that 39.67% of teachers were teaching in the elementary school and 27.9% in the first course of high school and 32.5% in the course year of high school.
According to the results of (Table 1), one can see that the mean of familiarity with the rules and regulations variable is less than the average. The familiarity of teachers in the field of rights and privileges and the field of education is in the average range (μ=3) and it is equal to 3. Also, the level of physical education teachers’ familiarity from sport equipment standards, commitment and duties, organizational liabilities of the manager and the general administration, and goals and missions of physical education in schools at the level of 0.95 is higher than the average because the upper and lower limits of this variable are positive, that is, these variables are more than 3 (Table 1).
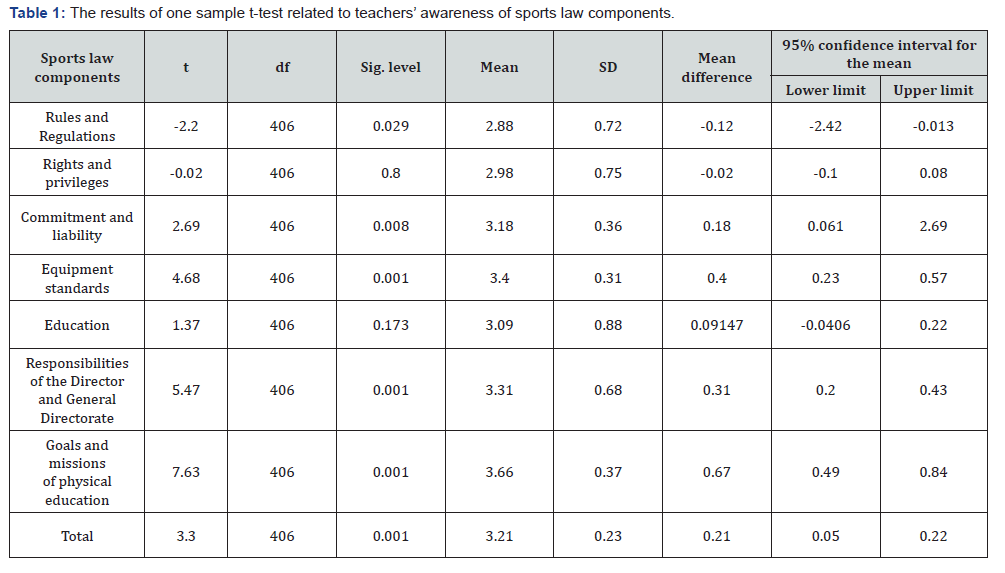
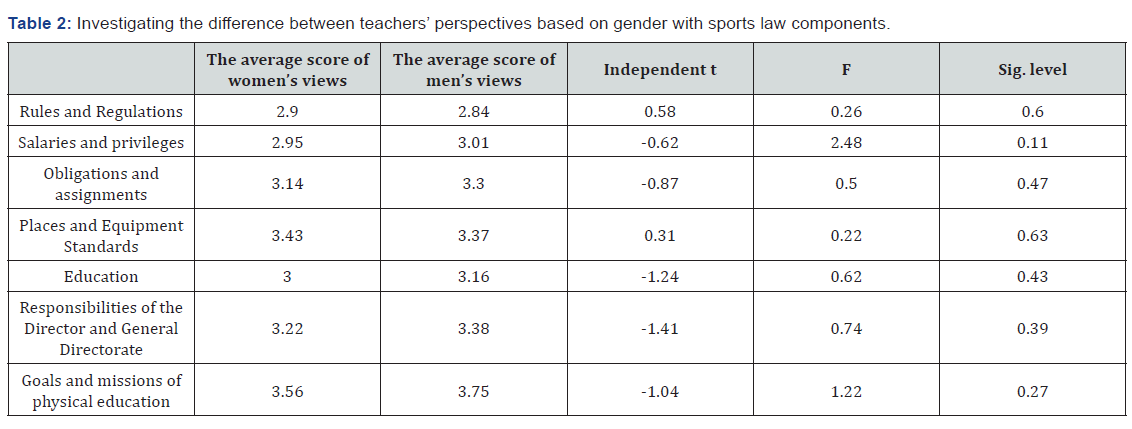
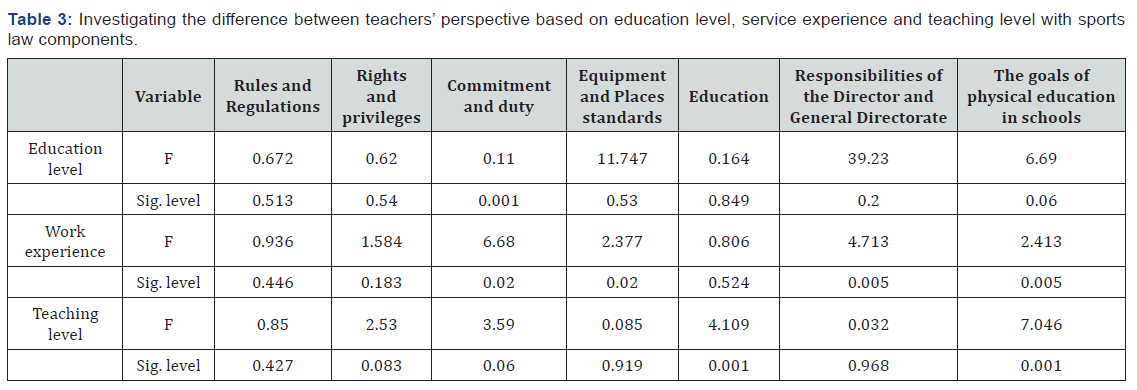
In this section, the independent t-test and ANOVA were used to scrutinize the difference between some demographic variables and sports law components. Based on the findings of (Table 2), the observed independent t has no significant difference in line with all components and there is no difference between the male and female teachers’ views. The results of (Tables 2), indicate that there is no significant difference between gender and any of the sports law components. Also, the amount of obligation to legal components based on the academic degree and service experience has difference only between the components of commitment and liability, equipment and facilities standards, the responsibilities of the manager and expert, and the objectives and mission with academic degree, and in line with examining the difference between the educational level with the sports law components, the difference is between the commitment and liability, the responsibilities of the manager and the expert, and the objectives and mission components (Table 2 & 3).
Discussion and conclusion
Physical education teachers in physical education classes should encourage students to exercise, if students face injuries in these classes, the teacher can be considered as responsible [24]. Significant and noteworthy point is the legal liability and responsibility of teachers and coaches in preventing and managing sports injuries, and sports teachers must accept that the process of preventing and managing injuries is part of the philosophy and method of sports coaching [2]. Obviously, it does not mean that the sports teacher must have professional information about serious damages and injuries and provide a complete function for any kind of damage, but it means that s/he must have basic information about injuries, first aid and calling specialized centers in distinct cases [32]. Due to the importance of the issue, the aim of this research was to inspect the practical commitment of physical education teachers to legal responsibilities and liabilities. The results of the research manifested that the level of physical education teachers’ familiarity with sports law is higher than average, because the upper limit and lower limit is positive of this variable are positive, which is consistent with the research of Bonyan & Kashef [3], Mostafapour Anzali [26] & Atashbar [33] Seyyedi et al. but it was not consistent with Foroughi Pour [23] research who investigated the level of familiarity of the teachers, teachers and sports managers of Tehran with sports law, because this researcher found that small percentage of sports coaches are familiar with the sports law issue, which could be due to differences in the cultural and geographical characteristics of these two statistical societies as well as raising the level of teachers’ and coaches’ awareness in recent years.
The results of familiarity of physical education teachers with the field of laws and regulations showed that the level of familiarity of physical education teachers in Isfahan province with the laws and regulations is less than average. Empirical observations demonstrate that in case of an incident, teachers in many cases, instead of acting legally, solve the problems friendly, for instance, math teacher act as physical education teacher in sports classes, or when physical education teacher is absent, other colleges manage the class. Paying attention to the number of students in the class and not allowing other students to attend classes in hours that they do not have other classes, lack of principal and vice-principal interference in the process of scoring and evaluation, not leaving the class even for justified reasons and with the agreement of the principle, not using other colleagues during illness and troubles, timely attendance in the classroom, are of the rules and regulations aspects of the physical education class that observing this category of laws will remove any liability from the physical education teacher. Consequently, if the accident, injury, and damage to students caused by action or abandonment of action in the correct and timely implementation of the rules and duties, physical education teachers will incur civil liability, this topic is consistent with the researches done by Yazdanian [25], Mohamadinejad [34], Montazeri [35], Safaei [36], and Nasiri [37] researcher (2004).
The results also indicated that the number of rights and privilege variable was equal to the mean (μ=3). The results of the current research are consistent with the results of Jabari’s & Shoariaan research and are inconsistent with Dehgani (2000) research. So, if physical education teacher is aware of the probability of an accident and does not accomplish the task of caring for students timely, he can be considered liable due to negligence and breach of this duty, and his immunity can be ignored. Controlling overactive and chaotic students who are deliberately or unintentionally leading to an accident, checking sport equipment and space, and ensuring that all the facilities in the schoolyard that may cause risks are sound and standard (movable equipment such as handball gates, volleyball bars), identifying talented and low-skilled students and with specific disease and holding organized exercises for them, and less involvement of these students in normal student programs, teacher’s familiarity with first aid and using them timely in case of an incident are among the activities that, by observing them, teacher can reject any liability arising from them. The level of teachers’ familiarity in the field of commitments and liability was higher than average.
Lack of commitment to physical education teachers’ assignments will provide civil liability for them, which are consistent with the results of Hekmatnia & Vishka I [38] & Bozorgmehr [39], researches. Hence to reduce any liability in line with student responsibility and commitment, all teachers are obliged to inform students about accidents and incidents around them. Physical education teachers informing students verbally, do not allow them to engage in dangerous movements, and not encouraging them to do these movements because of their commitment to their physical and mental health, warning notices in line with using dangerous devices, acquainting students with accidents caused by their unusual and non-standard movements and skills, as well as equipment related incidents both verbally and by means of installing notices on walls of the hall and schoolyard or alongside any sporting equipment are of the easy ways to do a teacher’s liabilities.
In the field of sports equipment and facilities standards, the results of the t-test indicate that the level of physical education teachers’’ familiarity is above average level. In confirmation of these results it should be indicated that since physical education teachers are involved objectively and tangibly with the sport environment and facilities and experienced the features, optimal standards of sport environments and facilities during the years, have gained knowledge and awareness in line with feature and standards of sport environments and facilities and have understood the consequences and liabilities of using inappropriate equipment and facilities. With increasing awareness of facilities and equipment standards, physical education teachers have been more aware of their legal rights. This awareness has been achieved due to this fact that concurrent with information technology development all over the country and better access to the internet, the information related to sports law and civil liability is accessible easier and more quickly.
In line with the awareness of physical education teachers in the field of education, the results indicate that the level of these teachers’ familiarity in the field of proper training is more than average level. According to the answers for this question, science, updated knowledge and enough studies that are consistent with the studies done by Salehi [40] and Dehghanniri et al. [41], eloquence and high physical fitness to convey information are of the necessary characteristics for the proper training by physical education teachers. Having these features and characteristics make it possible for teachers to have partial knowledge while teaching and training and create a safe place for their students or in a place where there is no risks or probable incidents, train the students and finally reduce the chance of incidence and his or her liability in line with these incidents.
The results of researches also indicated that physical education teachers’ level of familiarity in the field of physical education goals and objectives is more than average level. The goal of physical education in the schools covers different and numerous dimensions of the students’ growth (physical, mental and emotional development of students) and have indicated the importance of physical education among different lessons. Teachers with this perspective that the goal of the physical education in the schools are in line with the goals of teaching and training, prepare a healthy human to have a healthy society. They do not just rely on teaching sports movements and skills, but they refine mind and thought of the students and these justifications are in line with the results of Abdollahi et al. [13] research. Even though the third paragraph of article 59 of the Islamic Penal Code of the Islamic Republic of Iran excludes criminal liability for accidents in sports activities, but its civil liability is not clear. While these sorts of incidents are increasing due to the growing popularity of sports activities [42] physical education teachers’ familiarity with sports law will be an advantage for them. Determining the level of teachers’ familiarity with sports law will help the teachers to improve their legal status and on the other hand, with more comprehensive studies of the fundamentals of sports law by sports law experts, a suitable context can be prepared for the formation of laws and regulations related to the liabilities and responsibilities of physical education teachers.
The results also indicated that there is no relationship between gender and sports law components and based on this fact, teachers’’ gender has no effect on their commitment to the legal component and this finding is consistent with the results of Foroughi Pour [23] & Atashbar [33]. In their study there was a significant relationship among the attitude of teachers toward the responsibility of taking care of students in the schools, noticing them in case of incidents and the responsibility of teaching and training them. Also, the level of commitment to legal components based on the degree of education and service experience has difference only between the components of commitment and liability, the standards of equipment and facilities, the responsibilities of the manager and the expert, and the objectives and mission with the degree of education. And in line with examining the difference between the educational levels with the sports law components, the difference can be seen between the components of commitment and liability, the responsibilities of the manager and the expert, and the objectives and mission.
Physical education teachers, trainers, and coaches have liabilities in line with the all their actions and they are obliged to compensate probable damage that has been incurred on students; it means that the basic principle in this regard is that teachers and coaches for all their harmful actions against athletes and students are responsible [42]. Using unskilled people is negligence. Of the most important factors that can cause many sport risks and incidents, are the lack of sports teachers and coaches in the desired context, awareness of athlete’s health condition, knowing the capacities of athletes by the coaches, familiarity with first aid, extreme number of athletes in a course or class that must be considered. The familiarity of sports coaches and physical education teachers with their legal liabilities and responsibilities and the way of using them will disclaim their liabilities for future events [43].
Also according to the findings of the present research, and moderate level of teachers familiarity with the legal components it is suggested that in order to promote the teacher s’ knowledge and familiarity with their liabilities and responsibilities, sports training courses be held and sports court experts should be used to hold training courses and as soon as issuing new rules and regulations in-service training courses must be held for teachers, and as soon as they receive research findings on the pathology of sport events they should inform teachers and managers. Legislators and sports law experts must formulate clear and transparent rules about the rights of physical education teachers. With the cooperation of Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting and Department of Education and other responsible institutions, to reduce sports accidents, civil liability will be a national discourse, especially among physical education teachers. Also, to prevent the incidents in sports facilities, the department of education must use the sports engineers in the construction of sports grounds and pay attention to the age of students in line with purchasing sport equipment and facilities.
References
- Mirsoleimani MH (2013) The globalization of sports law and sports jurisprudence. Master’s thesis. Faculty of Physical Education and Sport Sciences, University of Isfahan, Iran.
- Aghaeinia H (2007) Tehran: Nashr Publication Sports Law. (7th Edn), p. 79.
- Bonyan A, Kashef M (2014) The difference in Law awareness and civic responsibility of men and women’s coach in sports events. Applied research in sport management 2(4): 79-90.
- Garakhani H (2017) Legal and Lawful responsibilities of sports coaches. Journal of Physical Education Teaching. p. 61.
- Ramezani A, Nazarian Madvani A (2013) How do safe environment for our sport? Journal of Physical education Learning 13(4): 10-17.
- James AR, Nafziger (2010) Globalizing Sports Law, 9 Marq. Sports. L. Rev. 13(2): 367–379.
- Naderian M, Soltan Hoseini M (2010) Skills and technical abilities for sports managers (indicators and criteria from the viewpoint of managers). Journal of Contemporary Research in Sport Management 1(2): 11-18.
- Naderian M, Rahbari S (2015) The feasibility of establishing sports law’s field in master’s degree of Iran’s university. Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies 6(4): 19-32.
- Goudarzi A (2013) Document of fundamental development of education, philosophy and physical education position. Journal of Physical education 13(47): 32-34.
- Yakasai MG (2000) Legal Issues in Sport Professionalization. Journal Nigeria Association of Physical, Health Education, Recreation Sport and Dance 130-135.
- Fabre-Magnan M (2007) Droit des obligations. T.2(responsibility civil et quasi-contract)1e. ed. presses universities de France.
- Hosseinpour E (2011) Safety and health of school sports spaces. Institute of Humanities and Cultural Studies 11(3).
- Abdollahi M, Farokhi A, Bagheri Kh (2001) Objectives, principles and methods of physical education in Islamic Education. Journal of motion 7: 101-110.
- Lisa H, Aaron B (2008) Increased mobility and physical activity with sports class. Translated by Nasibe Hashemi. Journal of physical education’s Development 8(3).
- Ramezani A (2006) Physical Education at Schools: Essentials and Requirements. Physical Education Growth Magazine 6(3).
- Mirsoleimani M, Shoaryan E (2009) The police civil responsibility in duty of care’s breach. Journal of security Knowledge Enforcement 11(3): 238.
- Young SJ (2001) The importance of legal aspects for new professionals in recreational sports: A perspective of practicing professionals. LARNet, The Cyber Journal of Applied Leisure and Recreation Research.
- Alla Joseph B (2012) Sources of legal liability among physical education Teachers. International Education Studies 5(3): 16.
- http://nirsa.net/nirsa/grow/
- Partington N (2016) Sports coaching and the law of negligence: implications for coaching practice. Sports Coaching Review 6(1): 36- 56.
- Anu MR, Jari P, Lotta K, Arja R (2016) Adolescent physical activityrelated injuries in sports club, school sports and other leisure time physical activities. Cogent Medicine 3(1): 1260786.
- Soligard T, Schwellnus M, Alonso JM, Bahr R, Clarsen B, et al. (2016) How much is too much? (Part 1) International Olympic Committee consensus statement on load in sport and risk of injury. British Journal of Sports Medicine 50(17): 1030–1041.
- Foroughi Pour H (2005) Investigation knowledge of the coaches, administrators and physical education teachers in Tehran from sports law and the provision of educational strategies. Master’s thesis. University of Tehran.
- Izadi B, Kozehchyan H, Ehsani M, Sadeghi-Boroujerdi S, Soleimani R (2013) The role of risk management actions to reduce litigation in pools of Tehran 2(2): 61-76.
- Yazdanian A (2012) The plan of civil responsibility’s teachers arising from the practice of student in the Iran law with a comparative study in French law. Journal of students’ civil responsibility (1): 37-48.
- Mostafapour Anzali Sh, Kashef Mohammad (2016) Practical Obligation of Sport Coaches to the Legal Responsibility from Athletes Viewpoint. Journal of Sport Management 8(4): 541-554.
- Nazarian Madvani A (2016) Evaluation of the determinant factors of the legal competencies of executive sport managers from the viewpoint of academic experts and sport managers. Journal of Sports Management 8 (4): 567-588.
- Katouzian N (2009) Transformation of the concept of blame on civil liability law. Quarterly Journal of Law. Faculty of Law and Political Science 39(1).
- Malekzadeh B, Alidousti K, Dervishi M, Sayyadi M (2011) Frequency of accidents and causes in primary school students in Fars. Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Faculty of Kerman 11.
- Montazeri Najafabadi H (2011) Sports law and athletic civil liability. Law Firm of Soroush Justice Publication.
- Nadi M (2005) Determination the educational needs of physical education teachers to triple management skills (Master’s Thesis). Islamic Azad University, Khorasgan Branch, Iran.
- Nokhostin Rohi B (2004) sport pathology. Publications of the Yavarian cultural institute.
- Atashbar Sh (2013) The Investigation of physical education teachers’ knowledge of civil responsibility in the four cities of Khuzestan province. Master’s thesis. University of Esfahan, Iran.
- Mohamadinejad A, Mirsafyan H, Sultan Hossini M (2011) The study of civil responsibility of judges in sports competitions. The sixth international conference of sports science. Hungary.
- Mohaghegh Montazeri L (2004) The Civil responsibility for damage caused by nuclear accidents in international treaties and domestic regulations of states. Journal of Dadrasi 8(46): 23.
- Safaei, H (2012) Civil responsibility of physicians with the Look at the new bill of Islamic Penal Code. Journal of Judicial Law views 17(56): 141-156.
- Nassiri M (2010) Civil responsibility of swimming trainers. Quarterly of legal views. Faculty of Judicial Sciences and Administrative Services 49: 127-140.
- Hekmatnia M, Abdullahi Vishka’I S (2011) Civil responsibility arising from the lack of information on medicinal products. Journal of Islamic law 8(29): 61.
- Bozorgmehr D (2006) Civil responsibility of goods manufacturers. Journal of Law Court 54: 54-33.
- Salehi H (2013) Schematics of nurse’s, civil responsibility. Journal of Ethics Medical 7(25): 163-186.
- Dehghan N, Negarandeh R, Yazdi Kh (2011) Look at the moral and civil responsibility’s nurse in Law’s Iran. Journal of Ethics and History of Medicine 4(4): 1-10.
- Naderian Jahromi M (2013) Principles and methods of coaching in sport. (1st edn), Moazami Press.
- Alavi Qazvini A, Meqdadi M (2011) Jurisprudential and legal foundations of civil responsibility’s Lack of athletes in the sport, Mofid magazine 85: 107.






























