Concept of Masculinity in Men
Shagufta Jabeen*
Department of Social studies, NUML, Pakistan
Submission: May 27, 2018; Published: September 18, 2018
*Corresponding author: Shagufta Jabeen, Department of Social studies, NUML, Pakistan, Telephone: 03315335295; Email: shaguftach201 @gmail.com
How to cite this article: Shagufta Jabeen.Concept of Masculinity in Men. Ann Soc Sci Manage Stud. 2018; 1(4): 555570. DOI: 10.19080/ASM.2018.01.555570
Introduction
The following study seeks to explain to what extent men role orientation influences by male perceptions of masculine imagery and their attitude towards women are according to culture and family environment. Usually meanings of masculinity are created, modified and put into action by individuals during the process of social interaction. Attributes such as being a provider for the family (the bread winner), a hard worker, good leader (decisive), a problem solver, being knowledgeable correspond to this category of masculinity. Men are often influenced by their religion and opinions gained from their parents’ roles, especially the father’s role [1]
Some male follows accept the concept of traditional masculinity for example; traditionally masculine men should be strong, aggressive, confident, etc. They hesitate to share their problem with others because they think others will consider them weak and it’s costly for them to admit that they are emotionally upset. Men follow the concept of masculinity as they think they are powerful in the light of Holy Qur’an just as and women have rights like the rights of men in a just manner, and the men have a degree (of advantage) over them...” (2:228) [2].
But some others accept the concept of nontraditional masculinity and they feel it true for example, nontraditionally masculine men might be nurturing, perhaps passive, and expressive. But reality is that masculinity consists of those behaviors, languages and practices, existing in specific cultural and organizational locations, which are commonly associated with males and thus culturally defined as not feminine because some how they feel women inferior to them. A key assumption here is that masculinity is not a fixed entity, there being no singular standard for this concept. The social construction of gender is actually a system of power that not only divides men and women as masculine and feminine but typically also assign roles to men and women according to their own strength like that men can do laboring work but women cannot do that easily if they do, male raise so many difficulties in front of them because they think that is against the natures and womankind. They also think it is ridiculous for women to run a locomotive and for men to doing the laundry.
Some men agree only for limited freedom of women, they do not understand a woman’s pride and needs to join politics, forces and engineering or medical fields only some men are agreeing to equality of both. Masculine men are courageous, able to resist the pressure of events around them. They have capabilities to fulfill all own and other’s needs. They are allowing others to be feel safe with them and do not permit anyone to overstep their boundaries. Early years of the twentieth century, woman walking alone on the streets was not considered safe or appropriate. At that time males think that Women should be confined with their duties of childbearing and house tending only. Now still some men want women must obey them without any question. They never care about the right of women and they want to confine them only in the house and want to make dependent of them by this way they make their supremacy on them [3].
While others facilitate them because they think their own responsibility and enhancing change to share both public and private space to lead prosperous life because it is an urgent need of modernization. They believe that empowerment of women cannot be achieved in a vacuum, men must support along in the process of change, like when women try to gain power and control over their own lives. Nontraditional men honor women and treat them with respect. Nontraditional men strongly act upon the Holy Prophet PBUH saying as he himself said: “He who has a daughter and who teaches her good manners and improves her education and then manumits and marries her will get a double reward.” Men try to maintain their masculinity by solving their problems alone without talking about those. Men take decisions without emotional affects. Some men think women should avoid the conflicts and ever try to spend a peaceful life. According to them, Women should not be allowed to raise voice for divorce. While nontraditional men are accepting this, both husband and wife should be allowed to have same grounds for divorce.
Literature Review
In 1987 Connell stated that concept of masculinity is developed by society and this concept dependent on that historical time, culture. He further described in 2000 as the culturally lofty form of masculinity which gives assurance to the dominant position of men. According to him construction of masculinity is often setup the men according to their nature of work, organization policies. Floge and Merril, in 1989 said that Men get benefits in career through the assumption of society that men have more leadership qualities and skilled over the females. In 1993Williams stated Men have a position of power, and they rewarded for their difference from women in terms of higher pay and other benefits as all consider men are stronger than women. Hochschild in 1983 described that in teaching, nursing and social work, women are superseding as these fields are required emotional attachment [4].
Levant& Richmond, in 2007 discussed masculinity ideology. Their ideology gives guidance to males how they should act to certain socially sanctioned masculine behaviors and this also provide guideline to men to avoid denounce behaviors. In 2000 Lupton found that men be afraid to work in female dominated occupations working in female dominated occupations as the other people will think that their power of masculinity is less than other men, or they are having less skills. In 1998 Alvesson viewed that men are engaged to get dominating position through compensatory gendered practices for maintain their masculinity. Learning theory discussed when child’s gender identity becomes established, then child try to display gender congruent attitudes and behaviors. Through direct and indirect instruction child learn appropriate gender roles, both genders lead their lives according to assign gender role. Just as Direct rewards or punishments are often given for outward appearance as in what to wear (girls in dresses and boys in pants) and behavior (passivity and dependence in girls and aggressiveness and independence in boys). Indirect learning of gender roles emerges from modeling same-sex parents, teachers, peers, or same-sex models in the media [5].
Kohlberg identifies two stages of gender identity development: 1) acquiring a fixed gender identity, 2) establishing gender identity constancy. Child’s identify their roles related to gender when hearing the labels “boy” or “girl” and applied these roles in their life. By about age 4, the child can apply these gender labels are appropriately to others. Within two or three years, the child reaches the critical phase of gender constancy. In 1985 Spence viewed that the important underlying construct is gender identity or one’s sense of being masculine or feminine. Culturally defined personality traits, physical attributes, attitudes, occupational preference and behaviors all are contribute in gender identification. Men choose those characteristics that are compatible for themselves and demanding from women for which they are responsible just as child bearing, maintaining relationship and house holding .
James and Clarke in 1993 conducted research on conversational behavior as they reported that males are more likely to use more assertive and dominant speech patterns in interaction than females but a recent review of the many empirical studies on interruptions and time spent talking show that men think women are more talkative and create interruption in conversation than men. Stets & Burke in 1996 stated that men maintain masculine gender identity by expressing negative, dominant and oppositional behavior, such as complaining, criticizing women to pull down them. Pleck and Sonenstein in 1973 defined Masculinity ideology as men accept culture’s definition of masculinity and they beliefs and act on culturally defined standards of male behavior [6].
According to Thompson (1986) men’s according to their needs follow norm of masculinity only for achieving status, position and other respect in 2006 Hammond stated that men follow the concept of masculinity by controlling their own emotions as other people may think about them they are emotionally weak. He also stated that men are compact in one’s emotions as a factor associated their emotional restriction, they always less willing to forgive racially discriminatory experiences. Gregory in 2011 pointed out that men define and redefine masculinity in the social context of their experiences throughout their life.
Goldberg argued that in his paper titled, Feminism against Science, on the base of physiologies, and that society, psyche and gender, men and women are different from each other with respect to the cognition and behavior, attitude and emotions.
Peterson contend that the social construction of gender is a system of power that not only divides men and women as masculine and feminine but also places masculinity above femininity and operates to value more highly those institutions and practices that are male dominated and representative of masculine traits and styles. According to the French feminist philosopher, Beauvoir, men pursue masculinity according to them develop image of gender identity, they think they are donor, liberator, redeemer of women. Men still desires the subjugation of women. Desai said that breadwinners accustomed to the idea that women are responsible to fulfill a domestic role whereas men are uniquely qualified to work.
Method
Objective
i. To study normative understanding of masculine identity in men related to professional and personal life.
ii. To study the relationship between concept of masculinity in men and their attitude towards women
iii. Hypothesis
iv. There will be a negative relationship between concept of masculinity in men and attitude towards women
Research Design
Survey based quantitative research design was used. For survey I used a predetermined likert type scale of Helmrich and snell to assess opinion, thoughts of population of interest.
i. Operational definition
ii. Concept of masculinity
The term concept of masculinity can be defined as stereotypical masculine behavior traits as measured by the Masculine Role Inventory, Snell, W. E.
Attitudes Toward Women
Attitudes toward Women can be defined as attitudes about the rights and roles of women relative to men in occupational, educational, and relational domains. As an attitude measure focusing on gender roles, it is measured by the AWS assesses opinions about the behavioral patterns deemed appropriate for men and women in society, Spence, Helmrich & Stapp (1978).
Instrument
Two scales have been used in the present study which is as follows
The Masculine Role Inventory
The Masculine Role Inventory (MRI) use to access the concept of masculinity in men, scale was developed by Snell, W. E in 2013. There were 30 statement with five response catgories. The five response categories were included agree, slightly agree, uncertain, disagree and slightly disagree. In this scale item 30 was negative item. Each item was coded like that: Agree = +2, Slightly Agree = +1, uncertain = 0, Slightly Disagree = -1, and Disagree = -2. The Masculine Role Inventory (MRI) consists of three subscales, success preoccupation subscale, inhibited affection subscale and restrictive emotionality subscale. Restrictive emotionality was defined as the restricted expression of privately felt emotions. Inhibited affection refers to the inhibition of feelings of affection and tenderness toward others. Success preoccupation was defined as a persistent preoccupation with success and career development to the exclusion of interpersonal pursuits and devotion [7-9].
Attitudes Towards Women Scale
This questionnaire assesses the men attitude towards women it’s a likert type scale. This scale was developed by Spence, Helmrich & Stapp in1978. The categories used were agree strongly, agree mildly, disagree mildly and disagree strongly. Each item was coded like that Strongly agree=0, mildly agree=1, mildly disagree=2, and strongly disagree=3 except for the items 2,3,6,7,8,9,11,12,18,21,24,25 in the scale were reversed. A high score indicates a pro feminist, egalitarian attitude while a low score indicates a traditional, conservative attitude.
Sample
The sample consist of (N=40) men. Accidental sampling was used to study men concept about masculinity and attitude towards women. The age of sample ranges from 20-50years. Demographic data sheet included instruction, age, occupation, education and marital status.
Procedure
The data was collected through convenience sampling from Wah Cantt. Participants were informed about the purpose of research. Questionnaires were administered to only men to study the concept about masculinity in men and their attitude towards women. The participants were personally reached. The participants voluntarily participated, and the participants were asked to read each statement and to indicate the response by selecting the appropriate response category which they consider in their opinion appropriate and applicable about their own self. They were eager to answer it. Informed consent was done. Consent was taken from every individual and it was briefed that their information will not be misused, and it will only be included in research work. The survey was generally completed within 25 minutes. Once participants completed the survey they were thanked for the participation
Results
Demographic information sought from the sample, included information like age, and marital status. Statistical description demographic variable statistical descriptions of the demographic variable of study are as follows in (Tables 1-4).

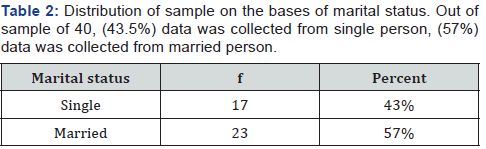
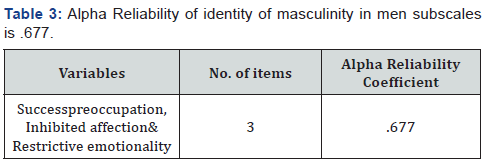
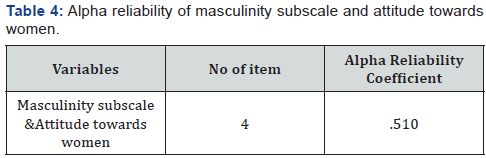
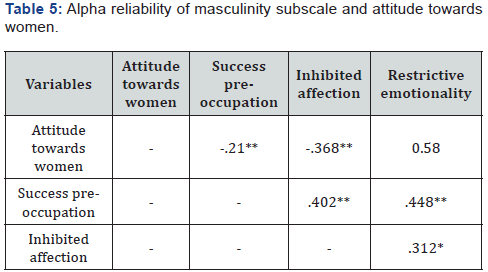
Table 5 shows that in subscales of masculine inventory statistically significant positive correlation is present among, success preoccupation, inhibited affection and restrictive emotionality are Correlated significantly at the 0.01 level, but inhibited affection and restrictive emotionality Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level. And statistically significant negative correlation is present between subscale of success preoccupation, inhibited affection, restrictive emotionality and attitude towards women at 0.01 levels.
Discussion
The basic purpose of the study is to find relationship between concept of masculinity in men and their attitude towards women. In our society, gender roles develop on the base of cultural pattern, in which men and masculinity place above the women and feminist, a woman’s value measure in her ability to bear children and raising children. Men are powerfully affected by the experiences of life and develop concept of masculinity on the base of how people respond to them what they do as male and what is expecting behavior of others as male from him. A traditional man never cares about the rights of women, they want women remain dependent on them. As I expected and discovered the high correlation between subscale of masculinity and negative attitude towards women which indicates they are traditional men because highly masculine men have negative attitude towards women role. Highly masculine men are hesitant to consider themselves as feminist. A possible explanation why Men reject the feminist label is that the connotation of this label is coded as female because they consider women are emotionally and physically weak than them
My hypothesis is partially supported when find correlation between masculine identity in men and their attitude towards women.
As seen in table 5 statistically significant negative correlation were found between success preoccupation in men and attitude towards women r=.21, p< .01.it represent a successful career means more to men but they are not consider importance of a successful career for women and belief women are less capable for contributing to economic production and they should be concerned with their duties of child bearing and house tending rather than desire for professional career. A statistically significant negative correlation was also found between inhibited affection of men and their attitude towards women r= .36. p<.01. as they control the expression of feelings of love, affection, and for others but wants from women not being active outside the home, should worry less about their rights and more about becoming good wives and mother, care provide every member of family. But non-significant positive correlation found between men restrictive emotionality scale and attitude towards women [8].
The present research is also concerned with the construction of a self-report instrument designed to assess several components of the traditional male experience. The MRI was developed to measure three aspects of the masculine role:
i. success preoccupation, the tendency to be so obsessed with the development of a highly successful career that interpersonal growth and involvement are constrained
ii. Inhibited affection, the tendency to control and check the expression of feelings of love, affection, and tenderness for others; and
iii. restrictive emotionality, the tendency to limit and temper the public expression and communication of one’s privately felt emotions and sentiments. The inter correlations of the three masculine role subscales within samples 40 were also examined.
The success preoccupation subscale was significantly correlated with the inhibited affection scale r = .40 p< .01, and with the restrictive emotionality subscale r= 0.44, p < .01. Inhibited affection scale correlated significantly with the restrictive emotionality scale r = 0.312, p < .05. Although the correlations are all statistically significant, they are modest in size but instead assess different aspects of the masculine role.
As Brannon & David reported in their research that traditional masculinity gender role showed that men should avoid famine behavior, strive for success and achievement, show no weakness and seek adventure by putting down women [7].
In 1999 Gilbert research study indicated that women should focus on relationship, remain silent for rights, must participate in nurturance of others, submissive and domestic. Traditional Men think they are superior over women, in professional opportunities men must be given priority for selection over women. By this woman are second citizen of society for them only specific opportunities in career in 1985 Spence viewed that the important underlying construct is gender identity or one’s sense of being masculine or feminine. Culturally defined personality traits, physical attributes, attitudes, occupational preference and behaviors all are contribute in gender identification. Men choose those characteristics that are compatible for themselves and demanding from women for which they are responsible just as child bearing, maintaining relationship and house holding.
Further Stets & Burke in 1996 stated that men maintain masculine gender identity by expressing negative, dominant and oppositional behavior, such as complaining, criticizing women to pull down them.
Men pursue masculinity according to them develop image of gender identity, they think they are donor, liberator, redeemer of women. Men still desires the subjugation of women [9].
Conclusion
Usually meanings of masculinity and attitude towards women are created, modified and put into action by individuals during the process of social interaction. My study represents the traditional concept of masculinity in men and their negative attitude towards women. Traditional men have a totally opposite concept about themselves and towards women. They are agreeing only for limited freedom of women, they do not understand a woman’s pride and want from women, they should have to obey them and should concerned with their duties of house tending but nontraditional men are agreeing to equality of both in career and daily life rotines.
Limitation
Every scientific research study is new step toward understanding and solution of problem but there are always certain obstacles and limitations that every researcher must face to accomplish his/her task. Sample size in the study is not larger enough and is collected from Wah can’t only. My finding contributes to the previous literature of gender studies. Although magnitude of the correlation low is than the gender role studies. In Future research work can be done on how gender role can be modified.
References
- Paige W Toller, Elizabeth A Suter, Todd C Trautman (2004) Gender Role Identity and Attitudes toward Feminism. Sex Roles 51(1-2): 85-90.
- Bam, Sandra L (1981) Gender Schema Theory: A Cognitive Account of Sex Typing 88(4): 354-364.
- Spence, Janet T (1884) Masculinity, Femininity, and Gender-Related Traits. Prog Exp Pers Res 13: 1-97.
- Burn SM, Abound R, Moyles C (2000) The relationship between gender social identity and support for feminist 42(12)1081-1089.
- Twenge, J.M. (1999) Mapping gender. The multifactorial approach and the organization of gender-related attributes. Psychology of Women Quarterly 23(3): 485-502.
- Badinter E (1995) XY: On masculine identity. Columbia University Press: New York, USA.
- Butler J (1990) Gender trouble, Feminism and the subversion of identity. Routledge, New York, USA.
- Connell RW (1995) Masculinities, Allen & Unwin, Sydney, Australia.
- Kaufman M (1994) Men, feminism, and men’s contradictory experiences of power. In Theorizing masculinities.






























