Electro-Reduced Water for Converting Heavy Crude
into the Light One
Shimkevich A*
Kurchatov Institute, Russia
Submission: June 12, 2017; , Published: June 20, 2017
*Corresponding author: Shimkevich A, NRC Kurchatov Institute, Moscow, Russia, Tel: : +79859241638/ +74991967621; Email: shimkevich_al@nrcki.ru
How to cite this article: Shimkevich A. Electro-Reduced Water for Converting Heavy Crude into the Light One. Recent Adv Petrochem Sci. 2017; 2(1): 002 555579. DOI:10.19080/RAPSCI.2017.02.555579
Abstract
The pure liquid water as a chemical compound with the wide band gap can change its chemical properties by forced shifting Fermi level in the band gap as the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP). The negative ORP is being realized when Fermi level is shifted to hydroxonium level, by electro-reducing water in the electrochemical cell with the strongly polarized anode and the quasi-equilibrium cathode. Then, the level, is being occupied by electrons. The obtained hydroxonium radicals, H3O, are forming as very active hydrogen donors in the form of hydrated hydrogen, H(H2O)n, with the high non-equilibrium concentration. Such strongly reduced water can be applied for enriching heavy crude by active atomic hydrogen.
Keywords: Fermi level; Band gap; Oxidation-reduction potential; Electro-reduced water; Hydrogen dono
Introduction
Liquid water is a chemical compound with the wide band gap, εg = 6.9 eV, [1] which is the difference between electron energies at the top of valence band and the bottom of conduction band. There are also two allowed energy levels in the band gap of pure liquid water as an occupied-by-electron level, SoH,of hydroxide ion, OH-, and the vacant one, εH3o, of hydroxonium ion, H3O+, located symmetrically nearby the band-gap middle with the energy difference between them of 1.75 eV [2]. The occupation of these levels by electrons defines Fermi level, ε2F [2-5], as an electrochemical potential which indicates the tendency of liquid water to donate or accept atomic hydrogen. When Fermi level is higher than the band-gap middle, liquid water becomes a reducer for easy donating of atomic hydrogen. Opposite, water is a strong oxidizer when Fermi level is below the band-gap middle [6].
Fermi Level in Liquid Water
The allowed electronic levels, εH3o and εOH in the band gap of pure liquid water are located in its inherent constituents as ions of hydroxonium, H3O+, and hydroxide, OH-, that are being generated by the reversible self-dissociation reaction [7].
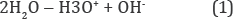
Their radicals (H3O, OH) are being interpreted as the mentioned levels occupied by electrons and holes respectively [2]. Changing the concentrations of these radicals shifts Fermi level, εf , in the band gap and changes the single-valued characteristic of water as ORP [3]:

Where e is the charge of electron and εSHE = -6.21 eV [2] for the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) described by the reaction
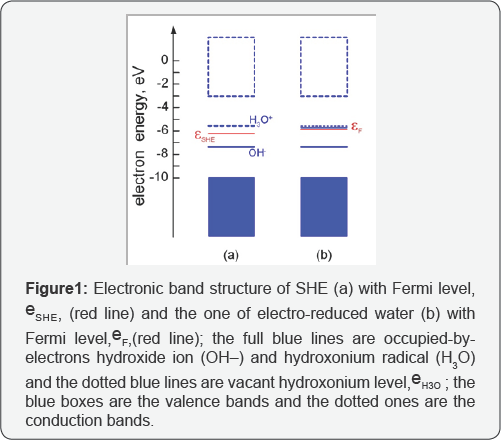
The ORP becomes negative when Fermi level is shifting above εSHE to the hydrogen donor εH3Oby
strongly polarized anodic reactions as shown in (Figurel) [5].
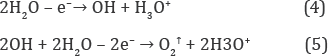
The Electro-Reduced Water
One can see from fig.lb that the energy level, εH3O,is partially occupied by electrons because hydroxonium ions forcedly migrate from the anode to the cathode under the action of electric field in the electrochemical cell (Figure 2) and discharging them by quasi-equilibrium cathode reactions [5].
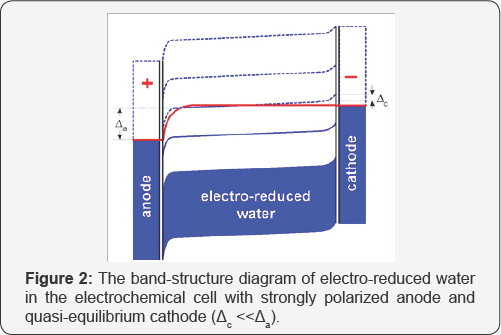
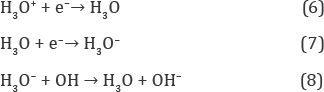
This forms the negative bulk charge in liquid water near the anode at the condition
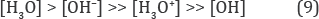
Which denote the strong basic reaction of electro-reduced water and the high molar fraction of hydroxonium radicals ([H3O] >> 10-7 M) in the bulk of water? Thus, the electrochemical production of the very active hydrogen donors is more effective than the gaseous hydrogen can produce them in SHE ([H3O] ~10 10 M) for keeping its negative ORP [2]. Besides, the formation of reducers, [H3O], in the aqueous emulsion of gaseous hydrogen is being limited by dissociation process of hydrogen molecules:
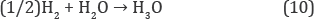
Opposite, the electrochemical one produces radicals without limitation by reactions (6) and (8) that increase dynamic portion of radicals in liquid water more than on three orders.
Conclusion
Ventilating the pure water by bubbles of hydrogen can change ORP without changing pH as well as processing liquid water in the electrochemical cell. It turned out in this case that ORP (Fermi level) of pure water easily and appreciably is being changed in this cell with one polarized electrode and the other in equilibrium with water. Thus, enriching of heavy crude by active atomic hydrogen of electrochemical production can be more effective than by the aqueous emulsion of gaseous hydrogen.
References
- Garbuio V, Cascella M, Pulci O (2009) Excited state properties of liquid water. J Phys Condens Matter 21(3): 1-15.
- Shimkevich A (2014) Electrochemical View of the Band Gap of Liquid Water for Any Solution. World Journal of Condensed Matter Physics 4(4): 243-249.
- Shimkevich AL, Yu Shimkevich I (2012) On 2D water chemistry. Proc Inter Conf on Nuclear Plant Chemistry, France, pp. 39-176.
- Shimkevich AL (2013) On arising nano hydrides in reduced alkaline solution. American Journal of Modern Physics 2(4): 185-189.
- Shimkevich AL (2014) On catholyte application for hydrogen water chemistry in PWR. European Nuclear Conf France 46(44): 698-705.
- Alexander Shimkevich AL (2014) On performance capabilities of alkaline anolyte in wastewater management. Inter Conf on Water Chemistry of Nuclear Reactor Systems. Japan 2: 882-893.
- Bard AJ, Parsons R, Jordan J (1985) Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solutions. Marcel Dekker, New-York, USA.






























