- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Advances in the Use of Health Education Models in Epilepsy Care
Junhong Zeng1, Taotao Shen2, Ying Gu3*, Guofeng Wu4 and Cui Xiong5
1,2Master’s student in Nursing, Guizhou Medical University School of Nursing, China
3Chief Nurse, Nursing Department, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, China
4Chief Physician, Associate Professor, Doctor of Medicine, Emergency Department, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, China
5Supervising Nurse, Emergency Neurology Department, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, China
Submission: April 23, 2024; Published: May 03, 2024
*Corresponding author: Wu Guofeng, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, China Ying Gu, Chief Nurse, Nursing Graduate Student, Nursing Department, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, China
How to cite this article: Junhong Z, Taotao S, Ying G, Guofeng W. Cui X. Advances in the Use of Health Education Models in Epilepsy Care. Open Access J Neurol Neurosurg 2024; 18(4): 556000. DOI: 10.19080/OAJNN.2024.18.556000.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Abstract
Epilepsy, a chronic brain disorder, is one of the most common neurological disorders, characterized by transient and recurrent seizures, and is prone to a variety of complications, which can be life-threatening and seriously affect the patient’s daily life. Therefore, patients need to be given systematic and targeted quality care. Health education is an effective way to maintain patients’ health and is essential in clinical work, and the effectiveness of different health education models in educating patients varies. Concerning the application of health education models in epilepsy care, this article focuses on collecting relevant literature in the past decade and describes various methods and intervention effects of health education for epilepsy patients in clinical practice, to correct patients’ misconceptions about the disease and their bad behavioral habits, improve the outcome of the disease and enhance the quality of life.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Health education; Care; Review;
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder that manifests as recurrent seizures, a transient brain dysfunction caused by abnormal neuronal discharges in the brain. The pathogenesis of epilepsy is caused by an imbalance between the inhibitory and excitatory control of the central nervous system. Some studies have shown that ion channels, neurotransmitter imbalances, and genetic and immune abnormalities are closely associated with causing this imbalance between excitability and inhibition [1]. Seizures are often accompanied by a range of social, family, emotional, and other psychological disorders, which can lead to severe sleep disturbances, lower seizure thresholds [2], and cause an increase in the number of seizures, seriously affecting the patient’s normal life. Studies have shown that the development of the disease is closely related to a patient’s lifestyle and behavioral habits, etc. Sufficient sleep, good lifestyle habits, compliance with medication, and appropriate physical exercise can effectively reduce the number of seizures and improve the condition. At the same time, the lack of public knowledge about epilepsy disorders increases the incidence of stigma and discrimination [3], leading to insecurity and low self-esteem, and shame in many patients with epilepsy [4]. Therefore, it is necessary to provide more comprehensive and scientific health education to epilepsy patients and the general public to further improve the quality of patient care and alleviate their physical and psychological suffering.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
The health education model [5] refers to an organized, planned, and systematic approach to eliminating or reducing risk factors for patients’ health through a variety of social education activities, so that people can consciously adopt healthful lifestyles, prevent diseases, promote health and improve patients’ quality of life.
Currently, the main and most basic treatment for epilepsy is long-term regular oral anti-epileptic drugs, which act as an anti-epileptic agent by reducing neuron excitability in the brain [6]. At the same time, patients have to make corresponding changes in their dietary structure, meal patterns and timing, medication, rest activities, emotional management, and other aspects, and the precautions are more complicated. Therefore, nursing staff must provide comprehensive and scientific health education and life guidance to patients, which can effectively improve the cure rate of the disease, reduce patients’ pain and increase nursing satisfaction. In an intervention study by Nan He et al. [7] in patients with epilepsy, personalized psychological and health education for patients with epilepsy achieved significant results in improving patients’ anxiety and depression, with significant improvements in medication compliance, self-management and quality of life.
Fan Fangfang [8] showed that face-to-face, internet, and messenger-based education methods not only improved medication adherence and quality of life in patients with epilepsy but also significantly reduced the number of seizures in patients. Muller-Godeffroy et al. [9]. conducted a comparative observational study of children and adolescents with epilepsy and their parents in an organized program of epilepsy knowledge education, The results showed an increased awareness and selfmanagement of epilepsy in affected children and adolescents, and a reduction in parental anxiety and family burden. Comprehensive and systematic health education can enhance patients’ knowledge of the disease, improve compliance behavior, reduce the number of seizures, improve their psychological status and improve their quality of life. Various health education models are listed and described below (Figure 1).
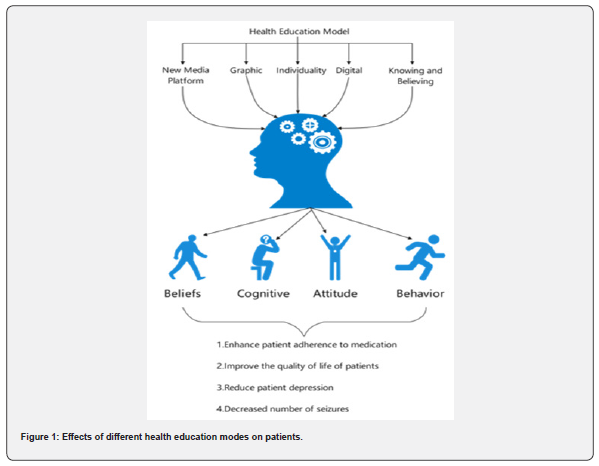
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Graphic Health Education Model
Pictorial health education refers to the planned combination of different carriers such as pictures and texts [10] to design health propaganda in a more scientific, vivid, and easy-tounderstand manner in the form of pictures and texts on the etiology of diseases, clinical manifestations, treatment principles, precautions in the treatment process and the prevention and care of their related complications. Health education is given at different times to fully mobilize the initiative and enthusiasm of patients [11] and to ensure that patients receive complete and consistent health education, thus improving their awareness and their consciousness of avoiding risk factors and improving their compliance with treatment. In a recent study Wang Yanli et al. [12] explored the effect of mind mapping mode health education on the state of mind and coping styles of children with epilepsy and their families.
Compared with conventional health education, health education in the form of mind mapping for patients and their families had a significant improvement on their state of mind, and the families were able to cope and handle the child’s seizures correctly through the graphic presentation, reducing This reduces the uncertainty of the disease and improves the prognosis of the child. A controlled study conducted by Gu Ruixin [13] concluded that patients who were given graphic health education had a higher quality of life and satisfaction with care (p<0.05) than the control group, had significantly less anxiety and depression, were able to actively remove disease triggers and had improved selfmanagement and caregiving skills. The graphic itself is diverse and open-ended and can effectively guide patients to use their senses to receive and reconstruct disease-related knowledge [14-15]. Therefore, through graphic health education, patients’ knowledge and awareness of the disease can be increased more effectively, and their compliance with medication can be improved, as well as their quality of life.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
The Knowledge, Attitude, Belief, Practice (KABP or KAP) model [16] is one of the models for changing human health-related behavior and is based on the knowledge, belief, and practice theory and is directed at the patient’s cognitive deficits. It divides human behavior change into three sequential processes. Knowing is knowledge and learning, believing is belief and attitude, and acting is behavior and action. In the Knowing, Believing, and Doing model, knowledge is the foundation, beliefs are the motivation, and the generation and change of behavior is the goal. Under the guidance of health education, people acquire relevant health knowledge and skills, gradually form healthy beliefs and attitudes, and develop good behavior slowly, thus contributing to the development of healthy behavior (Figure 2).
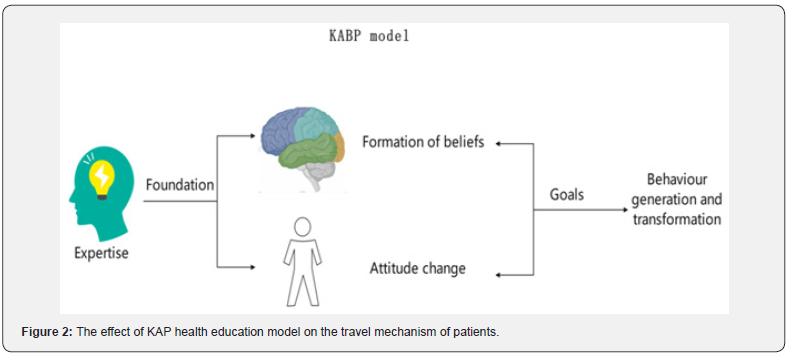
By organizing health care professionals to form a health education team to manage trauma-focused cognitive behaviors in children with epilepsy and their parents, parents can be enabled to cope calmly with their children’s seizures, improve their medication compliance, and the children can gradually control their thinking and effectively eliminate their negative emotions [17]. Liu Mei [18] and other health care professionals formed a Knowing, Believing, and Doing (KABP) health education pathway based on the clinical presentation of the children. The study showed that the scores of medication compliance, social skills, and emotional functioning of the children in the experimental group were higher than those of the control group (p<0.05). The use of KABP health education can not only improve the knowledge of patients and their families about the disease [19] but also promote medical compliance, reduce the number of seizures and improve the prognosis of patients.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Individualized Health Education Model
The individualized health education model refers to targeted, personalized health guidance and behavioral intervention activities for service users in response to the health problems and health risk factors of different individuals. It is a health education plan for each patient based on a comprehensive assessment of the patient and according to the patient’s different physical and psychological needs such as knowledge of the condition, disease, learning ability, lifestyle, behavioral habits, etc. To meet the reasonable needs of patients, to achieve a person-centered approach [20], to promote effective patient-nurse communication while being able to better cooperate with treatment and care, thus promoting the cure of the disease. Studies have shown that the self-care behaviors of people with epilepsy improve their ability to manage their disease and reduce the number of seizures.
Analysis of inter-individual differences in the epilepsy population has gained attention [21] and providing individualized health education based on the patient’s condition has a strong persuasive effect in improving the patient’s awareness of the disease, enabling effective medication use, appropriate diet, and activity, and enhancing the outcome of the disease. In the study by Altmann Anna [22], individualized psychological guidance and health education programs were developed according to each patient’s specific situation. It can effectively reduce patients’ psychological stress and anxiety, eliminate their inner loneliness and enable them to return to society in a good frame of mind and face life with a positive attitude. It can be seen that the individualized health education model ensures a seamless transition from hospital to home to a certain extent, reduces the blindness of conventional care, and can better improve the overall quality of life and clinical prognosis of epilepsy patients, and the method is worth promoting.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Interactive Health Education Model
Traditional health education focuses more on the oneway output of nursing staff to deliver relevant information to patients, in which case patients’ acceptance and memory of the health education content is not optimistic. The interactive health education model views the treatment and care process as a dynamic process of mutual influence and interaction [23], receiving and responding to patient feedback in a timely and accurate manner, and through the four processes of educationinteraction- feedback-re-education [24], the health education content can be taught to patients in a more standardized and comprehensive manner, increasing their motivation to cure the disease. Zhou Shang [25] trained patients who had recovered well from epilepsy to conduct mutual health education with fellow patients who had epilepsy. The study showed that the interactive exchange and discussion of knowledge about the disease and the experience of the disease effectively relieved the psychological burden of the patients, greatly eliminated the internal stigma of the disease, and significantly improved the quality of life. Zhou Yumei, et al. [26] used an online platform to push out diseaserelated care knowledge in real-time, communicate interactively with patients and their families, and provide timely responses to questions raised by patients and their families, effectively ensuring patients’ mastery of disease-related knowledge and practice, thereby promoting compliance behavior, improving lifestyle and increasing the cure rate of the disease.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
New Media Platform-Based Health Education
With the accelerated development of the economy, society, health care, and information technology, the digital age has arrived and new media have entered the picture with unprecedented advantages. Traditional health education modes such as outpatient consultation and community education have become more diverse. While being much sought after and loved, new media has also become an important way to disseminate information and disease knowledge. Huang Xiaodi [27] pointed out that using the new media WeChat platform to push out graphic and video health education guidance about epilepsy medication management can effectively reduce disease recurrence rates and improve patient compliance with medication. Yang Yanhong [28], et al. demonstrated through their study that diversified health education led by new media can reduce the disease recurrence rate of patients, establish good medication habits and significantly improve the quality of life of patients. Using new media as a platform for health education can save human resources and nursing time at the same time [29], is not restricted by time and space, and can be watched anytime, anywhere, and repeatedly, making it more convenient for patients to receive and learn disease-related knowledge [30], improving patient compliance with treatment and facilitating disease prognosis.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
Epilepsy, a chronic condition, can extend over years to decades. According to the latest epidemiological data, Epilepsy affects more than 50 million people worldwide [31]. About 70 percent of people with epilepsy can be treated to avoid seizures, and once seizures are significantly controlled, the management of antiepileptic drugs, lifestyle and other factors are the key points to revent epilepsy recurrence. Therefore, health education is an important way to convey health knowledge and improve the quality of care for patients with epilepsy.
With a high recurrence rate and a long treatment cycle, health education is particularly important throughout the disease cycle, including prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation, in addition to basic treatment. The patient’s condition is closely observed and the patient’s needs are understood promptly, according to the different stages and time points during admission, hospitalization, and after discharge. After discharge, patients are regularly followed up and asked about their seizures and the number of times they have them, to improve their compliance with medication and quality of life, reduce unnecessary medical waste [32] and improve their anxious and depressed psychological condition.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
Conclusion
The occurrence and development of epilepsy are closely linked to factors such as the irregular use of medication, diet, smoking, and poor lifestyle habits. Effective and systematic health education plays a crucial role in the treatment and rehabilitation of epilepsy patients. With the rapid advancement of the internet, big data, and artificial intelligence technologies, health education is undergoing a profound transformation. These technologies have made health education models more personalized, intelligent, and interactive, significantly enhancing the accessibility, efficiency, and effectiveness of educational content. Healthcare professionals can utilize AI and big data analytics to provide personalized health education services tailored to individual patients, such as AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants that offer 24-hour support and real-time interactions. Augmented and virtual reality technologies create immersive learning experiences that enhance patient engagement and interest.
Additionally, online communities and social media networks strengthen communication and support among patients. The future of health education for epilepsy will be a multidisciplinary field that integrates medical, psychological, educational, and computer science knowledge, driven by technology to enhance patients’ self-management capabilities, improve quality of life, and effectively control and manage chronic diseases like epilepsy. The aforementioned summary discusses five health education models in epilepsy care, revealing through various literature that different forms of health education have achieved effective outcomes, guiding patients towards healthier lifestyles and improving disease prognosis. As health education content and methods continue to evolve, healthcare professionals must commit to lifelong learning and deep clinical practice and research to understand patient needs better and encourage active patient participation, ensuring the orderly and efficient progress of health education efforts.
Funding: This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Face-to-Face Fund Cultivation Program Project (gyfynsfc-2022-01) of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University.
- Commentary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- The Use of Health Education Models in Patients with Epilepsy
- Graphic Health Education Model
- Knowing, Believing and Acting Health Education Model
- Individualized Health Education Model
- Interactive Health Education Model
- New Media Platform-Based Health Education
- The Importance of Health Education in the Care of Patients with Epilepsy
- Conclusion
- References
References
- Zhang LQ (2021) Research on the pathogenesis and treatment of epilepsy. J Med Info 34(16): 44-46.
- Girma B, Nigussie J, Tamir T, Etaferaw B (2022) Public knowledge toward Epilepsy and its determinants in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy & Behav 133: 108764.
- Li X, Shen L (2021) Effect of family-centered collaborative care combined with feedback health education on self-management ability and hope level of postoperative cervical cancer patients. J Clin Rese and Pract 6(27): 180-182.
- Linu CK, Phansalkar D, Stalin P, Sing Z, Mohnish P (2015) Interactive 'Audio-Visual' Symposium: An Effective Mode of Health Education. J Res Med Educat & Ethics 5(3): 217-219.
- Fan ZH, Zhao YM (2018) The impact of using health education tools during hospitalization on patient acceptance and outcomes. J Nurses Training 33(6): 543-545.
- Karan C, Chirag G, Archita C, Sandeep K, Gagandeep S (2018) Impact of Repeated Health Education Delivery on Antiepileptic Drug Adherence in People with Chronic Epilepsy in the Community. Int J Epilepsy 5(2): 59.
- Nan H,Huang D (2020) Effect of psychological and health education on quality of life and anxiety and depression status of patients with epilepsy. Chinese J Gerontol 40(10): 2209-2211.
- Fan FF (2022) Effectiveness of health education based on cluster care in patients with epilepsy. Continuing Med Cambriaducation 36(6): 149-152.
- Müller Godeffroy E, Jantzen S, Krisi T, Hager S, Aksu F, et al. (2006) FLIP&FLAP: Development and evaluation of a structured epilepsy education program for children and adolescents with epilepsy and their parents. Neuropediatrics 37(3).
- Zhang AH (2020) Effect of a graphic health education model on self-management ability and quality of life of elderly patients with inguinal hernia surgery. Chinese J Comparative Med 30(4): 147.
- Liu Y, Shao N (2019) Effect of graphic health education model in patients with osteoporosis. J Clinical Rational Drug Use 12(21): 138-140.
- Wang YL, Sun J, Zhang W (2022) Effects of thought leadership model health education on the state of mind and coping styles of families of children with epilepsy. China J Health Psychol 30(3): 357-361.
- Gu RX (2018) The effect of multiple forms of health education in patients with epilepsy. China Modern Med 25(28): 170-172.
- Zhou MY, Bi ZZ (2022) From "graphic symbols" to "picture language": the shift of educational communication forms in the digital era. Theory and Practice of Education 42(10): 8-12.
- Li Shichuo, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhou D, Zhang H, et al. (2021) The National Comprehensive Governance for epilepsy prevention and control in China. Epilepsia Open 7(1): 27-35.
- Fehrenbach DJ, Justine MAB, John Henry D, Hayley L, Theodore K, et al. (2020) Sexual Dimorphic Role of CD14 (Cluster of Differentiation 14) in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Renal Injury. Hypertension 77(1): 228-240.
- Wang WF, Wang YB, Wang F, Yang MM, Jiao XJ (2022) New advances in the clinical application of the 5A nursing model. China Med Pharm 12(1): 47-50.
- Liu ML, Li Y (2019) Application of the Knowing, Believing, and Acting Model Pathway Form in integrated health education for children with epilepsy in medical care. J Epilepsy 5(5): 356-362.
- Fan WJ (2022) The effect of the Knowing, Believing and Acting health education model on the efficacy and coping style of patients with myocardial infarction. China Medical Herald 19(4): 182-185.
- Sun J, Zhi-Wei Z , Yue-Xian M, Wei L , Chun-Ying W (2019) Application of self-care based on full-course individualized health education in patients with chronic heart failure and its influencing factors. World J Clin Cass 7(16): 2165-2175.
- Caciagli Lorenzo, Bassett Dani S (2022) Epilepsy imaging meet machine learning: a new era of individualized patient care. Brain 145(3): 807-810.
- Altmann Anna (2021) [Personalised epilepsy treatment]. Ideggyogy Sz 74(7-8): 227-233.
- Wu GF (2021) Effect of interactive health education model on compliance and postoperative indicators in children with pneumonia. Today Nurse 28(8): 149-150.
- Li X, Shen L (2021) Effect of family-centered collaborative care combined with feedback-based health education on self-management ability and hope level of postoperative cervical cancer patients. Clin Res and Practice 6(27): 180-182.
- Zhou S, Chen HM (2019) Effect of interactive health education for patients on self-care skills and illness stigma in adults with epilepsy. Modern Practical Med 31(12): 1658-1659.
- Zou YM, Liu HM (2018) The effect of online interactive health education on medication adherence in children with epilepsy Evidence-Based Nursing 4(3): 258-260.
- Huang XD (2018) The effect of health guidance by WeChat platform in epilepsy patients. Chinese Contemp Med 25(19): 151-157.
- Yang YH, Cao MJ, Cui XQ (2022) The application of WeChat APP-based tracking care management in epileptic patients. Chinese Evidence-Based Nurs 8(10): 1393-1396.
- Huang Mei C, Hung Chich H, Yu Ching Y, Kuan CL (2022) [Multimedia Health Education on Insulin Injection Skills for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes]. J Nurs Sci 69(2): 44-54.
- Miao F,Zhang L (2022) Effects of mobile multimedia health education on coping style, compliance behavior and quality of life of peptic ulcer patients. China J Health Psychol 30(3): 368-372.
- Papoutsi C, Christian DEC, Alexandra C, Sara ES, Trisha G (2021) Interrogating the promise of technology in epilepsy care: systematic, hermeneutic review. Sociol Health Illn 43(4): 928-947.
- Gurcan L, Eve M, Jane G, Dan JG, Fiona AM, et al. (2022) Improved understanding of non-epileptic seizures and reduced emergency health care usage following a single psychoeducational group for children and their parents. Seizure: Eur J Epilepsy 101: 1-7.






























