- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
Importance of Modern Awareness Strategies in the Field of Physiotherapy Practice Using Advanced
Jaison Kiran Dsouza*
Al Rashid General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Submission: October 31, 2017; Published: December 07, 2017
*Corresponding author: Jaison Kiran Dsouza, Senior Physiotherapist/Cupping, Therapist/Fitness Consultant, Al Rashid General Hospital, Hail 1380, Saudi Arabia, Tel: ; Email: jaisonphysio2001@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Jaison K D. Importance of Modern Awareness Strategies in the Field of Physiotherapy Practice Using Advanced Social Media. J Yoga & Physio. 2017; 3(3) : 555615. DOI: 10.19080/JYP.2017.03.555615.
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
Aims and Objectives
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- Power Point
- Aims and Objectives
- Do I Need Social Media?
- Few social Media Usage Examples
- Delimitations of the Study
- Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
- Social Media Selection
- 24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
- AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals
- Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
- Conclusion
- References
- https://getreferralmd.com/2013/09/healthcare-social-media-statistics/
- http://worldofdtcmarketing.com/role-social-media-healthcare/ social-media-and-healthcare/
- http://medcitynews.com/2012/06/does-medical-industrys-perception-of-social-media-use-match-reality-infographic/
- http://www.cathlabdigest.com/articles/Recruitment-Cath-Lab-Setting-Optimizing-Social-Networking-Opportunities
- http://resource.onlinetech.com/secure-use-of-social-media-ensuring-the-privacy-of-protected-health/
a. Think through the opportunities that social media presents for new ways of working, researching and learning.
b. Understand relevant legal, regulatory professional framework which determines appropriate use of social media in health and professional context.
c. Explore what a professional and employer’s social media policy means in practice.
d. To understand what good practice looks like in relation to the use of social media in the health and social care context.
e. Develop appropriate behavior in relation to personal and professional use of this technology.
f. Understand the personal and professional consequences of inappropriate use of social media.
Do I Need Social Media?
Answer is a BIG YES.
a. Meet people and health professionals worldwide to share ideas and debate
b. (Facebook, LinkedIn, Google+ etc )
c. Find Jobs and Recruitment agencies ( LinkedIn is a good Recruitment media )
d. Social media platforms are great source of information for various things
e. ( News, Jobs, Updates, Announcements, Articles , etc )
f. It’s an in expensive way to advertise your professional needs (Google ads, websites, Facebook ads, Twitter, etc )
g. For feedback and approaching patients in General (Figure 1).

Few social Media Usage Examples
Commonly used social media examples by Physios around the world (Figure 2).
a. Physiofacebook www.facebook.com/#!/topphysios
b. Talking Sense www.talkingsense.org/
c. Patient Opinion www.patientopinion.org.uk/
d. Campaigning
e. #globalPT
f. www.facebook.com/physiofriends
Worldwide Social Media Usage by Professionals
Australian physiotherapy association (APA)
APA’s social media accounts Facebook 22,000 Likes and Twitter has 11,000 followers by 2011.Marketing Manager Ms.Barry now overseas 12 different channels and now also including YouTube, Instagram, and LinkedIn. They create shareable content for their members who can be shared and help in getting it reach to maximum people. They evaluate their social media strategies effect using different tools like
a. Hoot suite for scheduling and analytics.
b. Facebook Insights.
c. Symplur for hastag analysis and twitter Analytics.
They access their success by follow words “We look at growth, engagement, daily reach and they help us to tell as we are on right track, But They wouldn’t say they define its success.”

#GlobalPT
Digital health consultant and Physiotherapist Dr. Mark Merolli, says “so many people in our community, potential patients and patients are now online now, it’s sort of where people live their lives “. He used a live demo example in 2015 APA conference and within 20 minutes of the Tweet he was replied by Swedish Physiotherapy association President, Maltase physiotherapy Members also. This showed a live example how fast it connects and reaches people (Figure 3).

NHS England, health department
They also got tremendous response and success using social media, their campaign #nhschangeday is the best example and it showed the power of social movements.
Blogger norman Mc Namara (@ Norman Mc Namara)
Living in Torbey she runs a blog and shares her personal experiences on Dementia on daily basis and it served a great place for resources and survey.
Physiofriends.com & physiofriends facebook page
Founder and Operated by me has a 2500 Likes and we receive a reach of 8000 views and more for each post we do there. ALL INDIA PHYSIOTHERAPISTS GROUP has 22,000+ members and serves a great place for sharing and discussions in India (Figure 4).
Online resource providers like Pub Med (Figure5) and Researchers like Peter O’sullivan (pain-ed.com) and Lorimer Moseley (bodyinmind.org) are best website usage examples.

Social Media Selection
a. Simple to use, most active social network
b. Images outperform text-based content up to 94% of the time
c. Demonstrative videos, infographics and images can be used
d. Inbuilt analytics tools to help the effects
e. Facebook Ads: Simple, allows to target messages to specific audiences, Can add desired budgets.
f. Facebook Groups: Free marketing place to promote business
a. Short and punchy posts
b. Has gained huge traction in physiotherapy world , #physio, #globalPT etc
c. Great tool to stay informed with new research
d. Great platform to network at conferences.
a. Worlds largest professional network with 400+ million users
b. 3.6 +million monthly active users in Australia only
c. Popular recruitment tool among employers
d. 94.2% journalist are registered
e. Allows to join peers who share common experiences and interests.
a. It is the visual identity of your business
b. 60+million photos uploaded per day, that means 700 photos per second
c. 70%users check feeds at least once a day, 35% several times a day
d. For right audiences, Instagram delivers brands 58 times more engagement per follower than Facebook, 120 times more per Twitter follower.
Snapchat
a. Share videos and images
b. Close to 200 million users
c. Around 26% of 18 -29 years Smartphone users report using Snapchat.
Periscope
a. Live video streaming
b. 2 million daily active users
c. Available in 25 languages
a. Messages, voice-notes , groups,images,videos can be used
b. Free of subscription charges
c. 1 billion monthly active users
Meerkat
a. Live video streaming
b. 2 million + users
c. More than 100,000 videos streamed
24 Outstanding Statistics & Figures on How Social Media has Impacted the Health Care Industry
a. More than 40% of consumers say that information found via social media affects the way they deal with their health (source: Mediabistro). Why this matters: Health care professionals have an obligation to create educational content to be shared across social media that will help accurately inform consumers about health related issues and out shine misleading information. The opinions of others on social media are often trusted but aren’t always accurate sources of insights, especially when it comes to a subject as sensitive as health [1].
b. 18 to 24 year olds are more than 2x as likely than 45 to 54 year olds to use social media for health-related discussions (source: Mediabistro). Why this matters: 18 to 24 year olds are early adopters of social media and new forms of communication which makes it important for health care professionals to join in on these conversations where and when they are happening. Don’t move too slow or you risk losing the attention of this generation overtime.
c. 90% of respondents from 18 to 24 years of age said they would trust medical information shared by others on their social media networks (source: Search Engine Watch). Why this matters: A millennial’s network on social media is a group of people that is well trusted online, which again, presents an opportunity to connect with them as health care professional in a new and authentic way [2].
d. 31% of health care organizations have specific social media guidelines in writing (source: Institute for Health). Why this matters: It is crucial to have social media guidelines in place for your health care facility to ensure everyone is on the same page, your staff is aware of limitations to their actions on social media and that a systematic strategy is in place for how social media should be run across your organization.
e. 19% of smart phone owners have at least one health app on their phone. Exercise, diet, and weight apps are the most popular types (source: Demi & Cooper Advertising and DC Interactive Group). Why this matters: This drives home the need for your health care organization to look into possibly launching a health related app focused on your specialty. This statistic doesn’t mean every health care facility should have their own app, but they should have a strong mobile focus across their marketing no matter their size [3].
f. From a recent study, 54% of patients are very comfortable with their providers seeking advice from online communities to better treat their conditions (source: Mediabistro). Why this matters: If the context of a group or community online is high quality and curated, then many trust that crowd sourcing of information from other like mind individuals is reliable. This shows how people perceive the Internet to be beneficial for the exchange of relevant information, even about their health [4].
g. 26% of all hospitals in the US participate in social media (source: Demi & Cooper Advertising and DC Interactive Group). Why this matters: If your hospital isn’t using social media, then you’re way behind the learning curve. Social media is really important for hospitals to communicate with past, present and future patients, despite the many regulations to what can and can’t be said on behalf of the hospital [5].
h. The most accessed online resources for health related information are: 56% searched WebMD, 31% on Wikipedia, 29% on health magazine websites, 17% used Facebook, 15% used YouTube, 13% used a blog or multiple blogs, 12% used patient communities, 6% used Twitter and 27% used none of the above (source: Mashable). Why this matters: Understanding where a majority of consumer health information comes from is important way of knowing of its value, credibility and reliability. It is important to differentiate sources of quality content from other less desirable sources of info.
i. Parents are more likely to seek medical answers online, 22% use Facebook and 20% use YouTube. Of non-parents, 14% use Facebook and 12% use YouTube to search for health care related topics (source: Mashable). Why this matters: Parents are more concerned about the well-being of their children then they were before having children, therefore they often source more information about a loved one’s health on social media and online more than ever before.
j. 60% of doctors say social media improves the quality of care delivered to patients (source: Demi & Cooper Advertising and DC Interactive Group). Why this matters: This statistic is important because it shows that many doctors believe that the transparency and authenticity that social media helps spur is actually improving the quality of care provided to patients. Let’s hope this is a continuing trend among the industry for patients at all levels.
k. 2/3 of doctors are use social media for professional purposes, often preferring an open forum as opposed to a physician-only online community (source: EMR Thoughts). Why this matters: It is interesting that a majority of doctors chose a more open forum as opposed to discussion in a health care specific community online. It is a fascinating statistic because it feeds into the same premise that a certain level of transparency spurred by social media is taking a hold of the entire industry.
l. YouTube traffic to hospital sites has increased 119% year-over-year (source: Google’s Think Insights). Why this matters: Video marketing converts to traffic and leads much more easily than other forms of content because it more effectively gets across the point, shares a human element and is able to highlight the value of the facilities more quickly. Other hospital facilities should look to create video content based around interviews, patient stories and more.
m. International Telecommunications Union estimates that global penetration of mobile devices has reached 87% as of 2011 (source: mHealth Watch). Why this matters: Once again, it’s time to think mobile first, second and third for your healthcare facility. With mobile penetration reaching an all time high, an age of connected devices is on the horizon for many healthcare facilities and it is time to develop a plan.
n. 28% of health-related conversations on Facebook are supporting health-related causes, followed by 27% of people commenting about health experiences or updates (source: Infographics Archive). Why this matters: This statistic supports and highlights two common uses of Facebook related to your health like sharing your favorite cause or interacting with others recovering. Social media has penetrated our society very deeply to the point where it has become a place where we share our interests and give support to others. This could be one of the many factors affecting why many trust the information found on social media about healthcare. The masses are continually accepting social media as a part of their everyday life, it is time your healthcare facility incorporated this marketing medium as part of your culture as well.
o. 60% of social media users are the most likely to trust social media posts and activity by doctors over any other group (source: Infographics Archive). Why this matters: Doctors as respected members of society are also highly revered for their opinions when they are shared on social media, which is even more reason to help boost your reach as a healthcare professional and actively use social media to discuss the industry.
p. 23% of drug companies have not addressed security and privacy in terms of social media (source: Mediabistro). Why this matters: This is an unsettling statistic about privacy concerns with drug companies that drastically needs to be addressed in order to guarantee that sensitive data is not accidentally released to the public on social media. It shows how many companies in health care still don’t know the first thing about the use of social media. This can be corrected by creating clear and concise guidelines on how social media should be used by the organization and its staff.
q. The Mayo Clinic’s podcast listeners rose by 76,000 after the clinic started using social media (source: Infographics Archive). Why this matters: This is a clear cut example of how to successfully bolster the reach of your organization’s messaging by echoing it appropriately on social media. Mayo Clinic already had a regular podcast that they helped grow by effectively using social media to share content and chat with their audience. Don’t get left behind in the digital age, take this example and run with it.
r. 60% of physicians most popular activities on social are following what colleagues are sharing and discussing (source: Health Care Communication). Why this matters: Many people on social media are passive participants since they aren’t creating or commenting on content, but instead reading and observing the content and conversations of others in their network. This is also true for many doctors that find value using social media to exchange information but don’t always choose to join the conversation. Many doctors are seeing the value of social media, regardless if they are a participant or an observer.
s. 49% of those polled expect to hear from their doctor when requesting an appointment or follow-up discussion via social media within a few hours (source: HealthCare Finance News). Why this matters: This is a surprising statistic because of how many people are comfortable with connecting with their doctor on social media, as well as how quickly they expect their doctor to personally respond to their outreach. This is a telling sign that the way in which we typically book appointments and handle follow-up conversations after an appointment, will continue to be disrupted by the use of social media in the process.
t. 40% of people polled said information found on social media affects how someone coped with a chronic condition, their view of diet and exercise and their selection of a physician (source: HealthCare Finance News). Why this matters: The opinion and viewpoints of the people in our social circles online are continuously influencing our decision making even it when it comes to our opinion on healthcare options. Health care professionals should take note of this fact by using social media in an impactful way to ensure they become a part of the process of forming an opinion of a person’s health care options.
u. More than 1,500 hospitals nationwide who have an online presence, Facebook is most popular (source: WHPRMS). Why this matters: The fact that most hospitals use Facebook over other social media channels is important to note because time, staff and budget are always limited and your efforts with social media should be targeted and focused to where your organization can make the most impact.
AMN Health Care Survey shows the increased use of social networking sites by Hospitals

US hospitals use of social networking tools has increased exponentially. According to an October 2011 survey 1,229 US hospitals are using some form of social networking tools (Figure 6). Such statistics reveal that as these sites become increasingly popular and relevant, highly skilled job seekers in specialized fields have the ability to connect with those in areas they find the most desirable, and health care facilities can reach these individuals on a broader stage (Figure 7).
Social Media Guidelines for Professionals
Confidentiality
Protect the privacy, security and confidentiality of client information.
Assume all online content is public and accessible to everyone and digital record.
Beware that privacy settings are imperfect and can be compromised.
Consent
Consent should be taken without fail before using any patient contents or data.
Maintain boundaries
Do not initiate personal contact with clients.
Be proactive and consistent, develop your own laws.
Professionalism
Be thoughtful, responsible, accounatble.
Separate personal and professional life
Refer patients in professional manner.
Do not disseminate information.
Do not post anything about other professionals.
Postings should be backed with evidences.
For Employers
Employer attitudes: Employer will act to protect their reputation and has rights to consider how, why and when their employees are using social media.
Balancing opportunities and risks: Talk to staff-what interaction accepted-limitations-digital professionalism-day to day basis to avoid miss use.
Establishing own policies: Design policies in favor of both employer and employees for a good professional behavior in digital world.
Employer action against inappropriate employee: Proper investigation-discussion-talks-guidance ad all inside the professional boundaries to maintain strict
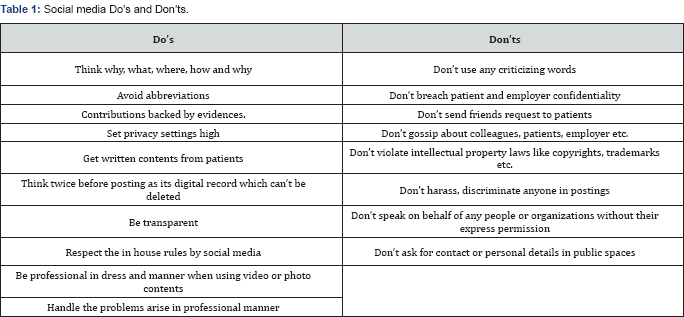
For Boards, Associations, Networks: They should design their own terms and conditions. Approval must be sought in advance before using their contents (Table 1).
Conclusion
Social media is a powerful, useful tool, it could help you be innovative in the delivery of education, service provision, or in undertaking research. It has the potential to provide tailored services that meet the personal preferences of your patients.
However, in order to avoid the pitfalls of social media which can have a detrimental impact on the reputation, professional status and employment prospects of health professionals, the CSP is now encouraging you to gain an understanding of how to use it, understand employers stands, appropriate professional behaviors, how different social media sites and apps work and not to forget under legal boundaries. The practical use of social media in health and social care is constantly developing at a considerable pace. In the end, when you look back at your life, you wanna have no regrets and say to yourself, “I have done everything I could to make the world around me a better place”.






























