Abstract
An Ayurvedic preparation called Rajata Bhasma (RB) is used to treat different disease conditions. Scientific validation using the most recent RB tool has not yet been carried out. Therefore, an evaluation of RB’s immunomodulating potential was proposed. Numerous diseases are known to have immune system involvement in both their genesis and pathophysiology mechanisms. Ayurveda has a strong focus on promoting health and strengthening the host. Rajata Bhasma, an Ayurvedic preparation of processed silver, has been traditionally utilized for its therapeutic properties, including its purported immunomodulatory effects. This study aims to assess the immunomodulatory potential of Rajata Bhasma through in vivo methodologies, integrating modern scientific approaches with traditional Ayurvedic principles. In vitro experiments focus on evaluating the effects of Rajata Bhasma on immune cell proliferation, cytokine production, and phagocytic activity. In vivo studies explore changes in immune organ weight, hematological parameters, delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response, and antibody production following administration of Rajata Bhasma. Molecular analysis, including gene expression studies and flow cytometry, provides further insights into the underlying immune-modulatory mechanisms. Preliminary findings suggest that Rajata Bhasma may enhance immune cell activity, modulate inflammatory cytokines, and exhibit antioxidant properties, all of which contribute to its immunomodulatory effects. These results align with its traditional use in enhancing vitality and immune function.
Keywords: Immunomodulatory; Rajata bhasma; Ayurvedic preparation; Immune cell proliferation
Abbreviations:RB: Rajata Bhasma; DTH: Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity; RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis; SEM: Scanning Electron Microscope; FCA: Freund’s Complete Adjuvant; WBC: White Blood Cell; RBC: Red Blood Cell; Hb: Hemoglobin; ESR: Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; COXs: Cyclooxygenases
Introduction
Many medical conditions are known for their immune system involvement in both their genesis and pathophysiology mechanisms. Ayurveda has a strong focus on promoting health and strengthening the host. Rasayana plants are especially advised for the treatment of immunological disorders. Ayurveda, especially in relation to plants, may be significant in contemporary healthcare, especially in situations where adequate treatment is unavailable. It is necessary to examine the cost-effectiveness of specific therapies in relation to contemporary therapeutic schedules and assess the ability of Ayurvedic medicines to offset the negative effects of contemporary therapy [1]. The creation of substances that could restore the immune system of “patients” from a condition of immunodeficiency to one or more normal functions would probably have a big influence on illness and the person it impacts. Such an agent would regulate the onset and progression of sickness but would not constitute a cure [2,3].
Synovial inflammation and permanent joint damage are hallmarks of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an inflammatory disease that causes severe disability. With a male to female ratio of 1: 2.5, it has impacted roughly 1% of the global population. This disease’s cause is currently unknown. This condition is caused by a variety of proinflammatory chemicals, such as reactive oxygen species, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and cytokines generated by macrophages. The suppression of enzymes like COX and LOX for the metabolic control of arachidonic acid and the regulatory checks of these mediators released by immune cells may be viable targets for the treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders. Being a systemic disease, RA can impact internal organs and the entire body, with some exceptions in relation with the same RA is associated as lack of Immunomodulating effect therefore the current study is corelated with RA and Immunomodulation functionality of the same RA was established.
The Bhasma’s made from a variety of metals are well-known for their many medicinal applications against terrible illnesses. For instance, Numerous degenerative disorders have been linked to Swarna Bhasma, or gold-based Bhasma. Copper-based Bhasma, also known as Tamara Bhasma, has been utilized to treat liver and stomach issues, leukoderma, and heart issues. Silver-based Bhasma, or Rajata Bhasma, is well known for its ability to prevent psychological disorders, fever, anemia, and diabetes. For patients with conditions like diabetes mellitus, asthma, anemia, and gastric ulcers, Vang Bhasma (tin-based Bhasma) is recommended. The goal of this study was to assess the hepatoprotective potential of two distinct samples that were purchased from Rajata Bhasma [4].
Materials and Methods
Preparation of rajata bhasma
Rajata 99.9% pure was obtained from the local marketplace
of Ranchi. Purity was examined by Energy Dispersive X-ray
spectroscopy / Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis
and it was found to be 100% pure. Rajata was processed through
Shodhana and Marana to prepare Rajata Bhasma. Departmental
equipment included a S. Steel jar, Khalwa yantra (mortar and
pestle), Sharava (earthen saucer), and Upala (cow dung cakes)
used in procedure.
i. Raw material purification, i.e. Gandhaka, Rajata
ii. Parada extraction is a process that involves extracting
Parada from its natural state
iii. Rajata Bhasma (RB1) and Rajata Bhasma (RB2) are
prepared using the puta technique.
Rajat Shodhana- Nirvapa (quenching) was used to purify the silver in Rajat Shodhan
Samanya shodhana of rajata
Materials required- Rajata- 245 g, Tila Taila (Sesamum indicum Linn.)- 1500 ml, Takra- 1500 ml, Gomutra-1500 ml, Kanji-1500 ml, Kullatha Kwatha (Dolichos biflorus Linn.)-1500 ml. Procedure- For Samanya Shodhana, thin silver foils were heated to red hot and dipped three times in each of Takra2 (Butter milk), Tila Taila (Sesame oil) ,Gomutra (Cow’s urine), Kulattha kwatha (decoction of Dolichos biflorus Linn.) & Aranala3 (Sour gruel made from rice).
Vishesha shodhana of rajata
Materials required-Samanya Shodhita Rajata, Nimbu Swarasa
(Citrus medica-3500 ml) Procedure‑Samanya Shodhita Rajata
was reheated till red hot, and then quenched seven times in
Nimbu Swarasa. After each dipping, the juice was replaced.
Finally, Shuddha Rajata was carefully collected [5]. Preparation of
Rajat Bhasma- Rajat Bhasma was prepared in two distinct ways:
RB1 was made using 9 puta and RB2 was made with 17 puta. The
method is outlined in full below [6].
a) Rajat foil was chopped into tiny pieces and amalgam was
produced in a mortar with parade.
b) Purified gandhaka was added to the amalgam and
triturated till a suitable Kajjali was formed.
c) Following that, impregnation with kumara swarasa is
used to prepare Chakrikas (Pellets).
d) In a sharvana, dried chakrikas were arranged, and laghu
puta was offered.
e) Rajata was fully powdered after the first puta.
f) Half of the kajjali was added to the next two putas, which
were then triturated with kumara swarasa and served.
g) In place of kajjali, half of a gandhaka was added from 4 to
9 puta (Considered as a RB1).
h) The other putas were completed without Kajjali or
Gandhaka.
i) To obtain Rajat Bhasma, 17 puta were supplied, which
passed all classical parameters (Considered as a RB2)
Experimental Design
Selection of animals
Either Sex Wistar rats (150-200gm), were used, and kept in
quarantine for 10 days under standard husbandry conditions
(27.3 oC, Relative humidity 65±10%) for 12hrs in dark and light
cycle respectively and were given standard food and water ad.
libitum. All experiments were approved by the institutional ethical
committee and were carried out according to the animal ethics
committee guidelines. One week before the commencement of the
experiment, the rats were randomly divided into five groups of six
rats per group. On day 0 rats were injected with 0.1 ml of Freund’s
complete adjuvant (FCA) in to the sub plantar (s.p) region of the
left hind paw of all the animals. This consists of Mycobacterium
butyricum suspended in heavy paraffin oil by thoroughly grinding
with a pestle and motor to give a final concentrate of 0.6mg/mL.
Administration of test compounds and standard drug was started
on the next day and continued for 28 days.. The experimental rats
were randomly divided into four groups of six rats per group and
treated as follows:
I. Group I (control group) – Arthritic rats treated with
distilled water
II. Group II – Arthritic rats treated with standard drug
Indomethacin at 10 mg/kg body weight
III. Group III – Arthritic rats treated with RB1 at 25 mg/kg
body weight
IV. Group IV – Arthritic rats treated with RB2 at 25 mg/kg
body weight
Hematological screening
On the 28th day blood samples for hematological assays were obtained through ocular puncture of the rats and collected into EDTA-treated sample bottles. White blood cell (WBC) and Red blood cell (RBC) counts were assessed as stated in the method of Chesbrough and McArthur [7]. Drabkin and Austin method was used to confirming the Hemoglobin (Hb) content. Estimation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was carried out by the method of Westergren [8].
Body and organ weights
Body weights of each rat were measured from each day of starting experiment to end of experiment. The rats are to sacrifice with appropriated intervals using automatic electronic balance. At sacrifice, the weight of liver, kidney and other major organs, was measured at g levels (absolute weights), and to reduce the differences from individual body weights, the relative weight (% of g or mg/g body weight) was calculated [9].
Result and Discussion
Hematological parameters
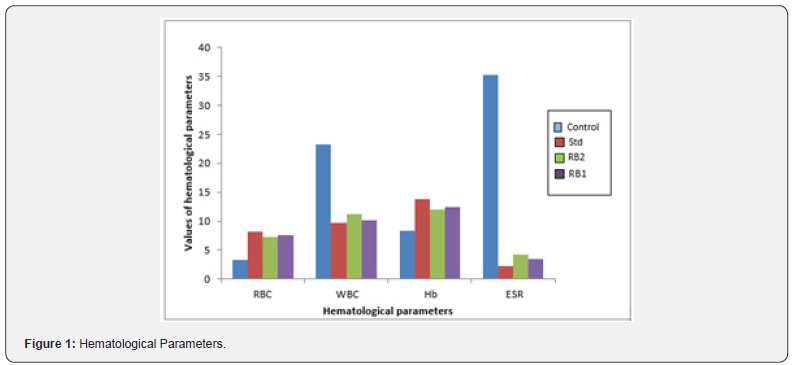
The administration of RB1, RB2 on Freund′s adjuvant induced arthritis animals enhanced the levels of RBC and Hb compared to control animals (Table 1 & Figure 1). The WBC count and ESR were significantly reduced after administration RB1 and RB2 compared to control animals. Rheumatoid Arthritis is a common autoimmune disorder, the immunologically mediated FCA induced arthritic model is considered as one of the outstanding animal model of RA. FCA induced arthritis is an animal model of chronic polyarthritis with features that look like RA. Inoculation of animals with FCA (which was prepared by suspending heatkilled Mycobacterium butyricum in liquid paraffin at a dose of 10 mg/ml Mycobacterium butyricum in paraffin oil), is known to produce a profound systemic inflammation.

* P<0.05 in comparison to the control group; values are presented as mean ⁱ SEM, n = 6 per group.
Determination of paw oedema is according to the grapevine simple, susceptible and rapid procedure for evaluate the degree of inflammation and assess the therapeutic effects of drugs. In adjuvant-induced arthritic rats developed a chronic swelling in multiple joints with influence of inflammatory cells, erosion of joint cartilage and bone destruction and remodelling which have close similarity to human RA. These inflammatory changes eventually result in the complete destruction of joint stability and mobility in the arthritic rats. Also, soft tissue swelling around the ankle joints appeared during the progress of arthritis in FCA injected rats, which was considered as oedema of the exacting tissues [10,11].
In the present study, experimental arthritis was reliably established with repeated and daily subcutaneous plantar injection of 0.1 ml of FCA over a period of 28 days which was characterized by plantar edema formation which maximized on day 7 of the treatment and subsequently increase for the remaining part of the study. The inflammation induced by FCA is primarily due to edema formation and cellular influx.
The progression of arthritis was confirmed in our study by scoring total arthritis lesions. The inflammation associated with AIA is mainly dependent on prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) generated by cyclooxygenases (COXs). Besides, the role of cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1 has also been implicated in this model. Now from the results observed it was found that RB1 and RB2 treated arthritic animals showed decreased inflammation of joints.
In present study, arthritic control rats showed a reduced RBC count, reduced Hb levels, and an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). All these symptoms indicate an anemic condition. The RB1 and RB2 treated groups showed a significant recovery from the induced anemia. The significant increase in leukocyte count in adjuvant induced arthritic rats may be due to the stimulation of immune system against the invading antigens and significant decrease in RB1 and RB2 treated groups showed its immunomodulation effect. This clearly indicates the Presence of Immunomodulating effect of Rajat Bhasma. Immunomodulating effect can also established by gain in body weight of major organs during completion of study. Further studies are carried for the possible mechanism and the identification of the bioactive component responsible for Immunomodulating effect.
Conclusion
The present findings inferred that the gathering treated with the most noteworthy convergence of Rajat Bhasma indicated great come about as that of the standard medication and was underpinned concentration of Rajat Bhasma can possibly overcome Immunodeficiency in albino rats. The treatment of Rajat Bhasma have indicated noteworthy changes in Hematological parameters. Our preliminary results are encouraging, but further molecular studies are needed to clarify the exact mechanism behind the Immunomodulating activity of Rajat Bhasma.
References
- Dhanukar SA, Thatte UM, Rege NM (1999) In: Wagner H, (Ed.), Immunomodulatory Agents from Plants. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhauser Verlag, pp. 289-323.
- Gottlieb A, Gottlieb M, Scholes V (1987) Reconstitution of immune function in AIDS/ARC. Concept Immunopathol 4: 261-274.
- Kanase V, Jain B, Yadav P (2013) Evaluation of in-vitro immunomodulatory activity of aqueous and ethanolic extract of Capparis mooni. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 4: 344-352.
- Pal D, Sahu CK, Halda A (2014) Bhasma: The ancient Indian nanomedicine. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 5: 4-12.
- Hebbar KR, Gokarn R, Madhusudhana K, Kallianpur S, Bhat S (2016) Anti-microbial study of calcined sliver (Rajatabhasma). Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm 7(6): 56-59.
- Austin JH, Drabkin DL (1935) Estimation of Haemoglobin. J Biol Chem 112: 67-69.
- David G, Sykes AJ (1951) Westergren and Wintrobe methods of estimating ESR compared. Br Med J 2(4746): 1496-1497.
- Seong M, Sang-CK, In-Kwon Chung (2012) Antioxidant and Protective Effects of Bupleurum falcatum on the l-Thyroxine -Induced Hyperthyroidism in Rats.
- Yend SR, Sannapuri VD, Vyawahare NS, Harle UN (2010) Antirheumatoid activity of aqueous extract of Piper nigrum on Freund’s Adjuvantinduced arthritis in rats. Int J Pharma Sci Res 1(1): 129-133.
- Mowat AG (1971) Hematologic abnormalities in Rheumatoid arthritis. Sem Arthr Rheum 1(3): 195-219.
- Montecucco, Mach F (2009) Common inflammatory mediators orchestrate pathophysiological processes in rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. Rheumatology 48(1): 11-






























