Correlation of An Excess Water Phobia with Presence of Urobilinogen in Urine
Muhammad Imran Qadir and Amna Ashraf*
Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Pakistan
Submission: September 10, 2019;Published:October 23, 2019
*Corresponding author:Atiqa Rehman, Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan J
How to cite this article:Muhammad Imran Qadir, Atiqa Rehman. Relation of Cigarette Smoking with Urine Bilinogen. J of Pharmacol & Clin Res. 2019; 8(2): 555732. DOI:10.19080/JPCR.2019.08.555732
Abstract
Aquaphobia is phobia which is associated with fear of water. This phobia shows many symptoms, like increase in pulse rate and sweating. The patient can be treated by therapies suggested by physician. Urobilinogen is generated from bilirubin. Its normal amount in urine is up to 1mg/dL. Its abnormal level shows malfunctioning of the liver. 100 samples of urine were collected from IMBB, BZU, Multan. These samples are then tested by some methods like dipstick test followed by microscopic examination of samples. Results obtained showed that 84.6% of males and 71.4% of females have aquaphobia and abnormal amount of urobilinogen in their urine samples.
Keywords: Fear of water; Urobilinogen; Microscopic examination
Introduction
It is a phobia which is particularly related to water. Aqua-phobia can be diagnosed by many symptoms. Firstly, person feel anxiety. His heart beats faster than normal. His blood pressure increases. This fear could lead to sweating and wooziness. These symptoms show that person has such fear. Sometimes, there is a pain in chest and a person feel that he will fell faint. Many therapies are there now to cure it like by using hypnosis [1]. A good psychologist after judging his patient will give him an appropriate therapy. Urobilinogen is produced from reduction of bilirubin by bacteria [2]. It is present in very low concentrations normally in urine [3]. It is produced in intestine, half of it become a part of urine and second half remains in intestine. Its concentration is 0.2-1mg/dL. Its high-level shows that many red blood cells are broken. While its low-level shows that there is some blockage in bile duct. High level of urobilinogen tells that liver is not functioning properly. Liver test is conducted to check its level. When cycle of urobilinogen is stopped in liver, urobilin is produced and released in urine. While the urobilinogen present in intestine forms stercobilin by its reduction. Test for checking the liver function are conducted by measuring the amount of urobilinogen in urine.
Materials and Methods
Material required
Sample of urine, microscope, a container and a microscope are needed for urinalysis
Sample collection
Clean catch urine samples of all males and females are collected in a container. The container should be covered by a cover slip properly.
Physical examination
The Samples are examined physically. The color and odour is noticed. If the smell is pungent and color is different from normal, then test is performed.
Dipstick test
In this test, there are several steps, firstly, the strip is dipped in urine present in container. The strip is suspended for at least 60-80 seconds in urine. Then it is taken out from container. Excess of urine is disposed of the strip. After 60 seconds, change in color is observed. The color of strip tells about an extent of change.
Microscopic examination
The samples are examined under a microscope. Microscopy tells about the reasons for abnormality in the values. It also tells about causative agents (Figure 1).
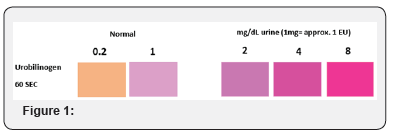
Results and Discussion
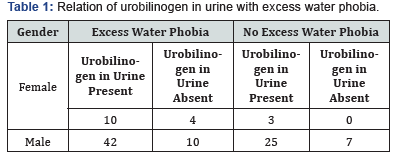
Results shown in (Table 1), demonstrates that 52 people out of 100 have an excess water phobia and presence of high amount of urobilinogen in urine samples. While 28 people have urobilinogen excess in their urine, but they have no such aquaphobia.
Conclusion
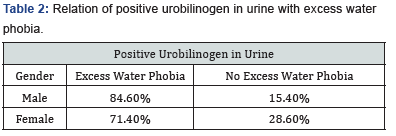
After performing this experiment, it is concluded that the aquaphobia influences the urobilinogen presence in urine. It affects both males and females. In 84.6% males and 71.4% of females, positive urobilinogen is found (Table 2).
References
- Balikov B (1955) A note on quantitative urobilinogen determinations. Clinical chemistry 1:264-268.
- Golden WL (2012) Cognitive hypnotherapy for anxiety disorders. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 54:263-274.
- Wilbur RL,Addis T (1914) Urobilin: its clinical significance. Archives of Internal Medicine 13:235-286.






























