Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is an Effective Treatment for Schizophreni form Disorder: A Case Study
Haroon Ur Rashid and Syeda Ishrat Fatima*
Armed force institute of mental health, Pakistan
Submission: May 18, 2018; Published: May 23, 2018
*Corresponding Author: Syeda Ishrat Fatima, Armed force institute of mental health, Pakistan, Tel: +923418929072; Email: syedaishratfatima@yahoo.com
How to cite this article: Haroon Ur R, Syeda I F. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is an Effective Treatment for Schizophreni form Disorder: A Case Study. J of Pharmacol & Clin Res. 2018; 5(5): 555672. DOI:10.19080/JPCR.2018.05.555672
Abstract
Background: Patient was 32 years old female, who visited Armed Force Institute of mental health with the symptoms of schizophrenia, delusion (paranoid), speech incoherence, shivering of head and hands, severe aggression, sleep disturbance, loss of appetite, severe conflicts with authority and malfunctioning of daily life.
Methods: Cognitive behavioral therapy was used to treat the client. Total 20 sessions was planned for treatment along with 04 follow up sessions.
Results: Patient showed significant progress in middle phase. She was motivated toward treatment in whole therapy sessions. In termination phase she overcome her ideation, conflict with authority and was able to face the realistic problems effectively.
Conclusion: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is useful for the treatment of schizophrenia
Keywords: Schizophrenia; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Introduction
Schizophrenia considered as one of the most severe mental disorder. Its abnormalities are in the form of delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, abnormal behavior and negative symptoms. Delusions are fixed believes that are difficult to amend through evidence. Delusions are of two types one is bizarre and other is non bizarre. Bizarre delusions are unusual odd believes that do not originate from daily life experiences. On the other hand non bizarre delusions are usual make sense and originate from daily life experiences. Delusions are specifying with erotomanic type, grandious type, jealous type, persecutory type (paranoid), somatic type and mixed type [1].
In paranoid type of delusion the content includes that he is going to be harmed, poisoned, cheated, spied, followed and harassed by someone. In paranoid delusion patient is not bizarre and socially cut off. He does his work properly but he thinks that people spy on him. The duration of delusion symptoms are one month [1]. Cognitive behavior therapy is useful for Schizophrenia Disorder. Different techniques were used with patients. Cognitive techniques that were used with psychotic patients: improved sympathetic and insight into psychotic experience, recover coping strategies, decrease distress that is linked with hearing hallucination and preservation of gains and avoidance from reversion [2]. Cognitive behavioral therapy for Schizophrenia helps the patient to make sense of delusional experiences through making association between beliefs and previous life events. Through discussing psychological formulation assists the people to formulate the logic of psychological experience that helped them to make links between apparently unlinked beliefs and upset psychotic symptoms [2].
Case Report
Ms. R. is 32 years old lady. She is last born in sib ship and she is unmarried. She has four sisters and one brother. Her brother is businessman and all sisters are professional. She was high achiever during her whole academic carrier. She is currently working as assistant professors in a renounced university last from three years. Her father is businessman and mother is house wife. She came with complains of: people are follow me and when I delivered lecture every student stare at me, speech incoherence, shivering of head and hands, severe aggression, sleep disturbance, loss of appetite, disturbed daily functioning,sensitive for criticism, and severe conflicts with authority. She thought herself as neglected child. She presented flat responses with lot of speech pressure. She also presented poor memory and concentration issues. She reported limited friends. Her problem started from approximately four months ago according to Ms. R and seeks assistance because she had attended a lecture on stress management by authors in her university.
She used anti psychotic medicine by the advice of psychiatrist but she discontinue medication because of heavy sedation by her own and adopted psychotherapy for future treatment. So she approached clinical psychologist treatment. Clinician-Rated Dimensions of Psychosis Symptom Severity [1] and Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) [3] were administered to gauge her severity of symptoms. After detailed assessment she was diagnosed as Schizophrenia according to DSM 5. Cognitive behavioral therapy was used to treat her problems. Total 20 sessions were planned for her treatment. First 16 sessions were therapeutic sessions in nature and 04 sessions were planned for follow up. Initial sessions were conducted to develop fair understanding of her etiology then preservation and further how to control her symptoms in a daily life functioning and finally how to overcome on relapse issue.
Ethical Consideration
Written consent was taken for the purpose of case study and assures her that all information will be confidential.
Discussion
Patient along with her father and elder sisters visited Armed Force Institute of Mental Health for the purpose of psychotherapy. She wanted to gain control on her psychological symptoms to make herself comfortable in normal life as soon as possible. First she assessed for Psychometric testing and further guided in the light of analysis that she is facing severe psychological which she is facing. She was recommended Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for treatment. To get good knowledge about CBT she assigned to consult internet and given some written in the form of pamphlets and booklets. Initial phase contained 4 sessions. Initially sessions were planned on alternative days per week. Treatment structure was discussed with patient to relay information about psycho therapeutic session. Firstly etiology of Paranoid schizophrenia was discussed to get the basic understanding of her pathology and illness history. Further basic symptoms were discussed in detail and to gain adequate control on the symptoms an activity program was developed with the interest of patient which was based on religious activities, social activities, job activities, physical activities, basis diet plan, sleep regulation techniques and creative activities (Tables 1 & 2).
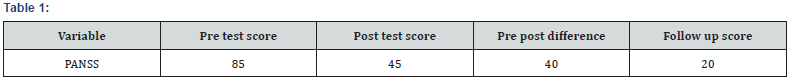
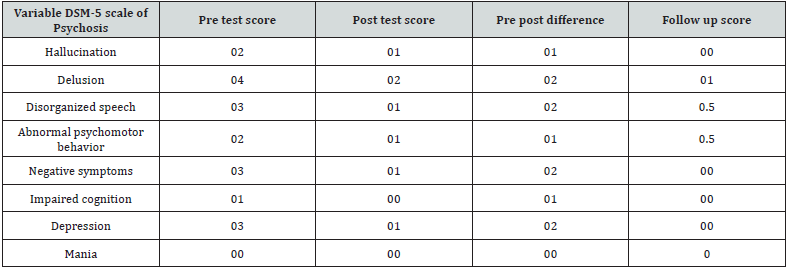
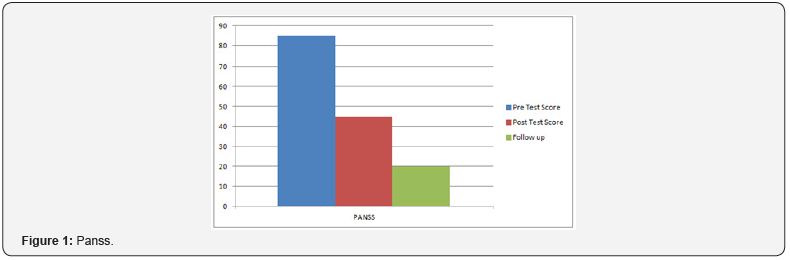
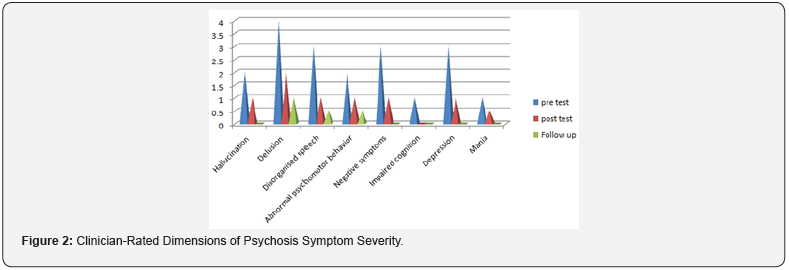
Home work was also assigned to keep her control on her symptoms and further to enhance her insight. She regularly followed the instructions. To address her cognitive errors she was given visual-gram and which improved her symptoms. By following the activity plan she gained confidence and developed better relationship with family member and her colleagues. To address her authority conflict, whole family member were invited in the sessions in the middle phase of the therapy. Cognitive errors and misinterpretation were focused and challenged during the family sessions. Family combined sessions remained fruitful and conflicts resolution techniques along with tolerance bearing (cognitive errors related to impulsivity and sensitiveness) were applied to address the issues. She shared childhood imageries which were based on verbal and physical abuse by her father on her mother and siblings when her family lived in joint family system which turned into severe psychological problems for her (Figures 1 & 2).
Mindfulness techniques were used to address these issues along with thoughts monitoring which explained the linked of negative thoughts and her current paranoia. Cognitive restructuring helped her to move out from false beliefs. In this phase stress model, mood monitoring, thought monitoring and cognitive restructuring was concluded and she feels relaxed and removed negative symptoms. In further session focused on early warning sign in which she learned how to cope with problems. She learned self management technique and learned how to face the problems.
References
- (2013) American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. (5th Edn). Washington, DC.
- Smith L, Nathan P, Juniper U, Kingsep P, Lim L (2003) Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Psychotic Symptoms. A therapist’s Manual © Centre for Clinical Interventions.
- Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13(2): 261-276.






























