Abstract
Construction materials which were once considered as a slow progressing field is now progressing with leaps and bounds by the end of year 2025 due to intervention of digital and artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. Such technologies will drive the smart construction materials research from being possible to being practical. More environment friendly materials will be produced with low carbon footprints, sustainability, reproducibility, reliability and reusability. Digital twins have made it easier to realize the actual field structures in the laboratory-controlled environment and computer-based AI generated numerical-digital models as well as real-life visualizations. The field of 3D digital concrete printing combined with AI has shifted use of construction materials into a next level. Various cementitious composites, concrete mix designs, corrosion resistant steel reinforcement bars, admixtures, additives, coatings, are all being reborn with the advancements in digital and AI technology. This editorial focuses on all the pros and cons of such technologies for use in construction materials with the end of year 2025 perspective. Figure 1 below presents the graphical abstract for this editorial.
Keywords:Smart construction materials; Artificial intelligence; Digital technology
Abbreviations:ANN: Artificial Neural Networks; ML: Machine Learning; DL: Deep Learning; AI: Artificial Intelligence; IOT: Internet of Things; BIM: Building Information Modeling; RM: Random Forest; LSTM: Long Short-Term Memory
Digital Modeling to Reality: Emergence of a New Artificially Intelligent Assistant
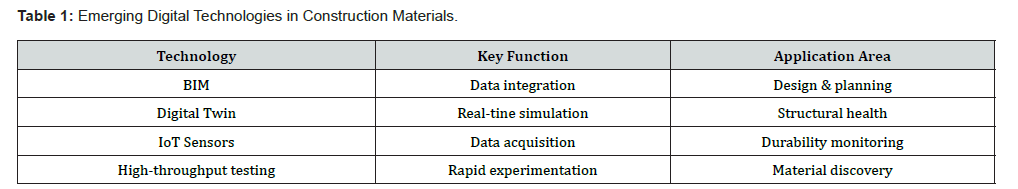
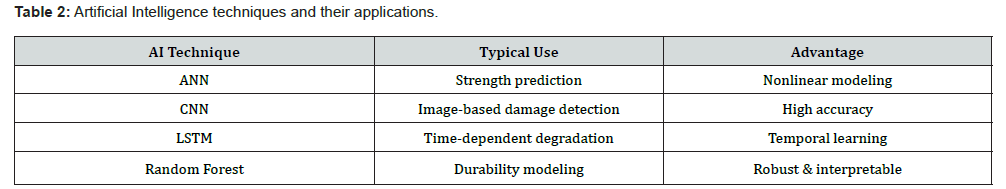
Construction materials [1] selection, mix designs as well as material optimization when done under AI [2] guidance and digital modeling [3] will be far better than conventional techniques. The research and practice are shifting the industry from relying merely on laboratory experimentation and field experience to AI driven digital technologies such as artificial neural networks (ANN), machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL) algorithms etc. These technologies will lead to the development of construction materials with properties such as strength and durability much better than before. Digital and AI generative tools-based optimization will result in novel compositions that will take care of multiple and conflicting requirements such as strength and ductility of rebars, corrosion resistance and cost of steel structures, reduced cement content without compromise on strength. Next year will probably see the evolution of AI as a digital material scientist which will relieve human input and effort for exhaustive experimentation. Table 1 presents the emerging digital technologies in smart construction materials, their expertise, primary functions and the usage field. These include internet of things (IoT), building information modeling (BIM) and digital twins. Table 2 presents the AI practices and their applications. These include random forest (RM), artificial neural networks (ANN) and Long Short- Term Memory (LSTM). Construction materials research shall evolve as a data driven protocol rather than a trial and error-based investigation.
Digital Twins Transformation from Structural to Material Level
Until 2025, the world has seen digital twins [4] for structural modeling in construction. Start of 2026 is expected to see its transformation into smart construction material digital twins. This will help to predict the behavior of construction materials in addition to its structural behavior. Thus, enabling the multiscale prediction at macro-micro-nano levels. This will help the researchers to simulate various mechanisms such as corrosion of rebars, hydration of cement, evolution of microstructure, degradation cracking etc. with more accuracy than when it was being done only with techniques such as finite element modeling. It will help in the analysis of realistic conditions and space and time domains. With the combination of such advances with embedded sensor monitoring it will be possible to design construction materials for more complex environmental stressors.
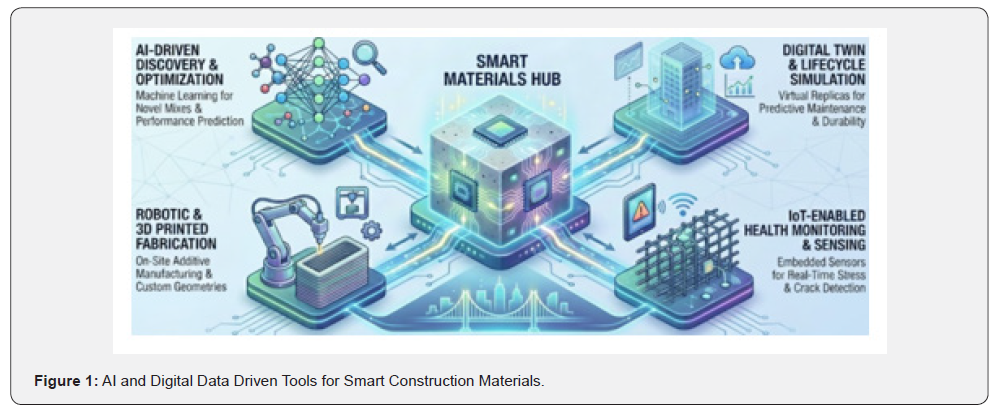
Manufacturing of Additives & Digitally Adapted Cementitious Smart Materials
2025 has seen more advancements and use in the field of 3D concrete printing [5]. For this to become a norm, it is important that the construction materials be optimized digitally to fulfil the narrow window of fresh concrete properties such as early strength, long term durability, buildability, rheology etc. Achieving these requirements will not be possible through conventional use of mix design methodologies beyond 2025. All this is now redefining the way cement-based construction materials were being developed and tested. Digital technology and AI driven schemes will be the foremost tools in 2025-2026 transformation of construction materials.
Next Generation Smart, Digital and Artificially Intelligent Construction Materials
Construction industry will now see more focus on self-healing and self-sensing smart materials. The integration of sensinghealing and actuation mechanisms of construction materials has shifted the industry and field from the past passive to future active material system. Use of construction materials such as conductive fillers, fibers, optics or sensitive neural networks can mitigate the environmental stressors in a real time artificially intelligent way. Along with that the self-healing construction materials based on encapsulated products, mineral-admixtures and/or microbialbacterial agents heal the cracks and recover the durability loss of structures. Digital technologies and AI when working side by side can make the above system very efficient and effective by understanding the large database available, separating the actual damage from the noise and examining the working of healing construction materials with the passage of time.
Cement, Lime, Gypsum, and Related Construction Materials
Digital and AI technology will see a rapid shift in molding the production, procurement, development and performance of these materials in 2025-26. This will transfer the experiment driven techniques to data informed construction material design. 2025 has seen the increasing use of machine learning for raw material selection, clinker replacement, reducing CO2 emission, mixture-proportioning etc. making it possible to improve the performance, durability and sustainability for future generations to come. Cement [6, 7], lime [7] and gypsum [8]-based construction materials are vital in the additive manufacturing and cement production industry. Their ability to get mixed with additives produces rapid curing materials which are suitable for 3D concrete printing. The use of digital twins can help in the real time and space simulation of processes such as cement hydration, its transformation in various phases, behavior in the kilns both thermally and chemically, making the manufacturing process energy efficient as well as improving the quality of products. Use of digital and AI technology in the rheology control as well as the manufacturing process is enabling digitally modified cement and gypsum-based materials for both general and special applications. Intelligent and digital material mix designs are reshaping these traditional binders into smart construction materials that are suitable for the requirements of modern world.
Challenges Beyond 2025
Despite the rapid progress until 2025, the future brings several challenges ahead for data validation and its standardization. AI is still prone to making mistakes, incorrect interpretations and selfgeneration of missing data. Digital technologies are limited to real life complex and unpredictable situations. The construction material data remains in-consistent, dispersed and / or copyright registered and unavailable. Thus, limiting the use of digital and AI technology which is still evolving. To move beyond 2025, it is important to have access to reliable database and proper reporting. Otherwise, AI based digital technology shall merely become black boxes [9] instead of scientifically reliable tools that can be relied upon with full confidence.
The Future of Construction Materials: Digital AI Industry, Research and Development
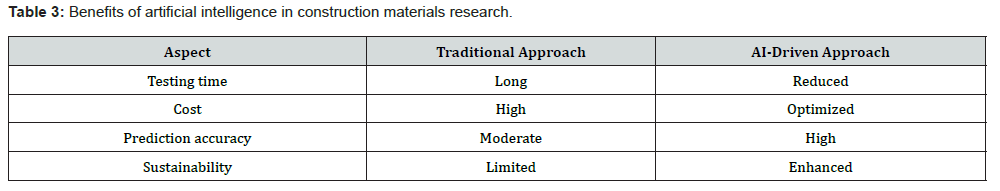
Leaping forward from 2025, some priorities stand out which include but not only confined to a) smart material-based AI digitaltwins which will bridge the design, durability and performance throughout the life cycle b) Digitally fabricated construction materials with incorporated artificially intelligent design c) Coupled empirical-digital AI workflows with limited testing and unlimited variable possibilities d) Use of ANN, ML and DL in construction materials industry. Enormous benefits of AI can be achieved in construction materials research and industry. Table 3 presents these artificial intelligence paybacks in a concise manner.
Conclusion
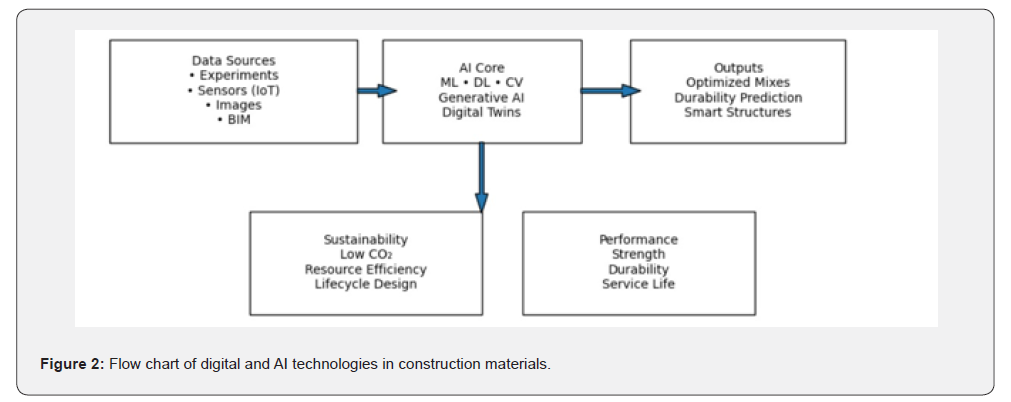
As we move towards the end of 2025, digital and AI driven technology is no longer a secondary tool but a mainstream construction material research and development expertise. The future challenge is not the limitation of technology but the responsibility of humanization for this advanced tool taking into consideration the database validation, accuracy of results and outcomes. If done well, these technologies can make future construction materials much better, smarter and very well aligned with the future demand. A futuristic, smart, sustainable, digital, optimized, innovative, low-carbon and intelligent construction materials industry is destined to evolve. This will meet the growing demand of high-performance construction materials with significantly reduced impact on the environment. A flow chart has been presented in the Figure 2 showing the 2025 perspective for the emergence of smart technology for construction materials through digital modeling and artificial intelligence.
References
- Doran D, Cather B (2013) Construction Materials Reference Book 2nd Routledge.
- Hunt EB (2014) Artificial Intelligence. Academic press.
- Vaughan W (2011) Digital Modeling. New Riders Berkeley CA.
- Batty M (2018) Digital twins. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science 45(5).
- Nematollahi B, Xia M, Sanjayan J (2017) Current Progress of 3D Concrete Printing Technologies. 34th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (ISARC 2017), pp: 260-267.
- Aïtcin PC (2016) Portland cement. Science and Technology of Concrete Admixtures, pp: 27-51.
- Eckel, Clarence E (1922) Cements, Limes, and Plasters. Their Materials, Manufacture, and Properties. John Wiley & Sons. New York Breinigsville.
- Karni J, EY Karni (1995) Gypsum in construction: origin and properties, Materials and Structures. Springer Nature: 92-100.
- Castelvecchi D (2016) Can we open the black box of AI. Nature 538(23): 1-4.






























