A New Korean Highly Concentrated and Cohesive Hyaluronic Acid Gel: Global Facial Rejuvenation In 97 Brazilian Patients
Maria Clara Almeida Issa1*, Carolina Airão Destefani2, Andrea Fogaça3, Eliandre Palermo4 and Maria Claudia Almeida Issa5
1Department of Dermatologist, Medical Doctor, Private office, Brazil
2Department of Dermatology, MSc student at Fluminense Federal University, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
3Department of Dermatology, Private office, Brazil
4Department of Dermatology at Fluminense Federal University, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Submission: February 27, 2023;Published: March 21, 2023
*Corresponding author: Maria Clara Almeida Issa, Department of Dermatologist, Medical Doctor, Private office, Brazil
How to cite this article: Maria Clara Almeida Issa, Carolina Airão Destefani, Andrea Fogaça, Eliandre Palermo and Maria Claudia Almeida Issa. A New Korean Highly Concentrated and Cohesive Hyaluronic Acid Gel: Global Facial Rejuvenation In 97 Brazilian Patients. JOJ Dermatol & Cosmet. 2023; 5(2): 555660. DOI: 10.19080/JOJDC.2023.05.555660
Abstract
Hyaluronic acid-based fillers are the most used dermal fillers today. Due to its safety, several types of products are on the market with different rheological properties. Recently a new Korean filler with high hyaluronic acid concentration was launched in Brazil. The rheological properties of this new filler caught our attention and encouraged its use for global facial rejuvenation. We report our clinical experience with these highly concentrated and cohesive hyaluronic acid gels, which have three different presentations according to the degrees of reticulation. All 97 patients had marked improvement sustained for at least six months of follow-up, with excellent patient satisfaction. Any significant side effect was noticed.
Keywords: Edema, Ecchymosis, Facial Rejuvenation; Shallow furrows; Chin projection
Introduction
Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers are injectable gels indicated for filling, volumizing, or contouring the face, improving folds, and promoting the facial lifting effect [1-6]. They bring immediate, longlasting, and natural-looking [1-5]. In addition to a few side effects, the reversibility of using hyaluronidase is a significant advantage [1].
The face is a dynamic and complex structure [2,3]. Before choosing the best filler for global rejuvenation, it is necessary to evaluate the patient, considering the anatomical layers, the thickness of the tissue, the intensity and strength of the muscular mimetic activity, and the external forces on the region to be treated [1-5]. Different techniques can be used for facial rejuvenation, but for all, we need to consider the facial shape, bone structure, fat volume, ligament, and muscle laxity before deciding the physicochemical characteristics of the HA gel for each area [1-5]. These properties include viscoelasticity, cohesivity, gel particles, and HA concentration [1-5]. The firmness and cohesion of the gel are responsible for the lifting effect [1-5]. A new Korean homogeneous HA gel is a highly concentrated HA (24 mg/ml) with moderate to high cohesiveness for all three presentations, varying the viscoelastic characteristics [4]. We aim to report the clinical results of global facial rejuvenation using these three fillers, positioning the indication for each.
Case Report
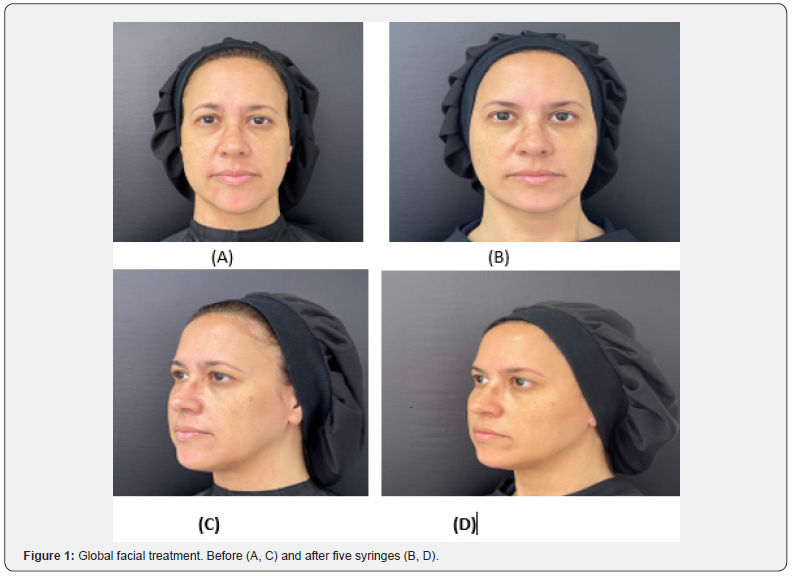
Ninety-seven female patients aged 24-71 were treated with this new filler (e.p.t.q., Jetema®). The three gels, e.p.t.q S500, S300, S100, with the same high concentration (24mg/ml) and particle size, moderate to high cohesiveness, varying only their crosslinking degrees, were used.
The strongest gel with the highest G’ (S500) was used for structuring and defining the lower face and, in some cases, the middle face. The intermediary G’ gel (S300) was mainly used for volumizing and sustaining the middle face, where it was applied in deep fat or the supraperiosteal layer. It was also used to treat the lips, applied above or under the orbicular oris muscle. The gel with the lowest G’ (S100) was used to refine the upper, middle, and lower faces and applied in the subcutaneous layer. All the procedures were performed with a cannula 22G, and the technique, the amount of product, and the anatomical layer varied according to the patient’s evaluation.
Results
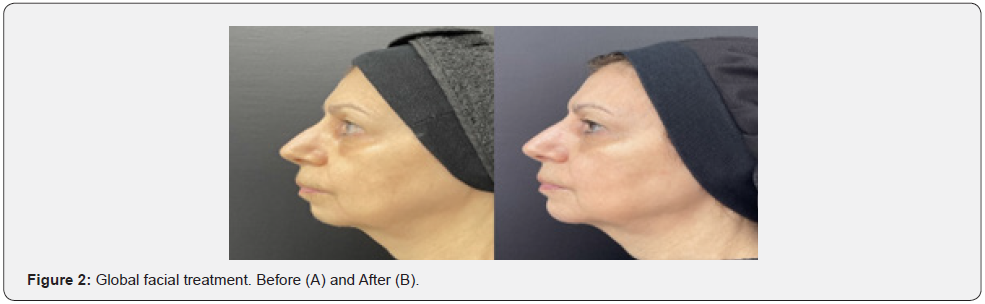
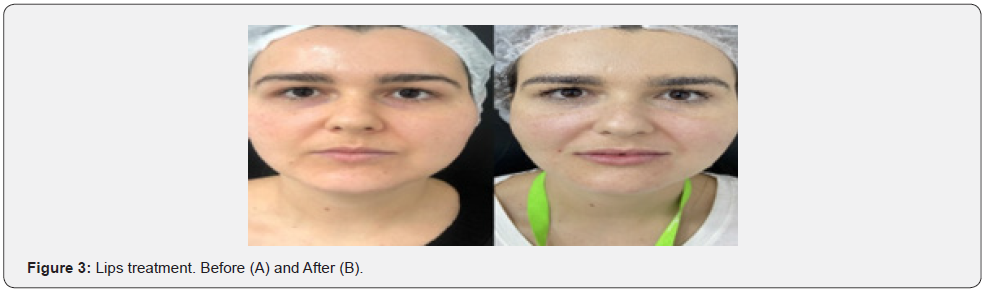
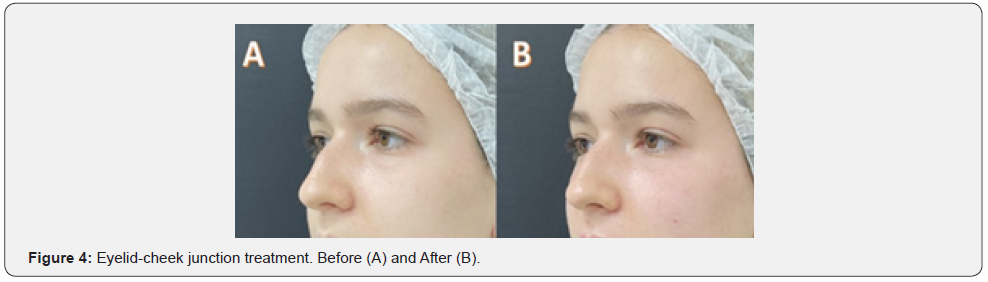
All 97 patients had marked improvement with great satisfaction. The range of syringes used for global facial procedures varied from three to seven (Figure 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D). Evident clinical results included an excellent jawline contour, chin projection (Figure 2 A, 2B), natural-looking with a soft touch of the lips (Figure 3A, 3B), and palpebromalar groove improvement (Figure 4A, 4B). None of the patients had significant side effects. Transitory edema, ecchymosis, and bearable pain were observed. Any late side effects occurred for one year.
Discussion
HA-based fillers available for cosmetic procedures differ in their rheological properties [1-5]. Despite that, there is a dearth of data for all of them, which is challenging for physicians when choosing the appropriate filler [1-5]. With the emergence of new products for clinical use, it is mandatory to interpret the physicochemical properties to place the gel in the correct indication [1-5].
In our clinical experience, S300 was indicated to the middle face and lips due to its intermediary firmness and cohesiveness [3-4]. It is essential to resist the shear forces and compression of the overlying tissue, maintaining the projection and avoiding displacement of the product in the medium and long term [3]. A few amounts of product are necessary for the lips to bring a natural-looking result [1,5]. S500 gel was suitable for structuring and defining the lower face, such as the chin and jaw areas, where a high G’ is necessary to override the bone [3].
Usually, the softest gel is indicated for refinement in the subcutaneous layer. In the upper (temporal region), middle, and lower faces, the S100 was used [3,6]. It is well-indicated to treat superficial wrinkles and shallow furrows [3]. Due to its high cohesiveness and high HA concentration, it differs from other soft gels in the market [4]. It promotes a significant restructuring in the perioral region [3].
The new highly concentrated Korean gel with moderate to high cohesiveness provided marked clinical results with a naturallooking for global facial rejuvenation and great satisfaction in all 97 patients.
References
- Fundarò SP, Salti G, Malgapo DMH, Innocenti S (2022) The Rheology and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Their Clinical Implications. Int J Mol Sci 23(18): 10518.
- Faivre J, Gallet M, Tremblais E, Trévidic P, Bourdon F (2021) Advanced Concepts in Rheology for the Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Soft Tissue Fillers. Dermatol Surg 47(5): e159-e167.
- Heitmiller K, Ring C, Saedi N (2021) Rheologic properties of soft tissue fillers and implications for clinical use. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(1): 28-34.
- Lee W, Yoon JH, Koh IS, Oh W, Kim KW, et al. (2018) Clinical application of a new hyaluronic acid filler based on its rheological properties and the anatomical site of injection. Biomed dermatol 22 (2018).
- De la Guardia C, Virno A, Musumeci M, Bernardin A, Silberberg MB (2022) Rheologic and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Overview and Relationship to Product Performance. Facial Plast Surg 38(2): 116-123.
- Lee W, Oh W, Hong GW, Kim JS, Yang EJ (2019) Novel technique of filler injection in the temple area using the vein detection device. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 72(2): 335-354.






























