Electrocardiogram Manifestations in Traumatic Right-sided Pneumothorax: Case Report
Eduardo Lapa Santos1*, Eduardo Alberto de Castro Roque2, Bianca Dadalto2, Luca T Dompieri3, Maria Amellia Aquino3 and Renato D Lopes4
1Cardiology Unit, Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal do Pernambuco, Brazil
2Hospital Metropolitano, Brazil
3Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Brazil
4Division of Cardiology, Duke University Medical Center, USA
Submission: March 10, 2018; Published: May 09, 2018
*Corresponding author: Eduardo Lapa Santos, Cardiology Unit, Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal do Pernambuco, Av. Prof. Moraes Rego, 1235 - Cidade Universitaria, Recife -PE, 50670-901, Brazil, Tel: +55 81 996864444; Email: eduardolapa@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Eduardo Lapa Santos, Eduardo Alberto de Castro Roque, Bianca Dadalto, Luca T Dompieri, et al. Electrocardiogram Manifestations in Traumatic Right-sided Pneumothorax: Case Report. J Cardiol & Cardiovasc Ther. 2018; 10(3): 555789. DOI: 10.19080/JOCCT.2018.10.555789
Abstract
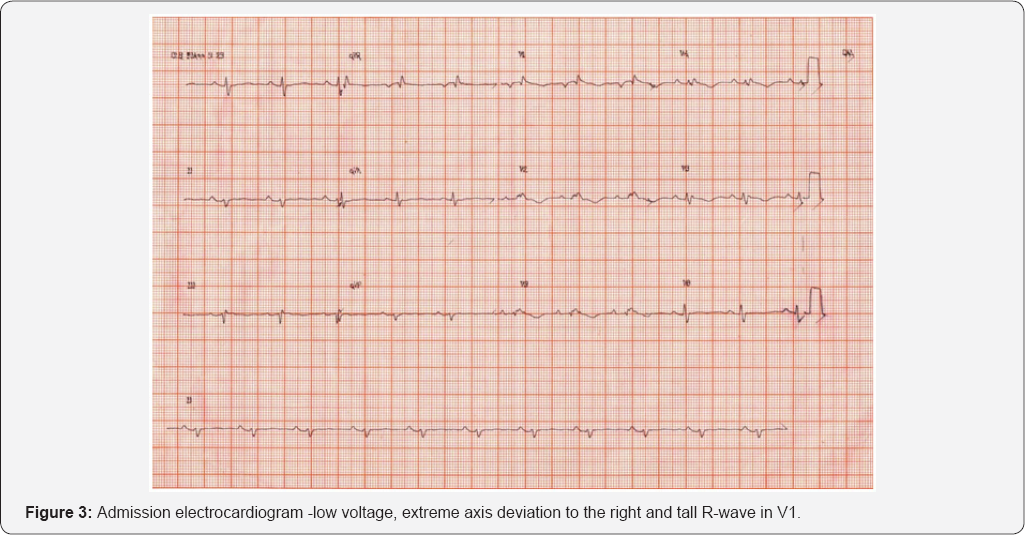
This report describes a case of a patient with right-sided pneumothorax presenting with classic electrocardiographic findings such as low voltage, extreme axis deviation to the right and tall R-wave in V1 suggesting right-ventricle overload. Drainage and aspiration were performed stabilizing the patient.
Keywords: Pneumothorax; Right-sided pneumothorax; Electrocardiography
Introduction
Electrocardiogram (ECG) findings such as right axis deviation, QSR abnormalities, T-wave inversions and ST-segment alterations [1] may lead to misdiagnosis of pneumothorax [2]. We describe a case of pneumothorax presenting with changes in ECG.
Case Report
A 74-year-old male was admitted to the emergency department with chest pain 72 hours after a fall. The patient had a past medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and smoking (5pack/year).
At admission, the patient was in antalgic position and with shortness of breath. Examination revealed blood pressure of 148/90mmHg, cardiac frequency of 66beats/min, oxygen saturation of 88% and decreased breath sounds at right hemi- thorax.
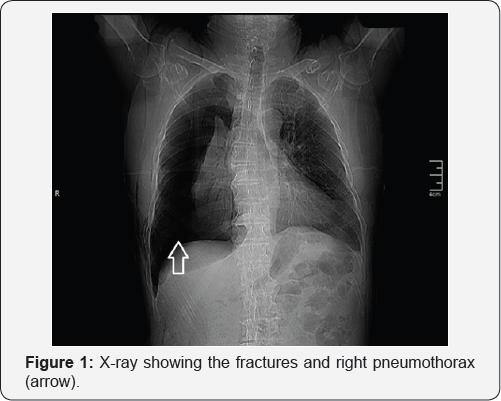
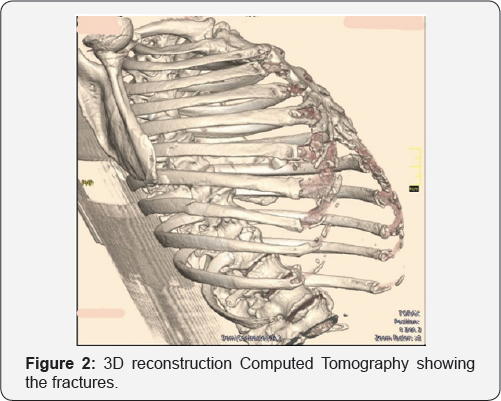
Admission X-ray and computed tomography showed fracture extreme axis deviation to the right and tall R-wave in V1 suggesting at the sixth, seventh and eighth right costal arches with significant right-ventricle overload (Figure 3). right pneumothorax (Figure 1 & 2). ECG showed low voltage,
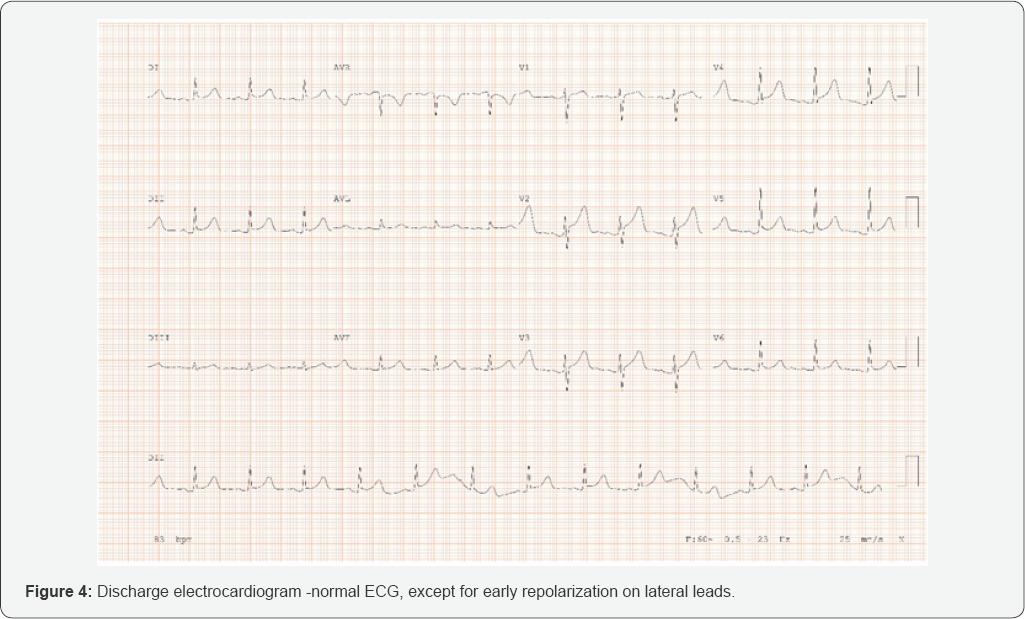
Drainage and continuous aspiration were performed for 48 ECG, except for early repolarization on lateral leads (Figure 4). hours; discharge after 72 hours of hospitalization and normal ECG, except for early repolarization on lateral leads (Figure 4).
Discussion
The main ECG findings in pneumothorax cases include decreased QRS complex amplitude, QRS axis deviation, electrical alternans, reduced precordial R-wave voltage and precordial T-waves [3], being present in approximately 25% of the cases [1,2]. ST-segment deviations are also rare findings in patients with pneumothorax [2,4].
The potential mechanisms behind the ECG changes in patients with pneumothorax are: the cardiac rotation around its axis; right ventricular dilatation due to increased pulmonary artery pressure; cardiac displacement; and air in the thoracic cavity acting as an insulator [3,5].
Depending on the size, amount of tension and the side involved on pneumothorax, the magnitude of ECG changes can vary substantially [3]. In left-sided pneumothorax, the most common findings include abnormal axis deviation and T-wave inversion [2]. Right-sided often include reduced QRS voltage and QRS axis changes [3].
Krenke et al. [2] showed that in right-sided pneumothorax the QRS axis deviation is mainly to the right without exceeding 30o and the QRS amplitude in V5 and V6 leads is increased [2].However, in the case described, there is an extreme axis deviation to the right and decreased voltage in all leads, including V5-V6.
Conflict of Interest
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
References
- Alzghoul B, Innabi A, Shanbhag A, Chatterjee K, Amer F, et al. (2017) Iatrogenic right-sided pneumothorax presenting as ST-segment elevation: a rare case report and review of literature. Case Reports Crit Care 2017: 3291751.
- Krenke R, Nasilowski J, Przybylowski T, Chazan R (2008) Electrocardiographic changes in patients with spontaneous pneumothorax. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(Suppl 6): 361-373.
- Pollack ML (2006) ECG manifestations of selected extracardiac diseases. Emerg Med Clin North Am 24(1): 133-143.
- Shiyovich A, Vladimir Z, Nesher L (2011) Left spontaneous pneumothorax presenting with ST-segment elevations: a case report and review of the literature. Hear Lung 40(1): 88-91.
- Yeom SR, Park SW, Kim YD, Ahn BJ, Ahn JH, et al. (2017) Minimal pneumothorax with dynamic changes in ST segment similar to myocardial infarction. Am J Emerg Med 35(8): 1210.e1-1210.e4.






























