Exploring a New Extra Point for Subacute Cough: a Case Report
Tong-Zheng Hong*
As-You-Wish Healthcare Institute, Taiwan
Submission: September 15, 2017; Published: September 26, 2017
*Corresponding author: Tong-Zheng Hong, As-You-Wish Healthcare Institute, MS in Acupuncture awarded by National University of Health Sciences in IL, Taiwan, Email: ty8876@ms24.hinet.net
How to cite this article: Tong-Zheng Hong. Exploring a New Extra Point for Subacute Cough: a Case Report. J Complement Med Alt Healthcare. 2017; 3(4): 555619. DOI:10.19080/JCMAH.2017.03.555619
Abstract
To observe the therapeutic effects of this brand new extra point Gangshui (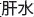 ) for sub acute cough, the combination of points on the traditional Fourteen Channels with this new extra point Gangshui (
) for sub acute cough, the combination of points on the traditional Fourteen Channels with this new extra point Gangshui (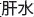 ) was conducted. On the other hand, the three level criteria were established for effect evaluation in this case. The patient's cough s 80% was cured with the first treatment, and no more treatments were given on the request of the patient after the second treatment. The result showsthisnew extra point Gangshui (
) was conducted. On the other hand, the three level criteria were established for effect evaluation in this case. The patient's cough s 80% was cured with the first treatment, and no more treatments were given on the request of the patient after the second treatment. The result showsthisnew extra point Gangshui (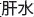 ) could work well with three traditional points on Channels for sub acute cough, and suggests this brand new extra point deserves much more concerns whether it remains effective alone for diseases related to Kidney quit deficiency and Liver quit stagnation patterns in the future.
) could work well with three traditional points on Channels for sub acute cough, and suggests this brand new extra point deserves much more concerns whether it remains effective alone for diseases related to Kidney quit deficiency and Liver quit stagnation patterns in the future.
Keywords: Subacutecough; Acupuncture treatment; Extra point
Introduction
From the perspective of conventional medicine, cough one of the major symptoms of lung disorder, may occur in the diseases such as upper respiratory infection, acute bronchitis, peruses, tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, pulmonary and pneumonia. Quality of life can be impaired by unexplained repetitively occurring chronic cough significantly [1], while cough is a problem disruptive to daily life as long as it lingers for weeks. Based on the duration, cough lasting for less than 3 weeks is classified as acute self-limiting cough, and chronic persistent cough, which can usually last for more than 8 weeks. When cough lasts for around 3-8 weeks, it's categorized as sub acute cough [2]. Acupuncture treatment can improve symptoms of cough [3] and the results of research also show this therapy stimulates the immune system for infections [4]. Signs and symptoms in Traditional Chinese medicine (hereafter TCM) are broader than those in Western medicine. In general TCM physicians usually do not follow typical Western pathological classifications of diseases, but rather rely on the patterns individualized by the imbalance of Yin and Yang, Qi, Blood, and body fluids in the body [5]. In clinical practice, the principles of selecting points for treatments refer mainly to the channels relating to Zhang and Fu, interiorly-exteriorly related channels, Ying-Yang pairing channels, the Yuan-Source points, the Mother-Child points, the Five-Shu points, Back-Shu points, and the Front-Mu points, etc. Extra points though not on the traditional Fourteen Channels can be often selected for the indications as the Fourteen Channel points. For example, Taiyuan (M-HN-9) can be used for one-sided headache as GB-20 when the pathogen is Wind. One of the reasons why extra points is named extra is simply because these points are not incorporated into the traditional Fourteen Channels, on which recognized 361 common points are located. However, some extra points like hinting (M-HN-3) are located on the Governing vessel and Taiyuan (M-HN-9) on the Santiago channel.
Case Presentation
The female patient is 45 who had been coughing for at least three weeks before the treatments. The chief complaints were shortness of breath on exertion, coughed quite often at night, and low back soreness with numbness in the right hand occasionally The patient also mentioned she felt chilled, cold limbs, poor digestion, itchiness in the throat, and didn't have the desire to drink water. When examined, she said she felt asthenia, tired and a little bit headaches on the lateral sides.
Differential diagnosis
Four diagnosis methods, Looking, Hearing, Asking and Feeling were conducted on the patient for the whole picture of the body for the objective and synthetic diagnosis before treatments.
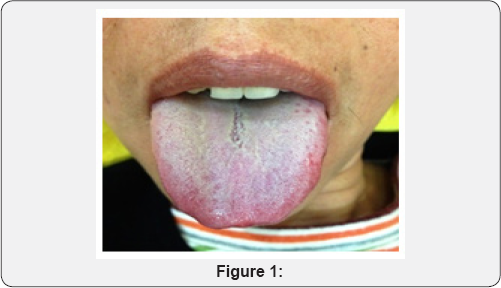
Looking: In Figure 1 the information of Looking indicated slight yellow & pale complexion, sticky coating in the lower Jiao, red spots at the tip and the left side, slight yellow on the right side and slightly purple on the lateral sides of the tongue. A little bit swollen with crack in the middle of the tongue.
Hearing: When the patient was questioned, her voice was weak and breathing could be heard with heaviness in the chest.
Asking: The patient responded she felt irritated easily, failed to sleep soundly and always slept dream-disturbed. She also felt hypochondriac stabbing pain when in bad mood and had clear frequent urination.
Feeling: Pulse checking indicated weak and wiry.
Diagnosis and Prescriptions
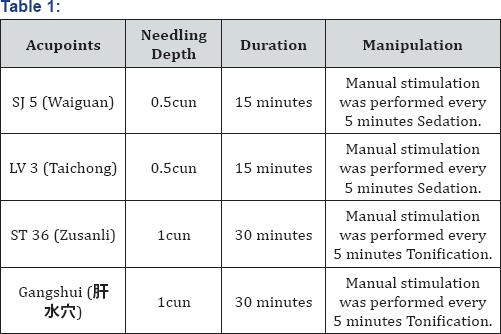
The information that weak voice, weak pulse, tiredness and pale complexion indicated Lung Qi deficiency which obstructed Qi flow leading to cold limbs; hypochondriac pain, red spots and slight purple on the lateral sides of the tongue and wiry pulse presented Live Qi stagnation. White coating in this case refers to coldness and Qi deficiency. On the hand symptoms such as low back soreness, cold limbs, clear urination and shortness of breath on exertion presented Kidney Qi deficiency resulted from Lung Qi obstructed in this case. The key symptoms in this case were shortness of breath on exertion and low back soreness, which can be presented in both Lung Qi deficiency and Kidney Qi deficiency. Low back soreness and frequent cough at night specifically verified the pattern of Kidney failing to receive Qi with Kidney Qi deficiency. Furthermore, hypochondriac stabbing pain when in bad mood indicated LV Qi stagnation. Both BL 13 (Feishu) and CV 22 (Tiantu) are commonly selected as major points for cough [5], but in this case ST 36 (Zusanli), the He-sea point of the Stomach channel that promotes spleen and stomach to notify the Lung with Qi and LV 3 (Taichong) for spreading stagnated Liver Qi were selected. Dead man, et al. state KD 7 (Fuliu) has an application in regulating Lung with the virtue of pre-heaven Qi in lower Jiao, and water passage by restoring Kidney Qi [6]. In the meantime, Kidney failing to receive Qi, as pointed out above, is the key to treating cough in this case, so the point that can stimulate Lung Qi descending functions and regulates water passage plays a key role [6]. KD 7 (Fuliu) is often selected by the author in the past experiences for the Kidney Qi deficiency pattern to notify Kidney Qi. However this extra point was selected in lieu of KD 7 (Fuliu) in this case in order to notify Kidney Qi and disperse stagnated LV Qi at the same time. When it comes to the treatment principle of the less needling, the less pain, of the author, the points above mentioned, except LV 3 (Taichong) and ST 36 (Zusanli), were not taken into consideration for convenience and safety. Instead, a combination of SJ 5 (Waiguan) for expelling Wind and releasing the exterior, LV 3 (Taichong) for dispersing stagnated Liver Qi, and ST 36 (Zusanli) for supporting the correct Qi and resolving dampness ,and the new extra point Gangshui( )for restoring Kidney Qi for descending Lung Qi was selected as shown in Table 1 for this case.
)for restoring Kidney Qi for descending Lung Qi was selected as shown in Table 1 for this case.
Introduction to extra point Gangshui ( )
)
The new extra point is found and named on the basis of clinical experiences. The notion presented in Spiritual Axis of Huang Di Nei Jing states both Liver and Kidney originate from the same source, so the name Gangshui point ( ) is given to this extra point, considering the actions related to Kidney and Liver. Gan (
) is given to this extra point, considering the actions related to Kidney and Liver. Gan ( ) represents Liver, and shui (
) represents Liver, and shui (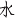 ) refers to Kidney, which is Water in the five elements theory. It is found when the patients with the patterns of Kidney Qi deficiency or Liver Qi stagnation are palpated, the area of this extra point tenders badly. Clinical experiences indicate the following information about this extra point:
) refers to Kidney, which is Water in the five elements theory. It is found when the patients with the patterns of Kidney Qi deficiency or Liver Qi stagnation are palpated, the area of this extra point tenders badly. Clinical experiences indicate the following information about this extra point:
Location: The extra point is located on the medial head of the muscle gastronomies. At the junction of the lines drawn 3cun inferior to SP 9 (Yinlingquan) or 12. Cun superior to KD 3 (Taxi) and 3cun posterior to the medial crest of the. Tibia, as shown in Figure 2.
Actions: Notify Kidney Qi and disperse Liver Qi.
Indications: Foot pain, soreness and weakness of the low back, cough, asthenia, chillness, insomnia, and frequent urination.
Needling: Perpendicular insertion 1~1.5cun.
Criteria for treatment evaluation
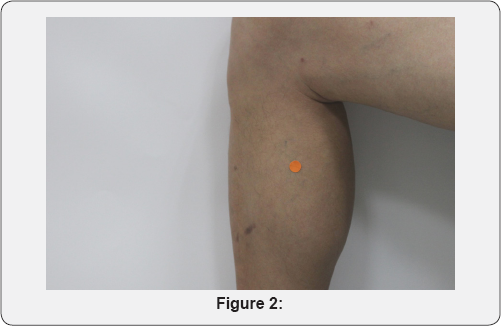
For the therapeutic effect evaluation the three-level criteria focusing on cough were set as shown in cc Table 2.
The results
With the first treatment, the patient's experienced a great result, showing Improved on the criteria. She stated 80% cough disappeared, felt more energetic and could sleep better Digestion, low back soreness and shortness of breath on exertion were also improved a lot. The same prescription was given for the second treatment two days later after the first treatment. The patient responded over the phone she had no cough, and didn't need treatments anymore because the 95% symptoms had disappeared.
Discussion
An experienced TCM practitioner can only rely on four skills for diagnosis and prescriptions, compared to Western medicine physicians. In terms of diagnosis and treatment, how to identify the key symptoms related to Qi deficiency, specifically Kidney Qi deficiency and Liver Qi stagnation patterns, such as low back soreness, hypochondriac pain, and shortness of breath on exertion in this case, plays an important role. The 16 clinical cases show in Figure 3 how this extra point was used alone or in combination with traditional channel points for the treatments. The literature of oxygen metabolism and the theory of channels and Qi in the channels highlight that both Qi and oxygen have informational, material, functional features, bearing high similarity in physiological functions and pathological reactions [7]. When oxygen in the blood is below the normal level, people may experience either breathing or circulation problems with signs and symptoms, such as wheezing, frequent cough, choking sensation, shortness of breath while resting, and shortness of breath after physical activity [8]. One of the functions of the kidney is to set the hematocrit at a normal value of 45% to maximize oxygen delivery [9]. The rising formation of red blood cells, which are promoted by the hormone Erythropoietin (EPO) produced by the kidney, increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. However, it is stated that the production of erythropoietin is determined by tissue oxygen pressure. In other words the kidney has much to do with the oxygen circulation [10]. In the author's viewpoint, this suggests that Qi equals oxygen and Kidney is the key to produce Qi. The personal experiences show KD 7 (Fuliu) is the best point for issues related to Kidney Qi deficiency. For example, patients with coughing lasting for over 10 days could get great improvements in less than 3 treatments in combination with other points. This extra point also resembles the efficacy as KD 7 (Fuliu) in this case. Itchiness in the throat indicated the exterior pathogenic factor Wind still remained in the body and bilateral headaches on Gall Bladder Channel should be taken into consideration. SJ 5 (Waiguan) in this prescription, which is the confluent point of the Yang Linking vessel, was important since it's presented in Classic of Difficulties that severe chills and fever occur when the Yang Linking vessel is diseased [6]. The use of Gangshui point ( ) alone could work for chillness and frequent urination, which were caused by Kidney Qi deficiency. To some extents, it is more effective in conjunction with traditional channel points for the other issues, in which Liver Qi stagnation is involved. The notion is presented in the Essential Questions of Yellow Emperor's Inner Classic (Huang Di Nei Jing) that "Waist is the residence of Kidney.” This notion explains why 4 out of 16 cases related to low back could be treated with this extra point in conjunction with traditional channel points. Whether or not the extra point can be as effective alone as traditional points on the Fourteen Channels for treatment needs more attentions. In the meantime, it also remains uncertain and deserves furthermost-disciplinary research if the extra point can be used in conjunction with other traditional Fourteen Channel points for better results in the specific TCM patterns. The results of the literature review show there are no points on the 14 traditional channel or extra points located as this extra point [11,12]. The location of Shuiquan point (
) alone could work for chillness and frequent urination, which were caused by Kidney Qi deficiency. To some extents, it is more effective in conjunction with traditional channel points for the other issues, in which Liver Qi stagnation is involved. The notion is presented in the Essential Questions of Yellow Emperor's Inner Classic (Huang Di Nei Jing) that "Waist is the residence of Kidney.” This notion explains why 4 out of 16 cases related to low back could be treated with this extra point in conjunction with traditional channel points. Whether or not the extra point can be as effective alone as traditional points on the Fourteen Channels for treatment needs more attentions. In the meantime, it also remains uncertain and deserves furthermost-disciplinary research if the extra point can be used in conjunction with other traditional Fourteen Channel points for better results in the specific TCM patterns. The results of the literature review show there are no points on the 14 traditional channel or extra points located as this extra point [11,12]. The location of Shuiquan point ( ) in Tung's orthodox acupuncture points is close to this extra point, but not exactly the same. The literature shows Shuiquan point (
) in Tung's orthodox acupuncture points is close to this extra point, but not exactly the same. The literature shows Shuiquan point ( ) point is located 2 cun posterior to medial malleolus and 11cun superior to Taixi (KD 3) [12].
) point is located 2 cun posterior to medial malleolus and 11cun superior to Taixi (KD 3) [12].

Conclusion
The extra point Gangshui (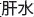 ), like other extra points, indeed works well with traditional points on the Fourteen Channels for sub acute cough in this case. There is no doubt this extra point could be also selected alone for the diseases related to Kidney Qi deficiency pattern. The development of the extra point in this case is based on the author's clinical experiences, so there has not beenenoughscientific evidence explaining if this extra point can be as effective as traditional channel points in treating specific health issues. In addition, the mechanism of this extra point still remains unknown. In other words, more experiments from the aspects of anatomy, neurology, and biology are requested to confirm the indications of this extra point.
), like other extra points, indeed works well with traditional points on the Fourteen Channels for sub acute cough in this case. There is no doubt this extra point could be also selected alone for the diseases related to Kidney Qi deficiency pattern. The development of the extra point in this case is based on the author's clinical experiences, so there has not beenenoughscientific evidence explaining if this extra point can be as effective as traditional channel points in treating specific health issues. In addition, the mechanism of this extra point still remains unknown. In other words, more experiments from the aspects of anatomy, neurology, and biology are requested to confirm the indications of this extra point.
References
- Gibson P, Wang G, Garvey LM (2016) Treatment of Unexplained Chronic Cough: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel. Report. Chest 149(1): 2744.
- Chung KF, Pavord ID (2008) Prevalence, pathogenesis, and causes of chronic cough. Lancet 371(9621): 1364-1374.
- Zhang RY, Wang D, Wu JP, Li XL, Li CX, et al. (2016) Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials for Acupuncture Treatment of Pneumoconiosis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 41(2): 163-168.
- Xu BQ (1986) Experimental studies on acupuncture treatment of acute bacillary dysentery-the role of humoral immune mechanism. In: Zhang XT (Ed.), Researches on acupuncture-moxibustion and acupuncture- anesthesia. Science Press, Beijing, China, pp. 573-578.
- Acupuncture and Moxibustion Therapies for Coughing.
- Deadman P, Al-Khafaji M, Baker KA (2012) Manual of acupuncture. Journal of Chinese Medicine Publications, England.
- Liang Z, Huang B, Chen J (2012) Oxygen metabolism and meridian qi. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 32(2): 183-186.
- Low Blood Oxygen and How it Affects the Body.
- Donnelly S (2001) Why is erythropoietin made in the kidney? The kidney functions as a critmeter. Am J Kidney Dis 38(2): 415-425.
- Nabili SN, Erythropoietin (EPO, The EPO Test).
- Wang FT (1999) Atlas of New Points and Extra Points. Scientific and Technical Documentation Press, Beijing, China.
- http://catalog.digitalarchives.tw/item/00/1d/69/1f.html






























