Examination of Immunological Effects of Homeopathic Escherichia coli extract (E. coli extractum 4x-8x) on Bladder Epithelial Cells
Dieter Sonntag*
Sanum Kehlbeck GmbH & Co. KG, Germany
Submission: January 31, 2017; Published: February 22, 2017
*Corresponding author: Dieter Sonntag, Head of Medical and Scientific Affairs, Sanum Kehlbeck, GmbH & Co. KG, 27318 Hoya, Germany, Tel: 49042519352332; Fax: +49042519352290; Email:dietersonntag@sanum.com
How to cite this article: Dieter S. Examination of Immunological Effects of Homeopathic Escherichia coli extract (E. coli extractum 4x-8x) on Bladder Epithelial Cells. J Complement Med Alt Healthcare. 2017; 1(4): 555566. DOI:10.19080/JCMAH.2017.01.555566
Abstract
The homeopathic extract E. coli extractum (Sanukehl®Coli) of gram-negative Escherichia coli bacteria in the potency 6Xis applied in treating bacterial infections, especially of chronic cystitis. As a cause of chronic cystitis, intracellular infections are discussed. This study analyzes the in vitro effect of E. coli extractum 4X-8X in T 24 human bladder cancer cells (T24) on the release of proinflammatory TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8 and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10.TNF-α and IL-8 are responsible for activation and migration of granulocytes into the tissue, a reaction of the innate immune system. Furthermore, the function of IL-6 goes even further It stimulates, inter alia, differentiation factors of B-cells to antibody-producing plasma cells, and consequently the humoral immune system. IL-10 is one of the anti-inflammatory cytokines.The results of this study show, that the homeopathic preparation of E. coli extractum can modulate the release of cytokines of the innate and humoral immune system.
Keywords: Cystitis; Cytokines; E. coli extractum; 4X-8X; Human bladder epithelial cells; Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Introduction
The urinary tract is extremely susceptible to infection by different pathogens. Most E. coli strains are facultative pathogenic gram-negative bacteria in cystitis, which could also exist intracellularly [1,2]. In homeopathic therapy E. coli extractum (DSMZNr. 14345) is used to treat cystitis [3], due to its ability to activate the innate immune system of the bladder and, in particular, of the bladder epithelial cells (BECs). The activation of the innate immune system to initiate the healing process is mediated e.g. by the binding of uropathogenic bacteria to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) [4]. Studies on TLR4 signaling in monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells have revealed that the binding of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to the TLR4 receptor triggers a signaling cascade, resulting in the activation of nuclear factor- kB (NF-kB) which in term regulates the expression of several immunomodulatory cytokines, like TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 [5-7]. TNF-α regulates the induction of apoptosis in epithelial cells, and is involved in the defense of intracellular pathogens which in turn leads to an exfoliation of diseased surface cells [8].
In this study, we analyzed the effects of the homeopathic E. coli extract in the potency 4X-8X and present here the data for potency 6X on the cytokine release in vitro, on both, non-inflamed, immunologically inactive, and on inflamed, immunologically active T24 human bladder cancer epithelial cells. In this cell culture system, the non-inflamed T24 cells are defined by the cells being cultivated without LPS. Inflamed cells, in contrast, are cultivated in the presence of LPS.
Cells were treated with different concentrations of the test substances for 24 hours, followed by an MTT assay (Sigma Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany). Only living cells can convert yellow MTT reagent to purple formazan by mitochondrial reductase enzymes. The absorbance of formazan was measured at 550nm. At 24h none of the tested concentrations were cytotoxic.
Discussion and Conclusion
In non-inflamed cells (absence of LPS), E. coli extractum6X increased the expression of IL-6 and IL-8 significantly. Also, a significant TNF-α release was also visible in T24 cells (Figure 1). A concentration dependency was detectable (data not shown). In inflammed cells (presence of LPS) E. coli extractum 6X slightly decreased IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α expression in presence of LPS, significantly (Figure 2). IL-10, the anti-inflammatory cytokine [9], was undetectable in the supernatants of T24 bladder cells.

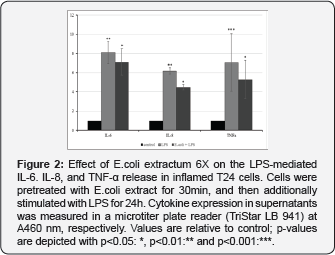
These results indicate, that homeopathic E. coli extractum 6X has an immunomodulating effect. In inflamed T24 cells, the release of proinflammatory cytokines is reduced while it is stimulated in non-inflamed, immunologically inactive, cells. This result supports the observation made in the therapeutic application, that E. coli extractum 6X reduces an existing inflammatory process. In contrast, in chronic infections caused,This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Licens inter alia, by intracellular E. coli strains, where immunological defense is not active, the E. coli extract stimulates the immune system by cytokine production. This may be a part of the mechanism of action that supports the healing process, which should be investigated in further studies.
Acknowledgement
The author would like to acknowledge CONVIDIA clinical research GmbH, Von-Steuben-Strasse 10, 48143 Muenster, Germany, for their collaboration in the manuscript development, and VivaCell Biotechnology GmbH, Ferdinand-Porsche-Str. 5, 79211 Denzlingen, Germany, for conducting the experimental investigation.
References
- Rosen DA, Thomas MH, Walter ES, Peter AH, Scott JH (2007) Detection of intracellular bacterial communities in human urinary tract infection. PLoS Med 4(12): e329.
- Hummers-Pradier E, Ohse AM, Koch M, Heizmann WR, Kochen MM (2005) Management of urinary tract infections in female general practice patients. Fam Pract 22(1): 71-77.
- Heidl R (2007) Statistische Auswertung einer Anwendungsbeobachtung mit der Präparateserie Sanukehl Coli. Sanum Post 79: 14-20.
- Reygaert WC (2014) Innate Immune Response to Urinary Tract Infections Involving Escherichia coli. J Clin Cell Immunol 5: 280.
- Backhed F, Söderhäll M, Ekman P, Normark S, Richter-Dahlfors A (2001) Induction of innate immune responses by Escherichia coli and purified lipopolysaccharide correlate with organ- and cell-specific expression of Toll-like receptors within the human urinary tract. Cell Microbiol 3(3): 153-158.
- Abdel-Mageed AB, Bajwa A, Shenassa BB, Human L, Ghoniem GM (2003) NF-KB-dependent gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines in T24 cells: possible role in interstitial cystitis, Urological Research 31(5): 300-305.
- Masmudur MR, Grant M F (2006) Modulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor by Microbial Pathogens. PLoS Pathogens 22(2): e4.
- Polunovsky VA, Wendt CH, Ingbar DH, Peterson MS, Bitterman PB (1994) Induction of endothelial cell apoptosis by TNF alpha: modulation by inhibitors of protein synthesis. Exp Cell Res 214(2): 584-594.
- Mosser DM, Zhang X (2008) Interleukin-10: new perspectives on an old cytokine. Immunol Rev 226: 205-218.






























