Discussion on Water Pollutant Discharge Standards System in China during 1984-2019
Lu Qin1,2*, Weili Ye2*, Songjun Guo1*, Rongzhi Chen3 and Wenjing Zhang2
1 School of Resource, Environment and Materials, Guangxi University, China
2Research Center for Total Amount Control and Emission Trading, Chinese Academy for Environmental Planning, China
3 College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Submission: March 16, 2020; Published: April 01, 2020
*Corresponding author: Lu Qin, School of Resource, Environment and Materials, Guangxi University, 530004, China & Research Center for Total Amount Control and Emission Trading, Chinese Academy for Environmental Planning, Beijing, China Weili Ye, Research Center for Total Amount Control and Emission Trading, Chinese Academy for Environmental Planning, Beijing, China Songjun Guo, College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19A, Beijing 100049, China
How to cite this article: Lu Q, Weili Y, Songjun G, Rongzhi C, Wenjing Z. Discussion on Water Pollutant Discharge Standards System in China during 1984- 014 2019. Int J Environ Sci Nat Res. 2020; 24(1): 556128. DOI: 10.19080/IJESNR.2020.24.556128
Abstract
As an index of the quality of water environment, water pollution discharge standards play an important role in the treatment of point source pollutants. Given the perspective of the technology and economic feasibility, this study for the first time, discusses the water pollutant discharge standards system (WPDSS), management of discharge standard limits and the problem of water pollution discharge standards in China. Accordingly, the current status of water pollution discharge standards in China is clarified, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. At the same time, it provide a reference for the revision and formulation of the discharge standards.
Keywords: Water pollutant discharge standards system; National discharge standards system; Local discharge standards system
Introduction
Water pollution discharge standards represent are the various forms of legal value and requirements stipulated to of pollutant discharge in the point source water pollutant discharge and requirements stipulated [1]. There is a large body of literature on the water pollution discharge standards of in China has been focused on the analysis and discussion of a certain type of discharge standards [2-5], however, there was no researches reported the discharge standards comprehensively in a consecutive period. Herein, in this study we integrated on the introduction and discussion of water pollutant discharge standards system (WPDSS) in China, and focused on characteristic and problems of discharge standards from 1983-2019. And, the water pollution discharge standards have a good technology and economic feasibility for all the provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities and industries; it is good references for formulating and improving the discharge standards.
Discharge Standards Situation
Discharge standards system
As shown in figure 1, WPDSS include National Discharge Standards System (NDSS) and Local Discharge Standards System (LDSS) in China. The NDSS represents the most basic requirement that all pollution enterprises should meet after certain efforts in a certain period of time under certain economic, technological and management conditions [6]. On the basis of NDSS, the LDSS is determined according to the local economy, technical management level and requirement of regional water quality improvement [7]. It is a supplement or improvement to the NDSS, which is generally required to be stricter than the NDSS [8,9].
According to the pollution source industry covered by the standards, WPDSS could be divided into integrated discharge standards and industry discharge standards (Figure 1). Industry discharge standards are applicable to specific industry, such as paper industry water pollutant discharge standards, textile industry water pollutant discharge standards, etc. [10,11]. Integrated discharge standards are used to manage and control all sources of pollution in industries other than those for which discharge standards have not been established [12]. On the national level, integrated discharge standards and industry discharge standards are not cross-enforced, those industries will not implement integrated discharge standards unless there is no industry discharge standards for it [13].
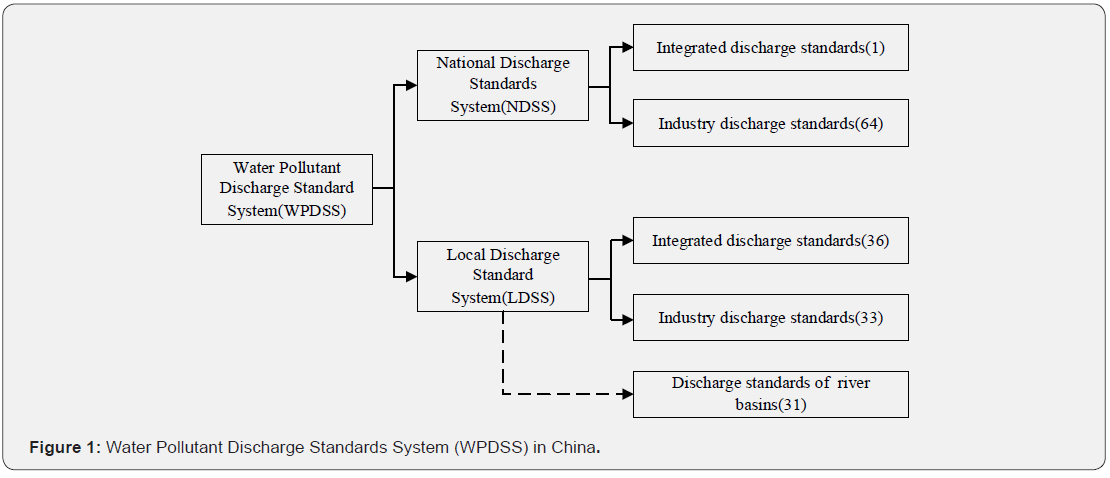
In recent years, many provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities in China have established discharge standards of river basins actively. This is a new serial of discharge standards, with limitations determined by water quality improvement target for river basin and region, regardless of the technical and economic feasibility in the single industry. Discharge standards of river basins established by local government have not been included in the WPDSS officially at present.
By the end of 2019, there were 64 industry discharge standards and 1 integrated discharge standard in NDSS, and 33 industry discharge standards and 36 integrated discharge standards in LDSS. Besides this, there were 31 more discharge standards of river basins established by local governments in Shandong, Hebei, Henan, Guangdong, Fujian, Shaanxi and Heilongjiang Province.
The characteristic of WPDSS
Technical and economic feasibility is the main factor for the limitations both in NDSS and LDSS since the year of 2008, while considering neither the direction of wastewater discharge nor the environmental function areas. It avoided the degradation of water environment quality caused by the lax pollution discharge limits in low functional areas, and also reflected the fairness and justice of the standards for enterprises from the same profession.
Most of the integrated discharge standards are divided into different grades according to the different directions for waste water discharge and the functional requirements of different river basins both in national and local level. Some provinces such as Fujian, Jiangxi and Shanxi have formulated local discharge standards based on water quality improvement requirements by river basins, which initially reflects the idea of environmental management changing from regional management to watershed management.
The pollutants are divided into two categories according to their toxicity and hazard degree [14,15]. The concentration limits of the first category of pollutants is relatively strict, and all of them are sampled and monitored at the outlet of the workshop or the outlet of the workshop treatment facility [16]. While, the second category of pollutant is sampled and monitored in the total outlet of a unit, and the discharge concentration is relatively loose, which reflects the idea of classification management according to the toxicity and hazard degree of pollutants [17].
In addition to the management of concentration discharge limit, some industrial discharge standards would also require limitations for the maximum displacement per unit product, which is convenient for the total amount control of some major pollution sources. The standards issued after 2008 redefined the displacement for enterprises, set the reference displacement, defined the compliance determination clause, and refined the provisions for the implementation and supervision of standards [18]. They set up a “special water pollutant discharge limitation” on land requiring special protection measures. These lands usually have the characteristics of large development density; weaken environmental carrying capacity, small environmental capacity, more fragile ecological environment and serious environmental pollution. The specific geographical scope and time of implementation shall be prescribed by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, China or provincial government [10].
The Problems and Discussion of WPDSS
Problems and discussion of NDSS
Firstly, some national standards in China are historical and have not revised for a long time, so that technical content is difficult to adapt the new situation. The body of national standards has not changed in recent years, but the terms in the standards are slightly changed for various reasons, however, this part of the changes are not included in the statistics. In general, the standard update quite slow, and relatively old. By the end of 2019, among the 65 sets of current national discharge standards, 60 were issued more than five years ago, accounting for 92.31%; moreover, 33 were issued more than 10 years ago, accounting for 50.77%. As the rapid development of technology, the technical contact of standards does not adapt to the situation, and hence the control level is backward, cannot supervise the progress of the industry technology, and lags behind the actual demand of environmental management.
Secondly, there are few industrial discharge standards, in which the integrated discharge standards cover a wide range of areas. The standards system before 2002 was established based on the comprehensive pollutant discharge standard and supplemented by the industrial pollutant discharge standards [19]. However, the implementation of integrated discharge standard is not efficient, and it lacks pertinence to the characteristic pollutants of many industries.
Thirdly, there is a decoupling relationship between discharge standards and environment quality standards of water [20]. Formulation of the limits in NDSS takes into account the technical level of the whole country and must be loose for some regions. The water environmental capacity (EC) and resources between south and north of China is unevenly distributed in China. For instance, the water quality requirements can be meet in the south regions, but may well exceed environmental capacity in the north regions under the same discharge standard, which make it difficult to meet local environmental management needs, such as regions with water shortages or relatively high concentrations of pollutant discharge.
Problems and discussion of LDSS
The framework of LDSS basically adheres to the national integrated and industrial discharge standards system, which is difficult to avoid the defects of NDSS. Some provinces in China have developed discharge standards based on river basins or even smaller unit in a basin, such as Hebei, Henan and Shandong provinces, in which, it reflects the transformation of environmental management from regional management to river basin management. However, the decoupling problems in discharge standard limits and water environmental quality standards has not been solved. The establishment of regional integrated discharge standards is difficult to achieve results, if water pollution control does not respect the characteristics of water resources. Therefore, the above standards fail to establish a connection between the water quality targets and the discharge standards of the river basins. In some regions where the discharge of pollution sources is relatively concentrated, it is possible that all pollution sources meet the discharge standards while the water body still exceeds the limitations.
Summary
After summary and discussion on WPDSS in China, we can conclude that both NDSS and LDSS were formulated based on the feasibility of the economic level, technological level and environmental management requirements, which have good constraint effect to the point sources of all the provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities and industries in China. However, there are still some problems in discharge standards, for example the decoupling relationship between discharge standards and water environmental quality. Due to the lackness of technology guidelines for setting discharge standards of the river basins, it fails to realize the connection between the water quality target and the discharge standards. Since EC and water resources between south and north of China unevenly distributed, more attention should be paid to the connection between water pollutant discharge standards and water environmental quality, in the next step.
Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (No. 2018ZX07111001), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Contract No.21806166), and Guangdong Foundation for Program of Science and Technology Research (Grant No.2017B030314057).
References
- Li T, Shi L, Ma Z (2020) Preliminary assessment and research on the discharge control policy of point source water pollutants in China. Resources and Environment in Arid Areas34(05): 1-8.
- Chen H (2019) Comparison and development trend exploration of pollutant discharge standards for urban sewage treatment plants and environmental quality standards for surface water. Water Purification Technology 38 (10): 56-61.
- Wang Lj, Xia XF, Zhu JC, Gao SW, Song CH, et al. (2019) Discussion on the establishment of discharge standards for water pollutants in rural domestic sewage treatment facilities. Environmental Science Research 32(06): 921-928.
- Xiang SC (2019) Study on discharge standard of water pollutants in synthetic ammonia industry. Chemical Industry Management (23): 46-47.
- Xu W, Dong L, Dong YY, Dong LM, Liu JY (2019) current situation and Suggestions of pollutant discharge in China's sugar industry. Modern Chemical Industry39(10): 5-8.
- Shi HJ (2015) Practice and innovation of water pollutant discharge standards in northern China. Environment and Sustainable Development40(01):68-71.
- Lu GJ, Chen ZF (2010) Research on the development of chloride discharge standards in hebei province. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information (05):130+275.
- Pan T, Liu GZ, Zhang N, Wang YG (2010) The general idea of improving the local water environment standard system in Beijing. Environmental Science and Management35(01):33-36.
- Ministry of Ecological Environment (2010) Measures for the archival filing of local environmental quality standards and pollutant discharge standards. Judicial Services (15):31-34.
- Wang JM, Li SY (2010) Discussion on national pollutant discharge (control) standard system. Environmental Science and Management 35(03):20-23.
- Li JY (2014) On the local standard of Fujian province discharge standard of water pollutants for pulp and paper industry. Strait science(07):44-45+48.
- Ran D, Li YQ, Zhang D, Yang P, Qie ZD (2012) On the status quo and characteristics of water pollutant discharge standards in China. Environmental science and management 37(12): 38-42.
- Hu C (2011) River basin ammonia nitrogen pollution control technology and countermeasures. Environmental protection and circular economy31(04):11-13.
- Jiang M, Zou L, Li XQ, Che F, Zhang GH (2015) Discussion on the definition and control index of volatile organic compounds in China. Environmental science 36(09): 3522-3532.
- Cui YJ (2019) Detection and analysis of wastewater discharge quality in an industrial enterprise. Technology vision (19): 91-93.
- Zhang HM (2019) Discharge standards of sewage treatment plants according to local conditions. Resources and human settlements (12): 53-55.
- Liu XR, Jian DW, Jian S (2019) Discussion on the upgrading of urban sewage treatment plants under high discharge standards. China water and drainage 35(20): 19-25.
- Si W (2010) Evaluation and analysis of China's water pollutant discharge standards. Environmental monitoring management and technology22(04): 7-9.
- Hu J (2017) A brief analysis of water pollutant discharge standard and its improvement path. Journal of Heilongjiang administrative cadre college of politics and law17(06):102-104.
- Chen W (2016) Effect discrimination of environmental standard tort law. Legal science (journal of northwest university of political science and law)34(01): 134-142.






























