Influence of Information Technologies on Competitive Strategies for SMES
José G Vargas-Hernández*1 and Saylis Cabrera Sierra2
1 Department of Administration, University of Guadalajara, México
2Master’s Degree in Business and Economic Studies, University of Guadalajara, México
Submission: August 25, 2018; Published: September 28, 2018
*Corresponding author: José G. Vargas-Hernández, Researcher Professor, Department of Administration University Center for Economic and Managerial Sciences. University of Guadalajara Periférico Norte 799 Building G-201-7, University Nucleus Los Belenes CUCEA Zapopan, Jalisco C.P. 45100; Mexico, Tel: +52(33) 37703340,37703300ext. 25685; Email: josevargas@cucea.udg.mx
How to cite this article: José G V-H, Saylis C S.Influence of Information Technologies on Competitive Strategies for SMES. Int J Environ Sci Nat Res. 2018; 14(5): 555899. DOI:10.19080/IJESNR.2018.14.555899.
Abstract
This research proposes the use of Information Technology (IT) as a way to generate efficient strategic management in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to achieve economic advantages. It focuses essentially on the ways in which storage is carried out, recovery, transmission and manipulation of information, since the way in which it is handled is of vital importance in the understanding of individual and organizational behavior. The main research question is: Why do people dedicate themselves to competitive strategies for SMEs? As part of the research methodology for the development of this work, the literature was thoroughly reviewed, and cases of success associated with the topic were reported and published. The work answered the questions raised and it was possible to conclude that in fact it is possible to achieve the quality strategies associated with business processes in terms of IT services, which as a final result in competitive advantages.
Keywords:Strategic Management Information; Swot Matrix; Information Technologies; Competitive Advantages
JEL:
Summary
This research proposes the use of Information Technology (IT) as a way to generate efficient strategic management in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to achieve economic benefits. It focuses essentially on the ways in which the storage, retrieval, transmission and manipulation of information is carried out, since the way in which it is handled is of vital importance in the understanding of individual and organizational behavior. The main research question is: Why do IT become competitive strategies for SMEs? As part of the research methodology for the development of this work, the existing related literature was thoroughly reviewed and cases of successes associated with the subject were analyzed. The work responded to the questions raised and it was concluded that in fact it is possible to achieve quality strategies associated with business processes in terms of IT services, which as a final result generate competitive advantages.
Introduction
The purpose of this research work is essentially focused on the study of existing literature on the influence of IT in the management of strategies in SMEs to achieve and subsequently maintain competitive advantages within an organization in the market where it is framed. While it is true that it is not possible to generalize too much in the aspects related to the implementation of new technologies, because each company conceives different processes or perhaps the same, but do not follow the same strategies, the hypothesis of the current trial is that they can be achieved quality strategies associated with business processes in terms of information technology (IT) services, which as a final result accrue in competitive advantages. The strategic management of information is structured by a set of actions through which it can be obtained data that meet the quality, persistence and costs that are appropriate to the needs of agents and administrators in a firm. To achieve this purpose, IT is an essential concept. The basic objective of information management is the organization and implementation of the information resources of the organization, which can be of external or internal origin, to ensure operability, knowledge and adaptability to constant changes in the environment Font, Lazcano and Ruiz [1]. Nowadays, companies are seen as huge information processors and the correct use of information helps to reduce uncertainty in organizations in increasingly competitive environments and to make much more efficient decisions by the authorities in charge of it.
As a consequence of the processes of globalization and the accelerated development of IT, there has been a novel advance in the information industry. Taking into account this development framework, it is essential the way in which the storage, retrieval,transmission and manipulation of information is carried out in a company, since the manner in which these activities are carried out is of vital importance in the understanding of individual and organizational behavior, as well as being a fundamental strategy to achieve competitive advantages within markets. Technology in general is gaining enormous importance in the processes of innovation, communication and efficient use of resources and dynamic capabilities in a company. Due to the facilities and options offered by IT in particular, the use of them is increasing worldwide, as organizations realize that they are strong points to achieve competitive strategies both locally and internationally. IT is currently providing the occurrence of changes in the ways of competing companies, which results in whether or not there are competitive advantages for the company that makes use of them. These technologies are also responsible for making important changes within the links of the chain of value production in organizations. The current expansion from the point of view of the activities that are dedicated to the elaboration, processing and distribution of information has caused that one may be thinking that the strategic variable by preference may become the information, taking into account the role relevant that plays the same in all processes of the company, which can be internal or external.
Background of the Problem
In order to make corporate governance more efficient and the decisions taken to respond correctly to the objectives of the organization, the solution may be that companies have a clear understanding of the spectrum of advantages offered by IT. As the main research question of this paper, is the following: Why do ITs become competitive strategies for SMEs? Other complementary questions are elaborated that in some way help to frame the context in which the research is based: Why are IT needed in a company? What represents the correct use and storage of information for SMEs?
Many entrepreneurs ask themselves the following question: What IT can I use in my business? To answer this question, it is valid to point out some concepts. Firstly, it is important and also necessary to understand what technology is. In the Dictionary of the Royal Spanish Academy (RAE), the word technology is defined as a “set of theories and techniques that allow the practical use of scientific knowledge”, as well as considered as a “set of instruments and procedures of a certain sector or product” RAE p.5677. The definition of IT is somewhat prolific, so a compilation was made based on the literature that most converge after analyzing several authors. According to Benjamin and Blunt [2], IT includes the technologies that are based on computers and communications, used for the acquisition and storage of information, in addition to allowing it to manipulate and transmit it to people and businesses, both internal and external. the company as external. On the other hand, Huber [3] refers that IT allows companies to improve the management and integration of the needs to perform information processing in all functional areas of it (Figure 1).
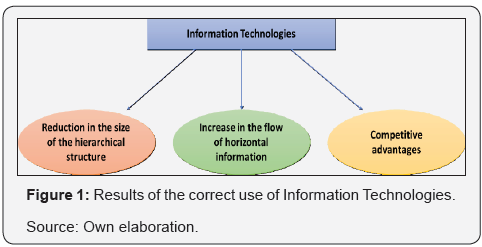
They are also defined as innovation processes that facilitate and enable the processing and accumulation of large amounts of information, in addition to which they can be distributed using social communication networks. One of the advantages of networks is that it facilitates the creation of information systems that have a common base, which allows the way to access information to be transformed and the scope of the network to have global dimensions. IT also constitutes tools that are used to share, distribute and centralize information. They are means that use both telecommunications and technologies associated with computing with the ultimate goal of transmitting information [4].
Porter and Millar [5] in their article titled How information gives you competitive advantage pose some questions: How do advances in IT affect the competition and are sources of competitive advantage? What strategies should a company follow to exploit the technology? The authors suggest that managers must first understand that IT is more than just talking about computers. This type of technology must be conceived in a broader way to cover the information that companies create and use. In the same way it is evident that the information revolution is affecting competition in several ways: It changes the structure of the industry and, in doing so, alters the rules of competition. IT is a sector that in summary covers not only all the internal and external information that a company creates and uses, but also is based on the wide spectrum of technologies, which are becoming increasingly convergent and linked and which are the ones that they are responsible for carrying out the processing of said information so that they generate greater efficiency Porter [6].
It is a real and convincing fact the increasing importance of IT in the modernization of companies and therefore in their processes of creating strategies to achieve and maintain competitive advantages in the market. Jones says that one of the biggest costs incurred by a company is given by the time that managers and employees spend in meetings, making decisions and solving problems. IT are tools that help and reduce these times and therefore the costs incurred by organizations associated with these issues; this makes managers and employees improve their productivity, by wasting less time in finding solutions to their problems Jones [7]. It was found that there are three types of IT that are very useful: Tele-Conferencing systems, information transfer and retrieval systems and those associated with personal information processing Monger [8].
The use of tele-conferences helps in the occurrence of communications even being far away. As a final result costs are reduced, since there would be no need to spend on transportation nor incur the expenses associated with the installation of people. In the same way you would be saving a lot in time because it is enough to quote a meeting in which all the parties involved participate. In these times of global competition is very important to use virtual media to enhance competitiveness. In the same way, information transfer and recovery systems are based on the use of networks and personal computers interconnected with each other, which allows users to share files and digital information. Finally, there are personal information processing systems, which also provide efficient use of the time and effort of all individuals in the company.
From the point of view of SMEs in the international arena, technological resources are incorporated that have allowed improving processes and achieving greater economic performance, where the methods used have been developed with resources based on the paradigm of new IT. However, one of the errors that slow down the development of SMEs is the absence of strategic analysis. The lack of accurate, reliable and real-time information that provides statistics on the performance of the company can lead to incorrect and inefficient decision-making. In general, SMEs experience challenges that are not different from those faced by large companies. By definition they have fewer staff, budgets are more limited and technological platforms are much less complex than their major competitors. However, they are subject to equal demands, so they should try to optimize the quality of their services and products to achieve the firm’s objectives, as well as minimize costs and adapt the activities of their IT departments to the requirements of the company
In order for a company to be competitive, the authorities must minimize the risks of uncertainty that inevitably exist in the market and the strategic actions taken by the decisionmakers must be seen as flexible and adaptable mechanisms to changing conditions. of the environment. With the purpose of making governance more efficient in companies and that the decisions taken respond in a correct way to the objectives of the organization, the solution could be to have a correct structure of information, external and internal, through IT. Goldhar and Jelinek [9] conclude in their research that it is possible to achieve a number of competitive advantages in a company through IT. Among these are the achievement of differentiated and personalized products following the preferences of consumers to maximize their profits. Innovation is implemented with which the design of the product is considerably improved. There are more direct sales and the productions are made in a more focused way in relation to the real variations in the demands. Marketing works are carried out more focused on highlighting the capacity of productive processes. In addition to that there is a differentiation of costs together with rapid changes in the differentiation of products with what accelerates the life cycle of them.
Theoretical-Conceptual Review
Companies are huge processors of information and the correct use of it helps reduce uncertainty in organizations and make more efficient decisions by the authorities Arrow [10]. The current and constant evolution of IT has had a profound effect on the management of organizations, improving the ability of managers to coordinate and control the activities of the organization and helping them to make much more effective decisions. Nowadays the use of IT has become a central component of any company or business that seeks sustained growth. The following figure shows the results of making correct use of IT in organizations. The theoretical - conceptual review carried out in this research shows that many authors believe that the incorporation of IT in SMEs can provide enormous competitive advantages if the use of such technology is correct. The vision of the industry-based strategy is supported by the framework of the five forces that was propagated by Michael Porter in 1981; this model forms the backbone of the theory or more commonly referred to as the industry-based point of view. The so-called Porter diamond was composed of the following elements: Intensity in the rivalry between competitors, the threat of potential entries, the bargaining power of the suppliers, the bargaining power of the buyers and the threat of the substitutes Porter [11].
Subsequently, Porter himself makes a series of observations on the competitiveness model that he himself proposed a few years ago, due to the changing environment and the uncertainty that these transformations brought to the industry. In 1991 he focuses his analysis on the concept of the company’s value chain, which consists in carrying out an exhaustive analysis of the different activities of the firm in order to discover where and how to obtain competitive advantages. The proper management of links between value-based activities is usually a good way to obtain competitive advantages because of the difficulty that competitors face in capturing the relationships between the different departments of the company Porter [12]. There are other authors such as Andreu, Ricart and Valor [13] who argue that obtaining competitive advantages can be mediated through the ITGAs (Information Technology Strategic Generic Actions). This concept tries to convey the idea of standard actions through whose application sustainable competitive advantages can be achieved.
Another of the great theorist’s states that there are three guidelines for finding competitive advantages and that is through cost leadership, differentiation and focus Porter [6]. Through the strategy of low costs, what the company intends is to be the leading producer in costs in the industrial sector in which it is framed. This advantage can be obtained through economies of scale, achieving access with preferences to raw materials and also through the use of IT which is what is the point of greatest interest for the present investigation. Following some of the guidelines of Porter [12], IT achieve sustainable competitive advantages taking into account a series of circumstances, among which are that the implementation of this type of technology reduces costs or increases the differentiation of companies and in consequence becomes sustainable technological changes. In the same way, these changes and the implementation of IT can modify the general structure of the industrial sector. IT influences the five competitive forces of Porter mentioned above. An example of this is that these technologies can increase the bargaining power of suppliers or constitute potential barriers to entry for producers, since it requires a large investment for its implementation.
One of the basic tools to recognize the role played by IT associated with competitive advantages are the company’s value chains Porter [14]. Similarly, for Porter [15] these constitute a theoretical model responsible for describing the development of the activities of a business organization and what is sought is to identify sources of advantage in the competition but in the activities that are generating value. In this sense, IT behaves as a valuable resource to add value to these activities in companies. These technologies have become a central element of any industrial company that seeks growth in the market, providing a sustainable base for the activities of production, trade, human resources, R & D, etc., to generate a final product that customers value. IT can be used in all activities that add value to the company, which is a key factor in achieving competitive advantages. Technologies are not important by themselves, they are significant if they affect the generation of competitive advantages in organizations Porter [16].
Review of the empirical literature
According to statistics from “Google Trends”, analyzed personally in April 2018 it is reported that during the last 5 years (from 2013 to the present), Mexico has reached the second position in searches associated with the words “Information Technology”, which shows that this concept has gained in importance and that both isolated individuals and companies recognize that it is one of the main means to achieve a successful organization and achieve competitive advantages both within local and international markets. Figures 2 & 3 show the results of searches associated with the term “Information Technologies”, filtering for the last 5 years and evidence of interest over time, as well as the regions that have searched the most concept based on a scale of 0 to 100, where 100 is the highest point in search levels performed in relation to the term in question.
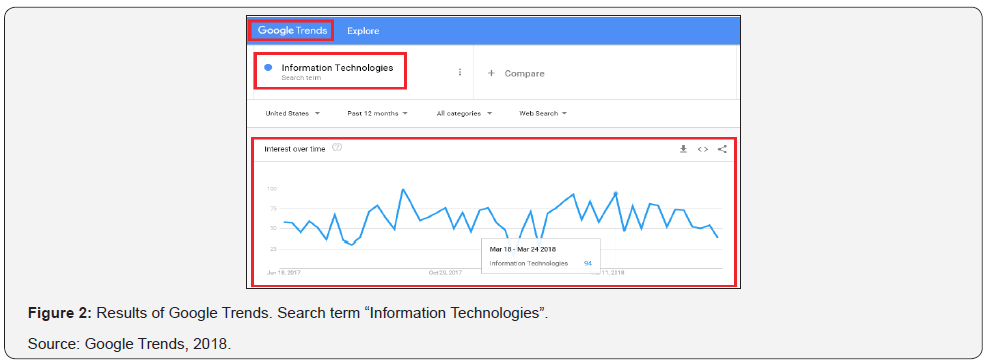
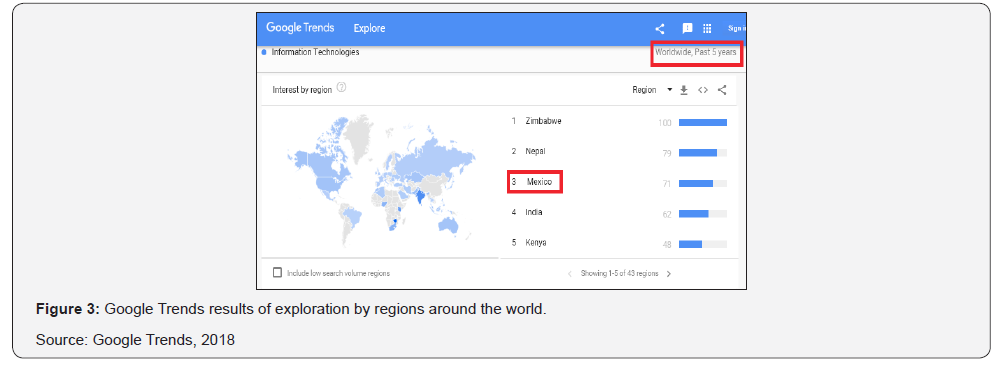
Google Trends is a free and open access tool provided by Google, which allows to compare the search popularity of several words or phrases. In this way, it can be known the search level of a term (keyword) during a certain period of time, allowing to identify the variations in searches in relative values based on a scale of 0 to 100, where 100 represents the highest point in levels of searches performed with respect to a term or keyword. In balance with the environment, both the Mexican government, and isolated companies and individuals recognize IT as an important concept that should not be left aside to achieve significant efficiencies in their objectives. So much so, that the Ministry of Economy (SE) shows that for some years there is a Program for the Development of the Software Industry (PROSOFT) and Innovation.
Being a program of the SE, it becomes a public policy that allows to promote the IT sector in Mexico and innovation in strategic sectors. The general objective of this program is to promote some of the industrial sectors that are in the strategic category to contribute to the generation of innovations. The call is aimed at companies from the mature sectors (textile, iron and steel, food, etc.), dynamic (automotive, chemical, electrical, etc.) and emerging (biotechnology, IT, pharmaceutical, etc.). The proposals must be related to IT innovation among other associated technologies. The PROSOFT Fund seeks to provide support to companies in the IT services sector so that they can increase their competitiveness in national and international markets and ensure their growth SE [17]. In the same way, in the online article says that “This self-financing infrastructure, based on the creation of semi-public goods, will generate Industrial Innovation Centers that promote the development of suppliers, clustering, value chains, and development of the human capital and specialized skills to facilitate the processes of adoption of information technologies for the control and design of productive processes aimed at increasing the productivity of manufacturing activities. SE [18].
On the other hand, in 2016 the National Institute of the Entrepreneur (INADEM) launched the call 5.1 of the project called “Incorporation of Information and Communication Technologies to micro and small enterprises”. The objective of this program is to provide support to micro and small companies in Mexico in the incorporation of these technologies, in order that they can optimize their management, production and trade capacities and strengthen the competitive advantages within the national and international markets. The support granted by the INADEM is based on meeting the needs of Internet connectivity, computer equipment and specialized software. Even companies receive specialized technical advice or business management in their own business centers SE [18].
On the other hand, in 2016 the National Institute of the Entrepreneur (INADEM) launched the call 5.1 of the project called “Incorporation of Information and Communication Technologies to micro and small enterprises”. The objective of this program is to provide support to micro and small companies in Mexico in the incorporation of these technologies, in order that they can optimize their management, production and trade capacities and strengthen the competitive advantages within the national and international markets. The support granted by the INADEM is based on meeting the needs of Internet connectivity, computer equipment and specialized software. Even companies receive specialized technical advice or business management in their own business centers SE [18].
There is a considerable amount of examples in which competitive advantages have been found through the efficient use of IT, which are documented in different publications, both specialized and dissemination and in national and international companies. It can be found examples of organizations that have won the National Technology and Innovation Award (PNTI), which is a Public Policy Instrument created by Presidential Decree in 1998 and that rewards companies that innovate and develop technologies in Mexico to solve problems of a high impact. The recognition is granted to Mexican companies that implement a model that offers them the possibility of competing in the national and international markets. Companies that generate technology and innovation management models are awarded with which new business models, products and services are created or that provide additional value to those already existing SE [19]. According to SE [19] in the XVII edition of the PNTI some of the winning companies turned out to be the following: Rotoinnovación S.A. de C.V., Seeds Papalotla S.A. of C.V. and Tooriginal Solutions (in the category of Technology Management), Horma S.A. of C.V. and Technologies EOS S.A. of C.V. (in the category of Product Innovation), Tecnotiferet S.A. of C.V. and Termoinnova S.A. of C.V. (in the category of Process Innovation).
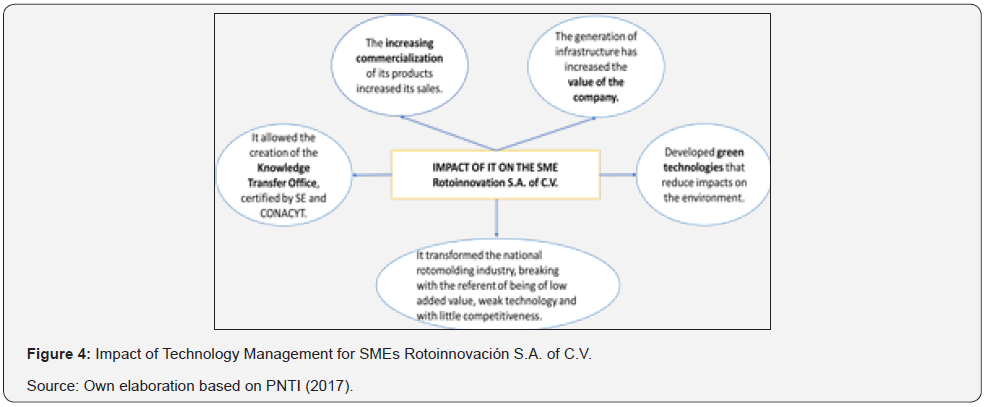
Rotoinnovación opted to create a Technology Management model focused on developing the necessary innovations to increase its competitive power, which has generated diverse projects in the fields of: basic science, applied research, technological development, etc. Its model arose with the creation of a technological road map and has a high distinction for adapting the strengths and opportunities of the company with the environment, being in synergy with the development of technological projects and business guidelines. The company has implemented in its model, surveillance activities that allow the analysis of data generated from a permanent monitoring of the technological environment and market, which can capture key information of capabilities, customers, markets and industry leaders to which they belong, thus making decision making possible SE [19].
According to SE [19] another of the companies awarded with this award is Papalotla Seeds, which developed its own management model, which has been a primary element of its evolution as a company. Given its relevance, the model is closely linked to the way in which the company operates, is part of its organizational culture, is self-managed and directly involved in its implementation by all business sectors. In its processes, intelligence and technological foresight provide strategic information to the entire organization to acquire and develop technology, among other activities that result from this process. For Seeds Papalotla, the management of the technology includes an efficient system for the management of the information, periodic delivery of reports, a high internal collaboration and a small and flexible, horizontal and vertical administrative organization, that is able to take advantage of the external human resources, in which all opinions count. There is no exclusion principle, each employee has the opportunity to grow and obtain well-defined benefits for their participation. Among its strategies, this company carries out a very efficient administration of its intellectual property, through tasks such as: protection of confidential information and secrets of the organization, promotion of brands, commercialization of its innovations, etc.
In the category of Technology Management, it also is to original Solutions, which considers five elements in its model: monitoring, planning and research to carry out technological development and innovation. On the other hand, its surveillance activities facilitate the obtaining of data and information about its technological, innovation and market environment, as well as the possibility of evaluating the efficiency, effectiveness and impact of the business SE [19]. The SE [19] refers that the model of the company Horma S.A. of C.V. It allows to advance in innovation processes, which helps to develop existing systems, processes and technologies, as well as to evaluate new technologies for efficient decision making that sustain your competitive strategy with positive impacts. Through technological surveillance, information is obtained from abroad on science, technologies and innovations that are closely linked to products, processes and services in the competition sectors and in some other selective sectors, identifying the impacts for the organization. The information generated is disseminated through controlled copies, which reveals the potential solutions for the problems encountered. For its part Technologies EOS S.A. of C.V. is an organization that created a model based on the protection of technological heritage. In order to safeguard the most sensitive information, EOS Technologies signed confidentiality agreements with all those involved in the project, both internal and external. In addition, they also implemented information access levels in their computer systems for internal control and supervision to allow data, in the process of developing the projects, to be available only to those who require it SE [19].
In the same way in the official site of the SE [19] regarding the company Tecnotiferet S.A. of C.V. In the technological and competitive surveillance processes, they obtain information for the implementation of the strategies that foster technological innovation, resulting in the state of the art. In addition to that in this process also acquires tools that make it possible to have more external information, such as market studies, academic articles, statistics and specialized print media. The last example corresponds to the company Termoinnova S.A. de C.V, which in its process of monitoring technologies has the objective of searching the environment for information that identifies threats and development opportunities for technology innovation that are ultimately channeled into positive impacts for the business. One of its strategies is to take information that comes from the technological surveillance process in order to identify the elements of competence.
Research Method
In order to know and evaluate the needs of implementing IT to generate competitive advantages in SMEs, this essay used a compilation of documentation exposed in books and different journal articles and companies specialized in the matter in question and that are proposals in its official pages. A group of SMEs that have implemented IT in their activities to generate the value chain were chosen to make a real measurement of the benefits that these organizations have achieved. These firms have been awarded prizes that show that they are successful cases with their current models of technologies. According to the objectives pursued by this research, based on the classification made by Hernández, Fernández and Baptista [20] it is argued that it is descriptive, since it refers to the description, recording, analysis and interpretation of the current nature and processes of the phenomena studied, related to the need for the incorporation of IT in SMEs. In this sense, a descriptive research was carried out, due to the fact that it was necessary to study the standard of use in terms of IT, in order to define the most representative aspects of the study phenomenon that allowed the formulation of the proposal. of using IT as a method to achieve competitive advantages (Figures 4 & 5).
Regarding the design of the research Hernández and other authors [20], they define it as the strategy developed in order to obtain the necessary information for a given study. Similarly; Arias [21], states that this modality refers to the location of the investigation according to the method or methodology used, understanding by them the techniques and procedures necessary to carry out the proposed investigation. On the other hand, according to the approaches of Sabino [22] this research has a non-experimental design, since the variable is not manipulated, so that only the phenomenon is observed or analyzed as it is presented in its real context, for the collection of data in a single moment, the latter aspect called transactional or transversal. In the same way, this research can be considered as one focused on its objective, with the purpose of analyzing the occurrence of one or more variables at a specific time; that is, the one whose purpose is to investigate the incidence and the values in which one or more variables are manifested, in order to provide their description, but which take the information in a single moment, in a single time, in order to study reality as it manifests Hernández [20].
Analysis of Results
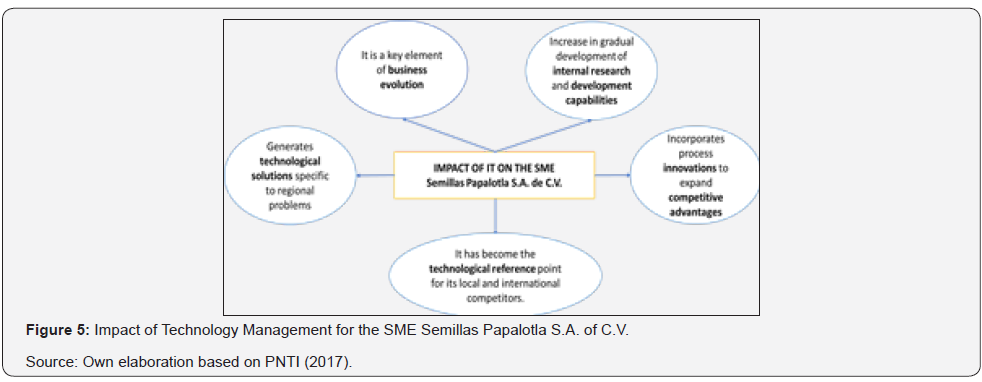
For the analysis of results, we investigated the impact that IT had on some of the companies awarded during the seventeenth edition of the PNTI that were mentioned above, as well as analyzing some figures related to the favorable repercussions that the economic management model had. who implemented these organizations, always associated with case study technologies of the current investigation. According to the PNTI [23]. Rotoinnovación, S.A. of C.V. has achieved results that increase its competitiveness and as a result achieve impacts in various aspects within society, as it is founded below: It is a certified company and also certified products. He is a member of the Mexican Network of Transfer Offices [24-26]. They obtained two trademark registrations before the IMPI, among many other merits. With the objective of analyzing the impact of Technology Management for SME Rotoinnovación S.A. of C.V. it can be visualized this fact in Figure 4 shown below: For the SME Semillas Papalotla S.A. of C.V. The impact of Technology Management is observed as follows:
Source: PNTI (2017).
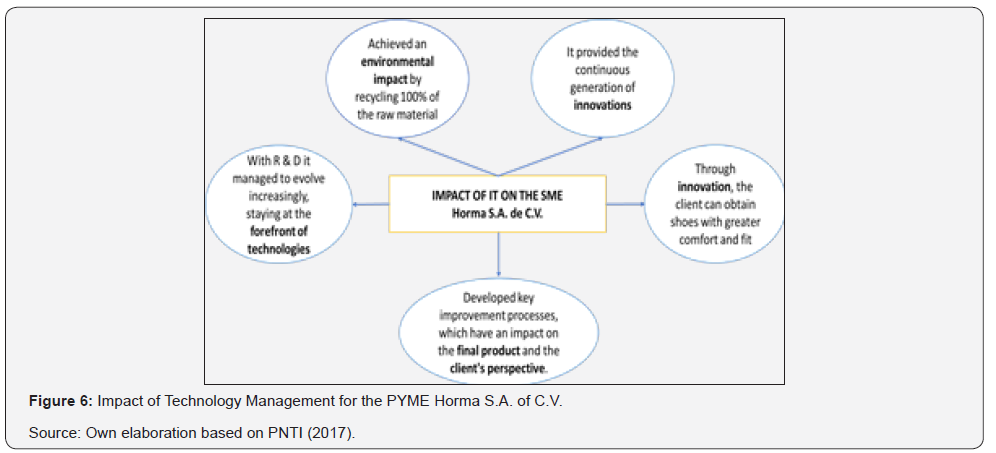
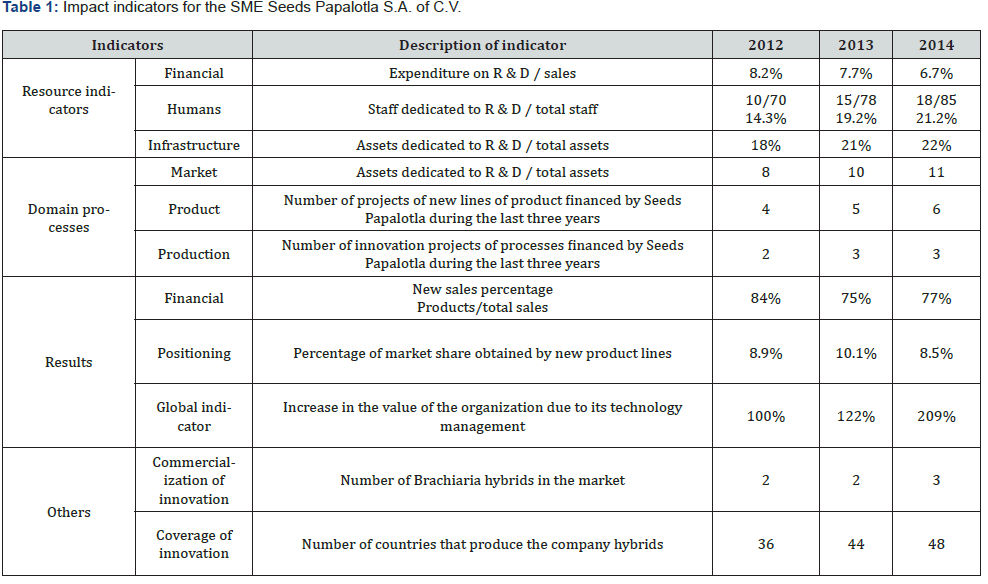
The Technology Management model has allowed Semillas Papalotla to progressively increase its internal R & D capabilities. Until 2014, the company had introduced to the market three new products that are being marketed in 48 countries (Table 1); increased its staff dedicated to R & D by 80%; It also managed to increase the number of projects to expand its target markets and was in the process of developing 6 new products and 3 innovative processes. Sales of new products up to 2014 accounted for more than 75% of the company’s sales; the new technological offer allowed to increase in more or less 28% of the influence markets and 12 new countries take advantage of this technology (PNTI, 2017). Taking into account the impact of Technology Management for SME Horma S.A. of C.V can be analyzed in Figure 6.
Conclusion
As initial questions of this research, we had: Why do IT become competitive strategies for SMEs? Why are IT in a company so necessary? What represents the correct use and storage of information for SMEs? With the realization of the current essay and the analysis of examples of successful cases associated with the implementation of technology management, it was possible to respond to the questions raised and it was found that in effect, quality strategies associated with business processes can be achieved. to IT services, which as a final result become competitive advantages. In general, the correct use of IT helps to reduce the uncertainty in organizations in increasingly competitive environments and to make much more efficient decisions. These technologies are also responsible for making important changes within the links of the chain of value production in organizations. The implementation of this type of technology reduces costs or increases the differentiation of companies and consequently results in sustainable technological changes. In the same way, these changes and the implementation of IT can modify the general structure of the industrial sector. It is concluded that IT can be used in all activities that add value to the company, which is a key factor to achieve competitive advantages. Technologies are not important by themselves, they are significant if they affect the generation of advantages to generate skills in organizations.
References
- Font EM, Lazcano C, y Ruiz MA (2014) La gestión estratégica de la información en las organizaciones: Una propuesta metodológica. Revista de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación 1(1): 1-10.
- Benjamín I, y Blunt J (1992) Critical IT (Information Technology) issues: The next ten years. Sloan Management Review 33(4): 7-19.
- Huber G (1990) A Theory of the Effects of Advanced Information Technologies on Organizational Design, Intelligence, and Decision Making. The Academy of Management Review 15(1): 47-71.
- Fernández R (2005) Marco conceptual de las nuevas tecnologías aplicadas a la educación: Universidad de Castilla, La Mancha, España.
- Porter M, Millar V (1985) How information gives you competitive advantage. Harvard Business Review 63(4): 149-160.
- Porter M (1987) Ventaja Competitiva: CECSA, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
- Jones G (1999) Organizational Theory: Texas A & M University, Estados Unidos, Texas, USA.
- Monger R (1988) Mastering Technology: The Free Press, Estados Unidos, New York, USA.
- Jelinek M, Goldhar J (1985) Economías de la variedad basadas en la nueva tecnología. Harvard Deusto Business Review 22(1): 71-80.
- Arrow KJ (1974) The Limits of Organization. Estados Unidos: WW Norton and Company, New York, USA.
- Porter M (1981) The Contributions of industrial organization to strategic management. The Academy of Management Review 6(4): 609-620.
- Porter M (1991) Toward a dynamic theory of strategy. Strategic Management Journal 12(S2): 95-117.
- Andreu R, Ricart J, Y Valor J (1991) Estrategia y Sistemas de Información. Mac Graw Hill.
- Porter M (1985) Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance.
- Porter M (1980) Competitive Strategy: Free Press, Estados Unidos, New York, USA.
- Porter M (2007) Ventaja Competitiva. Creación y sostenimiento de un desempeño superior. Sexta reimpresión, Editorial Grupo editorial Patria, México, USA.
- Secretaría de Economía (SE) (2016) Programa para el Desarrollo de la Industria de Software (PROSOFT) y la Innovación 2018. Ciudad de México, México, USA.
- Secretaría de Economía (SE) (2016) Lanza el INADEM la Convocatoria 5.1.
- Secretaría de Economía (SE) (2017) 19a Entrega del Premio Nacional de Tecnología e Innovación (PNTI). Dirección General de Comunicación Social, Distrito Federal, México, USA.
- Hernández R, Fernández C, Y Baptista M (2014) Metodología de la Investigación. McGraw-Hill/Interamericana Editores.
- Arias F (1991) Introducción a la metodología de investigación en ciencias de la administración y del comportamiento. Editorial Trillas.
- Sabino C (2007) El proceso de investigación. Editorial Humanitas.
- Premio Nacional de Tecnología e Innovación (PNTI) (2017) Organizaciones Ganadoras del Premio Nacional de Tecnología e Innovación® XVII Edición.
- Carrión G (1998). Gloria Ponjuán Dante. Gestión de información en las Organizaciones: Principios, conceptos y aplicaciones 12(24).
- Diccionario de la Real Academia Española (RAE) (2011) Diccionario de la Lengua Española. Adobe Digital Editions, eBooks con estilo.
- Google Trends (2018) Descubre qué está buscando el mundo.






























