Abstract
The healthcare sector has undergone a transformative journey, evolving from traditional practices such as herbal medicine, Ayurveda, and Unani systems to advanced digital healthcare driven by technology. This paper examines the historical evolution of healthcare, emphasizing the role of technological innovations, including artificial intelligence, robotics, nanotechnology, telemedicine, 3D printing, genomics, and blockchain, in reshaping diagnostics, treatment, and patient care. The study also explores the economic implications of these innovations, highlighting how investments in research, digital infrastructure, and health technologies contribute to global economic growth, cost efficiency, and job creation. Through case studies and real-world applications, including AI-powered diagnostics, robotic surgery, and nanoparticle-based therapies, the paper illustrates tangible improvements in clinical outcomes and healthcare accessibility. Additionally, future directions such as quantum computing, augmented reality, and sustainable integration of medical technologies are discussed, with a focus on equity, affordability, and policy development. By integrating historical, technological, and economic perspectives, this paper provides a comprehensive overview of how evolving technologies are shaping the future of medicine and the healthcare economy, offering insights for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners seeking to advance global health systems.
Keywords:Healthcare; Technological advancements; Artificial intelligence; Robotics; Nanotechnology; Telemedicine; Genomics; Blockchain; Healthcare economy
Abbreviations: R&D: research and development; IoT: Internet of Things; AI: artificial intelligence
Introduction
Healthcare has always been a dynamic field, shaped by evolving social, cultural, and scientific contexts. From the herbal remedies and ritual-based healing practices of ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and India, to the structured methodologies of Hippocrates and Galen, medicine has consistently sought to balance empirical observation with theoretical understanding. Traditional practices such as Ayurveda, Unani medicine, oral traditions, and herbal remedies formed the backbone of early healthcare systems [1]. The Middle Ages saw the rise of Islamic scholars like Avicenna, whose Canon of Medicine influenced both Eastern and Western medical traditions, while Europe’s Renaissance and Enlightenment periods ushered in systematic experimentation and the scientific method, setting the stage for modern evidence-based practice [1]. The rapid development of healthcare technologies not only transforms patient care but also stimulates international trade through the global exchange of medical devices, AI systems, and telemedicine services.
The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed unprecedented advances: the discovery of germ theory by Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch, the development of anesthesia and antibiotics, and the establishment of hospitals as centers of both treatment and research [1,2]. These milestones not only reduced mortality rates but also transformed healthcare into a structured system supported by governments, institutions, and professional organizations [1,2]. By the late 20th century, innovations in imaging, molecular biology, and computing further accelerated progress, positioning healthcare as one of the most innovationdriven sectors in human society [1,2].
In parallel, economic factors have played a defining role in shaping healthcare systems worldwide. The costs of new technologies, access to medical services, and allocation of resources have fueled ongoing debates about equity, efficiency, and sustainability [1,3]. As medicine transitions into the digital era-driven by artificial intelligence, robotics, nanotechnology, telemedicine, and blockchain-the interplay between technological transformation and economic feasibility has become more critical than ever [2-4].
This paper makes three key contributions to the existing literature on healthcare innovation Figure 1. First, it provides a historical overview of healthcare transformations, tracing the progression from traditional practices to the modern era of digital medicine. Second, it integrates technological and economic perspectives, offering a holistic analysis of how innovations such as artificial intelligence, robotics, nanotechnology, and blockchain are reshaping both clinical outcomes and healthcare delivery models [2-7]. Third, it identifies future trajectoriessuch as quantum computing, augmented reality, and sustainable healthcare systems-highlighting their implications for global health equity and policy. By combining historical, technological, and economic dimensions into a unified framework, this paper offers a comprehensive review that bridges the gap between fragmented discussions in prior research [1-4].
Literature Review
Healthcare technologies have dramatically transformed patient care, diagnosis, and treatment. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have enabled personalized medicine, allowing treatments to be tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup [3]. Telemedicine and video consultations have made healthcare more accessible to previously underserved populations, reducing the burden on traditional healthcare providers [3].
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness bands, allow real-time monitoring of vital health metrics, including heart rate, blood glucose, and sleep quality Table 1. These technologies facilitate timely interventions to prevent disease progression and manage chronic conditions effectively. Advances in genomics and precision medicine further enable individualized treatment plans, maximizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Robotic surgery and 3D printing enhance surgical precision, reduce recovery times, and improve overall clinical outcomes. Together, these technologies not only improve patient care but also offer economic benefits through increased efficiency, reduced human error, and enhanced preventive monitoring. By integrating AI, robotics, genomics, and digital tools, modern healthcare is evolving into a more precise, proactive, and cost-effective system Table 2.
The transition from traditional to modern healthcare, driven by technological innovations, has profound economic implications. Traditional practices were generally cost-effective, utilizing local resources with minimal infrastructure and low monetary exchange. In contrast, modern healthcare requires significant investments in research and development (R&D), advanced AI systems for diagnostics, robotic surgery, electronic health records, and data analytics. Additionally, training medical students, interns, and professionals to effectively operate advanced equipment adds to overall costs [3].
AI-powered tools and technologies have reduced errors in testing, diagnosis, and treatment while also decreasing the workload of healthcare professionals. Globally, the adoption of healthcare technology has contributed significantly to economic growth. For example, in the United States, healthcare expenditures account for approximately US $3.5 trillion, representing 18% of the overall GDP, while in Germany, healthcare spending amounts to US $0.4 trillion or 11.5% of GDP [3]. The production and export of advanced medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and digital health services contribute significantly to international trade, fostering economic growth in countries leading healthcare innovation. Big Data analytics plays a crucial role in identifying public health trends, informing policy decisions, and reducing healthcare costs through preventive measures.
However, the expansion of high-tech healthcare solutions remains expensive and often disproportionately benefits developed countries. Rural and underdeveloped regions may lack the infrastructure to implement advanced technologies effectively Table 3.
Technological growth in healthcare has also fueled job creation and innovation. Startups in health tech and pharm-tech attract venture capital, develop AI-driven diagnostics, healthcare apps, and robotic solutions. Pharmaceutical companies contribute significantly to R&D in gene therapy, gene editing, biologics, and drug development. Yet, the proliferation of advanced technologies raises concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity, potentially leading to legal and regulatory challenges that carry financial implications [3].
The integration of emerging technologies is rapidly transforming the healthcare sector, driving innovation, efficiency, and patient-centered care. Advanced tools such as blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, 3D printing, deep learning, data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are converging with modern medical science to redefine healthcare delivery [8-10]. These technologies facilitate more accurate diagnostics, personalized treatment, remote patient monitoring, and streamlined hospital operations.
Blockchain ensures secure and tamper-proof management of patient data, improving interoperability, transparency, and trust across healthcare systems. AI enhances diagnostic accuracy, enables predictive analytics, and supports personalized medicine. Robotics and 3D printing improve surgical precision, enable customized prosthetics, and expand the possibilities of tissue and organ bioprinting. Deep learning and data analytics allow healthcare providers to extract actionable insights from large datasets, optimizing clinical decisions and operational efficiency. IoT connects medical devices and wearable sensors, enabling continuous patient monitoring and proactive interventions.







Together, these technologies form the foundation of digital healthcare, creating systems that are not only more precise and efficient but also scalable, accessible, and responsive to the evolving needs of patients and providers worldwide. Figure 2 illustrates the current and future technologies shaping the healthcare sector.
Methodology
This study employs a comprehensive literature review and qualitative synthesis approach to analyze the impact of emerging technologies in healthcare Figure 3. Peer-reviewed articles, government reports, industry publications, and case studies were systematically examined to assess the role of artificial intelligence, robotics, nanotechnology, genomics, telemedicine, wearable devices, blockchain, IoT, 3D printing, and data analytics in transforming patient care, diagnostics, and healthcare delivery. Key parameters analyzed include technological applications, economic implications, accessibility, patient outcomes, and future prospects Table 4. Data were critically synthesized to identify trends, challenges, and opportunities in the digital healthcare landscape, providing a holistic understanding of current advancements and their potential impact on global healthcare systems Figure 4.


Data collection
Data for this study were collected through a systematic review of secondary sources, including peer-reviewed journal articles, industry reports, government publications, and credible online databases such as Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science. Search keywords included “digital healthcare,” “AI in medicine,” “robotics in healthcare,” “blockchain healthcare,” “3D printing in medicine,” and “IoT in healthcare.” Articles published between 2010 and 2025 were prioritized to capture recent trends and advancements. Relevant studies were screened for relevance, credibility Table 5, and contribution to understanding technological applications, economic implications, and patient outcomes Figure 5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to the research, authorship, or publication of this article.
Role of blockchain in digital healthcare
Blockchain, known for its decentralized governance and security, can transform digital healthcare by enhancing data integrity, privacy, and patient control [8]. It enables secure storage and selective sharing of medical records, improves interoperability, reduces errors, and minimizes fraud in insurance and research. Blockchain also safeguards clinical trial data from tampering and strengthens cybersecurity in centralized databases Figure 6. Its evolution Blockchain 1.0 (digital currency), 2.0 (digital economy), and 3.0 (digital society) has expanded its applications in healthcare [8].
Role of artificial intelligence in digital healthcare
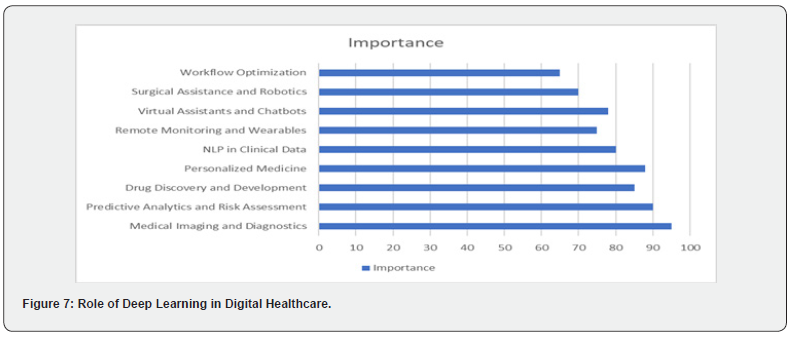
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing digital healthcare by improving diagnostics, treatment planning, patient monitoring, and operational efficiency [9]. AI enhances early disease detection through radiology and medical imaging, including CT scans, MRIs, cancer, and neurological assessments. Personalized treatments are enabled by AI algorithms analyzing genetic, lifestyle, and health data, optimizing drug responses, and minimizing adverse effects. Chronic disease management is enhanced with real-time monitoring and tailored interventions. Mental health support is delivered via AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots, such as Woebot for cognitive behavioral therapy [10]. Additionally, AI accelerates drug discovery and clinical trials, exemplified by platforms like Atom wise, improving efficiency and accuracy in pandemic responses. AI-driven robotic surgeries and real-time clinical support are expected to further advance digital healthcare Figure 7.
Role of robotics in digital healthcare
Robotics has transformed healthcare by enhancing precision, efficiency, and accessibility in medical treatments and operations [11]. Surgical robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, enable minimally invasive procedures, improving accuracy while reducing risks and postoperative complications. Robotics also facilitates complex microsurgeries, including neurosurgery and open-heart operations, without damaging surrounding tissues Figure 8. AI-powered robotic systems enhance diagnostic accuracy by analyzing imaging data from X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. In pharmaceutical settings, robotic drug dispensing ensures accuracy and streamlines supply chains. Additionally, robotics has revolutionized medical training, allowing healthcare professionals to practice complex procedures safely in simulated environments. Overall, robotics integrates precision, efficiency, and accessibility to improve patient outcomes and healthcare delivery.
Role of 3D printing in digital healthcare
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has revolutionized healthcare by enabling patient-specific products with high precision and effectiveness. Applications include personalized prosthetic limbs, orthotic devices, and surgical models derived from CT or MRI scans to guide complex procedures, such as cardiac surgeries. Bioprinting with bio-inks allows the creation of living tissues and organs for transplantation, while customized drug production improves therapeutic outcomes. Since 2010, hospital adoption of 3D printing has grown rapidly-from a few regional labs to over 400 by 2022-demonstrating its expanding role in enhancing patient care, efficiency, and innovation in digital healthcare Figure 9.
Role of deep learning in digital healthcare
Deep learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, employs neural networks to analyze vast datasets, uncover patterns, and support medical decision-making. It has transformed healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and operational efficiency. Applications include medical imaging, enabling early detection of tumors, fractures, arrhythmias, and diabetes through X-rays, CT scans, and other modalities. Deep learning also powers virtual health assistants and AI chatbots for appointment scheduling, patient education, and support. Additionally, it automates data entry and management, improving administrative accuracy. By integrating deep learning into clinical practice, healthcare systems worldwide achieve higher efficiency, precision, and improved patient outcomes.
Role of data analysis in digital healthcare
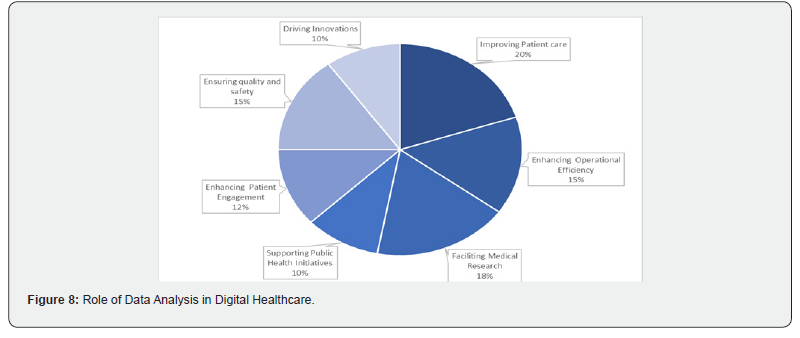
Data analysis transforms digital healthcare by leveraging large datasets to improve patient outcomes and drive research. It enables personalized treatments based on genetics, lifestyle, and medical history. Real-time monitoring through wearables, robotics, and IoT sensors provides continuous patient data for early alerts. Workflow efficiency, including billing and administrative tasks, is enhanced, while data privacy regulations ensure secure handling of sensitive information. Data analysis will continue to be pivotal in advancing patient-centered, precise, and efficient healthcare systems [12,13].
Role of Internet of Things (IoT) in digital healthcare
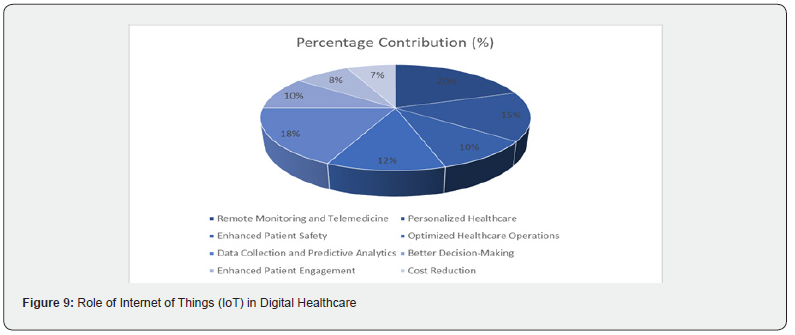
IoT connects medical devices, sensors, and health systems to collect and analyze patient data, enabling real-time monitoring of metrics like glucose, blood pressure, and heart rate. It improves operational efficiency by tracking medical equipment and supports data-driven clinical decisions. IoT enhances accuracy, patient care, and cost-effectiveness. Key industry leaders include Apple, Fitbit, Samsung, Garmin, Xiaomi, Sony, and Qualcomm Technologies [14].
Case Studies and Real-world Applications in Healthcare Technology
AI-powered healthcare systems
AI systems are set to change the conduct of healthcare from diagnostics and management to selecting a suitable personalized therapy protocol. These systems allow for quick and concise decisions regarding the care of a patient.
Case Study 1: Mayo Clinic’s AI Diagnostic Tool [15]
A Mayo Clinic study applied AI techniques to a new screening tool for patients who face certain types of heart problems that do not exhibit obvious symptoms, termed left ventricular dysfunction. This AI screening tool detected people at risk of this condition 93% of the time. To put this in perspective, a mammogram is 85% to 90% reliable. AI developed by the Mayo Clinic also powers an application on Apple Watches to detect weakened heart pumping.
Case Study 2: Babylon Health Startup
Babylon Health, a UK-based startup, developed AI-powered chatbots to triage patient symptoms and recommend appropriate care pathways. Since its inception in the UK in 2013, this startup has conducted international consultations in millions. In the UK, the usual wait for an appointment with a GP would range from a week to two. The patients are registered with the GP at Hand through Babylon’s NHS service, and 39% of those registered generally get their appointment on their phone within 30 minutes, while about 89% receive it within 6 hours.
Robotics in complex surgeries
Robots have helped in surgeries with greater precision while causing less complication and reducing postoperative recovery time. These innovations are significant for a larger part of minimally invasive procedures.
Case Study 1: Da Vinci Surgical System [6]
Though in practice in many institutions such as Johns Hopkins, Da Vinci robotic systems turn surgery completely inside out for the urology and gynecology sectors. Robots further assist rapid recovery by forcing the recovery of patients treated with roboticassisted procedures to become 50% less than traditional surgery.
Case Study 2: King’s College Hospital’s Robotic Brain Surgery
The year 2023 saw King College Hospital achieve great strides in removing tumors by operating its new robotic system; with the system, the accuracy of operation equals 0.1mm while lessening postoperative recovery time by 40% and postoperative complications by 35%.
Nanotechnology in cancer treatment
Nanotechnology changes the look of oncology with its ability to allow targeted drug delivery and early diagnosis of diseases while increasing treatment effectiveness and decreasing side effects.
Case Study 1: Nanoparticles in Chemotherapy
Nanoparticle-based chemotherapy allows a direct delivery of drugs to the ca ncer cells, 60% reduction of the side effects, thus making the patients accept the new line of treatment. Nanoparticle (NP)-based drug delivery systems have shown many advantages in cancer treatment, such as good pharmacokinetics, precise targeting of tumor cells, reduction of side effects, and drug resistance [16].
Case Study 2: Early Detection of Lung Cancer
Researchers at Stanford University developed a nano sensor that could detect lung cancer biomarkers at an early stage. Clinical trials yielded a 35% staging increase in the 5-year survival rate with patients diagnosed early with lung cancer.
Future Directions in Healthcare Technology
Advancing healthcare technologies not only reform but indeed promises a transformative future for medicine and health outcomes globally. The future will focus on technological innovations, economic outlooks, and sustainability central to the future of a promising, equitable healthcare ecosystem [17-20].
Technological innovations
i. Quantum computing can provide a potential for drug
discovery by simulating the molecular precision that traditional
computers are unable to achieve.
ii. Pfizer and IBM are exploring quantum algorithms for
designing and testing drug molecules at an accelerated process.
iii. Drug discovery can be shorter from the current 10
years to about 2-3 years, making it affordable for research and
development.
iv. 3D Bioprinting: The future of bioprinting could elaborate
multi-layer materials for organ transplantation.
v. Augmented Reality can become a surgical tool that
allows surgeons to see anatomical structures as they proceed with
the operation, thus increasing surgical accuracy.
Economic projections
The market will grow exponentially with the rate of adoption
of AI, robotics, and biotechnology increasing in the healthcare
technology sector.
i. The global healthcare technology market is projected to
hit $1.3 trillion by 2030, growing at a compound annual rate of
15.8% from 2023.
ii. AI alone has the potential to save the global healthcare
system $150 billion a year by reducing diagnostic errors and
optimizing treatment pathways.
iii. For many advanced technologies, the increasing reliance
is expected to create millions of jobs, such as AI specialists, data
scientists, and robotics engineers [21,22].
Sustainability
Challenges in sustainability
i. Alternatively referred to as sustainable technology
integration, this is a balancing act between innovation, resource
expenditure, and environmental concerns [23].
ii. The carbon consumption of technology: The AI systems
and data centers are energy hogs. Moving away from fossil fuels
and getting to renewable energy is key.
Proposed solutions
Equitable Access: It is still a challenge to provide equal access
to advanced healthcare technologies in low- and middle-income
countries.
i. Circular Economy in Medical Devices: Recycling and
reuse of the components of the advanced medical devices can
eliminate waste [24].
ii. Frameworks to Establish Policy: Governments and
international health agencies must put into place a framework
to enable sustainable technology integration into healthcare [25-
27].
Conclusion
The rapid evolution of healthcare technologies has transformed medicine, reshaping diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, robotics, nanotechnology, genomics, telemedicine, and wearable devices have improved health outcomes, expanded access, and created opportunities for economic growth. Realizing their full potential, however, requires addressing challenges in policy, affordability, and accessibility [28].
Recap of the transformative role of technology in medicine
AI enhances diagnostics and personalized medicine, reducing errors and improving accuracy. Robotics enables minimally invasive surgeries with faster recovery, while nanotechnology allows targeted therapies with fewer side effects. Telemedicine and wearable devices overcome geographical barriers, and genomics enables precise, effective, and resource-efficient treatments, collectively improving care quality and patient experience worldwide [29].
Health and economic impact
Healthcare technologies provide dual benefits: improved precision and accessibility, alongside market growth and job creation [30]. AI reduces diagnostic errors, telemedicine reaches remote areas, and wearable devices empower patients through real-time monitoring. Predictive analytics optimizes resources, and health tech expansion generates skilled employment, reflecting the synergy between innovation and socioeconomic progress.
Bridging gaps and ensuring sustainability
Equitable adoption requires coordinated strategies in policy, affordability, and access. Regulatory frameworks, cost-sharing models, infrastructure investment, and localized technologies are essential to reach underserved populations. Long-term sustainability depends on environmentally conscious practices, energy-efficient AI, and circular models for medical devices.
The future of healthcare lies in integrating innovation, accessibility, and sustainability. Collaboration among policymakers, providers, and technologists can ensure transformative healthcare technologies benefit all, fostering a healthier and more equitable world.
Research Limitations and Future Implications
This study is primarily based on a review of existing literature and secondary data, limiting the ability to draw conclusions from primary empirical evidence. While major technological advancements such as AI, blockchain, robotics, 3D printing, IoT, and data analysis are discussed, not all emerging technologies or region-specific contexts are fully covered. Much of the data and examples pertain to developed countries, which may limit the generalizability of findings to low-resource or rural settings. Rapid technological evolution means some insights may become outdated as new innovations emerge. Future research should focus on empirical studies to evaluate the real-world effectiveness, economic impact, ethical considerations, and long-term sustainability of these technologies, particularly in underrepresented regions, to guide policy and implementation strategies. As healthcare technologies continue to advance, their cross-border adoption and commercialization will play a crucial role in international trade, facilitating collaboration, technology transfer, and global access to quality medical care.






























