Natural Birdwatching CanReduce Anxiety, Depression and Other Mental Illness
Ravish H*1, Srinivas H2 and Shravan3
1Department of Neurochemistry,NIMHANS, India
2Department of Biochemistry, MAMC, India
3Department of Oncology, India
Submission: July 07, 2018; Published: July 13, 2018
*Corresponding author: Ravish H, Department of Neurochemistry,NIMHANS,Bangalore, India, Email: docravish@nimhans.ac.in
How to cite this article: Ravish H, Srinivas H, Shravan. Natural Birdwatching Can Reduce Anxiety, Depression and Other Mental Illness. Glob J Oto, 2018; 16(4): 555941. DOI: 10.19080/GJO.2018.16.555941
Introduction
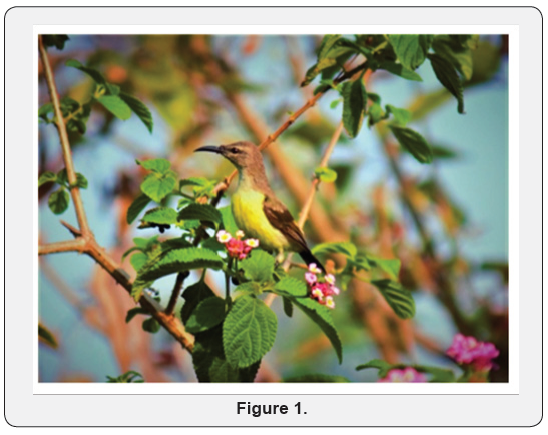
Watching birds by binoculars might be embarrassment for others, but recent studies suggest to do it often for your mental wellbeing. Livingness towards watching birds helps an inviduals with mental illness like anxiet, depression and stress to overcome. This is seen across the age groups, according to research studies done in United Kingdom. Birdwatching can be as simple as common birds in neighborhood like sunbrids, robins, pigeons, parrotsand even crows(Figure 1). Some of the research publications also suggested that, people spending less time outside world have reported more with anxiety and depression disorders.Research studies have not concluded on a particular species of birds which were able to reduce mental illness, but they have suggested that number of birds of different species where observed at parks, urban gardens, etc.,could morelike to impact on positively on their mental wellbeing(Figure 2).

Earlier studies say’s that person who have ability to identifythe species of bird had less chances of depression, which means that interaction with nature and birds have an positive impact on mental health. Such studies and exploration have led to think of some key components of nature which plays in our mental wellbeing. Thus, birds and nature around the home has a preventive measure in menthal wellbeing, hence will make cities healthier, relaxed, happier and connected to nature(Figure 3)[1].

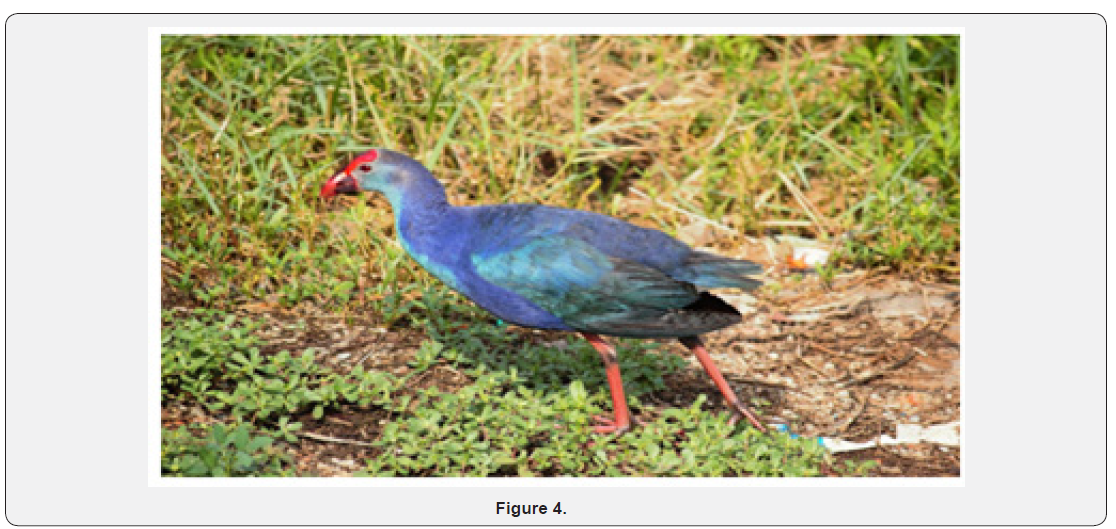
Increase in the urbanization, has lead to slow disconnection of men from nature, leading to increase in stress, anxiety and mood disorders. Activities in the nature has also resulted in the resortation of mental health which are cost effective measures which can be easily implementable. Many theortical work suggest that nature helps in restoring the mental and cognitive decline[2-3]. Increasing studies have shown that by implementing more quality green neighborhood havepromoted greater well-being and lowered anxiety and depression among population.Green neighbourhood i.e., by having more green parks & gardens have attracted more birds. Watching greenery, viewing birds andlistening to bird’s songs have reduced the anxiety and depression among communities residing there(Figure 4)[4].

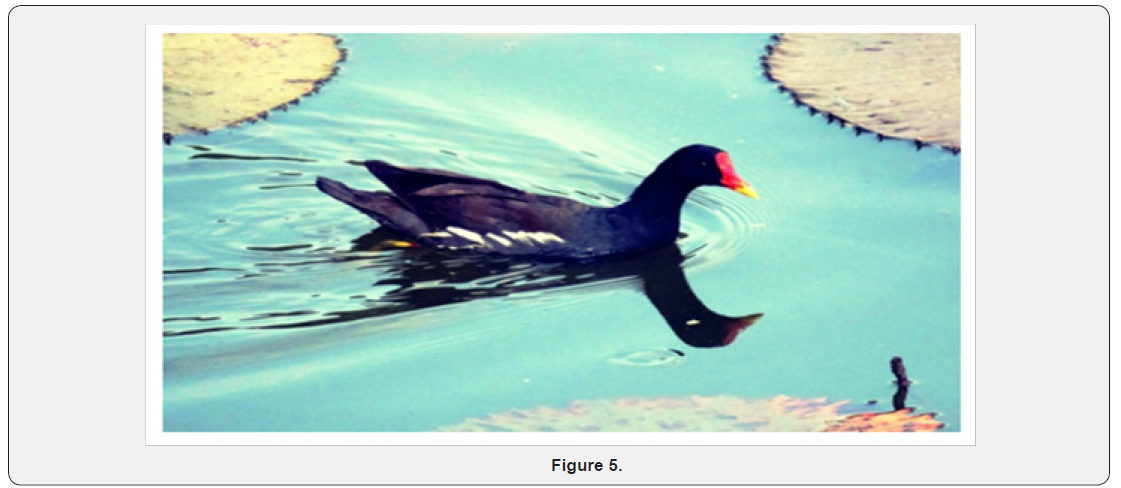
There are many evidences suggesting that decrease level of nature interaction leads to negative impacts in various mode to mental wellbeing. It is also indicated that any physical or mental activity done in nature with presence of birds are more effective than doing the same activity in other places. Decrease in hormone cortisol, lowering of blood pressure, pulse rate with better cognition is observed due to birding activity[5]. These mental health benefits due to interaction with nature, like bird watching, walking in garden and trekking etc., have been termed as nature doses for mental illness. There is different intensity of pleasure people experienceby watching birds, whichmay correspond to both the number of birds(i.e. Quantity) and species (i.e. Quality) of birds present of the nature dose(Figure 5)[6].

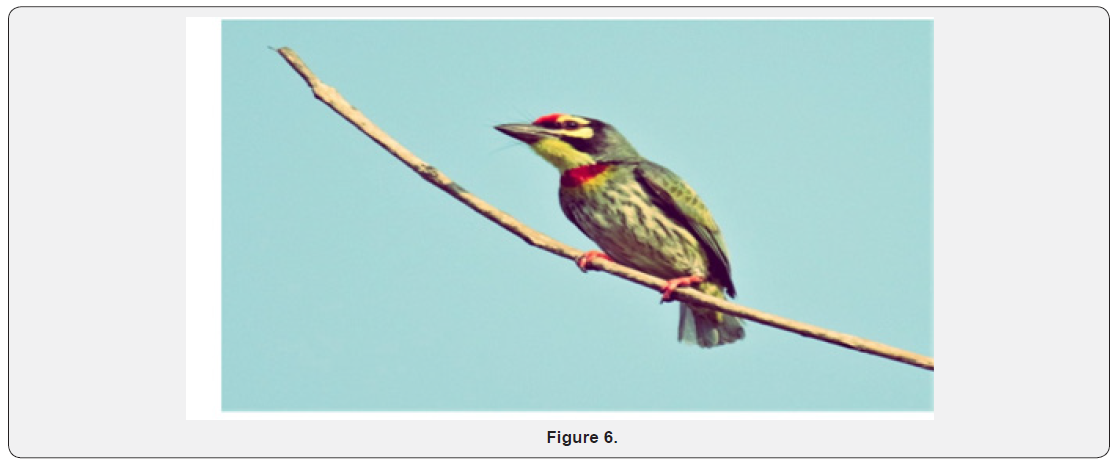
Most of people in urban experience their interactions with wild birds as their prime experience with wild nature in their busy daily life. Hence, providing food or feed birds in their gardens or urban parks can be cheap and best means of opting for preventive mental health activity. Present days there is growing popularity garden bird feeding amongurban population in western countries.It is also known fact that bird feeding helps gardens to flourish with diverse species of birds. Feeding birds and watching birds feeding at urban gardens gives a immense pleasure and satisfaction of connecting with nature. Thus, it is significant for an individual to relate with nature, which is an indicator of that individual in his overall happiness levels(Figure 6)[7].
However, not every species are given importance, some are not preferred over others. A bird species conversation and its preference are considered by funds allocated and other aspects of people livingness to watch them regularly on demand. Factors like how appealing and how satisfied an individual feel upon watching a particular species of birds mainly implies in its conversation [8]. There is huge variation in likeability with songbirds being liked over non-song birds.Songbirds are highly colored with behaviors and rarely a source for human- bird conflicts.Few mental illnesses like attention deficit fatigue known to be get better by engaging in watching songbirds. Conversely it is seen that small number of non-song birds known to be in conflicts with human by their calling, aggression and causing damage to properties. Starling birds are also least positive in terms of tendency to strip of feeds from the songbirds, thus contributing to dislike among UKresidents(Figure 7).


Birding is now a common global event andit will continue to grow in popularity. Feeding birds in urban garden birds canprovide great deal of pleasure.Hence, understanding of birding& its implications for economics, conservation and ultimately, creating green spaces indulgepeoplewith nature and so maximize the mentalhealth benefits[9]. Thus, person’s or community liking towards a bird species is a main factor influencing mental well-being of community or an individual who areobserving it frequently. Bird species survival will also affect by its interaction with human, by its acceptance of its feeds from human compared to birds surviving in the bushes without any interaction.Many urban residents are totally unaware & not interestedof the bird species around them. Hence, such population shall also receive less benefits from seeing the same birds compared to individuals who are more interested from within to interact with nature and birds[10
It’s very important to be connected with nature for a species to survive from getting extended. Increasing loss of interaction of humans with nature, will make humans to be in the extinction path. Urban garden. Gardens can evoke strong feelings of ownership and sense of place with many urban dwellers spending significant amounts of time there.Therefore, the nature that is found in gardens may act as an important stepping-stone in providing this connection, because it is the nature that people will experience on a daily basis and so be more familiar with. As such, relevant stakeholders and initiatives should focus on increasing urban residents’ awareness of the nature around them. Citizen science initiatives have shown that this can be an effective approach to increasing people’s nature awareness.
Conclusion
This study provides evidence that the well-being benefits that people receive from interacting with the birds in their garden is dependent on their familiarity with different species, and that these benefits are enhanced by increased species richness. Attention should be given to strategies that focus on increasing the diversity of songbirds within urban green spaces, along with increasing the ability of recreational green space users to recognize different components of the natural environment. Combined these approaches will enhance both the well-being benefits that people receive from interacting with nature and the biological complexity of urban green spaces. Bird feeders provide a powerful tool for people to engage with the natural world in their own garden, and so act as an important stepping-stone for a wider connectedness to nature. People with a greater connection to nature are more likely to be aware of, and support, conservation issues in the wider landscape. So, feeding birds can be seen as an important tool in reconnecting people to the natural world, so helping to mediate the extinction of experience.
References
- Cox DT, Shanahan DF, Hudson HL, Plummer KE, Siriwardena GM, et al. (2017) Doses of neighborhood nature: The benefits for mental health of living with nature. BioScience 67(2): 147-155.
- Kaplan S (1995) The restorative benefits of nature: Toward an integrative framework. Journal of environmental psychology 15(3): 169-182.
- Bratman GN, Hamilton JP, Hahn KS, Daily GC, Gross JJ (2015) Nature experience reduces rumination and subgenual prefrontal cortex activation. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences 112(28): 8567-8572.
- Ratcliffe E, Gatersleben B, Sowden PT (2013) Bird sounds and their contributions to perceived attention restoration and stress recovery. Journal of Environmental Psychology 36: 221-228.
- Selhub EM, Logan AC (2012) Your brain on nature: The science of nature’s influence on your health, happiness and vitality. John Wiley & Sons.
- Cox DT, Gaston KJ (2015) Likeability of garden birds: Importance of species knowledge & richness in connecting people to nature. PLOS One 10(11): e0141505.
- Galbraith JA, Beggs JR, Jones DN, McNaughton EJ, Krull CR, et al. (2014) Risks and drivers of wild bird feeding in urban areas of New Zealand. Biol Conserv 180: 64-74.
- Gunnthorsdottir A (2001) Physical attractiveness of an animal species as a decision factor for its preservation. Anthrozoos 14(4): 204-215.
- Kaplan R (2001) The nature of the view from home-psychological benefits. Environ Behav 33: 507-542.
- Caula S, Hvenegaard GT, Marty P (2009) The influence of bird information, attitudes, and demographics on public preferences toward urban green spaces: the case of Montpellier, France. Urban For Urban Gree 8(2): 117-128.





























