Shadbindu Taila Nasya in Allergic Rhinitis: a Controlled Clinical Trial to Compare its Efficacy with Topical Azelastine hydrochloride Nasal Spray
Gangaprasad A Waghmare*
K G Mittal Ayurved College, India
Submission: November 30, 2016; Published: December 15, 2016
*Corresponding author: Gangaprasad A Waghmare, K G Mittal Ayurved College, Charni road, Mumbai-02, India
How to cite this article: Gangaprasad A W. Shadbindu Taila Nasya in Allergic Rhinitis: a Controlled Clinical Trial to Compare its Efficacy with Topical Azelastine hydrochloride Nasal Spray. Glob J Oto 2016; 2(4): 555594. DOI: 10.19080/GJO.2016.02.555594
Abstract
With the aim to evaluate the efficacy of shadbindu taila Nasya and topical Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in the management of Allergic Rhinitis, a Single blind randomized clinical study was done. For the clinical study of Allergic Rhinitis 60 subjects was selected and studied. Subject’s fulfilling the criteria of diagnosis was studied irrespective of their religion, caste, sex and socio-economic status from shalakya-tantra (ENT) department of the institute after thorough scrutiny and proper consent in his/her language. The Subject’s having age between 20-60 yrs was selected for the clinical study. Detail history of the patient were elicited, pathological investigation including Hb, TLC, DLC, RBS and required radio logical investigation were done in a diagnostic Centre.
The examination of the Nose is also carried out with the help of modern viewing techniques like Anterior Rhinoscopy, Posterior Rhinoscopy and Spatula Test etc. After observation and analytical study with the help of Wilcoxon sign rank test and Man-whiteny test it was concluded that in Allergic Rhinitis treatment with shadbindu taila Nasya shows more effectiveand long lasting Result in relieving sign and symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis than Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray.
Keywords: Shadbindu taila; Nasya; Azelastine hydrochloride; Rhinitis
Introduction
The human life is full of competition due to which his life style has been completely changed, we has to face excessive exposure to pollution, cold Along with these factor consumption of chilled foods, cold drinks, ice cream etc. produces phlegm diseases which gives rise to respiratory tract diseases. As respiration is soul of physiological activity, Pranvaha strotas has its special importance. Dushti of Pranvaha Strotas may disturb the physiological activity of body. Nasa is commencement of pranvaha strotas. Nasa protects pranvaha strotas by adhering the harmful factors like pollen, dust to the mucous membrane, also humidifies air entering the nose and regulate the temperature of air entering the nose. Hence Pranvaha Strotas will be affected if physiological activity of protection of nose is not performed well. The pollution and the above said factors affect the nose and its mucosal membrane leading to various nasal diseases. Allergic Rhinitis is also a disease among them which is described by all Ayurvedacharya’ [1-4].
In modern medical science, there is medical treatment for Allergic Rhinitis. Complete cure of these diseases is not yet possible by medical treatment. So looking towards the importance of above said points, there is a great need to look forward for the Ayurvedic management of Allergic Rhinitis. There are number of references in Ayurvedic texts suggest various regimes of treatment for Allergic Rhinitis. All these management have one common concept and this is nasya karma. Ayurvedacharya have already praised the role of nasya Karma in urdhav jatrugat vikar [5,6].
Aims and Objectives
- To study efficacy of shadbindu taila Nasya in Allergic Rhinitis.
- To study efficacy of Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in Allergic Rhinitis.
- Comparing the efficacy of shadbindu taila Nasya and Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in the management of Allergic Rhinitis.
Taking above said point in consideration, we have plan to study and compare shadbindu taila Nasya and Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in the management of Allergic Rhinitis which includes patients’ history, sign, symptoms , diagnosis ,clinical examination and management by above said trial drugs [7].
Hypothesis
- H0-shadbindu taila Nasya and Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray do not have any effect on Allergic Rhinitis.
- H1-shadbindu taila Nasya and Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray do have effect on Allergic Rhinitis.
Materials and Method
Patients having signs and symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis was randomly enrolled from the OPD of department of Shalakya- Tantra (ENT) of the institute after thorough scrutiny, proper consent and permission from ethical committee [8,9].
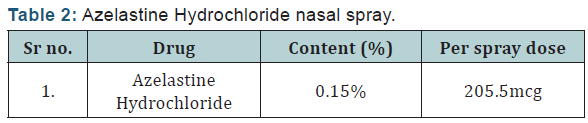
Composition of trial drug (Tables 1 & 2).

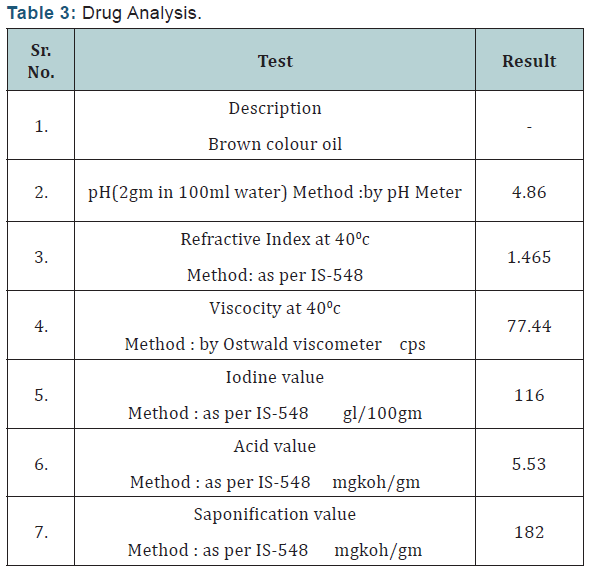
Drug Analysis (Table 3).
Grouping: 2 groups
- Group A: The Subjects of this group was treated with shadbindu taila Nasya
- Group B: The Subjects of this group was treated with Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray (Table 4) [10-15].

Examination of the patient
Nasal examination of the patient includes
- Examination of external nose.
- Examination of Vestibule.
- Anterior Rhinoscopy.
- Posterior Rhinoscopy.
- Functional examination of nose [16].
Criteria of diagnosis
- Foul Smell
- Anosmia
- Dryness of Nose
- Crusting
- Nasal discharge
- Blocking of Nose
Grading (0-Absent, 1-occasional, 2-frequent, 3-continuous)
A.Investigation
- Pathological: CBC, BSL, HIV
- Radiological: x-ray PNS
- Endoscopic: Functional nasal endoscopy (Rigid) [17- 19].
Criteria for assessment:
Criteria for selection:-
- Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis was based on clinical examination which will be supported with Radiological and pathological investigation [20-22].
- Age group between 20 to 50 years [23-27].
- Both male and female subjects, having sign and symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis, irrespective of their socioeconomic status, educational status, caste and religion [27- 32].
Criteria for rejection
- Subjects having previous history of nasal surgery.
- Subjects suffering from nasal polyposis, nasal carcinoma, epistaxis.
The data collected from all the 60 Subjects of both groups was summarized and statistically represented in terms of Vital Statistics, Observations during study, Results of the study and Statistical comparison of both the groups [33-37].
Result
In the Group A the Mean Foul Smell of Nose was observe to be 2.133 before treatment that reduced to 0.9333 after treatment (p value <0.05) , the Mean Anosmia of Nose was observe to be 1.633 before treatment that reduced to 1.567 after treatment (p value >0.05), the Mean Dryness of Nose was observe to be 2.5 before treatment that reduced to 0.6667 after treatment (p value <0.05),the Mean Crusting of Nose was observe to be 2.467 before treatment that reduced to 0.7000 after treatment (p value <0.05), the Mean Nasal Discharge of Nose was observe to be 1.333 before treatment that reduced to 0.5667 after treatment (p value <0.05), the Mean Blocking of Nose was observe to be 2.133 before treatment that reduced to 0.9000 after treatment (p value <0.05) [38,39].
In the Group B the Mean foul smell of Nose was observe to be 2.233 before treatment that reduced to 1.067 after treatment (p value <0.05), the Mean Anosmia of Nose was observe to be 1.500 before treatment that reduced to 1.400 after treatment (p value >0.05), the Mean Dryness of Nose was observe to be 2.333 before treatment that reduced to 1.367 after treatment (p value <0.05), the Mean Crusting of Nose was observe to be 2.300 before treatment that reduced to 1.067 after treatment(p value <0.05), the Mean Nasal Discharge of Nose was observe to be 1.467 before treatment that reduced to 0.8333 after treatment(p value <0.05) [33,40,41], the Mean Blocking of Nose was observe to be 2.033 before treatment that reduced to 1.167 after treatment (p value <0.05).
To examine either the groups differs from each other significantly or not, further data are treated by Mann whiteny U score test. For Foul Smell of Nose the mean difference in value in group A was 1.200 while that in Group B was 1.167(p value >0.05). For Anosmia of Nose the mean difference in value in group A was 0.06667while that in Group B was 0.1000(p value >0.05). For Dryness of Nose the mean difference in value in group A was 1.833 while that in Group B was 0.9667(p value <0.05) [42-44]. For Crusting of Nose the mean difference in value in group A was 1.767 while that in Group B was 1.233(p value <0.05). For Nasal Discharge of Nose the mean difference in value in group A was 0.7667 while that in Group B was 0.6333(p value >0.05). For Blocking of Nose the mean difference in value in group A was 1.233 while that in Group B was 0.8667(p value <0.05).
Discussion and Conclusion
In this series, 60 patients of Allergic Rhinitis were studied out of which 36.66% patients found in Aged group between 20- 30 yrs and 40-50yrs respectively, No any difference in sex ratio is found i.e. both male to female ratio is equal, 73.33% patients belonging to Hindu religion, maximum number of patient are educated up to mid school and high school i.e. 26.66% each. 80% of patients are from lower socio-economic level, 50% patient were suffering from Allergic Rhinitissince more than 5 yrs, 71.66% patient were having kaphavataj prakriti, 38.33% patient were having mandagni, 78.33% patients were taking sheet gunatmaka Ahar while 71.66% patient were taking rukshagunat mak Ahar, 48.33% patient were taking dominant katu rasatmaka Ahar and 83.33% patients were taking mixed type of diet [44].
In this study 100% patients of both groups were having vata dosh dushti while 75% patient were having kapha dosh dushti, 100% patients of both groups were having Rasa dushya dushti while Mansa and Rakta dushya dushti were 80% and 71.66% respectively.85% patients were living in Unhygienic residential area, 58.33% patients were doing labor work and 35% patients were having history of addictions. After doing inference confidently by Wilcoxon Sign Rank Test, it is found that in group A except for Anosmia difference between before treatment and after treatment are statistically highly significant for foul smell, dryness, and crusting, nasal discharge and blocking of nose [42]. Also in group B treatment with Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray are effective relieving symptoms of Allergic Rhinitisexcept for symptom anosmia.
After doing Mann-Whiteny U Test to examine difference between effect of treatment in both groups it is found that for dryness, crusting and blocking of nose the inference is highly significant. I.e. for above symptoms Group A shows better result than Group B .But for foul smell, anosmia and nasal discharge the inference are in-significant. The properties of shadbindu taila i.e. acidic nature, excess of hydrogen ions are useful for capillary circulation. Increased H+ ions concentration dilate the capillary. As shadbindu taila is having excess of H+ ions concentration it causes dilatation of capillary. Irritation of the skin produces vasodilatation in the locality. In neurology this reflex is known as Axon reflex. As shadbindu taila is being acidic in nature, it acts as irritant to nasal mucosal membrane, which produces vasodilatation [23,36]. The acidic nature of shadbindu taila also inhibits the photolytic organism and also helps in removing crust. Thus shadbindu taila acts as vasodilator and Germicidal which are helpful in minimizing the symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis. From the above discussion, it is clear that Subjects having clinical features of Allergic Rhinitis are more significantly reduced in Group A than Group B which itself prove that treatment with shadbindu taila Nasya is better than treatment with Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in Allergic Rhinitis.
References
- Venimadhavshastri Joshi (1968) Ayurvediya Shabdakosha, Maharashtra Rajyasahitya and Sanskruti Mandal, Mumbai, India.
- Arundatta (1933) Ashtang Hridaya-Sarvanga Sundaracomm, Edited by Nirnaya Sagar, Press, Mumbai, India.
- Yadunadan Upadhyaya (1993) Vagbhatvidyotini Hindi comm Atrideva Vidyalankar, Ashtang Hridaya-, Chaukhumbha Prakashan P.O. Box No. 32, K-37/117 lane, Gopal Mandir lane, Varanasi, India.
- Vridha Vagbhat with comm. of Indu (1980) Edited by Vd. Anant Damodhar Athawale Ashtang Sangraha, Shrimal Akshaya Prakashan, Pune, India.
- Yadavj trikamji aachrya (1941) Ayurned Deepika- Chakrapanidatta comm. on -Charak Samhita, Nirnaya Sagar Press, Mumbai, India.
- KB Bhargava (2000) Short text book of ENT Diseases, Usha Publications Gopalbhavan, Tagore Road,Mumbai 54, India.
- Brahma Shankar Mishra Shastri Vidyotini Hindi comm, Bhavprakash, Chaukhamba Sanskrit Sanstha, Varanasi, India.
- Kaviraj Ambikadatta Shastri Vidyotini (1970) Hindi Comm Edited by shri Rajeshwar Datta Shastri Bhaishajya Ratnavali-Choukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.
- Agnivesha (1983) Edited by Brahmanand Tripathi, Charak Samhita, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.
- PV Sharma (English Translation) (2000) Charak Samhita, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.
- Yadavaji Trikamji Acharya (1994) Dalhan, Nibandha Sangraha comm. on Sushruta, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.
- Vd PG Athawahe (1984) Drishtartha shalakya Tantra, Drishtartha Mala Prakashan, Padmdlaya, Bajaj Nagar, Nagpur, India.
- Acharya Priyawat Sharma, Dravya Guna Vignyana, Published By Chaukhambha Bharti Acadamy, Varanasi, India.
- Vd AP Deshpande (1996) Dravya Guna Vignyana, Anamol Prakashan, Pune-2, India.
- Alxender Rosinkin, VT Palchun, NL Voznesenky, Diseases of Ear, Nose and throat, MIR Publishers, Moscow, Russia.
- Simson Hall, Barnard H (1981) Colman Churchill, Diseases of Ear, Nose and throat, Livingstone, Robert Stevension House.1-3 Baxter place leith walk, Edinburgh, Europe.
- PL Dhingra (1998) Diseases of Ear, Nose and throat, B. I. Churchill Livingstone Pvt. Ltd.54, Janapath, New Delhi, India.
- AC Deb (1996) Fundamentals of Biochemistry, New Central Book Agency Pri. Ltd., 8/1 Chintamani Das lane, Calcutta-9, India.
- Peter L (1989) Williams, Roger Warwick, Mary Dyson, Lawrence H, Bannister Gray’s Anatomy, (37th edn) Published by Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London, Melbourne and New York, USA.
- Harit (1985) Edited, By Ramvallabha Shastrimprachya by Asha Hindi comm, Harit Samhita, Varanasi, India.
- Chandi Charan Chatterjee (1992) Human Physiology, Medical Allied Agency, 82/1 Mahatma Gandhi Road, Calcutta-9, India.
- RN Chapra (1958) Indigenous drugs of India, Edited by Dharaand Sons Pvt. Ltd.Calcutta-12, India.
- AK Nadkami (1956) Indian Materia Medica, Popular Book Depo, Mumbai, India.
- Prakash Paranjape (2001) Indian Medicinal Plants Published by Chaukhambha Sanskrit Pratisthan, Delhi, India.
- OM Parmar (1985) Karna nasa Kanth ke Samanya Rog Hariyana Sahitya Acadamy, Chandigarh, India.
- B K Mahajan (1999) Methods in Biostatistics, Jaypee Brothers Medical Publisers Pvt. Ltd. Dariyaganj, New Delhi, India.
- Yadunandan Upadhyaya (1992) Madhavkar Vidyotini comm, Madhav Nidan Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.
- Madanpal, Madanpal Nighantu, Published by Gangavishnu Shrikrishnadas, Kalyan, Mumbai, India.
- Baplal G (1998) Vaidya, Nighantu Adarsha, Published by Chaukhambha Bharati Acadamy, Varanasi, India.
- Raghuveer Sinh seth (1978) Naka, Kana, Gale ki Chikitsa, Uttar Pradesh Hindi Santhan, Lakhnau-226001, India.
- Sharangdhar (1966) Hindi comm. by Prayagdatta, Sharangdhar Samhita Published by Chaukhambha Sanskrit Series, Varanasi, India.
- Raja Radhakantdeo Barhaduren (1961) Edited by Sundarlal Jain, Shabdakalpadruma, Published by Motilal Banarasidas, Javaharnagar, Delhi-6, India.
- Sushrut (1989) Edited by Kaviraj Dr. Ambikadatta Shastri, Sushrut Samhita Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi-221001, India.
- Bhishagratna (1991) Sushrut Samhita (English translation) Published by Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.
- Vd RR Padmawar (1990) Shalakya Tanra (karna, nasa, shiroroga), Published by Shri. Baidyanath Ayurved Bhavan Ltd., Great nag road, Nagpur-9, India.
- RC Choudhary (1983) Shalakya Vigyan (Sachitra),Chaukhambha orientalia Varanasi, India.
- Shivnath Khanna (1985) Shalakya Tantra (Karna, Nasa, Kantha Rog), Choukhambha Surbharti Prakashan, Varanasi, India.
- Ramnath Dwivedi, Shalakya Tantra, Choukhambha Surbharti Prakashan, Varanasi, India.
- Vd RR Padamawar, Vd HN Umale (2000) Shalakya Tantra Rugna Parikshan, Published By Godawari Publisher and Book Promotors, 148, Shastrinagar, Nagpur, India.
- Pandit Dharmanand Sharma, Rasa ratna samucchayas, published by Motilal Banarasidas, Jawahar Nagar, Delhi-7, India.
- Taber’s Encyclopedic Medical Dictionary (1993) Jaypee Brothers Medical Publisher (P) Ltd., EMCA House, 23/23B Ansari Road, Dariaganj Delhi, India.
- Kapildeo Dwivedi, Vedo Mein Ayurved, Published by Vishva bharati Anusandhan Parishad, Ghyanpur, Varanasi, India.
- Shri Chandraraj, Vanaushadhi Chandrodaya, Published By Bhandari Visharad. Shri Taranath, Vachaspatyam. Counil of Scientific and Industrial Research, Wealth of India, Publication and Information Directorate CSIR, New Delhi, India.
- Yogatnakar, Vidyotini Hindi Comm. By Vd. Laxmipati Shastri, Yogratnakar, Choukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, India.





























