Foreign Body (Coin) in the Nasopharynx of a child and its Management
Sushil Kumar Kashyap1 and Siva S2*
Department of ENT, MLB Medical College, India
Submission: August 24, 2016; Published: September 01, 2016
*Corresponding author: Sushil Kumar Kashyap, Bundelkhand University, MLB Medical College, Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh, India, Tel: 7309403881; Email: selvarajk.siva@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Sushil K K. Foreign Body (Coin) in the Nasopharynx of a child and its Management. Glob J Otolaryngol. 2016; 1(5): 555575. 10.19080/GJO.2016.01.555575
Abstract
Cases of foreign bodies in the aero digestive tract are common in children. But their presence in nasopharynx is rarely encountered as they present with vague set of symptoms. We encountered a female child with history of coin ingestion without any symptoms like nasal blockade and mouth breathing. On X- ray it was found to be in nasopharynx and was removed immediately. Hence any suspected foreign bodies in aerodigestive tract should be thoroughly evaluated for their location.
Keywords: Nasopharynx; Foreign body; X ray neck
Introduction
Foreign body ingestion is a common entity in children [1]. The fate of the ingested foreign body is that it can either pass further down the aerodigestive tract, can be expelled by cough or can get stuck at the narrow parts of the upper aero-digestive tracts [2]. The common site for the foreign body to get struck is crico-oesophageal junction. Ingested foreign body to get lodged in the nasopharynx is a rare entity as the direction of movement is against gravity [3]. Impaction of the FB in the nasopharynx may result due to failed attempt in removing it or due to dislodgement of the FB from initial site of impaction by vomiting or cough. Here we are going to discuss a case of foreign body in the nasopharynx of a 2 year old girl, how it presented to us and how we managed the case in emergency.
Case Report
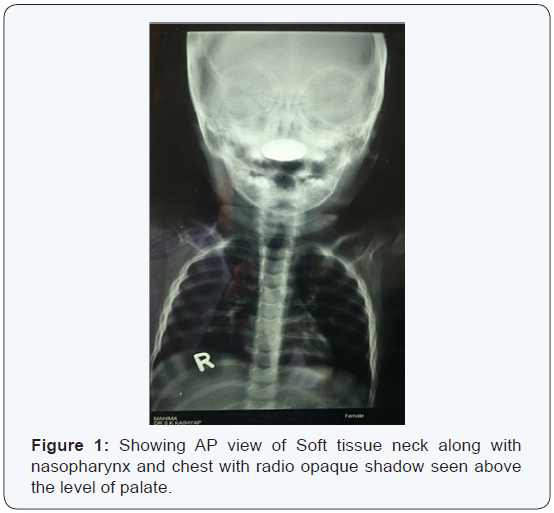
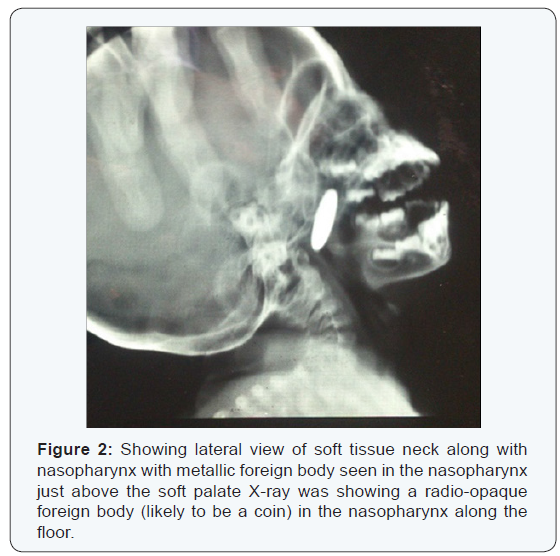
A 2 year old girl was brought to the emergency department with a history of accidental coin ingestion in the morning. On examination of the child, there was no Stridor or chest retraction. The oral cavity and oropharynx were normal and no foreign body was found. Anterior rhinoscopy showed minimal mucoid discharge in the nose. X-ray neck along with chest was ordered to confirm the presence and position of the foreign body. The X ray showed the presence that the coin was lodged in nasopharynx in coronal plane which was quite unusual. The pictures of the X-rays are shown as (Figures 1 & 2).
Immediately when the position of the coin was located with the help of X-ray, the girl was posted for removal of the FB. The patient was kept in supine position with head end lowered. Soft palate was slightly retracted and with the help of angled forceps, the foreign body was held and removed. There were no post operative complications and the patient was discharged on the next day.
Discussion
The presence of the foreign body in nasopharynx is a rare entity as the normal route for an aero digestive foreign body is mouth. In case of foreign body nasopharynx, it is nose [4]. In our case, the foreign body (coin) was present in nasopharynx. But the mode of entry of foreign body is mouth. We suspect the route of entry into the nasopharynx in this case is mouth and the way how it reached there is mystery. There are literatures saying ingested foreign bodies can reach the nasopharynx by regurgitation/ vomiting/ coughing or by failed attempt to remove the foreign body by parents or physicians [5]. Patients with nasopharyngeal foreign body present with symptoms like difficulty in breathing, nasal obstruction, nasal bleeding or nasal discharge [6]. Diagnosis of the case is not challenging when there is clear history but sometimes when there are no nasal symptoms as in our case only radiological investigations can guide us to the diagnosis [7]. Removal of the foreign body from nasopharynx is always safe to be done with head end low position so that the risk of the foreign body to enter the lower airway is avoided [6].
Conclusion
From the discussion of the above case and review of previous literature we come to the conclusion that examination of nasopharynx and radiological evaluation is necessary in cases of suspected foreign bodies in aero digestive tract. Immediate removal is indicated with the patient in supine position with head end down.
References
- Krishnappa BD (2013) Endoscopic removal of an unusual foreign body in the nasopharynx in a 3 year old child. International Journal of Head and Neck Surgery 4(3): 140-141.
- Jagdish Kumar (2011) Nasopharyngeal Foreign Body in a Young Child. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 63(3): 285-286.
- Satheesh Bhandary, Biniyam Kolathingal, Vadish Bhat, Balakrishna Padubidri Srinivas (2011) Common Foreign Body, Unusual Site. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 145(6): 1060-1061.
- Kiger J, Brenkert T, Losek J (2008) Nasal foreign body removal in children. Pediatr Emerg Care 24: 785-792.
- Pallab Kumar Majumder, AK Sinha, PB Mookherje, SN Ganguly (1999) An unusual foreign body (10 N. P. COIN) in nasopharynx. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 52(1): 93.
- Manish Gupta (2014) Endoscopic removal of an unusual foreign body from nasopharynx. Research 1: 871.
- Raman Wadhera, SP Gulati, Ajay Garg, Anju Ghai (2008) Two rare case reports of nasopharyngeal foreign bodies: bobbin and safety pin. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 3(1): 14-16.





























