Mitigation of Dust Impact on Solar Photovoltaics Performance Considering Libyan Climate Zone: A Review
Abdulgader Alsharif*
Communication Engineering Department, College of Civil Aviation Technology and Meteorology, Espiaa, Libya
Submission: July 5, 2023; Published: August 4, 2023
*Corresponding author: Abdulgader Alsharif, Communication Engineering Department, College of Civil Aviation Technology and Meteorology, Espiaa, Libya
How to cite this article: Abdulgader A. Mitigation of Dust Impact on Solar Photovoltaics Performance Considering Libyan Climate Zone: A Review. Eng Technol Open Acc. 2023; 5(3): 555662. DOI: 10.19080/ETOAJ.2023.05.555662
Abstract
The research aims to evaluate the impact of dust accumulation on the performance of solar panels in the Libyan climate zone. The study conducted a series of experiments to measure the degradation of solar panel efficiency due to the deposition of dust on their surface of the solar panels. The results indicate that the accumulation of dust has a significant negative impact on the performance of solar panels, reducing their efficiency. Furthermore, the study examined the frequency and cleaning methods required to maintain the solar panels’ performance over time in this harsh climate. The findings highlight the importance of routine cleaning and maintenance of solar panel installations in dusty and arid regions to ensure optimal performance and maximize energy efficiency.
Keywords: Libya; Dust; Solar Panels
Introduction
Libyan climate zone is known to have high levels of dust events, which can have a significant impact on the performance of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems [1]. The accumulation of dust on the surface of solar panels can cause a reduction in their efficiency, ultimately leading to a decrease in power output [2]. Many utilizations of solar panels are employed such as traffic light, street lighting, and home energy supporting and effected by the dust that may be defined as minute particles with a diameter of 500 μm [3]. To evaluate the impact of dust disposition on the solar panels, it is necessary to first determine how much dust accumulates on the panels [4]. Solar panels are known as one of the leading sources of renewable energy, and they work by converting sunlight into electrical energy [5]. Governments of more and more countries are pushing for usage of solar panels in lieu of non-renewable energies such as coal and petroleum [6]. While their low environmental impact is a strong incentive for increased implementation, solar panels still face some challenges which hinder their ability to reach their full potential [7]. One of those challenges is dust accumulation on the solar panel, which acts as a layer of shade preventing sunlight from penetrating the cell and being converted to electrical current [3]. Dust conditions vary around the world, with desert regions such as the Middle East and North Africa having some of the most elevated dust concentrations in the world; interestingly, these regions also receive the most solar irradiation [8].
The main contribution of the article is by providing a general view of dust impacts on solar photovoltaic along with the limitations of the dust and future perspective of the aforementioned problem. the reminder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 consists of the general background of the dust impacts on the solar panels and in the environment. The case study region details is placed in Section 3 along with dust mitigation methods. The disadvantages of dust on the solar panels are positioned on Section 4. Eventually, summary of the conclusion and list of recent references are ending the article.
Background History on Dust Impacts
The dust impacts has taken a place of scholars as one of the faced challenges that reduces the productivity of the solar photovoltaics. Based on numerous climatology changes along with various regions, the solar panels got effected [3]. The most common renewable energy source (RES) that has some issues dependent on the site’s radiation that affects the power outcome is solar energy. Besides, various conducted studies on calculating the amount of dust on photovoltaic and thermal systems [4]. Additionally, the main consideration on this article is met along with citied study in order to measure the impacts on the solar panels and presenting solutions.
Libyan Geography Zone
Libya is located in north African region as figure out in (Figure 1), and it is a part of northern hemisphere with 25 N and 17 E latitude and longitude effected with dust and some storms [1]. The presence of dust in the air can negatively impact air quality by increasing levels of particulate matter, which can have adverse effects on respiratory health and reduce visibility. If you are concerned about air quality in a specific location, it is recommended to check with local air quality monitoring agencies or authorities for more information. There are several methods for mitigating the impact of dust on PV performance as formulated in (Table 1).
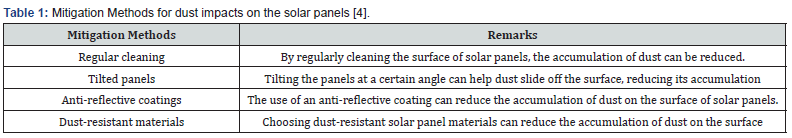
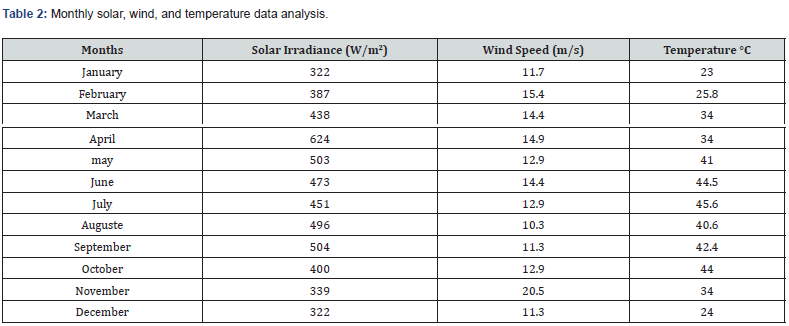
It is important to note that the efficacy of these methods can vary based on the specific conditions in the Libyan climate zone. Close attention must be paid to the conditions and specific measures taken to alleviate dust impact on solar photovoltaics performance. Monthly solar, wind, and temperature data analysis is arranged in (Table 2) (Figure 1).
Dust accumulation on solar photovoltaic (PV) panels can significantly reduce their performance and efficiency. Dust can have an insulating effect, reducing the amount of sunlight that reaches the solar cells and decreasing the amount of electricity produced. In areas with high levels of dust or pollution, the impact can be even greater. Therefore, it is important to regularly clean the solar PV panels to prevent dust buildup. Regular cleaning can help maintain optimal performance and increase the lifespan of the solar panels. Additionally, it is important to choose a location for solar panels that is less prone to dust accumulation. In terms of gaining a sustainable environment, solar power is a great alternative to traditional sources of energy that rely on fossil fuels. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and using clean, renewable energy sources like solar power, we can work towards a more sustainable future with less pollution and a healthier planet.
The first key term to define is dust. Dust may be defined as minute particles with a diameter of under 500 μm. It comes from solid material and can be visible or invisible, floating or settled. To evaluate the impact of dust deposition on the solar panels, it is necessary to first determine how much dust accumulates on the panels. We can define the thickness of dust on the solar panel, which we can define by the formula that presented in Eq. (1) and
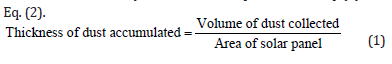
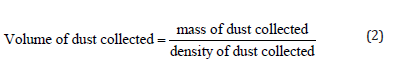
Most research papers define the amount of dust on the panel by grams per meter squared, and therefore determine the power lost from the solar panel per grams per meter squared of dust. The amount of dust that accumulates on the panel varies geographically. For example, an experiment performed in Tehran, Iran shows that the dust concentration on a local solar panel (accumulated over a period of 70 days) ranges from 4.0599 g/ m2 to 10.3129 g/m2. In the Middle East and North Africa, the dust accumulation rate was said to be around 0.3 g m-2 day. If we want to compare that value to Tehran›s, 0.3×70=21 g/m2, which is a reasonable amount, considering that these regions have the highest dust concentrations on Earth.
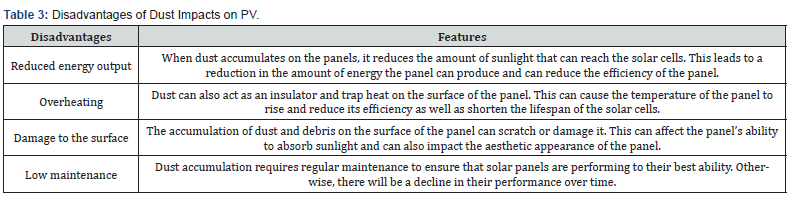
Disadvantages of Dust
The dust causes a negative impact, some of the disadvantages of dust impacts on PV performance as tabulated in (Table 3). Regular cleaning and maintenance can help to mitigate the disadvantages of dust impacts on PV performance to ensure that the panels are generating as much energy as possible (Table 3).
Cleaning Solar Panels
There are a few prominent methods to clean solar panels. One of them, carried out by the Adani group in India, involves the use of tractors that clean the panels with water, cleaning wipers, and brushes. However, this technique requires heavy usage of water and manual labor, which is both unsustainable and economically unviable. Another technique to remove dust from solar panels is called electrostatic dust removal, which applies a high AC voltage to repel dust particles from soiled solar panels. This has a maximum cleaning efficiency of 100% when dust settled is roughly 1 g/m2, which corresponds to dust accumulation over a period of three days in the Middle East and North Africa. The power consumption of this cleaning system is very low compared to the solar cell’s power output. It takes around 5 minutes to clean a 1 m × 1 m solar panel with an electricity consumption of roughly 0.9 Wh. If we assume that the power generated by the panel averages 300 W/ m2 over 7 hours, then the fraction of the energy collected by the panel that must be used for cleaning is calculated by Eq. (3).
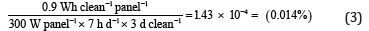
This cleaning method is especially useful in increasing the efficiency of mega solar panels in deserts. Overall, while more and more power plant companies are cleaning their solar panels to reduce the dust settlement, multiple techniques are still being explored and optimized to keep a net positive power generation and to remain sustainable for the future.
Possible Solution in Future Perspective
Self-cleaning, by ensuring regular maintenance and cleaning, we can increase the lifespan of solar panels and promote sustainable energy practices. This not only helps to reduce our reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels but also decreases our carbon footprint and contributes to a cleaner environment. In addition, promoting sustainable energy practices and maintaining solar panels can also lead to job creation in the renewable energy sector and stimulate economic growth. Therefore, it is essential to prioritize sustainable energy and take steps towards promoting it in our daily lives.
Conclusion
The energy sector has undergone enormous growth and development on a global scale and attempts to improve energy efficiency are now seen as necessary to build a power generation infrastructure that is sustainable. The impact of dust on solar photovoltaic performance is significant as it reduces the efficiency of the panels by blocking sunlight and reducing the amount of energy produced. Therefore, regular cleaning of solar panels is crucial to maintaining the efficiency of the system. If left uncleaned, the dust can accumulate and cause permanent damage to the panels, leading to costly repairs and replacements.
References
- Maka AOM, Alabid JM (2022) Solar energy technology and its roles in sustainable development. Clean Energy 6(3): 476-483.
- Mohamed AO and Hasan A (2012) Effect of Dust Accumulation on Performance of Photovoltaic Solar Modules in Sahara Environment. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research 2(11): 11030-11036.
- HM Khalid, Zimran Rafique , Muyeen SM, Abdul Raqeeb , Zafar Said, et al. (2023) Dust accumulation and aggregation on PV panels: An integrated survey on impacts, mathematical models, cleaning mechanisms, and possible sustainable solution. Solar Energy 251: 261-285.
- Kazem AA, Chaichan MT, Kazem HA (2014) Dust effect on photovoltaic utilization in Iraq: Review article. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 37: 734-749.
- Yamnenko J, Osypenko K, Hnatyuk B (2017) Modeling of the solar panel diesel-generator system stability. Proceedings - EPNet 2016 Electric Power Networks, pp. 0-4.
- Raugei M, Hutchinson A, Morrey D (2018) Can electric vehicles significantly reduce our dependence on non-renewable energy? Scenarios of compact vehicles in the UK as a case in point. J Clean Prod 201: 1043-1051.
- Kamal MM, Mohammad A, Ashraf I, Fernandez E (2022) Rural electrification using renewable energy resources and its environmental impact assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 29(57): 86562-86579.
- Mustafa RJ, Gomaa MR, Al-Dhaifallah M, Rezk H (2020) Environmental Impacts on the Performance of Solar Photovoltaic Systems. Sustainability 12(2): 608.






























