- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Sonographic Evaluation of Liver Cirrhosis: Causes and Pathophysiology
Dr. M Ayub Hussain*
Program Director Deportment of Diagnostic Medical Ultrasonography, New York Medical Career Training Center, USA
Submission: December 06, 2017; Published: December 15, 2017
*Corresponding author: Dr. M Ayub Hussain, Program Director, Deportment of Diagnostic Medical Ultrasonography, New York Medical Career Training Center, USA, Email: mahussain59@gmail.com
How to cite this article: M Ayub Hussain. Sonographic Evaluation of Liver Cirrhosis: Causes and Pathophysiology. Adv Res Gastroentero Hepatol 2017; 8(3): 555737. DOI: 10.19080/ARGH.2017.08.555737
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Introduction
Liver cirrhosis existed since ancient times. It is widely speeded all over the world various causes:
a. Known and unknown
b. Signs and symptoms may be different for patients in
Biopsy is not the only and 100% positive test for Liver cirrhosis diagnosing. Clinical history, physical examination, signs and symptoms, blood works and Ultrasound evaluation can diagnose liver cirrhosis most of the time without the need of biopsy. Ultrasound is a helpful modality. Inexpensive, quick, available, noninvasive, portable, repeatable and more over non radiation. Elastography is a kind of ultrasonography recently started commercially.
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Goals and Objectives
At the end of this session, we will learn the impact in details about:
a. Patient history
b. Details physical examination
c. Selective blood works
d. Sonography evaluation in order to diagnose the liver cirrhosis without biopsy (Figure 1-5).
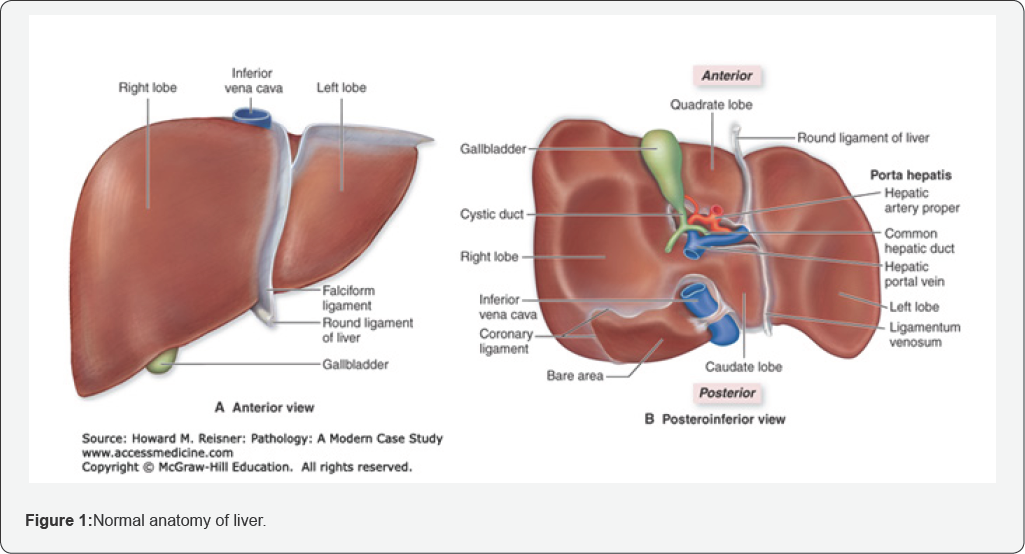
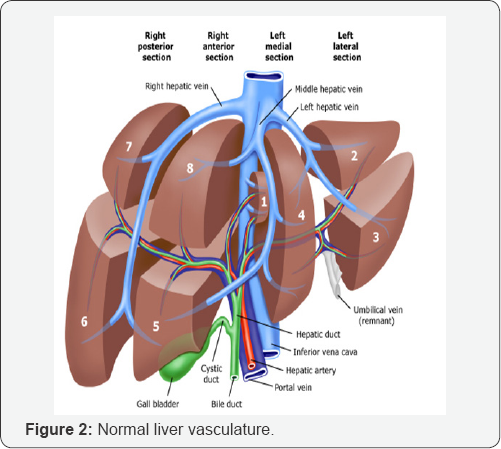
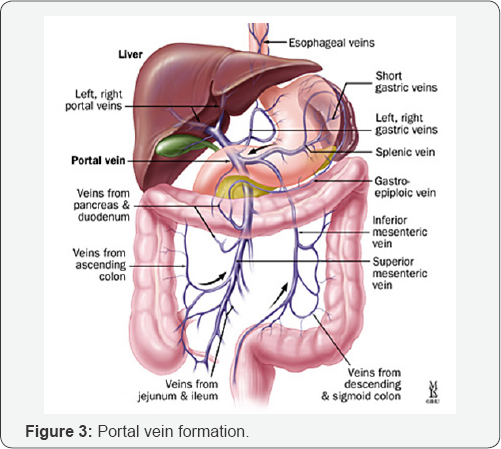
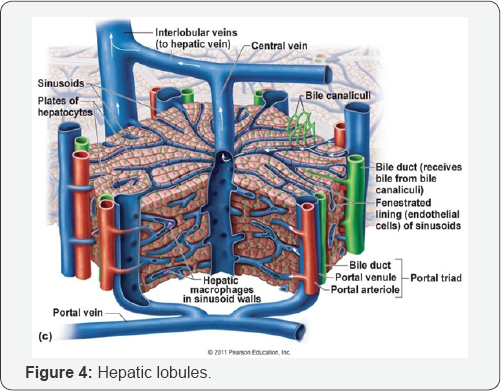

- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
a. Alcoholic cause is more prevalent in western countries 60-70%.
b. Non Alcoholic viral causes: Hep B and C
c. Higher in developing countries, especially Asia and Africa.
d. Inadequate screening test for blood transfusion and contamination from dialysis machine.
e. Unprotected sexual activity (Figure 6).
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
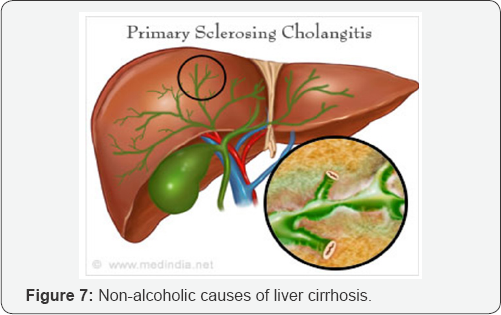
Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
a. NASH (Non Alcoholic Steatohepatitis).
b. Metabolic: Haemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, fatty infiltration and Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
c. Auto-Immune hepatitis.
d. Biliary disease: primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cirrhosis.
e. Vascular disease: congestive hepatopathy, Budd-chiari syndrome and hepatic veno-occlusive disease.
f. Medications: Methotrexate.
g. Cystic fibrosis: uncommon (Figure 7).
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
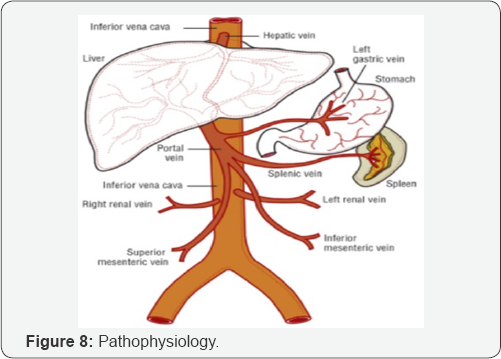
Pathophysiology
Steps
a. Fibrosis.
b. Nodular regeneration.
c. Distortion of liver architecture (Figure 8).
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
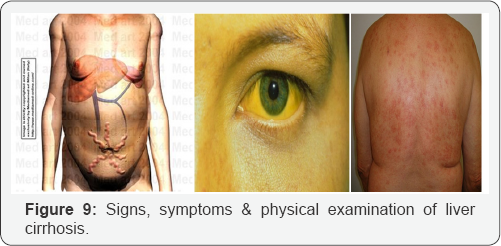
Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
There’s no typical signs or symptoms of liver cirrhosis because depends on the stages and athophysiology of the disease.
I. Early stage: Asymptomatic
II. Late stage:
a. Malaise
b. Fatigue
c. Lack of appetite
d. Frequent loose motion after eating
e. Distended and heaviness of abdomen
f. Pain in left hypochondriac
g. Muscle wasting
h. Hemorrhoids
i. Dizzy
j. Jaundice
k. Skin itchy
l. Hepatic faces
m. Caput medusa
n. Disorientation: Dementia and amnetia (Figure 9).
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
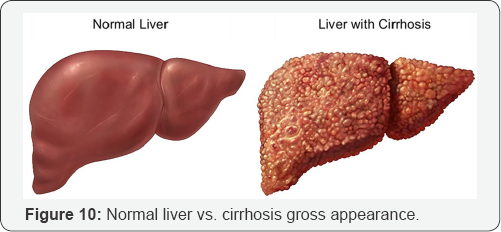
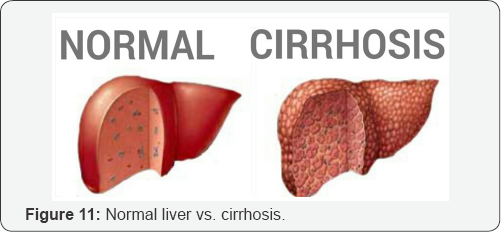
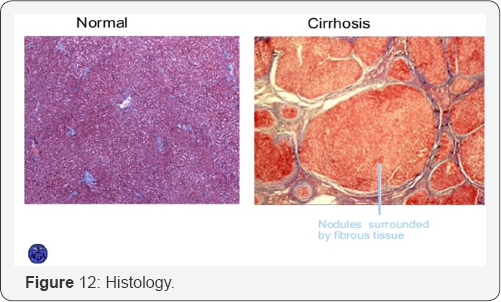
Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
a. Blood tests to check liver functions: Albumin and Total serum protein.
b. Prothrombin time/INR.
c. Bilirubin
d. Liver enzymes: AST, ALT and lactate dehydrogenase.
e. Alkaline phosphatase.
f. Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C antigen and antibody.
g. Alpha 1-antitrypsin.
h. Blood alcohol test.
i. Antinuclear antibody (ANA), Anti- smooth muscle antibody (ASMA), Anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA).
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
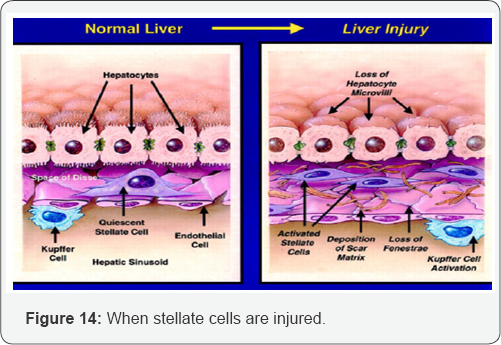
Insult of Liver Cells
A. Stellete cells
a. Fibrin, collagen and intercellular matrix release.
B. Hepatocytes
a. Formation of regenetive nodules.
C. Sinusoid compression
a. Obstruction of blood flow.


- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
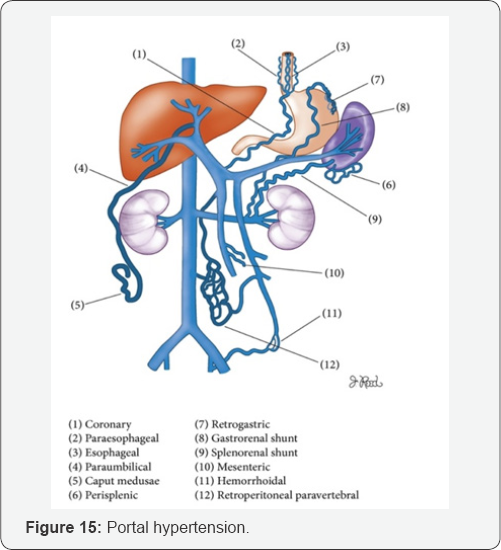
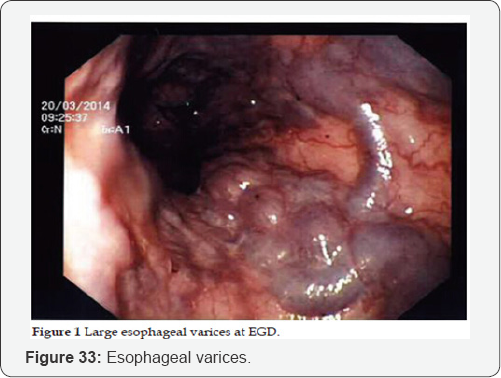
Portal Hypertension
PV dilation due to obstruction. Reverse flow to SMV, IMV, and SV. Blood that cannot enter into PV must return to systematic circulation via anatomotic sites. Results: Esophageal varices, rectal hemorrhoids, caput medusa, etc (Figure 15-29).




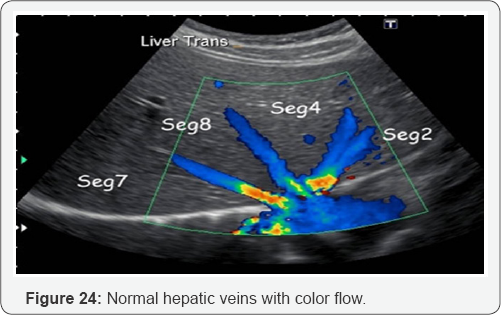
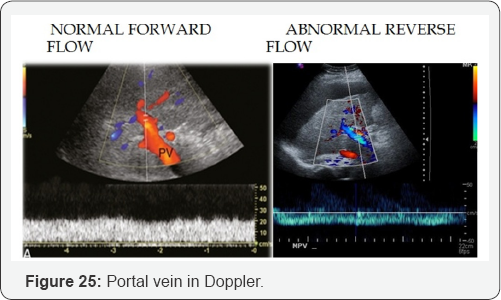
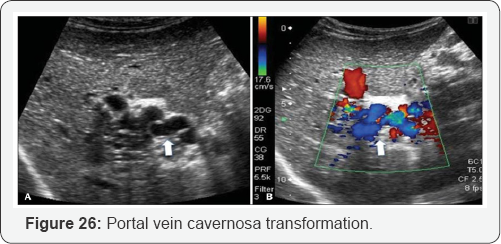
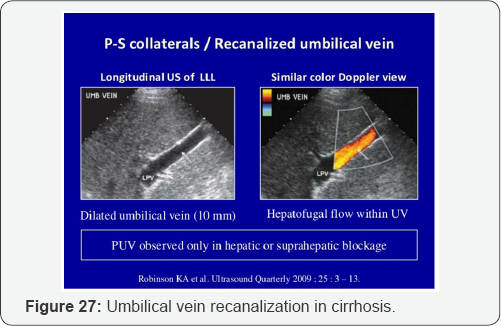
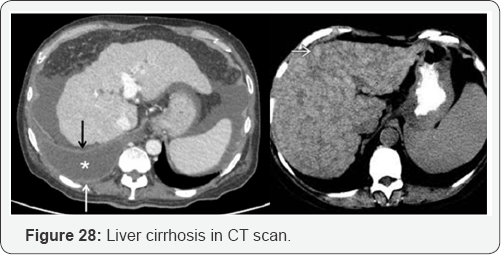
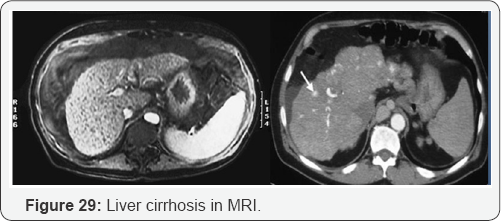


- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
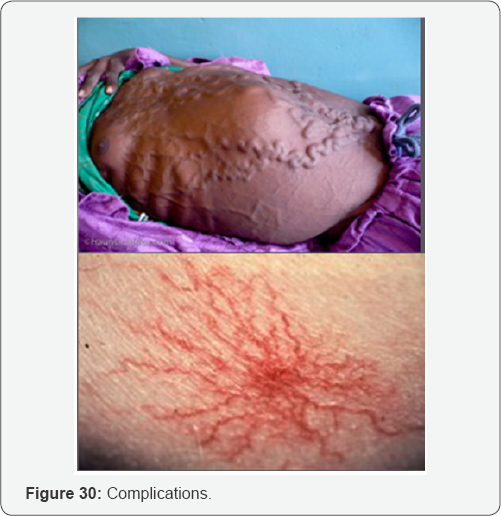
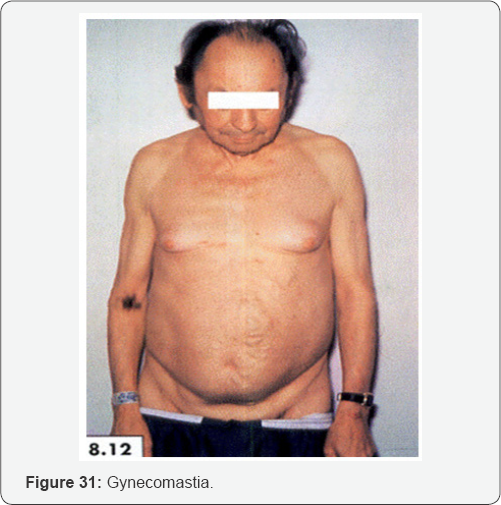
Complications
a. Portal hypertension, liver failure and liver cancer
b. Distended abdomen due to ascites.
c. Wasting of muscles.
d. Blood vomiting.
e. Rectal bleeding.
f. Defect in blood clotting.
g. Gynecomastia.
h. Spider angioma.
i. Electrolyte imbalance.
j. Caput medusa: Visible veins around the umbilicus.
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Results of Liver Failure
a. Accumulation of toxic materials in blood.
b. Decreased production of clotting factors.
c. Decreased production of plasma proteins.
d. Poor metabolism of estrogen.
e. Enzymes abnormalities.
f. Increase Bilirubin.
g. Platelets count decrease.
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
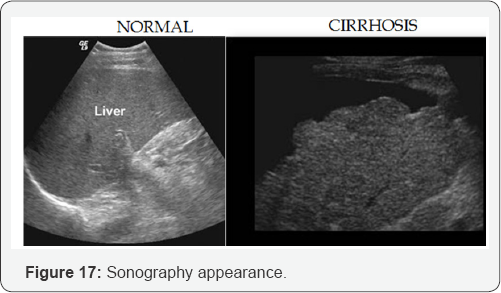
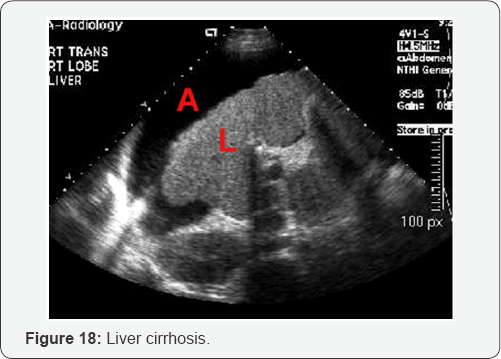
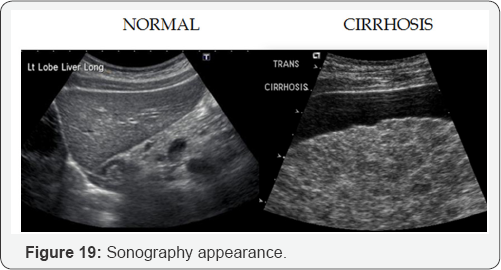
Conclusion
A. Diagnostic procedures
a. Patient history.
b. Bedside physical exams.
c. Blood works.
d. Ultrasonography of liver (Figure 34).
B. Sonographic characteristics of cirrhosis:
a. Hyper echoic liver
b. Course texture.
c. Irregular/nodular surface.
d. Small liver
e. Caudate lobe hypertrophy and decrease echogenicity.
f. Non visualization of hepatic veins.
g. Portal vein dilation >13mm.
h. Portal vein reverses flow.
i. Portal vein hypertension.
j. Dilation of splenic veins, SMV, IMV with reverse flow
k. Splenomegaly.
l. Ascites.
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Acknowledgements
a. Karen Soto, DMS program full-time Student, New York Medical Career Training center
b. Miao Chen, Bachelors in science, DMS extern student, New York Medical Career Training Center
c. Institutional staffs of New York Medical Career Training Center
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
Questions?
A. What is the most common cause of Liver Cirrhosis in western countries?
B. What are the most common viruses that cause liver cirrhosis?
C. Which cell in the liver has a greater impact on producing cirrhosis?
D. Most of the complications of liver cirrhosis is due to?
E. All of the following are sonographic appearances found in advanced stage of liver cirrhosis except?
a. Hyperechoic liver
b. Course texture
c. Hepatomegaly
d. Irregular nodular surfaces
F. Most of the liver cirrhosis can be diagnosed by taking clinically history, physical examination, lab tests and sonographic evaluation of the liver?
a. True
b. False References
- Power Point
- Introduction
- Goals and Objectives
- Causes of Cirrhosis & Epidemiology
- Non-Alcoholic Causes of Liver cirrhosis
- Pathophysiology
- Signs, Symptoms & Physical Examination of Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnosing Cirrhosis: Blood Works
- Insult of Liver Cells
- Portal Hypertension
- Complications
- Results of Liver Failure
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgements
- Questions?
- References
References
- Kobold D, Grundmann A, Piscaglia F, Eisenbach C, Neubauer K, et al. (2002) Expression of reeling in hepatic stellate cells and during hepatic tissue repair; a novel marker for the differentiation of HSC from other liver myofibroblast. J Hepatol 36(5): 607-613.
- Geerts A (2001) History, heterogeneity development biology and function of quiescent hepatic stellate cell. Semin Liver Dis 21(3): 311335.
- Winau F, Hegasy G, Weiskirchen R, Weber S, Cassan C, et al. (2007) Ito cells are liver-resident antigen-presenting cells for activating t-cells responses 26(1): 117-129.
- Eng FJ, Friedman SL (2000) Fibrogenesis I new insights into hepatic stellate cell activation; the simple becomes complex. American journal of physiology, gastrointestinal and liver physiology 279(1): G7-G11.
- Iranpour P, Lall C, Houshyar R, Helmy M, Yang A, et al. (2016) Altered Doppler flow patterns in cirrhosis patients: an overview. Ultrasonography 35(1): 3-12.
- Jesus Carale, Samy AA, Parit Mekaroonkamol (2017 ) Portal Hypertension. Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy
- http://www.ultrasoundcases.info
- Mansour T. Liver ultrasound. Faculty of medicine, Al-Azhar University Egypt.
- David C (2017) Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology.
- Gaillard F, Henry Knipe Cirrhosis. Radiology Reference Article.
- Lunsford BM, Diane MK (2012) Abdomen and superficial structures, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, USA, p. 841.






























