Dual Plating of Intra Articular Distal Femoral Fractures by Single Incision Anterior Midline Approach: A Case Series
Abhishek Garg*, Rakesh Sharma, Ankur Sahu, Manmeet Malik and Aditya Seth
Department of Orthopedics, UHS Rohtak, Haryana
Submission:March 29, 2021; Published: April 19, 2021
*Corresponding author: Abhishek Garg, Senior Resident, Department of Orthopedics, UHS Rohtak, Haryana, India
How to cite this article: Abhishek G Rakesh S, Ankur S, Manmeet M, Aditya S. Dual Plating of Intra Articular Distal Femoral Fractures by Single Incision Anterior Midline Approach: A Case Series. Ortho & Rheum Open Access J. 2021; 18(1): 555979. DOI: 10.19080/OROAJ.2021.18.555979
Abstract
Background: Despite advances in surgical techniques and various implants, the treatment of intra-articular distal femoral fractures poses a challenge to the clinicians worldwide. In this study we aimed to evaluate the clinical outcomes of lateral locking plate combined with medial assisted plate for treating intraarticular comminuted distal femoral fractures. Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective study which consisted of 10 cases of distal femur fracture with intraarticular extension and treated with open reduction and internal fixation with dual column plating using single incision anterior midline approach. Results: The mean age was 40.75±12.39 with a range of 20-70 years. There were 7 males and 3 females. Mean time for union was 16.15±1.35 weeks. 1 patient had decreased ROM due to stiffness at the knee joint. 1 patient had superficial infection. No deep infection was noted. 1 case of nonunion was noted in this study. Range of motion at knee at final follow up was 124.25±17.34 degrees. The mean NEER score was 82.15±9.19 with a range of 54-91. Conclusion: Single-incision dual plating approach for distal femoral fractures is effective and provides stable construct without loss of reduction and allows early rehabilitation and good functional outcomes.
Keywords: Distal femur fracture; Intra articular; Dual plating; Anterior approach; Single incision
Introduction
Distal femoral fractures account for 4-6% of all the femoral fractures and are caused by high-impact injury. Distal femoral fractures are also caused by low energy trauma in elderly patients with severe osteoporosis. These fractures are characterized by multiple onsets, comminution at the fracture site, instability and intraarticular extension [1,2]. The principles of management are to achieve anatomical reduction of the articular surface and preservation of the distal femoral blood supply with stable internal fixation allowing early functional mobilization. During fixation of these fractures, reconstruction and anatomical reduction of the articular surface should be the aim of the surgery [3]. Various methods of internal fixation have been used like 95° angled blade plate, dynamic condylar screw plate (DCS), condylar buttress plate and retrograde distal femoral inter-locking nail. However, when dealing with complex intraarticular distal femoral fractures, these implants may not prove to be effective for stable fixation [4]. In this study we aimed to evaluate the functional outcome of dual plating for the management of distal femoral fractures.
Materials and Methods
The present retrospective study was conducted in the Department of Orthopedics, PGIMS Rohtak and included 10 cases aged between 20-70 years, who were operated for distal femur fractures over last 3 years with dual plating by Anterior midline approach. Patients were retrospectively followed up with all their previous surgical records and radiographs. Patients were clinically examined and functional outcomes were noted. Patients with distal femur fractures with intra articular extensions based on AO classification were included in the study. Patients with age more than 70 years, having congenital or acquired deformity of injured limb before surgery, pathological fractures and open fractures were excluded from the study. Radiographs were taken in two planes, anteroposterior view and lateral view before planning for surgical fixation for distal femur fractures. All patients were operated in supine position through an anterior midline approach with incision length around 10-15cm extending equally on either side of patella. Tourniquets were not used in the surgery. The standard anterolateral arthrotomy was performed. The quadriceps tendon was split in line of incision and arthrotomy continued along either the lateral or medial border of patella keeping adequate tissue margin with the patella for resuturing at the end of the surgery.
First reduction of condyles is performed using pins and clamps, later condyles are reduced to the shaft. After reduction of the fragments, fracture was provisionally fixed with K wires. Both medial and lateral surfaces were fixed with an individual locking plate. Distal Femoral locking compression plate (DFLCP) was used on lateral side and Locking Recon plates were used on medial side (Figure 1). Postoperatively vitals and drain were monitored, intravenous antibiotics and analgesics were given. Radiographs were taken to ascertain implant position and mobilization of the limb was started from 3 to 5 days. Partial weight bearing was started after confirmation of commencement of healing process till fracture union. The Functional outcome was assessed using NEER score at final follow up. Total range of motion of knee joint was noted at least 6 months after the surgery and patient’s satisfaction based on surgical outcomes were assessed individually. Statistical analysis was done with SPSS version 16 using descriptive statistical methods including the Pearson Chi squared test and student-t test. A p value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant
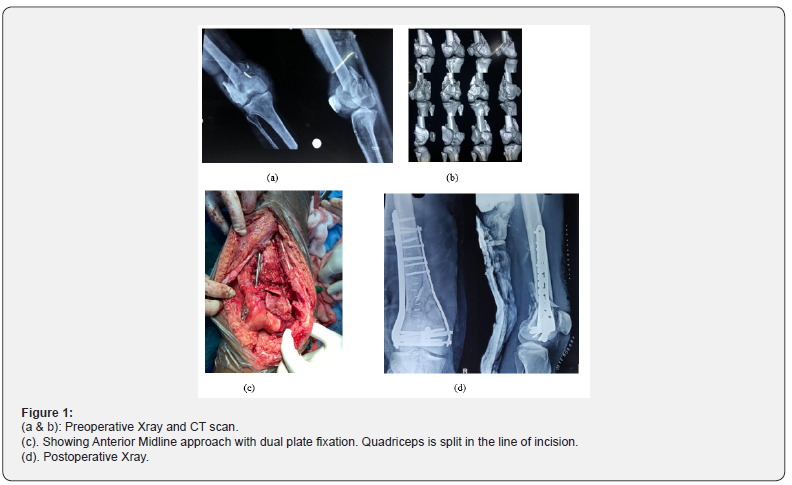
Results
The mean age was 40.75±12.39 with a range of 20-70 years. There were 7 males (70%) and 3 females (30%). Right side was involved in 6 patients (60%) while left side was involved in 4 patients (40%). 8 patients (80%) had Roadside accident (RSA) as mode of trauma for their fracture, 1 patient (10%) had simple fall and 1 patient (10%) had assault as the mechanism of injury for their fracture. All the patients were of C3 type according to AO classification. All the patients had closed fractures. Mean time for union was 16.15±1.35 weeks (Table 1). 1 patient had decreased ROM due to stiffness at the knee joint due to poor compliance of physiotherapy exercises. 1 patient had superficial infection which was managed with intravenous antibiotics. No deep infection was noted. One case of nonunion was noted in this study (Table 2). Range of motion at knee at final follow up was 124.25±17.34 degrees. Final results using NEER scoring system showed excellent outcome in 5 patients (50%), good results in 3 patients (30%), fair result in 1 patient (10%) and poor result in 1 patient (10%). The mean NEER score was 82.15±9.19 with a range of 54-91 (Table 1).
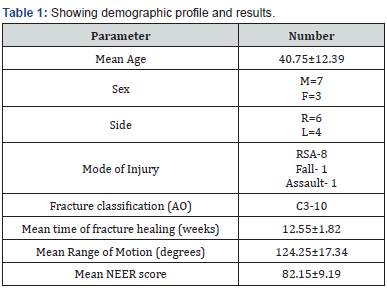
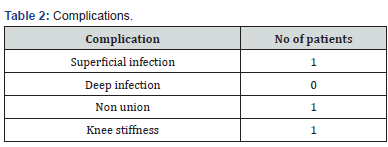
Discussion
Distal femoral fractures are challenging injuries for the orthopedic surgeons worldwide due to the complexity of fractures and articular extension. The damage caused to the periarticular soft tissues by the initial trauma and subsequent surgery by the surgeon, poses challenges in early postoperative rehabilitation. Hence, the outcome of management of intraarticular distal femoral fractures remains unpredictable, and these fractures are associated with many complications such as malunion, nonunion, knee stiffness and secondary osteoarthritis [5]. A plethora of surgical approaches are currently in use for fixation of distal femoral fractures. However, each approach has its advantages and disadvantages. In the lateral approach fascia lata is incised and vastus lateralis requires to be reflected anteriorly. Although with the lateral approach damage to the extensor mechanism of the knee can be reduced to some extent, but with this approach iliotibial band is damaged and the medial compartment of the knee is exposed inadequately [6]. The anterior midline approach is a surgical approach that can be used for intra articular fractures of the distal femur. Anterior approach has been commonly used for joint replacement. Adequate exposure of both the femoral condyles can be achieved using a single midline anterior incision with appropriate arthrotomy and fixation on both medial and lateral surfaces of distal femur becomes easy. Lateralization of femur which is sometimes seen after isolated fixation of lateral condyle by lateral approach is avoided by using the anterior approach [7,8]. These fractures are often a result of high-energy injuries and are accompanied by metaphyseal comminution, thereby complicating the treatments and are associated with various complications like inadequate fixation, infection, nonunion, knee valgus and joint stiffness [9].
The mean age in our study was 40.75±12.39 with a range of 20-70 years. Our results are comparable to the results of Bachu et al. [10,11] who had median age of 40 years ranging from 20-75 years and Parmar et al who had mean age of 39.8 years (Range: 18- 75 years) in their respective study. Or results are comparable to the results of Agrawal et al. [12] who had mean age of 44.3 years in their study, thus showing high incidence of these fractures in young population. Roadside accidents were major mode of injury in this study seen in 8 patients (80%) which is in collaboration with Bachu et al. [10] who reported Road traffic accident as mode of injury in 76% patients. Muller et al. [13] proposed the treatment of low condylar fractures having medial comminution and loss of medial cortex, with a lateral plate combined with a medial buttress plate and bone grafting. Ziran et al. [14] assessed 19 patients with AO C3 type distal femoral fractures and operated all the patients with anterior approach and dual plating. In their study they proposed that dual plating of the distal femur using a single incision anterior approach is an effective approach for fixation of distal femoral fractures with minimal medial dissection with adequate exposure of the surgical field. Zhang et al. [15] obtained similar results in their study of clinical efficacy and feasibility of double plating fixation via anterior/middle approach in treating type C3 distal femoral fractures. They concluded that dual plating fixation via anterior approach has advantages of good exposure, anatomical reduction of the fracture fragments and stable fixation.
Many authors in the literature in the past had evaluated the efficacy of lateral locked plates in the management of the distal femoral fractures and have shown good union rates ranging from 81% to 95% but various complications were seen in their studies that were related to the use of single plate such as loss of reduction of the fracture fragments, nonunion, varus malpositioning, and implant breakage leading to revision surgeries [16,17]. The average time to union was 16.15±1.35 weeks. Imam et al. [18] in their study who evaluated 16 patients with C3 fracture type managed using the anteromedial skin approach had average time to union of 6.0 + 3.5 months (range of 3 to 14 months). The average time to union of distal femoral fractures managed by MIPPO technique is 3.5 to 6.1 months as documented by many authors in the literature in their respective studies. Metwaly et al. [19] in their study had average time to union of 9 months (range 3-12 months) which was slightly higher in comparison to our study as the mean age of the patients in their study (69.6 years) was higher than our study (40.75 years), thus increasing the union time. In our study we encountered 1 case of superficial infection, 1 case of knee stiffness and 1 case of nonunion which was lost to follow up. Metwaly et al. [19] in their study reported Two cases of superficial wound infection and 1 case of DVT. Final results using NEER scoring system showed excellent outcome in 5 patients (50%), good results in 3 patients (30%), fair result in 1 patient (10%) and poor result in 1 patient (10%). Bachu et al. [10] in their study had excellent score in 56.66% of the study group while good to excellent results were seen in 83.33% of the patients, thus confirming our results. Limitation of our study is small number of cases and short-term follow-up.
Conclusion
The surgical approach chosen for the surgery is the key factor that dictates the surgical outcome of the patient and is of utmost importance in obtaining good functional outcomes in the distal femoral fracture management. Dual plate fixation using single incision anterior midline approach for intra articular distal femoral fractures is an effective and safe method of management of these fractures. It has several advantages such as adequate exposure, easy manipulation of the fracture fragments, anatomical reduction, and stable fixation of the distal femoral fractures.
References
- Kayali C, Agus H, Turgut A (2007) Successful results of minimally invasive surgery for comminuted supracondylar femoral fractures with LISS: comparative study of multiply injured and isolated femoral fractures. J Orthop Sci 12(5): 458-465.
- Henderson CE, Kuhl LL, Fitzpatrick DC, Marsh JL (2011) Locking plates for distal femur fractures: is there a problem with fracture healing? J Orthop Trauma 25: S8-14.
- Wang A, Zong S, Su L, Liang W, Cao X, et al. (2016) Meta-analysis of postoperative complications in distal femoral fractures: retrograde intramedullary nailing versus plating. Int J Clin Exp Med 10: 18900-18911.
- Khalil Ael S, Ayoub MA (2012) Highly unstable complex C3-type distal femur fracture: can double plating via a modifed Olerud extensile approach be a standby solution? J Orthop Traumatol 13: 179-188.
- Bolhofner BR, Carmen B, Clifford P (1996) The results of open reduction and internal fixation of distal femur fractures using a biologic (Indirect) reduction technique. J of orthop trauma 10(6): 372-377.
- Marcy GH (1947) The posterolateral approach to the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 29(3): 676-678.
- Starr AJ, Jones AL, Reinert CM (1999) The" swashbuckler": a modified anterior approach for fractures of the distal femur. J of orthop trauma 13(2):138-140.
- Butler MS, Brumback RJ, Ellison TS, Poka A, Bathon GH, et al. (1991) Interlocking intramedullary nailing for ipsilateral fractures of the femoral shaft and distal part of the femur. The J of bone and joint surg (Am) 73(10): 1492-1502.
- Petsatodis G, Chatzisymeon A, Antonarakos P, Givissis P, Papadopoulos P, et al. (2010) Condylar buttress plate versus fixed angle condylar blade plate versus dynamic condylar screw for supracondylar intra-articular distal femoral fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 18(1): 35-38.
- Bachu S, Ramulu L (2017) A study of surgical management of distal femoral fractures in adults using locking compression plate. Int J Res Orthop 3(2): 253-258.
- Parmar HP, Chavali VH (2019) Anterior midline approach to distal femur fractures requiring dual plate fixation: A study of forty cases. Int J of Orhtop Sciences 5(1): 487-490.
- Agrawal A, Kiyawat V (2017) Complex AO type C3 distal femur fractures: Results after fixation with a lateral locked plate using modified swashbuckler approach. Indian J Orthop 51(1): 18-27.
- Gwathmey FW Jr, Jones Quaidoo SM, Kahler D, Hurwitz S, Cui Q (2010) Distal femoral fractures: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 18(10): 597-607.
- Ziran BH, Rohde RH, Wharton AR (2002) Lateral and anterior plating of intra-articular distal femoral fractures treated via an anterior approach. Int Orthop 26(6): 370-373.
- Zhang ZM, Jiu L, Huang CX, Zhao ZF, Wang G, et al. (2012) Treatment of type C3 distal femoral fractures with double-plating fixation via anterior middle approach. 25(12): 1049-1052.
- Watanabe Y, Takai S, Yamashita F, Kusakabe T, Kim W, et al. (2002) Second-generation intramedullary supracondylar nail for distal femoral fractures. Int Orthop 26(2): 85-88.
- Ricci WM, Streubel PN, Morshed S, Collinge CA, Nork SE, et al. (2014) Risk factors for failure of locked plate fixation of distal femur fractures: an analysis of 335 cases. J Orthop Trauma 28(2): 83-89.
- Imam MA, Torieh A, Matthana A (2018) Double plating of intraarticular multifragmentary C3-type distal femoral fractures through the anterior approach. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 28(1): 121-130.
- Metwaly RG, Zakaria ZM (2018) Single-Incision Double-Plating Approach in the Management of Isolated, Closed Osteoporotic Distal Femoral Fractures. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil 9: 1-8.






























