Wastewater Treatment Plant of Loung Te Industrial Park the Study for Increasing the Number of Microbes in the Mixed Liquid Suspended Solids (MLSS).
Chih Kuei Chen1* and Guan Ying Chen2
1Department of Environmental Engineering, National Ilan University, Taiwan
2Department of Environmental Science, Tunghai University, Taiwan
Submission: March 23, 2021;Published: April 15, 2021
*Corresponding author: Chih Kuei Chen, Associate Professor, Department of Environmental Engineering, National Ilan University, Taiwan
How to cite this article: Chih Kuei C, Guan Ying C. Wastewater Treatment Plant of Loung Te Industrial Park the Study for Increasing the Number of Microbes in the Mixed Liquid Suspended Solids (MLSS). Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2021; 10(4): 555795. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2021.10.555795
Abstract
The number of microbes in the activated sludge in the wastewater treatment plant of Loung Te Industrial Park has not been able to increase. After investigation, we found out that there are two upstream wastewater sources which contain alkyl-benzene sulfonate (ABS) released from detergent and produce bubbles that compromised the sedimentation effect of the sludge sedimentation pool and lowered the density of the return sludge. Thus, the total number of the return sludge was less than enough. Since the detergent could not be decomposed easily by the microbes, and it inhibited microbial growth, and therefore led to the decrease of the number of microbes in the activated sludge. Eventually the above situation led to the fluctuating quality of the discharged water. The two polluting sources are the Yilin factory of Medtecs International Corporation Limited (interfacial active agent used in the laundry industry) and San Agriculture Biotech (which manufactures fertilizers with the dead bodies of animals or poultry). The two factories used large number of detergents in their production process. The pollution created by the two factories led to low number of microbes in the mixed liquid suspended solids (MLSS), and the number of microbes could not be increased. It was around 500mg/L, and the wastewater treatment efficiency was instable. After discussions with the management of the two factories, they no longer discharge wastewater containing ABS, and the problem has been solved.
The groundwater level in the Lanyang Plain is very high, and there is groundwater 1 meter below the ground. The groundwater level is higher in rainy days, and the groundwater seeps into the sewage collection pipe, diluting the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Based on the calculation of the Food-to-Microorganism Ratio (F/M), it could be concluded that the microbe number of the MLSS would decline and the quality of the discharged wastewater would deteriorate [1]. After the completion of the sewage collection pipeline renewal project, there is no groundwater infiltration, and the problem has been improved. The microbe number in the MLSS has been increased, improving the ability to decompose organic matter in the wastewater, and achieving better and more stable effluent water quality.
Keywords: Alkyl-benzene sulfonate; Groundwater; Food-to-Microorganism Ratio; Microbe number in the MLSS
Introduction
Long Te Industrial Park is located next to Xincheng Creek in Yilan County. The main unit of the wastewater treatment plant is a microbial treatment system. The microorganisms in the aeration tank use dissolved oxygen in the wastewater for biological metabolism, decomposing organic pollutants in the wastewater, and removing organic substances to reduce environmental pollution and improve the quality of discharged water [2,3].
About the low microbe number in the MLSS, we assume the possible causes are as follows.
A. There were two ABS-containing wastewater sources: The long chain structure containing sulfur (S) in the cleaning agent (ABS) is not easy to be decomposed by microorganisms. Industrial wastewater with high content of cleaning agent (ABS) will inhibit the reproduction and growth of organisms, and will also generate air bubbles, which will be reduced efficiency of the sludge sedimentation tank, leading to the loss of activated sludge from the overflow weir, and causing the concentration of the returned sludge is only about 1000 mg/L [4].
B. Groundwater seeps into the wastewater collection pipeline, so that the BOD concentration of the inflow water is too low. According to F/M ratio, it is known that microbe number in the MLSS will be reduced as a result:
a. The BOD value of the inflow water is too low, resulting in too little organic matter in the water to cultivate a high concentration of microorganisms.
b. The sludge load (F/M ratio) is the ratio of the number of organic matters flowing into the aeration tank daily to the number of sludges in the aeration tank. The F/M ratio can be calculated as follows.
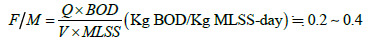
Q = wastewater flow(m3/d)
V = Volume of aeration tank(m3)
MLSS = Concentration of mixed liquid suspended solids(mg/L)
BOD = Influent organic matter concentration(mg/L)
Because the sewage flow rate and the aeration tank volume are fixed values, so the lowering of the concentration of organic matter (BOD) in the influent will affect the biomass of the MLSS. The biomass of the MLSS of the wastewater treatment plant in Long Te Industrial Park used to be measured at about 500mg/L, which could not be increased upwards, resulting in the instability of the quality of the discharged water. It is urgent to find out the causes, develop an improvement plan and countermeasures.
Wastewater treatment plant design plan
a. The design value is 5000 CMD.
b. Design water quality: original incoming wastewater quality, average water quality after treatment, and effluent water quality are shown in Table 1
Wastewater treatment flow and floor plan
Figures 1 & 2


Study Methods and Improvement Steps
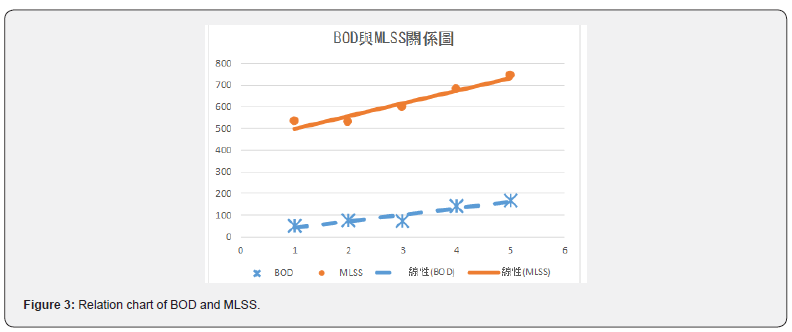
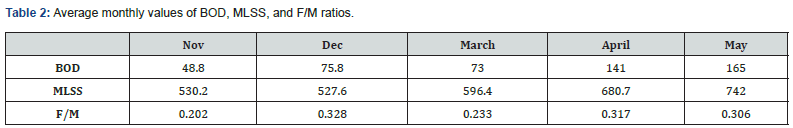
Table 2 and Figure 3 show that MLSS and BOD belong to a positive correlation. When the value of BOD increases, the concentration of MLSS also increases. After the improvement of underground pipelines, the increase of BOD concentration also indirectly increases the MLSS concentration. The theoretical range of F/M is 0.2 ~ 0.4, as shown in Table 2 and Figure 4 F/M ratio chart: the maximum F/M value is 0.32, minimum value 0.20, and average value 0.27. These values are all within the theoretical range.
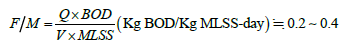
In which, Q = wastewater flow(m3/d)
V = Volume of aeration tank(m3)
MLSS = Concentration of mixed liquid suspended solids(mg/L)
BOD = Influent organic matter concentration(mg/L).

Because the sewage flow rate and the aeration tank volume are fixed values, so the lowering of the concentration of organic matter (BOD) in the influent will affect the biomass of the MLSS. The biomass of the MLSS of the wastewater treatment plant in Long Te Industrial Park used to be measured at about 500mg/L, which could not be increased upwards, resulting in the instability of the quality of the discharged water. It is urgent to find out the causes, develop an improvement plan and countermeasures.
Cause 1
Our investigations found out there are two factories (Medtecs International Corporation Limited and San Agriculture Biotech) discharging a large amount of sewage containing detergents, poisoning the microorganisms in the wastewater treatment plant, and causing low microbe number in the MLSS. The foams created by the wastewater compromised the treatment efficiency of the sedimentation tank, bringing down the concentration of the returned sludge. The reduced concentration of the returned sludge losing the function of maintaining a certain concentration of microorganisms in the activated sludge tank. Therefore, we hope to replace the existing hard detergent with a milder one to reduce the harm to microorganisms.
MedTech international corporation limited
Type of business: Laundry. Medtecs International Corporation Limited is a multinational company formally listed in Singapore in 1999. It is a major supplier of medical textiles and consumable products in the Asia-Pacific region. In addition to needle, plain weaving, yarn, and cloth making, its business covers dyeing, printing and disposable non-woven products production. Its business has expanded to special-purpose work clothes, dust-free cloths, clothing, and functional cloth products for the electronics industry.
Main products
This factory is mainly engaged in laundry business. Detergents are added in its laundry process. Its wastewater containing highconcentration detergents were discharged into the wastewater plant of the Industrial Park.
San agriculture biotech
Business type: Fertilizer manufacturing. San Agriculture Biotech was founded in 1983, focusing on white feather chicken production. It has been in business for 35 years and is headquartered in Guangze County, Nanping City, Fujian Province. It combines chicken raising and all businesses related to chicken raising, including chicken breeding, egg hatching, feed processing, chicken meat processing, food processing, product sales, and fastfood chains. Its businesses consist of a vertical industry chain based on white feather chickens.
Main product: This plant manufactures fertilizer using sick and dead pigs. Therefore, the plant has been using large amount of ABS-containing cleaning agent. That was why the plant used to discharge large amount of ABS-containing wastewater.
' '
Cause 2
To increase microbe number in the MLSS, the concentration of BOD should be increased first. Our study found that due to the infiltration of a large amount of groundwater, resulting in the dilution of BOD concentration. Since the underground sewage collection pipeline renewal project was completed on August 1 this year, the problem was resolved.
After repairing the leakage problem of underground pipelines and changing to non-polluting cleaning agents, the BOD value was successfully increased from 71.8mg/L to 126.3 mg/L, a total increase of 1.76 times. The increase in BOD has driven the concentration of the MLSS from 529.0mg/L to 672.7mg/L, an increase of 27%.
Wastewater treatment plant tank dimensions and specifications
The main mechanical equipment and specifications are shown in the Tables 3&4.
On-site Examination
Figure 5

Results and Conclusion
Discussion on water quality improvement of wastewater treatment plant in Long Te Industrial Zone before and after the improvement: Before the pipeline renewal project because the pipeline is located below the groundwater level, when the groundwater water level was high, the groundwater would get into the pipeline through the pipeline gaps to dilute the concentrations of chemical oxygen demand (COD), suspended solids (SS), and BOD. After the pipeline renewal, the indicators of the COD and SS improved substantially, the average value of COD was 203.7 mg/L, and the average value of the effluent water was 24.4mg/L (with a removal rate of 88%). The average value of the incoming water was 8.4 mg/L (the removal rate was about 92%) Tables 5&6.
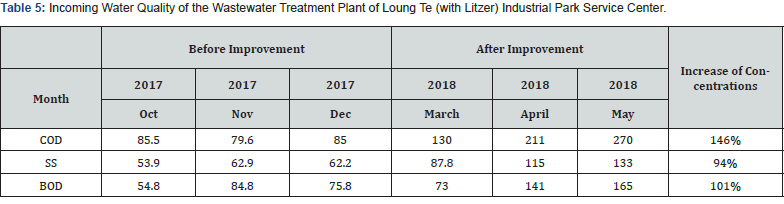
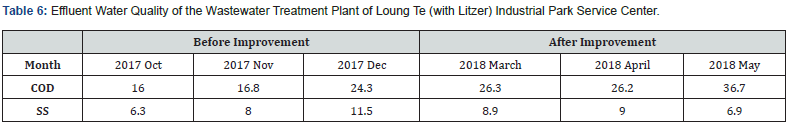
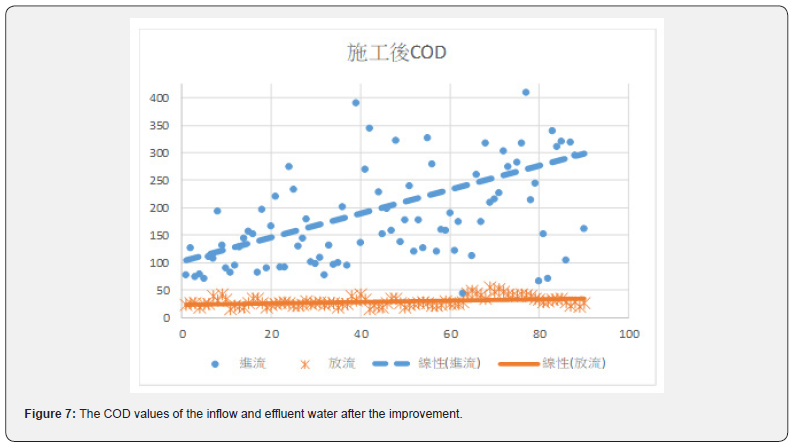
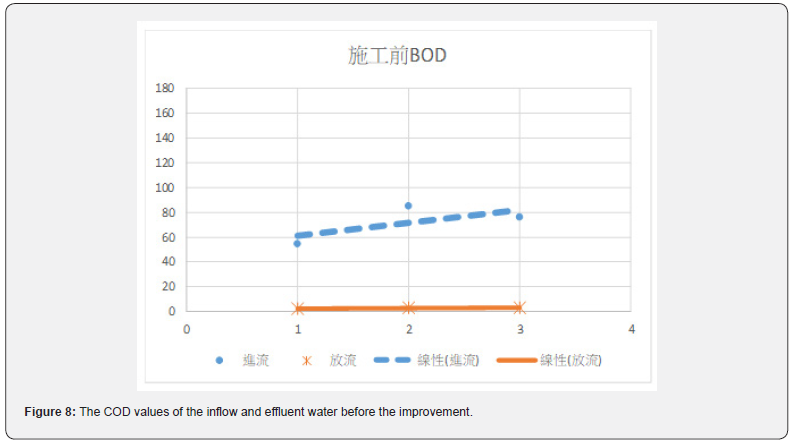
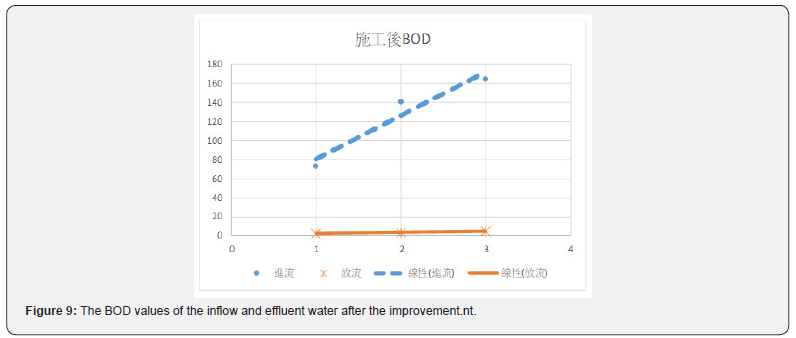
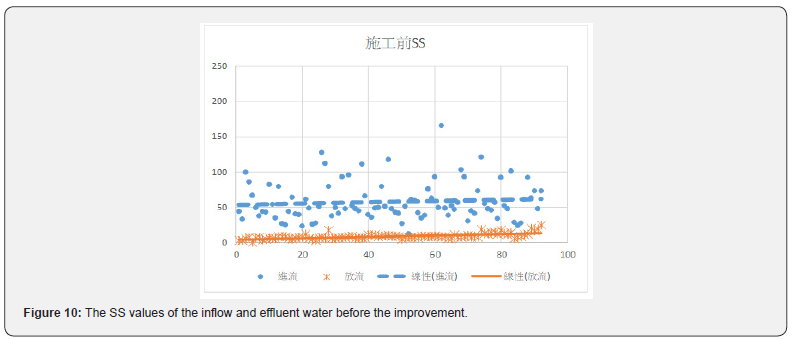
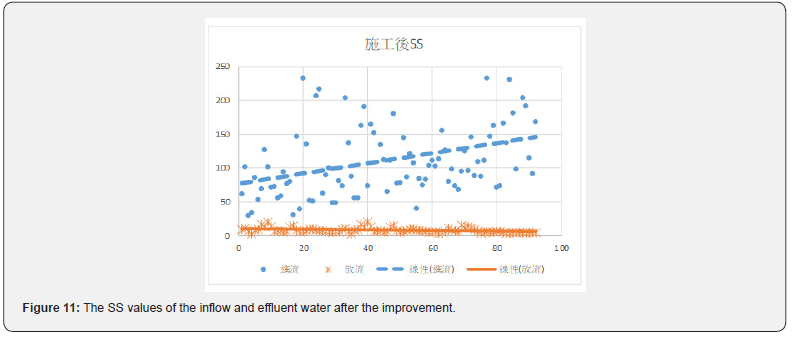
Figures 6 & 7 show before the improvement, concentration of the COD in the incoming water was diluted by the infiltration of groundwater. After the improvement, the average value of COD had been improved from 81.2mg/L to 214.6mg/L, or a 2.64 times improvement. Table 7 and Figures 8 & 9 show the concentration of BOD had been improved from 71.8mg/L to 126.3mg/L, an improvement of 1.76 times. Figures 10 & 11 show that the concentration of SS had been improved from 57.7mg/L to 111.9mg/L, an improvement of 1.94 times. It was observed that the concentration of each pollutant in the inflow water has been increased to about twice after construction, which is of great help to the wastewater treatment plant to cultivate high concentration of microbes in the MLSS. After the pipeline improvement project (dredging and cleaning of clogged public sewage pipes, and improvement of ventilation safety facilities, repairs around the manhole frame and cover, spray lining to manhole inner walls and anti-corrosion treatment, and pipeline renewal), the wastewater plant treatment was very efficient, and the concentration of effluent is much lower than the standard discharge.
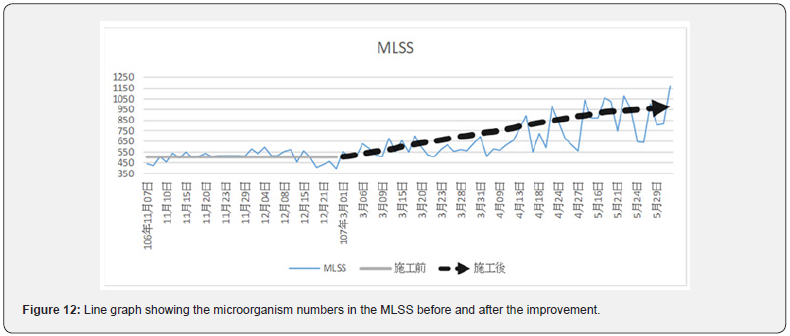
The improvement project started in January 2018. Before construction for the improvement, the microbe number in the MLSS was low, with an average of 529.0 mg/L. After the construction, the microbe number in the MLSS gradually increased. The average became 672.7 mg/L, an increase of 27%, as shown in Figure 12. The increased microbe number in the MLSS could decompose more organic matter in the inflowing water, and the quality of the discharged effluent water became stable. Another factor that inhibited the biomass of activated sludge pool (MLSS) was that the detergent (ABS) inhibited the proliferation and growth of biomass of activated sludge pool. The harmful effects of surfactants on microorganisms are as follows:
a. emulsification,
b. permeability,
c. difficult to decompose.
The stronger cleaning ability, the greater the impact on the microorganisms. By helping the upstream factories to replace the ABS-containing detergents with less harmful cleaning agents, the concentration of microbe inhibitors in the discharged wastewater became lower. After the improvement, the microbe number in the MLSS grew gradually as shown in Figure 12.
To effectively improve the quality of the effluent water, pretreatment of the wastewater should be made to avoid possible interference. It should be noted that the values of COD, BOD, SS, and MLSS should be controlled appropriately. After effectively controlling the concentration of influent wastewater, there should be enough nutrients in the activated sludge pool for microbial reproduction and growth. After the biomass is stabilized, the organic pollutants in the sewage will naturally be degraded and removed, and microorganisms will grow and reproduce, and wastewater would be purified.
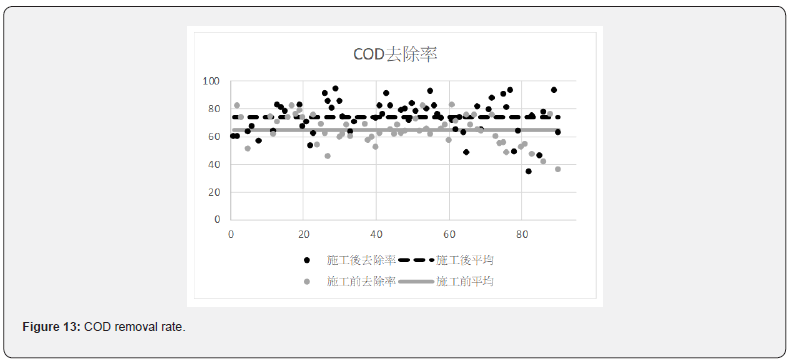
After the improvement of the pipeline and the improvement of the water quality of the discharge sources, the wastewater treatment plant of Loung Te Industrial Park effectively improved the MLSS value. The removal rates of each value are shown in Figures 13-15. The average removal rate of COD increased from 64.9% to 74.0%; the average removal rate of BOD increased from 93.0% to 94.4%; the average removal rate of SS increased from 58.6% to 76.4%.
Conclusion and Suggestions
The study results show two main causes that failed to increase microbe number in the MLSS, and the study solved the problems completely:
There were two sources of ABS-containing wastewater
a) Cause: ABS-containing cleaner is a sulfide-containing substance with long molecular chain structure, which is difficult for microorganisms to decompose. It also inhibits the growth of microorganisms. The fine foams will attach to the microorganisms, leading to the low efficiency of the sedimentation tank and to the concentration dilution of the returned sludge. The result was that the microbe number of the MLSS in the activated sludge tank has been unable to increase.
b) Improvement: We successfully persuaded the upstream factories, which were discharging ABS-containing wastewater, to replace the ABS-producing detergents with cleaning agents which can be easily decomposed.
Aging of wastewater pipeline
a) Cause: The old pipeline was damaged and was located below the groundwater surface. After heavy rain, the groundwater level rises. A large amount of groundwater will flow into the wastewater collection pipeline through the pipeline’s seams. The infiltration of groundwater into the wastewater collection pipeline lowered the BOD values, and the lowered BOD values would also lower the microbe number in the MLSS.
b) Improvement: The underground pipelines are renewed section by section so that groundwater no longer flows into the underground pipelines and the wastewater was no longer diluted, leading to the increased concentration of organic matter which can be absorbed by microorganisms. This leads to the increased microbe number in the MLSS.
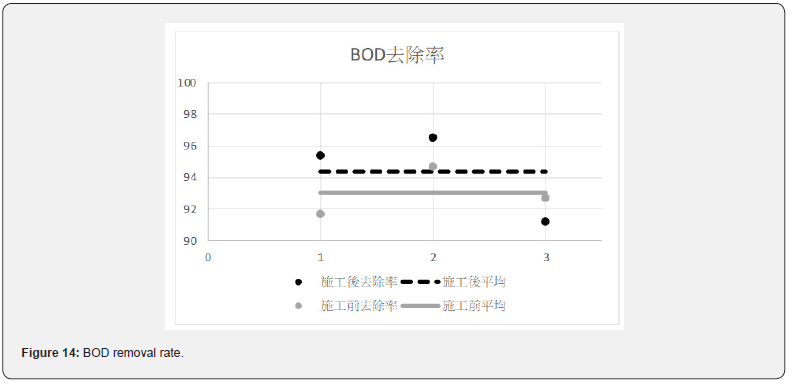
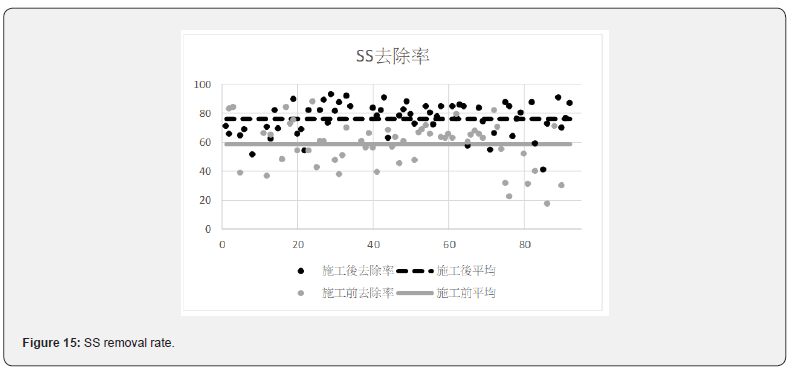
Before the improvement, the COD in the wastewater was diluted. After the improvement, the COD values were increased from 81.2mg/L to 214.6mg/L, with a concentration increase by 2.64 times. Figures 8 & 9 show the average BOD values of the inflow of wastewater after the renewal of the underground pipeline improved from 71.8 mg / L to 126.3mg/L, with a concentration increase by 1.76 times. It can be seen in Figures 10 & 11 that the average SS value before the construction was 57.7 mg/L, and the SS value was improved to 111.9 mg/L. The concentration increased by 1.94 times. The concentration of each pollutant in the inflow wastewater has been increased to about twice after construction. It has greatly helped the wastewater treatment plant to cultivate high concentration of microbes in the MLSS. The concentration of microbes in the MLSS has also increased by 27%, and the average COD removal rate has increased from 64.9% to 74.0 %; BOD average removal rate increased from 93.0% to 94.4%; SS average removal rate increased from 58.6% to 76.4%.
In the future, it is necessary to continue monitoring the wastewater being discharged from the two upstream plants to see if it contains ABS. It is also necessary to keep on monitoring the wastewater discharge to examine if there is sudden increase of discharged wastewater or if the wastewater is diluted. If there is sudden increase of discharged wastewater or the wastewater is diluted, it is necessary to check if the wastewater disposal pipeline has leaks or the renewal of the pipeline has not been done perfectly. Periodical inspection and maintenance of the wastewater disposal pipeline may be required.
Future Prospect
The wastewater treatment plant in Loung Te Industrial Park is now capable of processing enough wastewater, but if treatment capacity is to be increased in the future, a combined system of activated sludge and biological contact aeration (AS/CA) can be used. A combined AS/CA system is so designed that the returned sludge carries the fixed biofilm in the sedimentation tank to the suspended activated sludge tank, and the suspended sludge in the activated sludge tank flow into the contact aeration tank to form bacterial flora [5]. The combined AS/CA system adds biological contact filter material. Such a system has both the advantages of the traditional activated sludge method and the contact aeration method [6]. The activated sludge from the activated sludge aeration tank flows to the contact aeration tank, attaches to the newly added biofilm, grows on the biofilm, and forms new strains on the biofilm. The biofilm which comes loose in the contact aeration tank and suspended microorganisms settle in the sedimentation tank, and then return to the activated sludge aeration tank, so that each biological aeration tank has both the biological flora of the activated sludge system and those in the attached biofilm system.
Unlike the conventional activated sludge method, the combined AS/CA system will reduce sludge production. It does not clog the biological filter materials easily. With the use of phase contrast microscope, it is discovered that each treatment tank contains various microorganisms of different sizes and with strong activity. Multiple and complicated microbiota existing in such tanks compete with one another to decompose the dead bodies of other microbes, leading to the substantial decrease of the biological sludge.
References
- Mutamim N S A, Noor Z Z, Hassan M A A, Olsson G (2012) Application of membrane bioreactior technology in treating high strength industrial wastewater: a performance review. Desalination 305: 1-11.
- Burgess J E, Quarmby J, Stephenson T (1999) Micronutrient supplements for optimisation of the treatment of industrial wastewater using activated sludge. Wat Res 33: 3707-3714.
- Mutamim N S A, Noor Z Z, Hassan M A A, Yuniarto A, Olsson G (2013) Membrane bioreactor: Applications and Iimitations in treating high strength industrial wastewater. Chem Engin J 225: 109-119.
- Farooqi I H, Basheer F (2017) Treatment of Adsorbable Organic Halide (AOX) from pulp and paper industry wastewater using aerobic granules in pilot scale SBR. J Wat Proc Engin 19: 60-66.
- Chen C K, Lo S L (2006) Treating restaurant wastewater using a combined activated sludge-contact aeration system. J Environ Biol 27(2): 167-183.
- Chen P C (2010) The study on Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) following Rotating Biological Contactor (RBC) for tertiary treatment of the Wuku Industrial Park. In: National Taipei University of Technology Taiwan, p. 2.






























