Synthesis and Antifungal Activity of Some New Fused Heteropolcyclic Nitrogen Systems Derived from 4-Aminoantipyrine
Ola A Abu Ali*
Department of Chemistry, Taif University, Saudi Arabia
Submission: February 25, 2021; Published: March 16, 2021
*Corresponding author: Ola A Abu Ali, Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Taif University, P.O. Box 11099, Taif 21944, Saudi Arabia
How to cite this article: Ola A Abu A. Synthesis and Antifungal Activity of Some New Fused Heteropolcyclic Nitrogen Systems Derived from 4-Aminoantipyrine. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2021; 10(4): 555794. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2021.10.555794
Abstract
Some new fused heteropolcyclic nitrogen systems as pyrazole-imidazo pyrimidinone (4) and pyrazolo-1,2,4-triazino pyrimidinone (5) have been synthesized from addition of aryl iso thiocyanate to 4-aminoantipyrine (1) followed by formation of Thio barbituric acids 3 then ring closure reaction with nitrogen reagents. Structure of the produce deduced upon their elemental and spectral analysis. Antifungal activity of these targets was also evaluated.
Keywords:Synthesis; Fused heterocyclic; Antifungal activities
Introduction
Fused pyrazoles constitute an important class of compounds exhibit diverse pharmacological activities as antimicrobial [1], bioisosteric with purine (7H-imidazo [4,5-d] pyrimidine (A), pyrazolo [4,3-e] [1,2,4] triazines (B) and / or nostocine spongiaeforme as psendoiodinine (C) agents [2-5]. Thiobarbituric acids fused with other heterocyclic nitrogen nucleus have a medicinal property as anti-HIV-1 and cyclin –dependent Kinase 2 (CDK2) agents [6-7]. On other hand, fused 1,2,4-triazines with pyrazalone moieties reported a wide-spectrum as bioactive systems [8]. Based upon these observations, the present work reports an attempt to obtain synthesis of various fused heteropolycyclic nitrogen systems derived from 4-amino-antipyrine in view of their biological activities.
Experimental
Stuart SMP3 (UK) was used to determine uncorrected Melting points of the products. Shimadzu UV and visible 310 IPC-Spectrophotometer was used to recorded UV absorption spectra (λmax nm) in DMF. IR spectra of the prepared compounds γcm−1 were recorded on A Perkins Elmer Model RXI-FT IR system 55529. A Brucker advanced D P X 400 MHz model using TMS as internal standard used for recording the 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the compounds on deuterated (CDCl3, d6, δ ppm). GCMS Q 1000 Ex at 70 eV was used to measured Mass spectrum. Elemental’s microanalysis was performed by the microanalytical at Cairo- University, Egypt
N, N –Disubstituted thioureas (2a, 2b)
A mixture of 4-aminoantipyrine (1) (0.01mol) and phenyl/4- chlorophenyl-isothiocyanate (0.01mol) in tetrahydrofuran (100ml) refluxed for 2 h then cooled. The solid thus obtained filtered off and crystallized from dioxin to give 2a and 2b as orange crystals, yield 88 %, m.p. 180 (2a), 190 (2b) ℃ respectively.
2a: Anal. Calcd (Found) % for C18H18N4SO (338); C, 63.90 (63.69); H, 5.32 (5.11); N, 16.56 (16.33); S, 9.46 (9.18) %. IR(γ) cm-1: 3160 (NH), 1380 (NCSN), 1200 (C=S), 1700 (cyclic C=O), 1480 (deformation CH3), 820 (aromatic ring). UV (ʎmax) = 288 nm.
2b: Anal. Calcd / (Found) % for C18H18N4SOCl (373.5): C, 57.75 (57.66); H, 4.54 (4.33); N, 14.97 (14.70); S, 8.55(8.35) %. MS (EI, m/z (%): 375(1.15), 112 (100, p-ClC6H4).
N, N –Disubstituted thiobarbituricacids (3a &3b)
A mixture of compounds (2a) and /or 2b (0.01mol) and malonic acid (0.01 mol) in glacial acetic acid (100ml) refluxed for 2 h then cooled. The solid obtained after addition ice, filtered off and crystallized from THF to give 3a and/or 3b as yellowish crystals, yield 75 %, m.p. 170 (3a); 175 (3b) ℃ respectively.
3a: Anal. Calcd (Found) % for C21H18N4O3S (398); C, 63.31 (63.01); H, 4.52 (4.33); N, 14.07 (13.88); S, 8.04 (7.90) %. IR (γ) cm-1: 3450 (OH), 2900, 2850 (CH3), 1680, 1650 (2C=O), 1440 (deformation CH3), 1385 (cyclic NCSN), 1190 (C=S). UV (ʎmax) = 258 nm .1HNMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 2.1, 3.4 (each s, C-Me, N-Me), 2.6 (s, 2H, CH2 thio-barbituric), 7.2-7.9 (m, 10H, aromatic protons). 13CNMR (DMSO-d6) δ : 180, 160, 155, 135, 133, 131,130-128, 77, 21, 18 ppm.
3b: Anal. Calcd / (Found) % for C21H17N4O3SCl (432.5): C, 58.81 (58.59); H, 3.92 (3.70); N, 14.85 (14.55); S, 7.39 (7.12) %. MS (EI, m/z (%): 435 (M+2, 13.11), 112 (100).
Pyrazolo [4,3 : 5,4] imidazole[2,1-c]pyrimidinones 4a &4b
A mixture of compounds (3a) and /or 3b (0.5 gm) and ammonium acetate (0.5 gm) with drops of glacial acetic acid, refluxed for 2h, cooled then treated with few methanol. The produced solids filtered off and crystallized from ethanol to give 4a and/or 4b as deep yellow crystals, m.p. 185 (4a); 182 (4b) ℃ respectively.
4a: Anal. Calcd (Found) % for C21H17N5SO (377); C, 66.84 (66.71); H, 4.50 (4.35); N, 18.56 (18.40); S, 8.48 (8.31) %. IR (γ) cm-1: 3500-3100 (b, OH=CH), 1580 (=CO=C-OH), 1590 (C=N), 1189 (C=S), 900, 820 (aromatic ring). UV (ʎ max) = 300 nm .1HNMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 2.2, 3.4 (each s, Me-C, Me-N), 8.8 (s, 1H, cyclic, CH=pyrimiden), 7.7-7.0 (m, 10H, aromatic protons) ppm.
4b: Anal. Calcd / (Found) % for C21H16N5SOCl (411.5): C, 61.16 (61.01); H, 3.88 (3.55); N, 16.99 (16.78); S, 7.76 (7.50). 13CNMR (DMSO-d6) δ : 185, 162, 158, 148, 133-122, 24, 15 ppm. MS (EI, m/z (%): 414 (M+2, 35.85), 112 (100, 4-ClC6H4).
Pyrazolo[4,3: s,b][1,2,4]triazino [4,3-c] pyrimidinones (5a &5b)
Equimolar mixture of compounds 3a and /or 3b with hydrazine hydrate in THF (50 ml) refluxed for 2h, cooled. The yielded solids filtered off and crystallized from ethanol to give 5a and/or 5b as yellowish crystals. Yield 70 %; m.p. 210 (5a); 215 (5b) ℃ respectively.
5a: Anal. Calcd (Found) % for C21H19N6SO (403); C, 62.5 (62.33); H, 4.71 (4.40) ; N, 20.84 (20.59); S, 7.94 (7.66) %. IR (γ) cm-1: 3080 (NH, 1,2,4-triazine), 2900, 2860 (CH3), 1660 (C=O pyrimidinone), 1180 (C=S), 880, 820 (aromatic rings). UV (ʎmax) = 310 nm .1HNMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 13.0 (s, 1H, NH-triazne), 8.9 (s, 1H, CH pyrimidine), 8.2-7.9 (d, d, 4H, 4-Cl C6H4), 7.6-7.3 (m, 5H, phenyl), 2.4, 3.18 (each s, Me-C & Me-N) ppm.
5b: Anal. Calcd / (Found) % for C21H18N6SOCl (433): C, 58.19 (57.88); H, 4.15 (3.90); N, 19.39 (19.30); S, 7.39 (7.01). 13CNMR (DMSO-d6) δ : 180, 166, 152, 147, 135, 130-120, 77, 25, 18 ppm. MS (EI, m/z (%): 435 (M+2, 75.88), 112 (4-ClC6H4 radical).
Results and Discussion
Thioureas and thiobarbituric acids exhibits a wide spectrum in the fields of biological and medicinal. Thus, two moieties use to obtain an importance bioactive system as starting materials [9]. Structure of the thioureas 2 and thiobarbituric acids 3 were characterized from correct elemental analysis and spectral date. IR spectrum of 2b recorded absorption band at 3200 and 3180 cm-1 with a new band at 1180-1200 cm-1 attribute to N1H, N2H and C=S, in addition two absorption bands in 1700, 1660 cm-1 for C=O groups. UV absorption of 2a recorded ʎmax at 288 nm, while that of 3a showed ʎmax at 258 nm, due to the isolated heterobicyclic systems. 13CNMR of 3a showed a resonated signal at δ 180, 160 and 150 ppm attribute to C=S, C=O and C-Cl carbons.
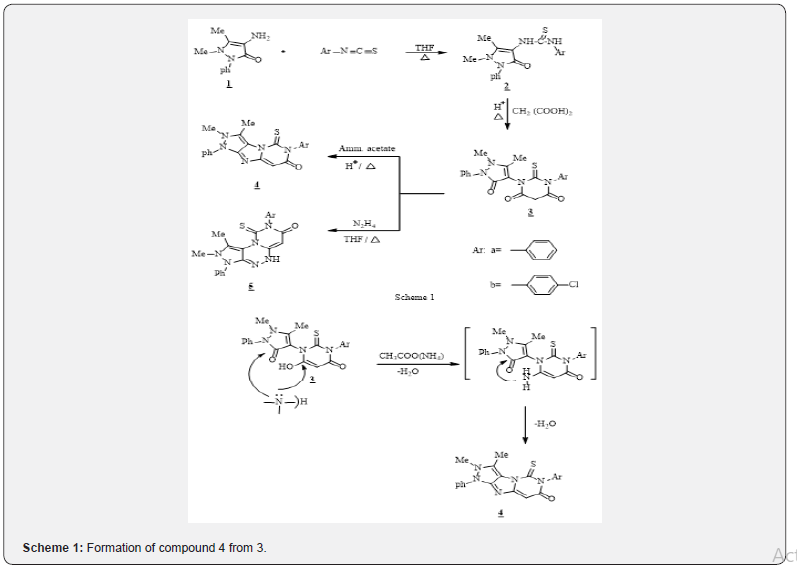
On the other hand, structures of compounds 4 and 5 were deduced from their elemental and spectral analysis. IR spectra of 4 and 5 recorded an absorption band at 3500-3100 and 1580 cm-1 for CO=C-OH of pyrimidinone with lacks NH group for 4, while that appears at 3080 cm-1 for 1,2,4-triazine of 5. UV absorption spectra both 4 and 5 recorded ʎmax at 300-310 nm higher than compound 3 which is due to a fused heteropolcyclic systems. 1HNMR spectra showed a lack’s of CH2 protons of the Thio barbituric acids. Mass spectrum of 5b showed a molecular and a base peak at m/z 435 (M+2) and 112 as 4-chlorophenyl radical. 13CNMR spectra of all the compound 2-5 exhibit the signal at 185-178 ppm for the present of C=S carbons. Also, all the 1HNMR of compounds 2-5 recorded δ at 2.2, 2.4 & 3.2-3.4 ppm of (Me-C & Me-N). Formation of compound 4 from 3 may be as shown in Scheme 1.
Antifungal activity
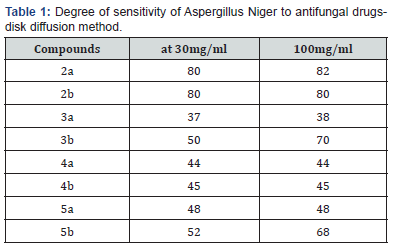
All the newly synthesized compounds were evaluated in vitro Aspergillus Niger as fungi employing the nutrient agar disc diffusion method [10], at 100 mg/ml concentration. DMSO was used as blank a long 16-20 h of in cu bastion at 37℃. Ketoconazole used as standard drug against fungi (at 30 mg/ml) the results obtained recorded in the table 1. Generally, the activity of compounds 5b- 3b- 4b- 2b were the chlorine atom present. Only 5 b & 3 b recorded a higher inhibition than the standard drug, which may attribute the contains of both three fused heterocyclic nitrogen systems and the Thio barbituric acid moiety. The derivatives 2 a, b recorded a lethal activity towards the tested fungi.
Conclusion

References
- TE Ali (2009) Synthesis of some novel pyrazolo[3,4-b] pyridine and pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives bearing 5,6-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazine moiety as potential antimicrobial agents. Eur J Med Chem 44: 4385.
- JW Gadek, I Chamrad, V Krystof (2009) Novel potent pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Future Med Chem 1: 1561.
- M Legraverend, DSGriersen (2006) Graphical contents list. Bio org Med Chem 14: 3987.
- T Gucky, I Frysove, JSlouka, M Hajduch, P Dzubak (2009) Cyclocondensation reaction of heterocyclic carbonyl compounds, Part XIII: Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of some 3,7-diaryl-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazines. Eur J Med Chem 44: 891.
- I Frysove, JSlouka, J Hlarac, A Lycka (2006) Cyclocondensation reactions of heterocyclic carbonyl compounds XII. † The double course of cyclization of 3‐(2‐aminobenzyl)‐1,2‐dihydro‐quinoxaline‐2‐one. J Hetter Chem 43: 759.
- ASAl harbi, RM Abdel Rahman, AMAsiri (2014) Synthesis of Novel Fluorine Substituted Isolated and Fused Heterobicyclic Nitrogen Systems Bearing 6-(2’-Phosphorylanilido)-1,2,4-Triazin-5-One Moiety as Potential Inhibitor towards HIV-1 Activity. Inter J Org Chem 4: 142.
- AS Alharbi, R M Abdel Rahman, AM Asiri (2015) Synthesis of some new fluorine substituted thiobarbituric acid derivatives as anti HIV1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) for cell tumor division: Part I. Eur J Chem 6: 63.
- RM Abdel Rahman , D A Bakhotmah (2016) A Review on the Synthesis and Chemistry of Bioactive Pyrazolines Bearing 1,2,4-Triazine Moieties. Mini Rev Org Chem 13: 62-77.
- M S T Makki, RM Abdel Rahman, M SEl Shahwy (2011) Synthesis of New Bioactive Sulfur Compounds Bearing Heterocyclic Moiety and Their Analytical Applications. Int J Chem 3(1): 181.
- E J Baron, S M Finegolq (1990) Baily and Scetr's Dignostic Microbiolag (13th ), CV Mosby St Louis, pp. 1056.






























