Design and Synthesis of Anthraquinone Derivatives Conjugated with Epitopes of Myelin Basic Protein MBP [1-11] [4Y] and IL-2Rβ(107-118).
Monica Periolatto*
Department of Applied Science and Technology, Italy
Submission: January 26, 2020;Published: February 01, 2020
*Corresponding author: Monica Periolatto, Department of Applied Science and Technology, Politecnico di Torino, C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24, 10129 Torino, Italy
How to cite this article: Monica P. Photografted Chitosan as Antibacterial Agent for Textiles. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2021; 10(4): 555792.DOI 10.19080/OMCIJ.2021.10.555792
Abstract
Anthraquinone derivatives have antineoplasmatic effects. Our goal was to design and synthesize, for the first time, an anthraquinone derivative conjugated with a couple of immunomodulatory peptide analogues of Myelin Basic Protein MBP [1-11] [4Y] and a peptide analogue of IL-2Rb receptor with inhibitory effects. MBP [1-11] [4Y] was the analogue of our choice because it has previously shown that is a very strong binder to T cell receptor and could limit cellular infiltration into the Central Nervous System, protecting male mice from EAE. Furthermore, IL-2Rβ (107-118) epitope, has shown inhibitory effect on proliferation assays in PBMCs.
Keywords: Anthraquinone derivatives; Multiple sclerosis; Peptide analogues; IL-2
Introduction
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of the Central Nervous System (CNS), characterized by activation of T-cells subset, CD4+ and other cells of the immune system. After the activation and proliferation of the above cells, they infiltrate into the CNS through the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB). Then, they are secondary activated against the Myelin sheath. The destruction of the Myelin sheath leads to neurological dysfunction and the emerge of neurological symptoms. MS is a devastated disease resulting in neurological disability if not treated from early stages [1-4].
Myelin Protein consists of major and minor lipoproteins which form the Myelin sheath. The major proteins are MBP, PLP and MOG. T-cells are activated against specific epitopes which are called immunodominant epitopes such as MBP83-99, MBP1-11, PLP139-145 and MOG35-55 [4-6]. Furthermore, IL-2, is a cytokine, playing a critical role on the activation of the immune system against foreign attacks by viruses and bacteria. It is known that the IL-2 receptor is ex-pressed on the surface of activated T-cells and not on the “rest” T cells [7-9]. The design was based on the binding information of the high affinity IL-2 receptor with specific epitopes, linear and cyclic, of the extracellular segment of the β chain. Monoclonal antibodies are bound to these epitopes and prevent the connection of the cytokine with the IL-2R.
1,4-bis(substituted alky-1-amino)-anthraquinones are considered as molecules with antineoplasmatic properties [10-12]. These compounds intercalate with the DNA helix and inhibit the DNA transcription. They have also shown a strong inhibitory effect on Topoisomerase II enzyme and demonstrate a down regulation effect on Pgp activity, resulting in inhibition of mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) [13-15]. Moreover, such derivatives act against Leukemia P-388 in mice [16]. 9,10-Dihydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1,4- anthraquinone (leucoquinizarin), is the derivative of our choice in the present synthesis.
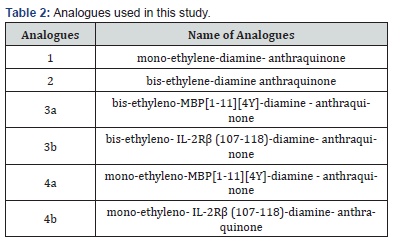
Numerous of organic compounds have been synthesized so far to modulate the MS patients’ immune system. In this study, we describe the synthesis of mono substituted amino, ethyl-amino anthraquinone and bis substituted 2-amino, ethyl-amino anthraquinone derivatives con-jugated with mutated peptide analogues (APLs) of the immunodominant epitope MBP(1-11) with mutation at position 4 (4Y) and a peptide inhibitor of the IL-2Rb receptor. The design of the peptide analogues was based on the primary structure of the MBP1-11 epitope and β subunit receptor extracellular area, IL-2Rβ (107-118). The peptide RELFRQSLSQRETALV does not share any amino acid sequence with the extracellular area of the IL-2 receptor β-subunit and in the present study was used as control.
In addition, the epitope AcMBP1-11 when injected in PL/J mice induced EAE. Replacement of Lys at position 4 with Ala and Tyr results in peptide analogues with antagonistic effects [17- 20]. Moreover, these peptide analogues demonstrate stronger binding affinity characteristics to Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC). Based on the above, we synthesized 4 peptidylanthraquinone compounds (mono and bis substituted) to discover new molecules towards the potential immunomodulation of MS. It is worth to note that the described conjugation was carried out in liquid phase for the first time.
Experimental Section
Synthesis of the mono and 1,4 bis-ethylene-diamine substituted anthraquinone.
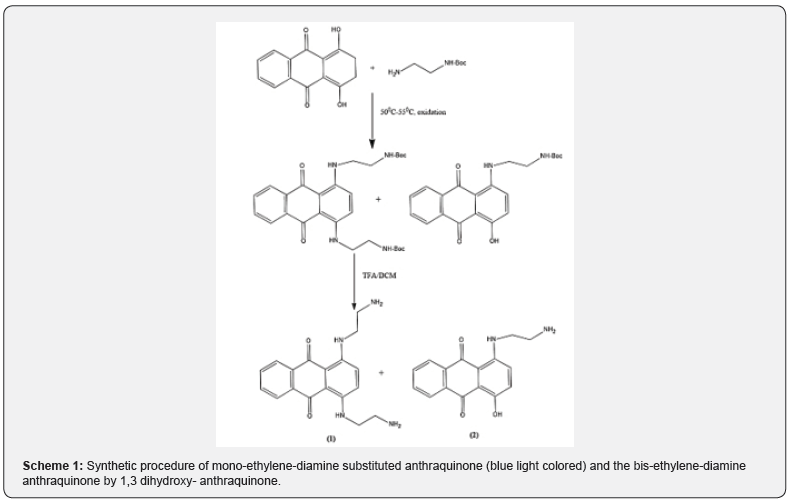
At first, the 1,4 dihydroxy-anthraquinone (1.5mmol) was dissolved in 25ml of methanol. Boc protected ethylene-diamine (1.5mmol) was added dropwise. The procedure was executed in N2 atmospheric conditions for 30min. The duration of the reaction was 1h reflux at temperature of 50-55oC. Control of the temperature is crucial due to the formation of “by-products” which decrease the final yield [21]. After 1h, the solution was freeze and was oxygen-exposed for 15h to get mild oxidation at atmospheric conditions. Two main products were isolated. The mono-ethylenediamine substituted anthraquinone product (blue light colored) and the bis-ethylene-diamine anthraquinone (dark blue colored). Both were Boc protected. The removal of Boc protecting group was accomplished by treating the solution with TFA/DCM (65/35, v/v) for ap-proximately 2h. Both products, were monitored by HPLC and were identified by Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) and Mass Spectrometry. In the following Schemes 1 & 2, the synthesis of the two products is described. The products were identified by ESI-MS, purified and isolated using HPLC semi-preparative and a Nucleosil 100-5 C18 (250x4mm) and 5μm particle diameter, using AcN and H2O gradient eluent (10% -60% AcN). More details are included in Table 1.
Peptide synthesis
The synthesis of the Bocamino protected peptide analogues used in this study has been accomplished in solid phase using Fmoc/tBu methodology. The mutated peptides (APLs) had amino acid alterations in critical positions for their activity known by recent literature. This synthetic procedure has been extendedly described by our group [22,23].

Conjugation of bis-ethylene-diamine anthraquinone with peptide analogues of MBP[1-11] [4Y] and IL-2Rβ (107-118) The conjugation of peptide analogues was carried out in liquid phase using N,N’-Dicyclo-hexyl-carbodiimide (DCC) as coupling agent. The excess of the protected intermediate that was used was 4x fold. Triethylamine was used as base, distilled Dimethyl formamide (DMF) as solution and the reaction was accomplished after 24h. The final products were identified by TLC and HPLC. The final deprotection mixture was consisted of Trifluoracetic acid (TFA) and specific scavengers [Dithiothreitol (DTT), anisole and water (25/65/4/6, v/v, 7ml) in Dichloromethane (DCM).The reaction was terminated after 5h and the final products 1 and 2 were identified and isolated as described above (Scheme 2).

Results
Preliminary assays of the synthesized analogues 3a and 4a were carried out using T cell line specific for AcMBP [1-9]. The proliferation assays were carried out in different concentrations, with a range of 0.00001μg/ml to 10μg/ml. The proliferation value effect of AcMBP1-9 epitope T-cell lines was used as a reference. Moreover, the proliferation of the analogue 3a was higher than the control in the concentration of 0.00001μg/ml. Whereas, in the concentration of 10μg/ml showed lower proliferation effect compared to control. The epitope IL-2 Rβ (107-118) has shown a decrease of 27.95% of PBMC and a decrease of 56.69% of IL-2 secretion compared to the control. The analogue 3b showed a respective decrease of PBMCs of MS patients but not of IL-2 secretion.
Discussion
This synthetic approach describes for the first time the conjugation of two immunodominant epitopes and an anthraquinone derivative in liquid phase. The peptide analogues were synthesized in solid phase according to Fmoc/tBu methodology. The anthraquinone derivatives were synthesized according to literature in liquid phase as well as the conjugation procedure. The isolation of mono and bissubstituted derivatives was accomplished using cation exchange chromatographic techniques. The characterization of the final conjugated products was carried out using IR and Mass Spectra.
The preliminary assays have shown that the IL-2Rβ (107-118) interfere with the extracellular β subunit of IL-2 receptor and may prevent the binding of IL-2. In addition, the synthesized analogues inhibit the activation and proliferation of T cells by an antigen or mitogen. This could happen because both analogues are found to have toxic characteristics. The IL-2 is a very important cytokine (Th1 immunological response), for the immune system activation. The regulation of IL-2 is a crucial step towards relief of the disease symptoms.
Conclusion
The use of several different peptide analogues conjugated to anthraquinone derivatives could be an attractive approach towards its biological evaluation. This new approach is giving us a new generation of molecules consist of two or more organic compounds and could be potential immunotherapeutic. Many research groups have used different carriers such as nanoparticles or PEGylated parts to combine organic molecules with biological activity, aiming in new synthetic compounds with limited side effects, to a specific target within the body. In conclusion, the synthesis of conjugated compounds consists of peptide analogues and anthraquinone derivatives could be a different methodology towards the modulation of the disease and to design more effective mimetic analogues against MS.
References
- Katsara M, Matsoukas J, Deraos G, Apostolopoulos V (2008) Towards immunotherapeutic drugs and vaccines against multiple sclerosis. Acta BiochimBiophys Sin 40: 636-642.
- Holmoy T, Hestvik A L (2008) Multiple sclerosis: immunopathogenesis and controversies in defining the cause. Curr Opin Infect Dis 21: 271-278.
- Polman C H, Uitdehaag B M (2003) New and emerging treatment options for multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 2: 563-566.
- Steinman L (1996) Multiple sclerosis: a coordinated immunological attack against myelin in the central nervous system. Cell 85: 299-302.
- Ota K, Matsui M, Milford E L, Mackin G A, Weiner H L, et al. (1990) T-cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature 346: 183-187.
- Martin R, Howell M D, Jaraquemada D, Flerlage M, Richert J, et al. (1991) A myelin basic protein peptide is recognized by cytotoxic T cells in the context of four HLA-DR types associated with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 173: 19-24.
- Zhang, J, Markovic Plese S, Lacet B, Raus J, Weiner H L, et al. (1994) In-creased frequency of interleukin 2-responsive T cells specific for myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multi-ple sclerosis. J Exp Med 79: 973-984.
- Liou Hs Ch, Jin Zh, Tumang J, Andjelic S, Smith K, et al. (1998)c-Rel is crucial for lymphocyte proliferation but dispensable for T cell effector function. InternatImmun 3: 361.
- Pahlavani M (1998)Does Caloric Restriction Alter IL-2 Transcription?Frondiers in Bioscience 3: 125.
- R K Zee Cheng, E G Podrebarac, C S Menon, C C Cheng (1979) Structural modification study of bis(substituted aminoalkylamino)anthraquinones. An evaluation of the relationship of the [2-[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]ethyl]amino side chain with antineoplastic activity. J med chem 22: 501-505.
- R K Zee Cheng, A E Mathew, P L Xu, R V Northcutt, C C Cheng (1987) Structural modifica-tion study of mitoxantrone (DHAQ). Chloro-substituted mono-and bis[(aminoalkyl) ami-no]anthraquinones. J med chem 30: 1682-1686.
- J O Morley, P J Furlong (2006) Synthesis and calculated properties of some 1,4 bis(amino)anthracene-9,10-diones. Org Biomol Chem 4: 4005-4014.
- Lown(1997) Lexitropsin Conjugates: Action on DNA targets. Current Medicinal Chemistry 4(5): 315-358.
- RJ Choi, TM Ngoc, K Bae, HJ Cho, DD Kim, et al.(2013)Anti-inflammatory properties of anthraquinones and their relationship with the regulation of P-glycoprotein function and expression. Eur J Pharm Sci 48272-48281.
- YH Peng, SP Lin, CP Yu, SY Tsai, MY Chen, et al. (2014) Serum Concen-trations of Anthraquinones after Intake of Folium Sennae and Potential Modulation on P-glycoprotein. Planta Med80(15):1291-1297.
- Ferrazzi E, Palumbo M, Valisena S, Antonello C, Palù G(1986) Antitumor activity of new and-thraquinone derivatives. Chemioterapia5(5):330-336.
- Katsara M, Deraos G, Tselios T, Matsoukas J, Apostolopoulos V (2008) Design of novel cyclic altered peptide ligands of myelin basic protein MBP83-99 that modulate immune re-sponses in SJL/J mice. J Med Chem 51(13):3971-3978.
- Martin R, McFarland H, McFarlin D (1992)Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Ann Rev Immunol 10: 153-187.
- Steinman L (1996)Multiple Sclerosis: A Coordinated Immunological Attack against Myelin in the Central Nervous System. Cell 85: 299-302.
- Zamvil S, Steinman L (1990)The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Annu Rev Immunol 8: 579-621.
- Katsara M, Deraos G, Tselios T, Matsoukas MT, Friligou I, et al. (2009) Design and synthesis of a cyclic double mutant peptide (cyclo(87-99)[A91,A96]MBP87-99) induces altered responses in mice after conjugation to man-nan: implications in the immunotherapy of multiple sclerosis. J Med Chem 52(1): 214-218.
- D E Smilek, D C Wraith, S Hodgkinson, S Dwivedy, L Steinman, et al. (1991)A single amino acid change in a myelin basic protein peptide confers the capacity to prevent rather than induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A88(21): 9633-9637.
- Ellery JM1, Nicholls PJ (2002) Alternate signalling pathways from the interleukin-2 receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13(1):27-40.






























