New Development Method for Determination of Cefuroxime Axetil (CUA) and Cefprozil (CZ) In Pharmaceutical Drugs By RP-HPLC
M A Alfeen 1* and Y Yildiz2
1Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Second Science, Al-Baath University, Homs, Syria
2Science Department, Centenary University, Hackettstown New Jersey, USA
Submission: July 7, 2019; Published: July 30, 2019
*Corresponding author: M A Alfeen, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Second Science, Al-Baath University, Homs, Syria
How to cite this article: M A Alfeen, Y Yildiz. New Development Method for Determination of Cefuroxime Axetil (CUA) and Cefprozil (CZ) In Pharmaceutical Drugs By RP-HPLC. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2019; 8(4): 555744 DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2019.08.555744
Abstract
High performance liquid chromatography was one of the most important technologies used in drug control and pharmaceutical quality control. In this study, an analytical method was developed using chromatography method for determination of two Cephalosporin as like: Cefuroxime Axetil (CUA), and Cefprozil (CZ) in pharmaceutical Drug Formulations. Isocratic separation was performed on an Enable C18 column (125mm × 4.6mm i.d, 5.0μm, 10A˚) Using Triethylamine: Methanol: Acetonitrile: Ultra-Pure Water (0.1: 5: 25: 69.9 v/v/v/v %) as a mobile phase at flow rate of 1.5 mL\min. The PDA detection wavelength was set at 262nm. The linearity was observed over a concentration range of (0.01–50μg\mL) for RP-HPLC method (correlation coefficient=0.999). The developed method was validated according to ICH guidelines. The relative standard deviation values for the method precision studies were < 1%, and an accuracy was > 98%. The results were within the limits allowed by the US Pharmacopoeia and successfully for determination of Cefuroxime Axetil (CUA) and Cefprozil (CZ) in Tablets and dry syrup of the local pharmaceutical formulations.
Keywords: Cefuroxime Axetil (CUA), Cefprozil (CZ), RP-HPLC method
Introduction
Cefuroxime Axetil (CUA) is a second-generation of cephalosporin using as antibiotic for Drug Pharmaceutical: (6R, 7R)-3-(carbamoyloxymethyl)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(furan-2-yl)-2-methoxyim inoacetyl] amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (Figure 1) [1]. Cefprozil (CZ) is a second-generation cephalosporin using as antibiotic for Drug Pharmaceutical: (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetyl] amino]-8-oxo-3-[(E)-prop-1-enyl]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (Figure 2) [1].

Most cephalosporins were used as broad-spectrum antibiotics, especially urinary and genital tract infections, and Gram-negative tests towards anaerobic or pathogenic bacteria were also important for the treatment of pharyngitis and MRI, since these two substances are of great local importance in Syria, as they were produced in multiple pharmaceutical forms. As a result of the great pressure on chemists to follow each production line on one, the conditions of method have been developed by researchers to save time and effort in quality control according to international and local standards. CUA and CZ have beenfound to reduce the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution [1]. According to literature surveys, there are different analytical methods reported for the determination of CUA and CZ. It includes UV-Vis spectroscopy [2-5], chemiluminescence [6], HPLC [7-10]. Specificity and stability parameters for the drug were assessed according to ICH [1].
Experimental and Chemical Reagents
Cefuroxime as Axetil (CUA) and Cefprozil (CZ) (purity of all > 99.80%) was obtained as a gift sample from Parabolic Pharmaceuticals Ltd., India. Analytical grade Methanol, Acetonitrile, Triethylamine (Merck GmpH). The Ultra-Pure water for HPLC was obtained by using TKA Water Purification System, Germany. All Pharmaceutical Drug formulation was bought from the local market (Table 1).
Instrumentation
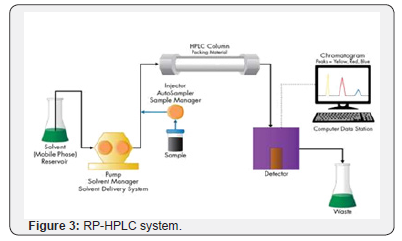
RP-HPLC System. An Enable C18 (125mm × 4.6mm, i.d 5μm, 10A˚) was used for separation. Triethylamine: Methanol: Acetonitrile: Ultra-Pure Water (0.1: 5: 25: 69.9 v/v/v/v%) as a mobile phase at flow rate of 1.5mL\min in isocratic mode. The PDA detection was carried out at 262nm (Figure 3).
Preparation of Standard and Sample Solutions
Standard stock solutions of CUA and CZ were prepared to make 1000μg\mL solutions. Make Sample solutions as standard by weigh of content Powder Tablets and Dry for oral suspension equivalent to 100mg of CUA and CZ was accurately measured, and transferred into two separate 100mL volumetric flasks, containing 10mL of diluents mobile phase and ultrasonicated for 15minutes; the volume was made up and mixed well. Solutions were filtered by a 0.2μm filter to remove particulate matter. Filtered solutions were properly diluted for analysis as already described. The drug present in the sample solutions was calculated by using the calibration curves. All the solutions were stored at (2-8) ºC for the future use.
Method Validation
Linearity
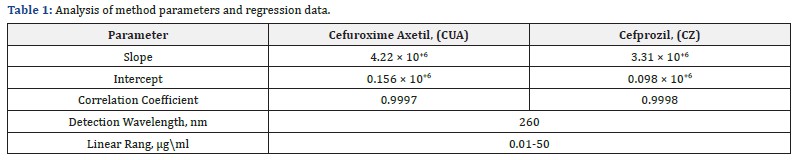
A ten-point (0.01, 0.02, 0.08, 1.0, 2.0, 8.0, 10, 20, 40, and 50μg\mL) calibration curves were prepared. The peak area for HPLC method was obtained by injecting 20μl into the column. Calibration curves were plotted by taking the peak area curve on the y-axis and the concentration μg\mL on the x-axis.
Precision
The intraday and interlay precision study was carried out to check the reproducibility of results. A concentration of 0.04, 0.4, 4.0 μg\mL and 12μg\mL of CUA and CZ (n=6) were analyzed to find out relative standard deviation RSD% for RP-HPLC method.
Accuracy
To check the accuracy of the proposed method, recovery studies were carried out at (1, 80, 100, and 120%) of the test concentration. The recovery study was performed three times at each level. The amount of CUA and CZ present in the sample was calculated using calibration curves.
Robustness
The robustness of RP-HPLC method was studied by deliberately changing method parameters like flow rate of mobile phase, detection wavelength, and organic phase compositions. A series of system suitability parameters like retention time, theoretical plates, and tailing factor were determined for each changed condition according to ICH [1].
Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation
The LOD and LOQ were determined separately according to the ICH guidelines. For HPLC method, concentrations providing a signal-to-noise ratio 3:1 and 10:1 were considered as the LOD and LOQ, respectively.
Results and Discussion
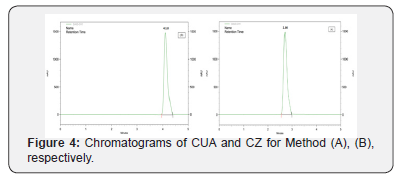
Optimization of mobile phase was carried out based on tailing factor and theoretical plates obtained for CUA and CZ. During the trial runs, the drug was tested with different mobile phase compositions like (Triethylamine: Methanol: Acetonitrile: Ultra-Pure Water v/v/v/v%) at various compositions (10:10: 20: 60 v/v/v/v%), (5: 15: 15: 65 v/v/v/v%), and (1: 5: 20: 74v/v/v/v%) and flow rates (1.0,1.5, and 2.0 mL\min). The mobile phase consisting of Triethylamine: Methanol: Acetonitrile: Ultra- Pure Water (0.1: 5: 25: 69.9 v\v\v\v%) at a flow rate of 1.5 mL\ min was selected which gave a sharp, symmetric peak for CUA, CZ. The retention time for CUA, CZ was found to be (2.86, 4.18 min) respectively. The run time was 5min. The tailing factor for CUA, CZ was found to be (1.12, 1.17). PDA detection was carried out at 260 nm. The separation was carried out at room temperature (Figure 4) respectively.
Specificity
To evaluate the specificity, PDA detector was applied to find out the peak purity of the chromatographic peaks obtained for the stress-treated drug solution. Peak purity results are indicative for finding out the peak homogeneity. The specificity of the RP-HPLC method was determined by checking the interference of any of the possible degradation products and Absorbances produced during study of CUA, CZ. The study of the drug was carried outwith Methanol, Triethylamine, Ultra-Pure Water for discovering the stability nature of the drug. The degraded samples were prepared by taking suitable aliquots of the drug solution, and then undertaking the respective stress testing procedures for each solution. The chromatograms (Figure 5) obtained for the blank and placebo show no interference due to solvent used and presence of the commonly used excipients suggesting the specificity of two methods.
Linearity
The calibration curves were found to be linear over a concentration range of (0.01–50 μg\mL) for method (correlation coefficient 0.999 for all method). The method parameters and regression data are shown in (Table1).
Precision
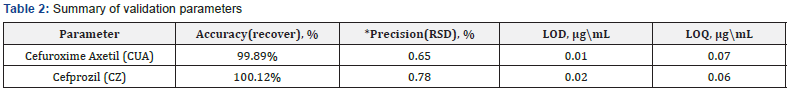
The methods were found to be precise as the RSD (%) values for the precision studies were well below 2% (n=6). The results are shown in Table 2.
Accuracy
The accuracy of the developed methods was found out by the standard addition method. High recovery values suggest that all three methods are accurate. The results are shown in Table 2.
Robustness
The HPLC method was found to be robust under deliberate changes in the mobile phase flow rate (±0.1 mL\min), detection wavelength (±5nm), and organic phase composition (±2%). For the UV spectroscopic methods, changing the slit width shows no significant effect on absorbance, indicating the robustness of the developed methods. No significant changes were obtained in the content of CUA, CZ during the solution stability studies by the developed methods. The recoveries for the solution stability by Method was found to be 99.89%, and 100.21%, respectively.
Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation
The LOD and LOQ values shown in Table 2 suggest that the developed methods are sensitive to determine CEM.
Analysis of Commercial Dry Syrup Formulation
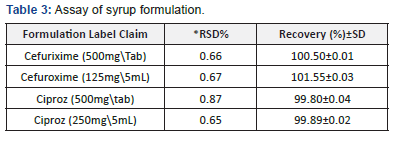
The developed methods were successfully applied for the determination of CUA, CZ in Tablets and the dry syrupformulations. The result for the assay of CUA, CZ is shown in Table 3.
Conclusion
The proposed chromatographic method in this study was characterized by high accuracy and excellent repetition through the very low standard deviation values, good health through the good return values compatible with the constitutional field, in addition to the ease and speed of quality control without obstruction of additives to the pharmaceutical, Using them in the analysis of pharmaceuticals, and their application in pharmaceutical control laboratories.
References
- Marzia Lazzerini a & David Tickell (2011) Antibiotics in severely malnourished children: systematic review of efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics Bulletin of the World Health Organization 89: 594-607.
- J Pritam, P Manish, S Sanjay (2011) Development and Validation of UV-spectrophotometric method for determination of cefuroxime Axetil in Bulk and in Formulation. International Journal of Drug Development & Research 4(3): 318-322.
- Md Rahman, Md Asaduzzaman, S M Islam (2012) Development and Validation of UV spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Cefuroxime in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. American Journal of Pharmtech Research 2(4): 352-358.
- S B, Amir, M A Hossain, M A Mazid (2014) Development and Validation of UV spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Cefuroxime Axetil in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Formulation. Journal of Scientific Research 6(1): 133-141.
- R Chavda, H Yadav, M Hinge, S Desai (2016) Development and Validation of UV spectrophotometric Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Cefuroxime Axetil and Linezolid in Tablet Dosage Form. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Bioscientific Research 6(3): 365-370.
- C Ramesh, G Reddy, T V Narayana, K V Rao, B Rao (2011) Assay of Cefaprozil in Bulk and Its Pharmaceutical Formulations by Visible Spectrophotometry. RASAYAN J Chem 4(1): 13–16.
- A Szlagowska, M Kaza, P Rudzki (2010) Valiated HPLC Method Method for Determination of Cefuroxime in Human Plasma. Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica-Drug Research 6(67): 677–681.
- M Sengar, S Gandhi, U Patil, V Rajmane (2009) Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for Simultaneous Determination of Cefuroxime Axetil and Potassium Clavulanate in Tablet Dosage Form. International Journal of ChemTech Research 1(4): 1105-1108.
- M Alfeen, B Elias (2016) Determination of Cefuroxime Axetil and Cefixime Trihydrate in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms by RP-HPLC Method. Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry 2(2): 1-5.
- D Gowrisankar, P Sarsmbi, S A Raju (2008) Reverse Phase-HPLC Method for The Analysis of Cefaprozil in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Int J Chem Sci 6(3): 1583-1589.






























