Crystal Structure and Disorder in Benzothiophene Derivative
Mohamed ziaulla*
Department of Chemistry, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, India
Submission: August 10, 2018; Published: August 24, 2018
*Corresponding author: Mohamed ziaulla, Department of Chemistry, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Bangalore-92, India, Email id: mohamed.ziaulla@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Mohamed z. Crystal Structure and Disorder in Benzothiophene Derivative. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2018; 7(5): 555721. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2018.07.555721
Keywords:2-Amino-6-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carbonitrile (1) and 2-Amino-7-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carbonitrile (2) with various N-H…O, N-H…O and N-H…S interactions
Introduction
Benzothiophenes are important heterocycles either as biological active molecules or as luminescent components used in organic materials [1-3]. One of the most important drugs based on the benzothiophene system is Raloxifene which was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [4-6]. Raloxifene is a representative of a class of compounds known as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) that exhibit estrogen agonist-like actions on bone tissues and serum lipids while displaying potent estrogen antagonist properties in the breast and uterus. Recently, 3-oxygenated benzothiophene has been reported to display a substantial (10-fold) increase in estrogen antagonist potency relative to raloxifene [7-11]. We report herein the Crystal structure of 2-Amino-6-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carbonitrile (1) and 2-Amino-7-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carbonitrile(2)
X-Ray Analysis and Refinement
The X-ray diffraction data for the compound 1 was collected on a Bruker Smart CCD Area Detector System. Intensity data were collected up to a maximum of 29.2° for the compound in the –ф scan mode. The data were reduced using SAINTPLUS [12]. A total of 11284 reflections were collected, resulting in 2441 independent reflections of which the number of reflections satisfying I>2 σ(I) criteria were 1878. These were treated as observed. The structure was solved by direct methods using SHELXS97 [13] and difference Fourier synthesis using SHELXL97 [13]. The compound Z3 crystallizes in monoclinic space group P21/c. The fused benzothiophene ring system is substituted with amino, methyl and carbonitrile groups. The thiophene ring is essentially planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.05Å). The carbon atoms C9 and C10 are disordered over two sites (C9A/C9B and C10A/C10B) with site occupancy factors 0.650(3) and 0.350(3) resulting in a major and a minor conformers (Figure 1).

X-Ray Analysis and Refinement
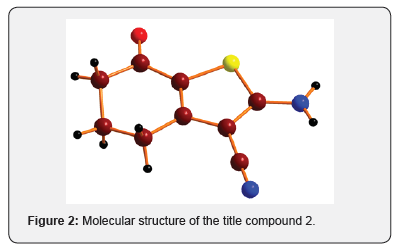
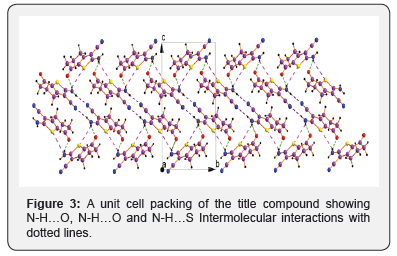
The X-ray diffraction data for the compound 2 was collected on a Bruker Smart CCD Area Detector System. Intensity data were collected up to a maximum of 27.0° for the compound in the –ф scan mode. The data were reduced using SAINTPLUS [12]. A total of 6202 reflections were collected, resulting in 2058 independent reflections of which the number of reflections satisfying I>2 σ(I) criteria were 1671. These were treated as observed. The structure was solved by direct methods using SHELXS97 [13] and difference Fourier synthesis using SHELXL97 [13]. The positions and anisotropic displacement parameters of all non-hydrogen atoms were included in the full-matrix least-square refinement using SHELXL97[13] (Figures 2 & 3) [14,15].
Acknowledgement
ZIA is thankful to Dr. Paul Mathulla, Chairman of governing council and Dr. Alice Abraham, President, Impact Group of Institutions for their constant support and encouragement.
References
- Shishoo CJ, Jain KS (1992) Synthesis of some novel azido/ tetrazolothienopyrimidines and their reduction to 2,4‐ diaminothieno[2,3‐d] pyrimidines. J Heterocyclic Chem 29: 883.
- Campaigne E, Bird CW, Cheeseman GWH (1984) Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry, Pergamon Press: Oxford 4: 863.
- Katritzky AR, Rees CW, Scriven EFV (1996) Conversions of Primary Amino Groups into Other Functionality Mediated by Pyrylium Salts. Pergamon Press: Oxford 2: 679.
- Jones CD, Jevnikar MG, Pike AJ, Peters MK, Black LJ, et al. (1984) Antiestrogens. 2. Structure-activity studies in a series of 3-aroyl- 2-arylbenzo[b]thiophene derivatives leading to [6-hydroxy-2-(4- hydroxyphenyl)benzo[b]thien-3-yl] [4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy]- phenyl]methanone hydrochloride (LY156758), a remarkably effective estrogen antagonist with only minimal intrinsic estrogenicity. J Med Chem 27(8): 1057-1066.
- Jordan VC (2003) Antiestrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators as multifunctional medicines. 1. Receptor interactions. J Med Chem 46(6): 883-908.
- Jordan VC (2003) Antiestrogens and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators as Multifunctional Medicines. 2. Clinical Considerations and New Agents. J Med Chem 46(7): 1081-1111.
- Mc Donnell DP, Clemm DL, Hermann T, Goldman ME, Pike JW (1995) Analysis of estrogen receptor function in vitro reveals three distinct classes of antiestrogens. Mol Endocrinol 9(6): 659-669.
- Kauffman RF, Bryant HU (1995) Selective estrogen receptor modulators. Drug News Perspect 8: 531.
- Sato M, Rippy MK, Bryant HU (1996) Raloxifene, tamoxifen, nafoxidine, or estrogen effects on reproductive and nonreproductive tissues in ovariectomized rats. FASEB J 10(8): 905-912.
- Palkowitz AD, Glasebrook AL, Thrasher TJ, Hauser KL, Short LL, et al. (1997) J Med Chem 40: 1407.
- Grese TA, Cho S, Finley DR, Dogfrey AG, Jones CD, et al. (1997) J Med Chem 40: 146.
- Jones CD, Jevnikar MG, Pike AL, Peters MK, Black LJ, et al. (1984) Antiestrogens. 2. Structure-activity studies in a series of 3-aroyl- 2-arylbenzo[b]thiophene derivatives leading to [6-hydroxy-2-(4- hydroxyphenyl)benzo[b]thien-3-yl] [4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy]- phenyl]methanone hydrochloride (LY156758), a remarkably effective estrogen antagonist with only minimal intrinsic estrogenicity. J Med Chem 27: 1057-1066.
- Grese TA, Cho S, Bryant HU, Cole HW, Glasebrook AL, et al. (1996) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 201.
- Bruker, Saintplus (1998) Program for data reduction. Bruker Axs Inc, Madison, Wisconcin, USA.
- Sheldrick GM (2008) A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst A 64: 112- 122.






























