Synthesis New Amid of Carboxylic Acids and Antimicrobial Activity – I
GH Torosyan*and NR Hovhannisyan
National polytechnic university of Armenia, Yerevan
Submission: May 24, 2018; Published: May 28, 2018
*Corresponding author: GH Torosyan, National polytechnic university of Armenia, Armenia, Yerevan, Email: gagiktorosyan@seua.am
How to cite this article: GH Torosyan, NR Hovhannisyan.Synthesis New Amid of Carboxylic Acids and Antimicrobial Activity – I. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2018; 6(5): 555701. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2018.07.555701
Short Communication
The amides of carboxylic acids are important organic compounds and have a wide range of applications. It`s known them wide range biological functionalities [1], they occur in the main chain of a proteins and in synthetic polyamide materials. Low molecular weight amide as formamide and dimethylformamide are common solvent [1]. Amide bond formation is a fundamentally important reaction in organic synthesis [2]. A convenient method for the formation of carboxamides from carboxylic acids and primary amines in the presence of molecular sieves is described. This process is very chemoselective [3,4].
The Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid Amid
N-allyl-N-pentadien-2,4-yl(furfuryl) amine and acetic acid chloride were reacted intensively over 6hour in in dioxane solution (with 2 molar ratio of alkaline solution). Additionally, the reaction mixture was added the water, extracted by chloroform, dried on MgSO4.
N-allyl-N-pentadien-2,4-yl amid of acetic acid : Bp 120-122oC/10mm, d420 0,9428, nD20 1,5018, IR: 920,980, 1605, 1640, 1670, 3080; UV: 230nm, Rf 0,58 (benzene:diethyl ether 5:1).
N-allyl-N-furfuryl amid of acetic acid: Bp 90-92oC/2mm, d420 1,0380, nD20 1,5050, IR: 920,955, 970, 1510, 1570, 1630, 1675, 3085; UV: 220nm, Rf 0,38 (benzene:diethyl ether 5:1).
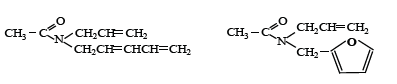
The Antimicrobial Activity
Antmicrobial properties of amid are studied by serial extraction in vitro method. It had been used as indicative microorganisms:
a) Staphylococeus aureeus # 209 “P”, as a stable, bacterial bacteria group;
b) Escherichia coli serotype 0 III B: 4, as is the fastest bacterial from families of intestinal microorganisms. The test was cultured on MPA and MPB with pH = 7,2-7,4. The acaric bacteria were used in the stages of the second genetics.
References
- J Boonen, A Bronselaer, J Nielandt, L Veryser, Guy De Tre, et al. (2012) Chemistry, occurrence and functionality of plant N-alkylamides. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 142(3): 563-590.
- E Valeur, M Bradley (2009) Amide bond formation: Beyond the myth of coupling reagents. Chem soc reviews 38(2): 606-631.
- J Cossy, C Pale-Grosdemange (1989) A convenient synthesis of amides from carboxylic acids and primary amine. Tetrahedron letters 30(21): 2771-2774.
- Labinskaya AS (1978) Microbiology with the technique of microbiological research. Medicina pp. 394.






























