Correction: Association between Technology Development and Rounder Substituted-lh-Indole-2,® 3-Dione Hiv-1 Inhibitors Who Have Displays Strategic Nanomolar Cytotoxicity
Ramesh Paranjape1 and Rahul Hajare2*
1National AIDS Research Institute, India
2Indian Council of Medical Research, Vinayaka Mission University, India
Submission: March 24, 2018; Published: April 09, 2018
*Corresponding author: Rahul Hajare, Indian Council of Medical Research, Vinayaka Mission University, India, Tel: 9921707584; Email: rahulhajare@rediffmail.com
How to cite this article: Ramesh P, Rahul H. Correction: Association between Technology Development and Rounder Substituted-1h-Indole-2, 3-Dione Hiv-1 Inhibitors Who Have Displays Strategic Nanomolar Cytotoxicity. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2018; 6(3): 555686. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2018.06.555686
Abstract
Model speeds drug discovery a series of novel, twenty 1,3,5-tri substituted-lH- indole 2,3-dione scaffold on a putative "U shape" molecular recognition of novel HIV-1 inhibitors were designed and synthesized using a parallel synthesis unit processes technology. Among synthesized and tested compounds 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1G and 1H found good quality of IC50 ranges from 4.91 to 32.01μg. One among those, compound 1C is the most potent inhibitor as a target compound against HIV-1. Target compound N-[(3Z) 5-methoxy-1-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro- 3H-indol-3ylidene]amino}benzene sulfamethaxazole (1C) tactically very low cytotoxicity (CC50>1mM). It is reported 7.15 μg/ml to engineered cell lines, TZM- l (JC53BL-13).
Keywords: N-[(3Z) 5-methoxy-1-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3ylidene]amino
Introduction
A human immunodeficiency virus strains is sloppy in its reproduction. However, due to the infidelity of HIV-1 during replication, the emergences of mutations (especially K103N and Y181C) rapidly develop resistance and high cytotoxicity rate to the first-generation with rigid structures, such as Nevirapine (NVP) and Efavirenz (EFV) [1-3]. In an effort to address the low resistance barrier issue, next generations have been designed with the structural feature of smaller building blocks, representative second generation improved drug resistance profiles are the recently marketed diarylpyrimidine analogues rilpivirine (TMC278, RPV) and etravirine (TMC125, ETR) [46]. At this moment, doing up about untapped chemical space in inhibitors binding pocket, also explore unresolved chemical modification obtaining more potent, quality, efficacy and safety back -up extraordinary series of unique 1,3,5 tri substituted- 1H-indole-2,3-dione connected by flexible linkers have been investigated.
Compounds and Reagents
Compounds were authorized from Sigma-Aldrich Company (MO,USA) and structure, compounds, HIV activity were amplified using Biqualys offers accurate analyses combining LC-SPE-NMR- MS and Agilent Cary 630 FTIR spectrometer, Luminometer for virus counts and ELISA analyzer.
Cells and Viruses
Engineered TZM-bl indicator cell line was provided by the TZM-bl NIH AIDS Reagent Program USA. This is a CXCR4-positive HeLa cell clone that was engineered to express CD4 and CCR5. Laboratory adapted strains, including HIV-1UG070, 7th PID dated 05/12/14 was obtained from the Department of Molecular Virology, Bio safety Laboratory -II NARI Pune. An automated, 96-well parallel array synthesizer for solid-phase organic synthesis has been designed and constructed. The instrument employs a unique reagent array delivery format, in which N-morpholinomethyl-indole-2, 3-dione utilized has a dedicated plumbing system. An inert atmosphere is maintained during all phases of a synthesis, and temperature can be controlled via a thermal transfer plate which holds the injection moulded reaction block. The reaction plate assembly slides in the X-axis direction, while eight nozzle blocks holding the glacial acetic acid reagent lines slide in the Y-axis direction, allowing for the extremely rapid delivery of sulphonamide reagents to 96 wells. In addition, there are six banks of fixed nozzle blocks, which deliver the same reagent or solvent to eight wells at once, for a total of 72 possible reagents. The system described herein is an efficient means for the parallel synthesis of compounds for lead.
Interpretation of Gold Dock
A computer program designed to screen rapidly by performed using Gold Dock Suite. The coordinates for X-ray crystal structure of HIV-1 (PDB code: 3M8Q) was downloaded from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) at the Research Collaboration for Structural Bioinformatics (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/ home.do) and Shanghai small molecular database (SSMD) has been utilized. Gasteiger charges were assigned to both protein and ligands. A grid with spacing of 0.375 A and 60x60x60 points in the x, y, and z axes was built and centred on the centre of mass of the bound ligand in the crystal structure. Energy grid maps for all ligand atom types were calculated, while keeping the protein structure rigid, we selected Lamarckian genetic algorithm (LGA) to search the conformational and orientation space of the ligands. Each small molecule, 100 separate docking calculations were performed with the breakpoint settings of parameters: population size of individuals at 350, a maximum number of 25 million energy evaluations, a maximum number of generations of at 27,000, a mutation rate of 0.02, a crossover rate of 0.8, and an elitism value of 1. Docking, cluster analysis was performed on the results with the root-mean-square (RMS) deviations less than1.0 A. The breakthrough docked conformation was then selected as the lowest energy stance in the most populated cluster.
Thus, the lowest binding energy complex of more populated cluster depicts more specific and highly reliable, greater efficacy binding conformation of the compound. Insertion of the hydrogen bonding with K101 was constraints for the specificity of binding of compounds in active site of strain as reported in previously. The computational simulation of active compounds showing higher inhibition was compared with that of etravirine, next generation drug. In docking study standard etravirine [a and b ]and compound [1C] showed the hydrogen bonding with K101 residue because the second position C= O group in ring brought to form hydrogen bonding with in hydrophobic pocket of enzyme, in this context C=O is a oxygen isolated in the active compound 1C they formed hydrogen bond with back bone of K101 residue which is crucial for drug resistance and thus compromised the untapped chemical space in IBP and this increase the affinity of compound toward strain inhibition. It is further conclude that region having OCH3, Br, CH3, Cl of C-5 and distance between interaction 2.44 and combined K103, prone to mutation at the IBP entrance. Like pyrrole ring substitution on C-1 by morpholine showed higher activity as it has made vander walls force that are acting upon TYR 188 with distance 3.307 between residue atom and ligand atom which going to stabilized the inhibitor binding pocket and it should be prevent the inhibitor from leaving the binding pocket. Vander walls force interaction act on TYR 188 which made flexible clamp, however mutation resulting in looses or any changes interaction (Figure 1).
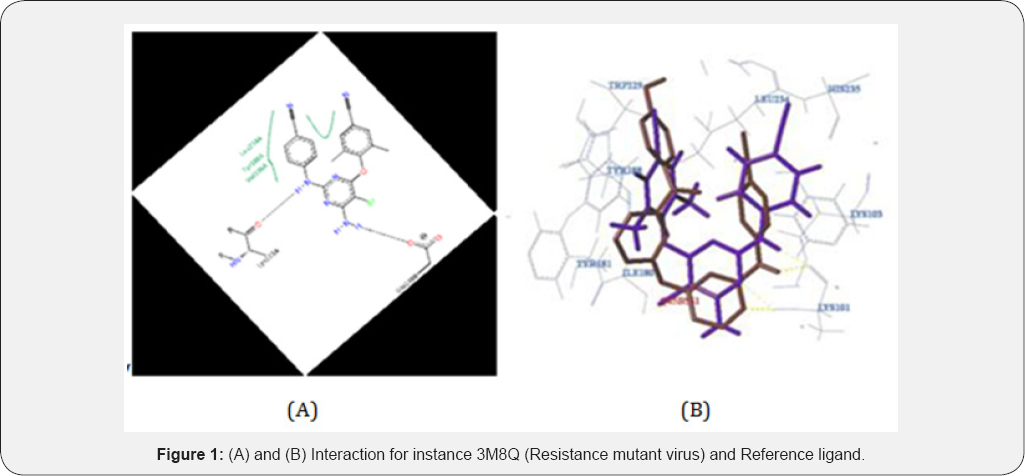
Most important in this research and finding substitution at C-3 by sulphonamide based substituent’s may be lead pi-pi stacking interaction between compound and aromatic amino acid residue TYR 181 with interaction distance 5.9 which is prone to mutation resulting loss or change of interaction. This clearly indicates that the inhibitor binding process and residues must facilitate to enter the binding pocket and adopt an appropriate conformation is the optimal interaction with the surrounding residue. This lead to change due to conformation of U, shoes horse like structure, made sites feedback inhibitor to regulate the activities and showed higher activity. Legend: black dashed line-hydrogen bond, salt bridge, metal interaction, green solid line- hydrophobic interaction, green dashed line-pi-pi, pi-cation interaction. Note: Covalent bonds to protein are not displayed. Image generated using pose view software. By downloading this image you confirm to follow citation rule (Figure 2).
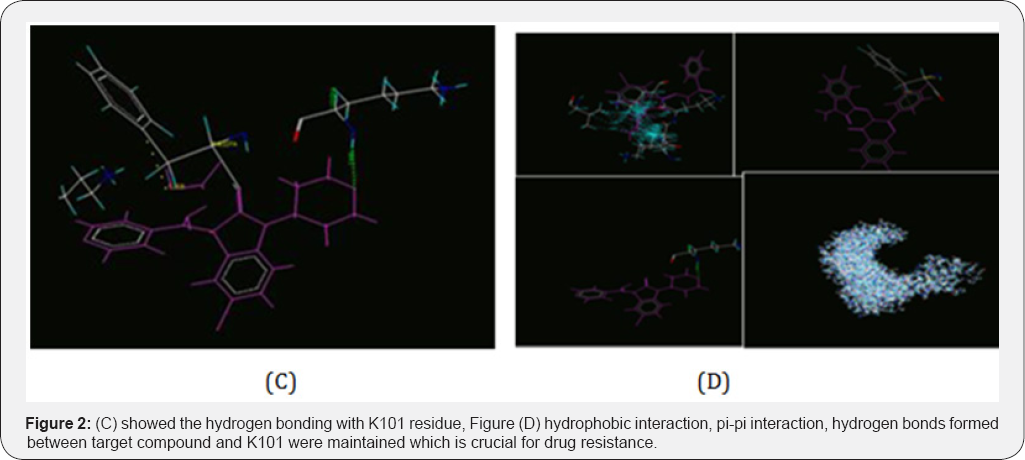
3D structure of the docked conformation of target compound, N-[(3Z) 5-methoxy-1 (morpholin-4-ylmethyl) -2-oxo-1,2- dihydro- 3H-indol-3ylidene]amino} benzene sulfamethaxazole (1C) and BP of K103N/Y181C mutant HIV-1 strain, (PDB code:3M8Q),showed interaction of target compound in purple colour and 3M8Q in green and blue colour. Predicted Figure 2C showed the hydrogen bonding with K101 residue, Figure 2D hydrophobic interaction, pi-pi interaction, hydrogen bonds formed between target compound and K101 were maintained which is crucial for drug resistance and (d) merged molecule insertions position in inhibitor-binding pocket (IBP) (PDB:3M8Q) cavity endorsed lock form in open position and stop the transcription.
Conclusion
A comparison of the designed, synthesized and evaluated novel 1, 3, 5- tri- substituted-1H-indole 2,3-dione which showed nano molar activity against HIV-1. Taste compounds 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1G and 1H possess inhibitory activity. Target compound N-[(3Z) 5-methoxy-1-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)- 2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3ylidene]amino} benzene sulfamethaxazole (1C) displays potency (IC50 at micro molar level) and detect low cytotoxicity (CC50s > 1mM) against HIV- 1 UG070 7th PID. In this study and model of binding energy complexes determination, characterized and examined selected new series of resistance mutation (refence protein 3M8Q PDB) and noted changes in interaction between target compound and HIV-1 mutant. At best, binding energy could be related to IC50 in assay, more negative of the binding energy results in the formation of stronger complexes belonging therefore when a ligand have a low binding energy its affinity towards the HIV- 1 target is bigger also points to the fact that target compound belonging to adaptable are circulating and giving rise to new. The detection of binding energy value of refence protein and reference ligand complexes shows -12.43 kcal/mol and average of experimental binding energy values of new ligands and refence protein complexes were shows -11.60 kcal/mol. Target compound [1C] has been shown binding energy -8.69 kcal/ mol, which was show its affinity towards the protein 3M8Q is sizeable in comparison with other lead ligands with higher binding energy. IC 50 of target compound N-[(3Z) 5-methoxy-1- (morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-2-oxo-1, 2-dihydro-3H-indol 3ylidene] amino} benzene sulfamethaxazole (1C) was found to be 4.91 μg/ ml. Also it has been clearly indicates strain- target compound inhibitor binding energy values highly correlated which is less than two reported determined binding energy values, which is high degree to cover all edges and outskirt in IBP and reduce the frequency of chemical space creation.
The differences in these correlations may reflect good ground of biological features of the interactions of HIV-1 inhibitor and its complexes. A thorough study was carried out over twenty computationally designed 1,3 5- tri substituted- 1H-2,3-dione analogs using gold dock suite and program with the goal of identifying potential lead molecules that bind to the HIV -1 mutant protein respectively. The comparatively higher interaction scores of lead compounds compared to Etravirine when docked with HIV-1 mutant protein at the IBP active site residue suggest these novel leads would potentially bind more strongly to the pockets of HIV -1 3M8Q proteins. Further, the leads are docked with Lys101, Val106, Leu234 and His235 this proteins residue to predict their binding efficiencies with HIV-1 protein. All the twenty designed 1,3,5- substituted-2,3-dione and its analogs with chemical substitutions at the X1,X3,X5 showing better interactive scores respectively than reference ligand ( Interactive score = -152.57), as a result of docking of among twenty analogs eight lead compounds 1A,1B,1C,1D,1E,1F,1G and 1H were shows interactive score -81.69, -88.28, -80.98, -55.92, -85.35, -74.04, -67.87 and -78.17 and in-vitro experiment IC 50 were found 25.65μg/ml, 31.18μg/ml, 4.91μg/ml, 32.01μg/ml, 4.59 μg/ml, 3.96 μg/ml, 5.02 μg/ml and 25.34 μg/ml. To date the target molecule 1C, when docked with 3M8Q, have shown better dock scores (Interaction Score -80.98 compared to reference ligand (Interaction Score -152.57). Hence these are expected to bind strongly onto inhibitor binding pockets and have suggested that above is highly functional novel lead has very low cytotoxicity (CC50>1mM) and it has been displays 7.15 μg/ml to cell lines, TZM-bl and displayed potent anti-HIV-1 activity found 4.91 μg/ ml against laboratory adapted strains UG070, 7th PID. Ethics statement, the study was conducted in accordance with basic principal and study of the Bio safety Laboratory II and Bio safety Laboratory III, National AIDS Research Institute (ICMR) Pune. This study and the informed consent processes were approved by the Indian Council of Medical Research Government of India.
Acknowledgment
I would like to express deep gratitude to my post-doctoral guide Renowned Scientist, Respected Dr. Ramesh S. Paranjape Retired Director & Scientist 'G' National AIDS Research Institute, India.
References
- Riedel D, Ghate M, Nene M, Paranjape R, Mehendale S, et al. (2006) Screening for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) dementia in an HIV clade C-infected population in India. J Neurovirol 12(1): 34-38.
- Lole KS, Bollinger RC, Paranjape RS, Gadkari D, Kulkarni SS, et al. (1999) Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of Intersubtype recombination. J Virol 73(1): 152-160.
- Manisha Ghate, Ramesh Paranjape, Bharat Rewari, Raman Gangakhedkar (2014) Transfer out Patients Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy from Programme Clinic: A Potential "Leak” in the HIV Treatment Cascade. World Journal of AIDS 4(4): 382-386.
- Raman R Gangakhedkar, Manisha V Ghate, Ramesh S Paranjape, Nilam P Gurav, Bharat B Rewari (2014) Retention of antiretroviral naive patients registered in HIV care in a program clinic in Pune. Indian Journal of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS 35(2): 124-128.
- De Clercq E (2009) Anti-HIV drugs: 25 compounds approved within 25 years after the discovery of HIV. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(4): 307320.
- Li X, Chen W, Tian Y, Liu H, Zhan P, et al. (2014) Discovery of novel diarylpyrimidines as potent HIV NNRTIs via a structure-guided corerefining approach. Eur J Med Chem 10(80): 112-21.






























