Correction: Generation and Characterization of New Entrance Antiretroviral Drug 2-Indolinone: Results of a Classical R & D Study
Ramesh Paranjape1 and Rahul Hajare2*
1National AIDS Research Institute, India
2Indian Council of Medical Research, Vinayaka Mission University, India
Submission: March 24, 2018; Published: April 06, 2018
*Corresponding author: Rahul Hajare, Indian Council of Medical Research, Vinayaka Mission University, India, Tel: 9921707584; Email: rahulhajare@rediffmail.com
How to cite this article: Ramesh P, Rahul H. Correction: Generation and Characterization of New Entrance Antiretroviral Drug 2-Indolinone: Results of a Classical R & D Study.Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2018; 6(2): 555685. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2018.06.555685
Abstract
HIV has true evolutionary history of a homologous of sequences. It has mutations do not have appreciated. It has some other property and impact on the fitness of the HIV carrier indicates how these analyses can be useful in the drug discovery process. HIV has same organ under every variety of form and function. It has variety of forms this definition still holds secrete even today. HIV has been come homologous proteins can differ in their specificities, specific activities, level of expression or some other basic property. However homologous will have some residual similarity in their form and function. HIV from all of its hiding places within the body has difficult. The approach can be used in bioinformatics innovation in practices, including complex binding energy estimation in novel HIV-1 inhibitors. Here we showed how a space filling model- based approach used infection HIV-1 inhibitors and role of target compound located insight into the host cell machinery. Process technology by parallel synthesizer major has used for the purposes of synthesized 2- Indolinones potential derivatives. In vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of new entrance compound 8-methoxy-5-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-4,4a,5,9b-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,3-b]indole-2,3 dicarbonitrile (1b) and studies have suggested that above has a novel reservoir has very low cytotoxicity(CC50>1mM) and it has been displays 15.5μg/ml to cell lines, TZM-bl. Also it displayed potent anti-HIV-1 activity and found 3.96μg/ml against laboratory adapted strains UG070, 7th PID.
Introduction
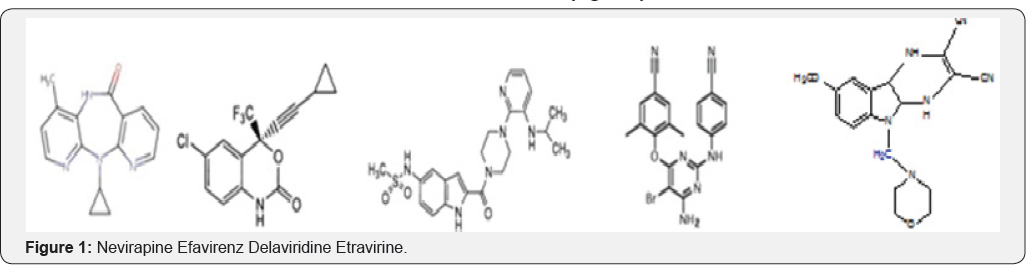
Among currently available HIV-1 inhibitors hamper the polymerase activity of HIV-1 through allosterically binding to the binding pocket but geometry of the DNA and its cycle emergence mutations (especially K103N,Y181C) rapidly develop resistance and potency, efficacy has an another effort to address the structural feature of novel smaller building blocks. Specific recognition of ligands by HIV -1 protein has at the crucial biological functions so that binding affinities characterizes the strength of such recognition. Space filling model hinges and binding energies on a better way to interatomic interactions and its vital for to build interaction in specific, precise more authoritative. In those research advancements in computing, prediction of the binding affinity based on principles of molecular interaction has come to the forefront of active research and has been the subject potentially offers accurate prediction of binding energies of ligands to protein. Currently drugs used to treat HIV AIDS (Figure 1).
Ethics Statement
The study has conducted in accordance with basic principles of the Bio safety Laboratory II and III National AIDS Research Institute (ICMR) Pune. This study and the informed consent process have been approved by the Indian Council of Medical Research New Delhi. Letter attached [1].
Compounds and Reagents
All chemicals used have procured from Sigma-Aldrich, Invitrogen company USA. The purity of chemicals has been checked before use and purified. Melting points recorded by open capillary tube method and uncorrected.
Cells and Viruses: TZM-bl indicator cell line has kindly provided by the TZM-bl NIH AIDS Reagent Program USA. The cells have further optimized and laboratory adapted strains, including HIV-1UG070, 7th PID has obtained from the department of molecular virology BSL-II laboratory National AIDS Research Institute (ICM R) Pune.
Experimental
Process technology and methodology to synthesized potential 2- Indolinones, total 16 derivatives using N-methyl morpholine-N-methyl piperidine, diaminomaleonitrile, halogens and alkyl group as substituent. Synthesized compounds have recrystallized by using ethanol-chloroform (9:1) mixture. Purity and characterization of synthesized compounds were done by chromatographic methods (TLC), infrared spectroscopy, NMR. Synthesized compounds 2-Indolinones and its derivatives screen for their Anti-HIV-1 activity [2].
Scheme
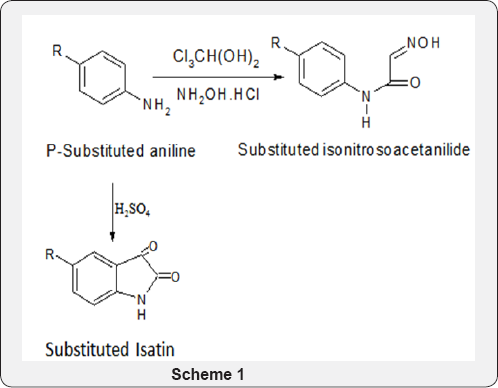
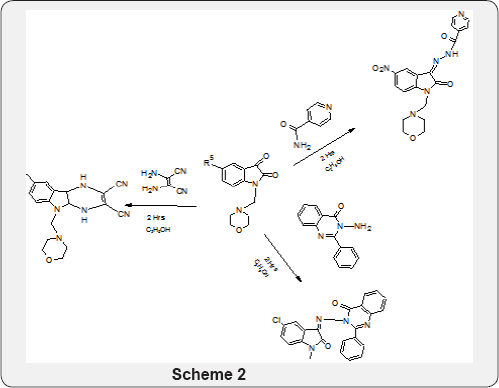
Synthesis of Basic Nucleus: Expansion of basic nucleus into new entrance ART 8-methoxy-5-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)- 4,4a,5,9b-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,3-b]indole-2,3- dicarbonitrile. Synthesis of preplanned, causal-pathway-based modeling analysis of more new entrance ART (Schemes 1 & 2) (Figure 2) .
Molecular Docking: Studies has performed using V Life MDSR 4.3 program (Crystal structure of mutant HIV-1 (PDB code: 4I2Q) has downloaded from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) at the Research Collaboration for Structural Bioinformatics (http:// www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do). The bound ligand and all water interfaces has been removed from the protein. Gasteiger charges has assigned to both protein and ligands. A grid with spacing of 0.375 A and 60x60x60 points in the x, y, and z axes ha built and centered on the center of mass of the bound ligand in the crystal structure. An energy grid map for all possible ligand atom types has calculated before performing docking. Lamarckian genetic algorithm to search the conformational and orientational space of the ligands. For each small molecule, 100 separate docking calculations has performed with the following settings of parameters: population size of individuals at 350, a maximum number of 25 million energy evaluations, a maximum number of generations of at 27,000, a mutation rate of 0.02, a crossover rate of 0.8, and an elitism value of 1.Cluster analysis was performed on the results with the root-mean-square deviations less than1.0 A. The best-docked conformation has then selected as the lowest energy pose in the most populated cluster Thus, the lowest binding energy complex of more populated cluster more specific and highly reliable for efficacy [3,4].

Result and Discussion
A model-based approach has proposed here as a tool for the designed, synthesized and evaluated 1, 2, 3, 5- substituted-2, 3- dione derivatives which showed nanomolar activity against HIV-1. Taste compounds 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, 1e, 1f, 1g and 1h showed HIV-1 inhibitory activity. New entrance compound 8-methoxy-5-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-4,4a,5,9b-tetrahydro-1H- pyrazino[2,3-b]indole-2,3-dicarbonitrile (1b) displays IC50 at micromolar level and low cytotoxicity (CC50s > 1mM) against HIV- 1 UG070 7th PID. Simulation scenarios were used to complexity of ligand and HIV-1 protein more tactically and response by binding energy. We developed and examined selected new series of resistance mutation (refence protein 4I2Q PDB) and noted changes in interaction between compound and HIV-1 strain. Developed and validated results as shown in supplemental (Figures 3 & 4).


The analysis reveals a role of space filling substitution in compound and binding energy could be related to IC50, changes noted more negative of the binding energy results in the formation of stronger complexes rightly assigned, therefore when a complexity have a low binding energy its affinity towards the target enzyme is bigger and highlights the role of space filling substitution in compound which is high degree to cover all hiding region in IBP. Also it has been clearly indicates the impact of different exposure levels as well as the effect of varying patterns of compounds on strain and its levels results show that inadequate as well as poor adherence to binding energy. In this study we found reported determined binding energy value of refence protein and reference ligand complexes shows -11.43 kcal/mol and average of experimental binding energy of newly ligands and refence protein complexes has shows -12.02 kcal/ mol. Target compound [1b] has been shown binding energy -13.59 kcal/mol, which has been showed its affinity towards the protein 4I2Q enzyme has bigger in comparison with other lead ligands binding energy also [5].
IC 50 of target compound 8-methoxy-5-(morpholin-4- ylmethyl)-4,4a,5,9b-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,3-b]indole-2,3 dicarbonitrile (1b) was found to be 3.96 μg/ml against laboratory adapted strains UG070,7th PID. In this work we also examined the ability of docking and G scoring methods to predict the binding of compound to a HIV-1 strain, somewhat surprisingly, the binding area observed in docking does not always overlap with the binding of the high-affinity ligand. The comparatively higher interaction scores of lead compounds compared to Rilpivirine when docked with HIV-1 mutant protein at the active site suggest these novel leads would potentially bind more strongly to the pockets of HIV -1 4I2Q proteins. Further, the leads have docked with prone to mutation Lys101, Val106, Leu234 and His235 residue to predict their binding efficiencies with HIV-1 protein. All the sixteen designed 1,2,3 5- substituted-2,3-dione and its analogs with chemical substitutions at the R1,R2,R3,R5 position showing better G Scores respectively than reference ligand (G Score = -65.57), as a result of docking of among sixteen analogs eight lead compounds 1a,1b,1c,1d,1e,1f,1g and 1h were shows G score -81.69,-88.28, -80.98, -85.92, -85.35, -74.04, -67.87,-78.17.
The target compound 1b, when docked with 4I2Q,have shown better dock scores, interaction score -88.28 compared to reference ligand and have suggested that above is a new highly functional novel derivative has very low cytotoxicity(CC50>1mM) and it has been displays 15.5μg/ml to cell lines, TZM-bl.low cytotoxicity(CC50>1mM) and it has been displays 15.5μg/ml to cell lines, TZM-bl. 3D of target compound, 8-methoxy-5-(morpholin- 4- ylmethyl)-4,4a,5,9b-tetrahydro-1H pyrazino [2,3-b]indole- 2,3-dicarbonitrile (1b) into K103N/Y181C mutant HIV-1 strain, (PDB code:4I2Q), showed interaction of target compound in purple colour and 4I2Q in green and blue color. Specified Figure 3 showed hydrophobic interaction, pi-pi interaction between target compound and HIV protein along with hydrogen bonds formed between isolated oxygen atom of target compound and K101 has maintained which is crucial for drug resistance and Figure 4 merged molecule creations in inhibitors binding pocket cavity endorsed lock form in open position.
Acknowledgment
I would like to express deep gratitude to my post-doctoral guide Renowned Scientist, Respected Dr. Ramesh S. Paranjape Retired Director & Scientist 'G' National AIDS Research Institute, India.
References
- Sen S, Tripathy SP, Paranjape RS (2006) Antiretroviral Drug Resistance Testing. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 52(3): 187193
- Vanangamudi Murugesan, Vinay Shankar Tiwari, Reshu Saxena, RajkamalTripathi, Ramesh S Paranjape, et al. (2011) Lead optimization at C-2 and N-3 positions of thiazolidin-4-ones as HIV- 1 non nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 19(22): 6919-6926.
- MV Ghate, SM Mehendale, BA Mahajan, R Yadav, RG Brahme, et al. (2000) Relationship between reported clinical conditions and CD4 lymphocytecounts in HIV infected subjects in Pune, India. National Medical Journal of India 13: 183-187.
- Hajare R, Paranjape R, Kulkarni S (2016) Tailored microwave technology forSynthesis N'-[(3Z)-5-chloro-1-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3Hindol-3 ylidene] pyridine-4 carbohydrazide as HIV-1 inhibitors. Drug Formulation & Bioavailability Congress, China.
- Rahul H, Smita K, Madhuri T, Ramesh P (2016) Variability interaction between etravirine and rilpivirine: A retrospective.KJACT-100103 2: 1-3.






























