Enzyme (Alpha Amylase) Inhibitory Activity of Ricinus communis
Faheem Ahmed1* and Mohsin Iqbal2
1BioceH Lab, Department of Biochemistry, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
2Industrial Biotechnology Lab, Department of Biochemistry, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
Submission: February 16, 2018; Published: March 06, 2018
*Corresponding author: Faheem Ahmed and Mohsin Iqbal, Department of Biochemistry, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan, Tel: 03136763676, Email: mohsiniqbal5050@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Faheem A, Mohsin I. Enzyme (Alpha Amylase) Inhibitory Activity of Ricinus communis. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2018; 5(4): 555669. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2018.05.555669.
Abstract
Ricinus communis is a weed whose leaves and seeds are widely studied and used in different medicines. Ricinus communis is commonly used medicinal plant. It is very important in herbal medicines. Potential of roots of Ricinus communis was undertaken in present work by determining its enzyme inhibitory activity. Seven extracts were prepared by roots. These were aqueous, ethanol, methanol, n-hexane, n-butanol, chloroform and ethyl acetate. All extracts showed enzyme inhibitory activity but n-butanol gave maximum inhibition (68%) after 30 minutes, methanol extract gave maximum inhibition (60%) after 60 minutes, aqueous extract gave maximum inhibition (40%) after 90 minutes and ethyl acetate gave maximum inhibition (45%) after 120mins. Ricinus communis is has good enzyme inhibitory activity.
Keywords: Ricinus communis; Alpha amylase; Enzyme inhibition; Glucobay; Extracts
Aims and Background
The amylase is a very important compound. It is basically present in the small intestine of human. It has the ability to hydrolyze the starch molecules to products including dextrin and it is further broken into smaller components like glucose. In biotechnology, it has great importance. It is used for the fermentation of food, paper industry and textile industry. There are many sources from which amylase can be derived. The major sources of amylase are animals, microorganisms and plants. The microbial enzymes are required to meet demand of industry. The Alpha Amylase which has chemical formula of 1, 4-a-D-glucan hydrolase is a widely distributed secretary enzyme and the important form of industrial amylases. There are other enzymes too which can hydrolyze the starch but the alpha amylase is still considered as one of the most important enzyme to hydrolyze the starch. Alpha amylase is very important and it is distributed in whole world and it is available from different sources like microbial, animals and plants. Lots of research has already been done for alpha amylase. Due to high demands of alpha amylase in whole world the microorganisms are used for the production of amylase. The microbes can produce the amylase in bulk quantity. It is economically very important. The alpha amylase is mostly derived from yeasts, bacteria, actinomycetes and different fungi. The enzymes obtained from fungi and bacteria have dominated the applications in industry. Baci!!us licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus stearothermophilus have quite a good ability to produce the alpha amylase which is thermally stable. These bacteria have ability to produce it at commercial level [1].
Diabetes mellitus is a disease which is spread in whole world. It is epidemic in whole world and it has multiple biochemical impairments. The diabetes mellitus is increasing at very high rate in whole world every year. The world health organization has statistics that there are 346 million people worldwide having diabetes mellitus. The 90 percent of them are suffering from T2DM. The T2DM is mainly because of inefficiency of body to use insulin. The most complicated form of diabetes mellitus is postprandial hyperglycemia which can be managed by a class of compounds called amylase inhibitors. Alpha amylase and compounds which have inhibitory effect for alpha amylase are on target to design the drugs in treating the obesity, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. Most drugs which are used for treating the diabetes in world have the ability to stimulate the absorption of insulin, release of insulin from pancreas, inhibition of alpha amylase and inhibition of alpha glucosidase. Two major concerns in the usage of these drugs are the side effects caused and drug resistance after prolonged treatment. To overcome these effects and to identify natural inhibitors of alpha amylases from plant based sources is now the primary concern of scientific research. The search for scientifically approved and safe natural antidiabetic agents is also emphasized by the world health organization. By keeping these things in view, the present study is carried out by selecting traditionally valued and exotic ornamental plants which do possess medicinal values, and evaluating them due to inhibitory potential of alpha amylase against alpha amylase taken from pancreas of porcine. Starch is used as substrate in this analysis [2].
The plants which are good for medicinal point of view are very good for producing herbal medicines which are very useful for healthy life of human with low side effect. There are 300 general and 7500 species in Euphorbiaceae family. This family belongs to tracheophytes which are plants with flowers and protected seeds. The Ricinus communis is one of the medicinal plants. For maintaining disease free life castor plant has been used by traditional and medicinal point of view. The castor plant is used traditionally as fungicide, laxative, fertilizer and purgative. The castor plant has very good medicinal properties like antiulcer, antioxidant, antinociceptive, antihistamic, antiasthmatic, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective, antifertility, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antiinflammatory, lipolytic, wound healing, central nervous system stimulant, larvicidal and insecticidal characteristics. There are secondary metabolites present which are the cause of this activity like flavonoids, glycosides, saponins, steroids and alkaloids [3]. Inhibition of alpha amylase enzyme was analyzed in this research.
Experimental
In Vitro Alpha Amylase Inhibition Assay
The alpha amylase inhibition assay was carried out using the Enzyme kinetic assay (DNS method) as described [4]. Porcine pancreatic a-amylase was purchased from Sigma Chemical Co.
Plant Extract Sample
Hundred microliters of 20% (v/v) plant extract and 100 μL of 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.9), containing alpha-amylase at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL were incubated at 25°C for 10 min. After pre-incubation, 500 μL of 0.5% starch solution prepared in (20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6.9) was added. The reaction mixtures were then incubated at 25°C for 10 min. The reaction was stopped with 1 mL of 3,5dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) color reagent. Then incubated in a boiling water bath for 5 min and cooled to room temp. Absorbance (A) was measured at 540 nm. Percent inhibition was calculated as follows:
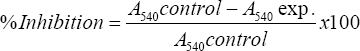
Synthetic Enzyme Inhibitor Sample
Hundred microliters of 20% (v/v) metformin/acarbose and 100 μL of 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.9, containing alpha- amylase at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL were incubated at 25°C for 10 min. After pre-incubation, 500 μL of 0.5% starch solution (20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6.9) was added. The reaction mixtures were then incubated at 25°C for 10 min. The reaction was stopped with 1 mL of 3,5dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) color reagent. Then incubated in a boiling water bath for 5 min and cooled to room temp. Absorbance (A) was measured at 540 nm. Percent inhibition was calculated as follows:
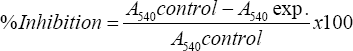
Control
Control incubations represent 100% enzyme activity and were conducted in a similar way by replacing extracts with vehicle (100 μL dimethylsulfoxide and distilled water). Twenty- five microliters of distilled water and 100 μL of 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.9, containing alpha-amylase at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL were incubated at 25°C for 10 min. After pre-incubation, 100 μL of 0.5% starch solution in 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6.9, was added. The reaction mixtures were then incubated at 25°C for 10 min. The reaction was stopped with 1 mL of 3,5dinitrosalicylic acid color reagent. Then incubated in a boiling water bath for 5 min and cooled to room temp.
Blank
For blank incubation (to allow for absorbance produced by the extract), enzyme solution was replaced by buffer solution and absorbance recorded. Two hundred microliters of distilled water and 100 μl of 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.9, were incubated at 25°C for 10 min. After pre-incubation, 100 μl of 0.5% starch solution in 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6.9, was added. The reaction mixtures were then incubated at 25°C for 10 min. The reaction was stopped with 1 mL of 3,5dinitrosalicylic acid color reagent. Then incubated in a boiling water bath for 5 min and cooled to room temp. Separate incubation carried out for 10 minutes. It was performed by adding samples to DNS solution immediately after addition of the enzyme. The concentration of the extract required to inhibit the activity of the enzyme by 50% (IC) was calculated.
Results and Discussion
Enzyme Inhibitory Analysis
Inhibition of enzyme alpha amylase was carried out by using the DNS method as illustrated [4]. Inhibition was carried out on all test fractions of Ricinus communis by analyzing activity at different time intervals and results are summarized in Table 1. The activity was found at different time intervals using glucobay as synthetic inhibitor. The alpha amylase enzyme inhibition is good technique to reduce glucose level in blood. The standard techniques were used to analyze it in Ricinus communis root extracts. It was seen that the roots of Ricinus communis has good enzyme inhibitory activity.
Mean similar letter in a row or in a column are nonsignificant (P>0.05). The capital letters are used for overall mean. The fractions were tested against control. The data was analyzed. All the fractions and glucobay (synthetic inhibitor) are significant as compared to control. The control is represented by The nonsignificant values will have similar to letters of control AB. The other fractions are also represented by different letters. (Tables 2 & 3).

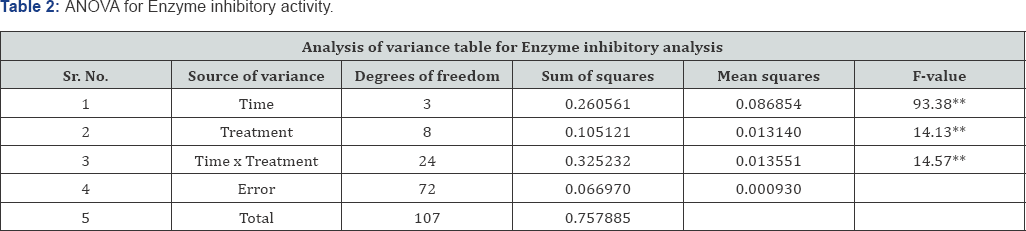
** = Highly significant (P<0.01).

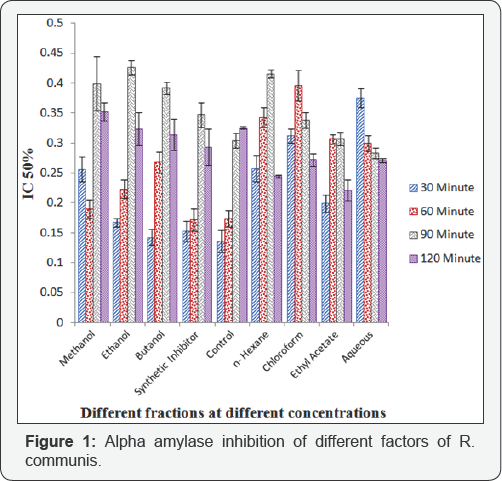
The Singhand guggul was analyzed for enzyme inhibitory activity. It had given good enzyme inhibitory activity. The control gave 100 percent activity. The methanol, ethanol and chloroform extracts were analyzed and they showed enzyme inhibitory activity after 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes. The methanol, ethanol and chloroform gave 65%, 58% and 62% activity after 30minute. The methanol, ethanol and chloroform gave 40%, 53% and 42% inhibition after 60minute. The methanol, ethanol and chloroform gave 27%, 33% and 26% inhibition after 90minute. The methanol, ethanol and chloroform showed 17%, 19 and 13% inhibition after 120 minutes. The inhibition was decreased with time [5]. The leaves of Thespesia populnea, Ricinus communis and Carica papaya were analyzed for inhibition of alpha amylase Different extracts were analyzed. All the extracts showed enzyme inhibitory activity. The methanol, butanol and ethyl acetate showed maximum activity for three plants. Which was in range of 60% to 72% [6]? The Syzium cuminiand Psidiumguajava were analyzed for alpha amylase inhibition. The aqueous, methanol and chloroform extracts were analyzed. They were tested after 30minute. They gave inhibition of 68%, 63% and 50% [7]. In my analysis, I used seven fractions in the analysis. Glucobay tablet was used as synthetic inhibitor. The activity was analyzed after 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes. The n-butanol gave better activity as compared to synthetic inhibitor after 30 minutes. Other extracts had less activity than synthetic inhibitor. The methanol gave 60% inhibition after 60 minutes. It was less than synthetic inhibitor but it was better than other extracts. The chloroform, ethyl acetate and aqueous extracts showed 28%, 35% and 40% activity respectively after 90minutes. These were better than synthetic inhibitor. The n-hexane, Chloroform, Ethyl acetate and aqueous extracts gave 39.5%, 32.5%, 45% and 33% inhibition respectively. It was better than synthetic inhibitor. The herbal extracts could prove to be good in the inhibition and could have good medicinal values (Figure 1).
Outcomes
The root part of Ricinus communis was used to analyze its ability for enzyme inhibitory activity against alpha amylase enzyme. Seven extracts were prepared and extracts from roots of Ricinus comunis showed good enzyme inhibitory activity. Seven extracts were prepared by roots. These were aqueous, ethanol, methanol, n-hexane, n-butanol, chloroform and ethyl acetate. All extracts showed enzyme inhibitory activity but n-butanol gave maximum inhibition (68%) after 30 minutes, methanol extract gave maximum inhibition (60%) after 60 minutes, aqueous extract gave maximum inhibition (40%) after 90 minutes and ethyl acetate gave maximum inhibition (45%) after 120mins. Ricinus communis is has good enzyme inhibitory activity. It had shown that roots of Ricinus communis have good enzyme inhibition potential. It could be used as good enzyme inhibitory agent for alpha amylase enzyme in medicinal analysis.
References
- Sani I, A Abduhamid, F Bello, M Yahya, AI Bagudo (2014) Isolation, partial purification and characterization of alpha amylase from Bacillus subtilis. J Microbiol Biotech Res 4(1): 49-54.
- Jyothi KU, M Jayaraj, KS Subburaj, KJ Prasad, I Kumudu, et al. (2013) Association of TCF7L2 gene polymorphism with T2DM in the population of Hyderabad. PLOS One J 8: 77-84.
- Jena J, AK Gupta (2012) Ricinus communis a phytopharmacological review. Int J Pharma Pharmaceutical Sci 4(4): 25-29.
- Apostolidis E, Y Kwon, K Shetty (2006) Potential of cranberry based herbal synergies for diabetes and hypertension management. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 15(3): 433-441.
- Tundis R, MR Liozzo, F Mechichini (2010) Natural products as alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitors and their hypoglycaemic potential in the treatment of diabetes. Mini Rev Med Chem 10(4): 315331.
- Tatun N, B Vajarasathira, J Tungjitwatayakul, S Sakurai (2014) Inhibitory effects of plant extracts on growth, development and alpha amylase activity in red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Eur J Entomol 111(2): 181-188.
- Singh A, T Marar (2011) Inhibitory effects of extracts of Syzygium cumini and Psidium guajava on glycosidases. J Cell Tissue Research 11(1): 2535-2539.






























