An Application of the Bibliometric Law of Fossil Fuel Literature in Science Citation Index Expanded
Chandran Velmurugan*
Department of Library and Information Science, Periyar University, India
Submission: December 14, 2017; Published: December 22, 2017
*Corresponding author: Chandran Velmurugan, Department of Library and Information Science, Periyar University, India, Email: murugan73@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Chandran V. An Application of the Bibliometric Law of Fossil Fuel Literature in Science Citation Index Expanded. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2017; 4(5): 555649.DOI10.19080/OMCIJ.2018.05.555649
Abstract
An attempt has been made to focus on the literature trends in fossil fuels in India, indexed in web of science database from Clarivate Analytics previously Thomas Reuters. Data was collected from Web of Science Core Collection database, the search string was "Fossil fuels" and refined by Countries/Territories "India" and the time span between 1989 and 2016 which were indexed SCI-Expanded. A total number of research output was 943 and its h-index was 73 and average citations per item was 28.63, total sum of times cited was 26,997, without self citations was 26,159, citing articles was 21,694, without self citations was 21,324 scores.
Keywords: Scientometrics; Bibliometrics; Fossil fuels; Web of Science; Research Output; Scholarly articles; TLCS; TGCS
Introduction
The fossil fuel, which comes under non-renewable energy, includes coal, crude oil, natural gas, and nuclear fuel. Primary sources of energy consisting of petroleum, coal, and natural gas amount to about 85% of the fossil fuels in primary energy consumption in the world [1,2]. Fossil Fuels are energy-rich substances that have formed from the accumulated remains of living organisms that were buried millions of years ago. For example, the gasoline that fuels our cars, the coal that powers electrical plants, and the natural gas that heats our homes are all fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of dead plants and animals by exposure to heat and pressure in the earth's crust over the millions of years. Fossil fuels contain high percentages of carbon and include mainly coal, petroleum, and natural gas [3].
Scientometrics describes the quantitative and qualitative features and characteristics of science and scientific research in the field of Library and Information Science which is used to realize research trends and progress in a particular science subject. During the last few years, scientometric analysis has been increasingly used and being used to compute the research performance or talents of researchers and the growth of various disciplines of science. The scientometric analysis has gained momentum in the recent years due to proliferation of science literature. Scientometrics means "Science plus Metrics” or "measurement of Science.” Otherwise, it refers to the application of statistical indicators to evaluate scientific productivity or a scholarly communication which is retrieved from the bibliographic databases are Scopus, Web of Science, Engineering Index, Pub med, and so on. This study tries to focus the research trends on fossil fuel literature in India during 1989-2016.
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to compute the research trends and growth pattern of Fossil fuels in India and the objectives are to depict the kinds document type on fossil fuel research; to trace the top ten country wise distribution; to identify the top ten productive authors; to investigate the top ten institutions; to identify top core journals on fossil fuels research and to evaluate the bibliographic law on fossil fuel literature.
Materials and Methods
The data were collected from Web of Science Core Collection, the search string was ''Fossil fuels” and refined by Countries/ Territories "India” and the time span between 1989 and 2016 which were indexed SCI-Expanded with a total of 943 records. This scientometric study has been carried out in the month of November 2017. For the purpose of data analysis, Hist Cite software used and then the data was transferred to an Excel spreadsheet for further statistical analysis.
Data Analysis
A. Document type: Seven types of documents were identified on fossil fuels literature in India during the study period. As expected, the huge number of document type was journal articles as they are the significant source of information for dissemination. 659 (69.9%) papers were journals and occupy first rank, and followed by review papers (24.5%), and articles in proceeding papers (4.6%) papers ranked third. The editorial materials (0.5%), Letters (0.3%), article from retracted publication and notes (0.1%) were each. It is found from the analysis towards documents that the highest number of documents was journal articles and 11236 citations which placed the top rank.
B. Top ten countries: Table 1 represents the country wise distribution of fossil fuels research output produced from India. A total number of 72 countries participated and only top 10 productive countries were selected for the current study. As expected, the huge number of productive research articles was produced by the United States (6.9%) and placed first. The next productive papers (2.3%) were published in Japan and followed by Canada ranked third productive country on fossil fuels research in India. It was also counted citation scores and the top global citations scores was 3897 from USA and followed by the United Kingdom with 1947 TGCS.

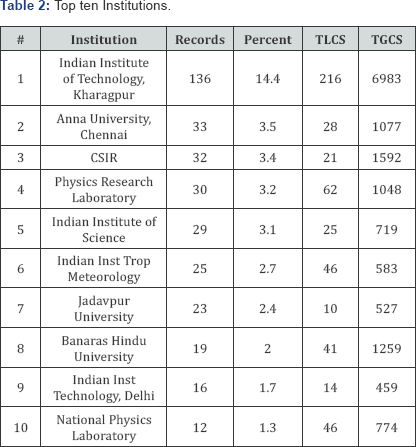
C. Top ten Institutions: It is counted and measured through the Table 2 that the institution wise contribution of distribution of fossil fuels literature in India for a period of 26 years from 1991- 2016. A total number of 1060 institutions are participated and out of 1060, only top most institutions in terms of research productivity almost 50% of research publications have chosen for the purpose of analysis. The huge number of (14.4%) papers with 6983 global citations was from Indian Institute of Technology of Kharagpur ranked first and followed by Anna University got ranked second (3.5%) papers with 1077 global citations. The third rank occupied by CSIR, Delhi with 32 research output and its global citations was 1592. The results indicate that the highest number of articles were from IIT and NIT institutions. The similar work [4,5] was done by the researcher on Journals on Information Literacy and Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics.
D. Top ten productive authors: Out of 3844 total authors, only top ten productive authors have been taken for the present study and it focused various elements of authors such as records, percentage, local citation score, and global citation score and cited references, etc. It was noted the most productive authors were among top ten authors such as 'Kumar A' with 17 papers, 'Kumar S' and 'Tiwari S' with 14 papers each. It was noted that based on the total local citation score was 80 and the global citation score was 1825 contributed by Venkataraman C. The same work has already done by the researcher using the Journal of Intellectual Property Rights during 2014 [6].
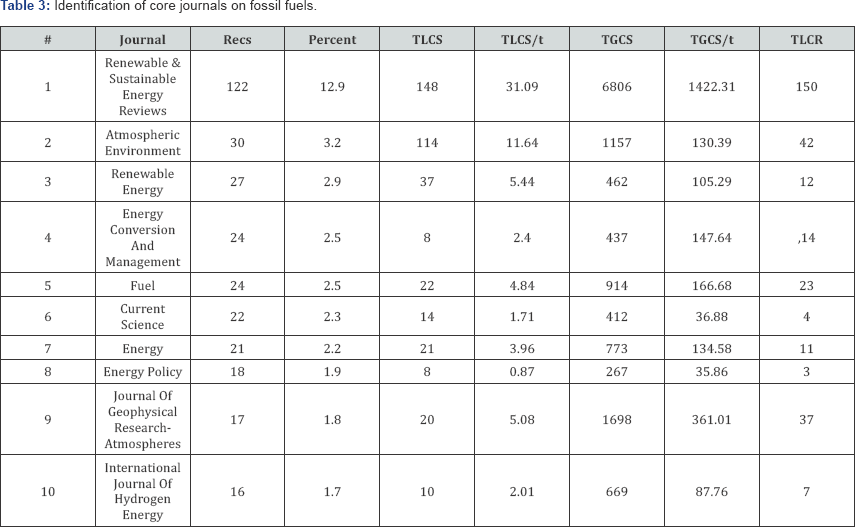
E. Core Journals: Of the bibliographic documents, Journals are the essential and primary source for information dissemination in the knowledge environment. Out of 319 journals with 943 publications on fossil fuel research on India during 1989-2016, it has been taken only top 10 journals with more than 10 scholarly communications along with global citations, local citations, total local citation references, etc. it is evident from the Table 3 that shows the significant academic publications on fossil fuels and their citation count. Out of 319 journals, "RENEWABLE & SUSTAINABLE ENERGY REVIEWS” has brought out a huge number of research output 122 (12.9%) along with 6806 total global citations (TGCS) and the total local citations (148) and its total local cited references (TLCR) is 150 and it dominates first rank among the top 18 journals. The next productive journal is ''ATMOSPHERIC ENVIRONMENT" with 3.2% and its global citations (TGCS) is 1157 and "RENEWABLE ENERGY" is the third productive core journal on fossil fuel research with 2.9% and its global citations is 462 (TGCS).
Application of Bradford Law of fossil fuels
Samuel Clement Bradford framed the Bradford's law of scattering to test the publications in 1934. He describes, "The Bradford's law is to elucidate that a group of journals could be arranged in an order of decreasing productivity and revealed that the journal which yield the most productive articles are coming first and the most unproductive in the last.” In this context, this law, the journals are to be grouped into a number of zones each producing a similar number of articles whereas the number of journals in each zone will be increasing speedily. Then the relationship between the zones is 1:n:n2. The formula has been used as F(X) = a + b log x, Where F(X)- is the cumulative number of references as contained in the first-x most productive journal and 'a' and 'b' are constants. Researchers have counted the total number of journals for this present study is 319.
Table 4 represents that the distribution of scholarly journals and contribution of research publications has grouped into three zones as per the law. According to Bradford, the zones will form an approximately geometric series as 1:n:n2. Based on the fossil fuel output, it is counted that the relationship of each zone is 3:10:306. The ratio shows that it does not fit into the Bradford's law of distribution. The results reveal that the distributions of core journals were published by a few numbers of journals. It finds here from the analysis, 63 refer to the number of journals in the Nucleus and the mean Bradford multiplier is 16.965. The similar result was identified in Plagiarism literature and the relationship of each zone was 19:95:371 and found the ratio does not fit into the Bradford's law of distribution [7].

*mean value
Conclusion
Scientometric analysis is one the metric study, which is widely used to identify the current research trends in particular disciplines, authors, journals, any institution and research and development on science and technology using the Web of Science, Scopus, Pub med databases. The results showed that the huge number of productive research articles was produced by the United States (6.9%) and placed first. The maximum number of document type was journal articles as they are the significant source of information for dissemination. 659 (69.9%) papers were journals and occupy first rank, and followed by review papers. The highest number of productive research articles was produced by the United States (6.9%) and placed first. The next productive papers (2.3%) were published in Japan. The most productive authors were among top ten authors such as 'Kumar A' with 17 papers. The journal 'Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews' has brought out a huge number of research output 122 (12.9%) along with 6806 total global citations. It is noticed that there is no such a study has been carried out on Fossil Fuel research and data retrieved from the Web of Science bibliometric database using Scientometric tools and techniques so far.
References
- (2010) International Energy Outlook.
- (2009) Towards Sustainable Production and Use of Resources: Assessing Biofuels. United Nations Environment Programme, Renewable Energy World.
- Demirel Y (2012) Energy, Green Energy and Technology, Energy and Energy Types. Springer London pp. 27-70.
- Velmurugan C, Radhakrishnan N (2015) Journal of Information Literacy: A Scientometric Profile. Journal of Information Sciences and Application 3 (1): 1-9.
- Velmurugan C (2014) Research Trends in Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics (IJPAP) for the Year 2009-2012. Asian Review of Social Sciences 3 (1): 24-28.
- Velmurugan C (2013) Research Trends in Journal of Intellectual Property Rights (JIPR): A Bibliometric Study, Library Philosophy and Practice (e-journal) p. 1-16.
- Velmurugan C, Radhakrishnan N (2017) Applications of Bradford's Law on Publication analysis of Plagiarism: A Scientometric Profile. ABC Journal of Advanced Research, 6 (2): 137-148.






























