Alkylation-Elimination Reaction in Quaternary Ammonium Salts
*GH Torosyan
National polytechnic university of Armenia, Yerevan
Submission: September 07, 2017; Published: September 12, 2017
*Corresponding author: GH Torosyan, National polytechnic university of Armenia, Armenia, Yerevan Gagik Torosyan, Doctor of Chemical sciences, professor, National polytechnic university of Armenia, Tel. 00374 93 998830; Email: gagiktorosyan@seua.am; gagiktorsojfan@poljrtecnic.am
How to cite this article: GH Torosyan. Alkylation-Elimination Reaction in Quaternary Ammonium Salts. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2017; 3(3): 555613. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2017.03.555613
Short Communication
During our work on the alkylation of organic acids containing carbonyl groups - as β-diketones [1,2], it was decided to study the possibility of alkylation of quaternary ammonium salts (QUAT) such as trimethylphenacyl ammonium bromide [3]. We have proceeded from the fact that such QUAT can't undergoes to Hofmann elimi-nation or on rearrangements (Sommele-Hauser, Stevens) also under this type of milder basic conditions.
It turned out that really studied QUAT alkylated by benzyl chloride. However, following the alkylation, the newly formed salt is eliminated to forms a chalcone. This process many time have been using in our laboratory to obtained chalcon type compounds. Along with the chalcone (alkylation-elimination product), the products of hydrolysis of benzyl chloride-benzyl alcohol and dibenzyl ether was formed.
Analogous transformations have also taken place in the case of a number of other salts with trimethyl and fourth alkyl group with not active β-hydrogen containing. The experiments show that elimination will occur rapidly, it is impossible to single out the original product of alkylation of the salt. We have already have been use the founded processes for a long time in practice Trimethylphenacyl ammonium bromide was chosen as the model object. Alkylation of this compound was carried out in a two-phase catalytic system in the absence of another QUAT as a PTC catalyst. It was suggested that the yield formed from mentioned QUAT would pass into the organic phase. Further in the organic layer, the yield will reacts with benzyl chloride.
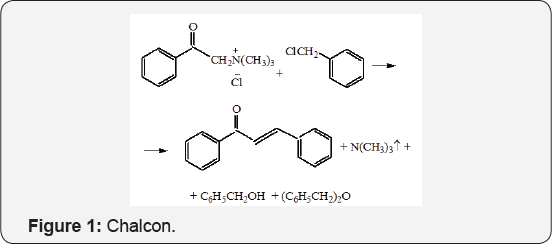
It turned out that he really studied QUAT was alkylated by benzyl chloride. However, following the alkylation, the newly formed salt is eliminated to forms a chalcone. This process had been opened in last quarter of last century, and have been using in our laboratory to obtain chalcon (Figure 1).
Trimethylamine is formed with chalcone for-ma--tion and benzyl chloride hydrolysis products as benzyl alcohol and dibenzyl ether have formed also.
Chalcones are valuable intermediates in orga-nic synthesis. Chalcones are naturally occurring compounds exhibiting broad spectrum biological activities including anticancer activity through multiple mechanisms. Chalcones are also inter⌝me⌝⌝diate compounds in the biosynthetic pathway of very large and widespread group of plants constituents the flavonoids the experiments show that this cleavage will occur rapidly, it is impossible to single out the original product of alkylation of the salt. We have named this process as alkylation-elimination reaction in QUAT It should be noted also, that our attempts to use in this reaction trimethylallyl- and trimethyl-proparyl ammonium bromides were not successful. These QUAT remain unchanged until the end of the reaction. This also indicates that the hydrogen atoms in the indicated salt not mobile, since this property depends to a large extent on the nature of the group adjacent to the methylene carbon. The impossibility of formation of ylides excludes the course of this reaction. These details are on the mechanism on the validity of our assumption about the mechanism of the occurrence of the process found in the two- phase liquid-liquid system [4].
Experimental Part
Alkylation of trimethylphenacyl ammonium bromide with benzyl chloride in two phase system.
To the reaction flask with a system of absorbers with a titrated solution of hydrochloric acid, the equimolar amounts of QUAT and alkyl halide were stirred. With stirring and heating on a boiling water bath for 20 minutes with double molar amount of powder potassium hydroxide in the reaction mixture also. The heating and mixing continued for more than 40 minutes.
Then reaction mixture was cooled, the organic part was extracted by diethyl ether. The ether extract was dried over MgSO4. After distilling off the ether, the reaction products were isolated by distillation. Inverse titration of the contents of the absorbers determined the number of fly amines. In the aqueous layer of the reaction residue, the amount of the formed ionic halide was determined by titration. At the end by neutralization of the aqueous layer, after by evaporation to dryness and extraction with absolute alcohol the non-primary salt was isolated, From 7,74gr (0,03 mol) of trimethylphena⌝cyl⌝am⌝monium bromide and 3,8gr (0,03mol) benzyl chloride and 3,4(0,06mol) of KOH at 90-95o, it had been obtained 3,2 grchalcone- (53,3 0%), 0,2gr (0,0018mol) benzyl alcohol, 0,73gr(0,0037mol) dibenzyl ether and 0,015mol trimethylamine.
Returned 0, 6 gr benzyl chloride and 3,6 gr initial QUAT. The structure synthesized chalcone was proved by IR, UV, 1HNMR and Mass spectrometry [5].
References
- A Kh Nazaretyan, GH Torosyan, AT Babayan (1985) Formales synthesis. Journal of Applied chem USSR n 11: 2580-2583.
- AT Babayan, GH Torosyan (1986) Phase transfer catalysis development stages. J Mendeleev Soc USSR 12: 129-135.
- GH Torosyan (1987) Reaction of inter- and internal alkylation for compounds with carbonyl and hydroxyl groups. Thesis for chemical doctor degree, Yerevan, Armenia p. 358.
- S Kumar, MS La ba, J K Makrandi (2008) An efficient green procedure for the synthesis of chalcones using C-200 as solid. Green chemistry letters & reviews 1(2): 123-125.
- DR Palleros (2004) Solvent-free synthesis of chalcones. J Chem Educ 81(9): 1345.






























