Petra, Osiris and Molinspiration: A Computational Bioinformatic Platform for Experimental in vitro Antibacterial Activity of Annulated Uracil Derivatives
Ajmal R Bhat1*, Rajendra S Dongre2 and Pervaz A Ganie1
1Department of Chemistry, S.B.B.S.University, Jalandhar Punjab-144030, India
2Department of chemistry, R.T.M., Nagpur University, Campus, Nagpur 440033, India.
Submission: January 21, 2017; Published: January 31, 2017
*Corresponding author: Ajmal R Bhat, Department of Chemistry, S.B.B.S.University, Jalandhar Punjab-144030, India, Tel.: +91-8283959724, +91-9797354802; Email: bhatajmal@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Ajmal R B Petra, Osiris and Molinspiration: A Computational Bioinformatic Platform for Experimental in vitro Antibacterial Activity of Annulated 007 Uracil Derivatives. Organic & Medicinal Chem IJ. 2017; 1(3): 555565. DOI: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2017.01.555565
Abstract
Annulated pyrano [2,3-d]pyrimidine/pyrano[2,3-d]uracil derivatives were synthesized using aromatic aldehydes, active methylene compounds and barbituric acid in presence of dibutylamine (DBA) catalyst in ethanol as solvent. The different substituents on phenyl ring in the fused pyrano uracil skeleton showed productive influence on its antimicrobial activity against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria like Pseudomonas aureus, E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia and Bacillus cereus. Antibacterial screening revealed that the presence of heteroaryl, cyano and amino groups on uracil skeleton increases its penetrating power on bacterial cell wall and product becomes more biologically energetic. The antimicrobial activity results showed some definite and interesting facts about the structure activity relationship (SAR) of synthesized molecules.
Keywords: Annulated uracils; Computational analysis; Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria; Pharmacophore sites
Introduction
The development of new chemotherapeutics is the major interest in academic and industrial research throughout the world so as to discover newer, more potent molecules, with higher specificity and reduced toxicity than the existing ones. These molecules (annulated Uracils) exhibit antimicrobial activity (kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms) against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria and becomes valuable building blocks in organic synthesis due to diversified functional groups. Heterocyclic compounds have received considerable attention owing to their variety of biological activities, especially as inhibitors of PDE5 extracted from human platelets[1], HIV-1 reverse transcriptase [2], human EPK2 [3], cyclin-dependent kinase [4].
The six membered nitrogen heterocyclic rings have great importance in pharmaceutical sector, because of theoretical as well as practical importance. Pyrimidine rings have significant pharmacological importance as being an integral part of DNA and RNA in several biological processes [5-8]. Therefore chemotherapeutic efficacy of annulated pyrano[2,3-d] pyrimidines is related to their ability to inhibit vital enzymes responsible for DNA biosynthesis such as dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), thymidylate synthetase (TSase), thymidine phosphorylase (TPase) and reverse transcriptase (RTase). Annulated uracil moieties that are annulated in to one molecule, then resultant derivative enhances its pharmaceutical activity such as antitumor [9], cardio tonic [10], antibronchitic [11], antihypertensive [12], antibacterial activity [13] and antileishmanial activity [14]. Therefore, for the preparation of these complex molecules large efforts have been directed towards the synthetic manipulation of annulated uracils that occupy a distinct and unique place in medicinal chemistry. Annulated pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine/uracil derivatives is unsaturated N-heterocyclic as a fusion of pyran and uracil rings, consisting of one oxygen atom at 8 and two nitrogen atoms at 1 and 3 positions respectively
Since we have already synthesized some bioactive products pyrano [2,3-d] pyrimidines/pyrano[2,3-d]uracils [15] in our research laboratory (Scheme 1). In this paper, we reported the screening of these bioactive synthesized products for antimicrobial activity against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria like Pseudomonas aureus, E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia and Bacillus cereus. A correlation structure and activities relationship of these compounds with respect to Lipinski rule of five [16], drug- likeness, toxicity profiles, and other physico-chemical properties of drugs is described and verified experimentally.
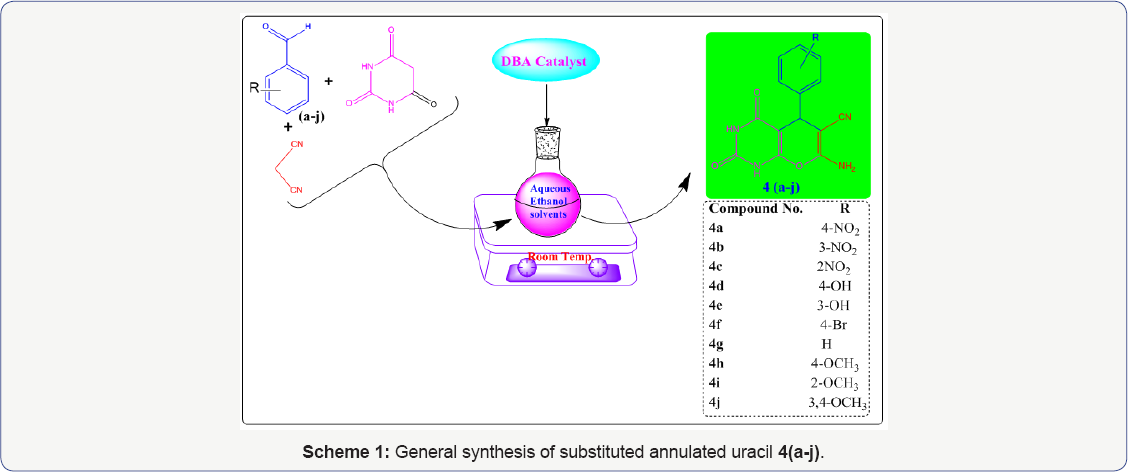
Material and Methods
Antibacterial activity (in vitro)
Antimicrobial activity of the synthesized annulated uracil derivatives were tested by the disk diffusion method. The sterilized Whatman No. 1 filter paper disks were autoclaved for one hr at 140°C. All the products were dissolved in N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) for dilution to prepare stock solutions of 20 mg/mL for antimicrobial assay. Agar plates were uniformly surface inoculated with fresh broth culture of gram positive and negative bacteria such as Bacillus cereus (ATCC-14579), Staphylococcus aureus (NCTC-7447), Klebshiella pneumonia (UC57), Pseudomonas aureus (ATCC 27853) and E. coli (ATCC 14169). These imp regnated disks were placed on medium suitably spaced apart and plates were incubated at 30°C for 1 hr to permit good diffusion and were then transferred to an incubator at 37±2°C for 24 hrs. The zones of inhibition were measured on mm scale. Streptomycin was used as standard antimicrobial drug. Antimicrobial activity test results as shown in (Table 1).

SD: Streptomycine; A = B. cereus (ATCC-14579), B = S. aureus (NCTC-7447),
C = K. pneumonia (UC57), D = P. aureus (ATCC 27853), E= E. coli (ATCC 14169).
*Inhibition zone around the discs for antibacterial activity: 11-18 mm: very strong activity; 5-10 mm: moderate activity; 1- 4 mm: weak activity.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest product concentration preventing visible bacterial growth. MICs of selected products 4(a-j) were determined by taking different concentrations of the product in DMF. The different concentrations were added by using sterilized pipettes to different test tubes containing sterilized broth medium inoculated with test organism. DMF alone showed no inhibition zone. Then all the test tubes were incubated at 37°C for 24 h and after incubation period, the presence of growth (turbidity) was observed.
Pharmacology
Antibacterial activity (In vitro)
All the synthesised annulated uracil derivatives [15] showed good antimicrobial activity against different gram positive and gram negative bacterial strains. The compounds with electron donating group at the different positions on phenyl ring and subsequent hydrophobic interaction with active site of enzyme increase the antibacterial activity. The antimicrobial agents are excellent derivatives for drug resistance issues in clinically used therapeutics and furnishes motivating model for studying interaction with antimicrobial targets as possible charge modification of the substituents and O/N of pharmacophore groups present in the skeleton. Electron donating substituent's -OH, -OCH3 and electron withdrawing substituents like -Br, - NO2 on the annulated uracil skeleton exerted positive influence on its antimicrobial activity against grame positive and grame negative bacterial strains when they are attached to phenyl ring.
Annulated uracil derivatives containing phenyl moiety are tested for potential antimicrobial activity and antimicrobial strains reveal that the presence of heteroaryl ring, cyano and amino groups on pyran ring make these more basic which increases its penetrating power on bacterial cell wall and the compounds becomes more active. In this case, the hydroxyl, methoxy, nitrile and bromo heteroaryl part is associated with the bacterial cell wall which makes them more active. Future flexible pharmacophore sites will assist to prepare derivatives for multi- therapeutic annulated uracil with high selectivity.
Results and Discussion
Antibacterial screening of series 4(a-j)
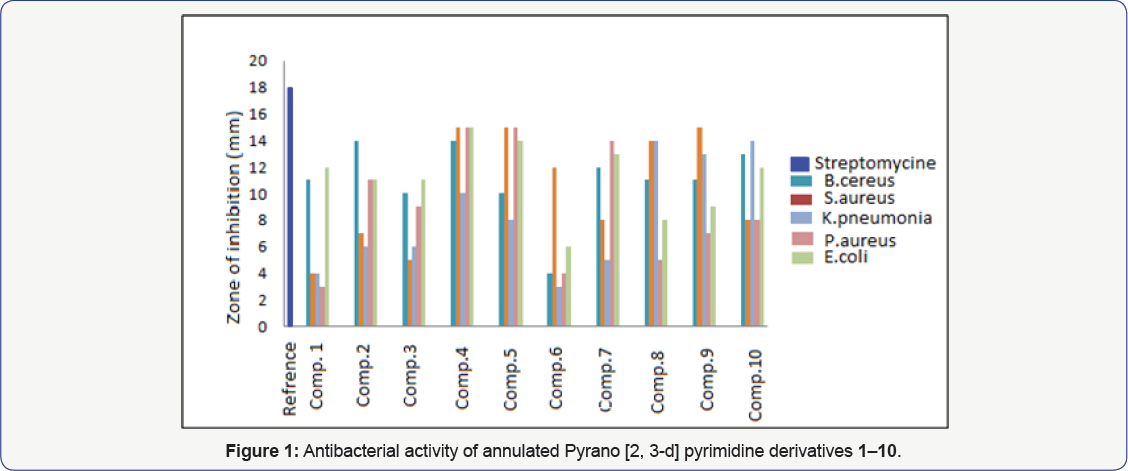
The structural function analysis contributes to design and elucidate the effects of structures and action mechanisms of antibacterial activities of annulated pyrano uracil derivatives. The requirement of the phenyl, OH, OCH3, NO2 and Br group for antimicrobial activity is strikingly demonstrated by the observation that these functional groups are very essential for activity against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria shows extensive effect on the membrane potential associated with bactericidal activity (Table 1). The relevant studies showed that steric, electronic effects and polar parameters of the phenyl in uracil were important for antimicrobial activity. These findings suggest that rather than disrupting cell membranes, the compounds acted outside the cell and became attached to surface groups of the bacterial cells increases its activity. Compound 4g exhibited broad Spectrum activity against Bacillus cereus, Pseudomonas aureus and E. coli bacteria, Compound 5 showed maximum antimicrobial activity againest Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aureus and E. coli, Compound 4h and 4i exhibited maximum activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia bacterial strains. Compound 4j showed maximum activity against Bacillus cereus, Klebsiella pneumonia and E. coli. Electron withdrawing groups reduced antimicrobial activity due to decreasing partial charge on nitrogen atoms of barbiturate moiety on annulated uracil ring which leads to decrease the antimicrobial activity. Compounds 4a-4c has good activity againest Bacillus cereus and Klebsiella pneumonia, product 3 showed also good activity againest Pseudomonas aureus and compound 4f exhibited maximum activity against Staphylococcus aureus (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Molecular properties calculations
Petra calculations
PETRA is a program package comprising various empirical methods for the calculation of physicochemical properties in organic molecules. All methods are empirical in nature and have been developed over the last 20 years in the research group of Prof. J. Gasteiger. The following chemical effects can be quantified: heats of formation, bond dissociation energies, sigma charge distribution, π-charge distribution, inductive effect, resonance effect and delocalization energies and polarizability effect.
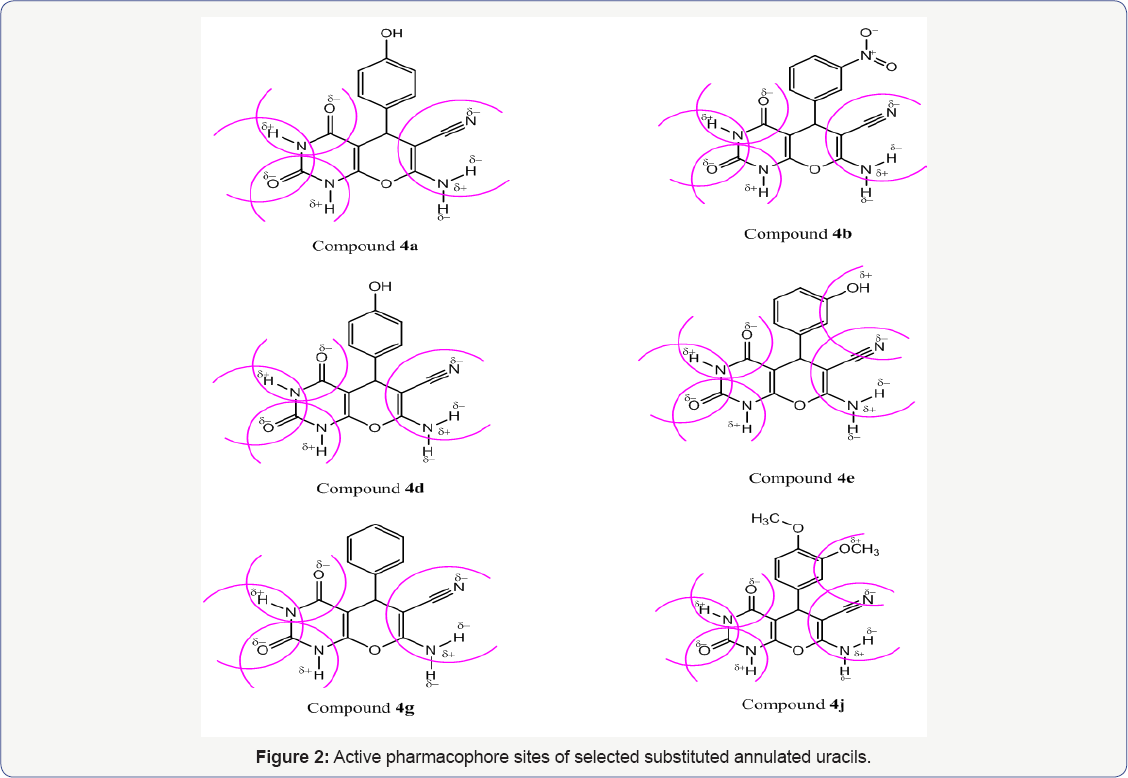
The series 4(a-j) of annulated uracils have been subjected to delocalised-charge calculations using Petra method of the non-hydrogen common atoms obtained from the partial pi-charge of the heteroatoms, have been used to model the bioactivity against bacteria and cancer. We give here, the antibacterial pharmacophore sites of the selected synthesised compounds 4a, 4b, 4d, 4e, 4g and 4j (Figure 2).
Osiris calculations
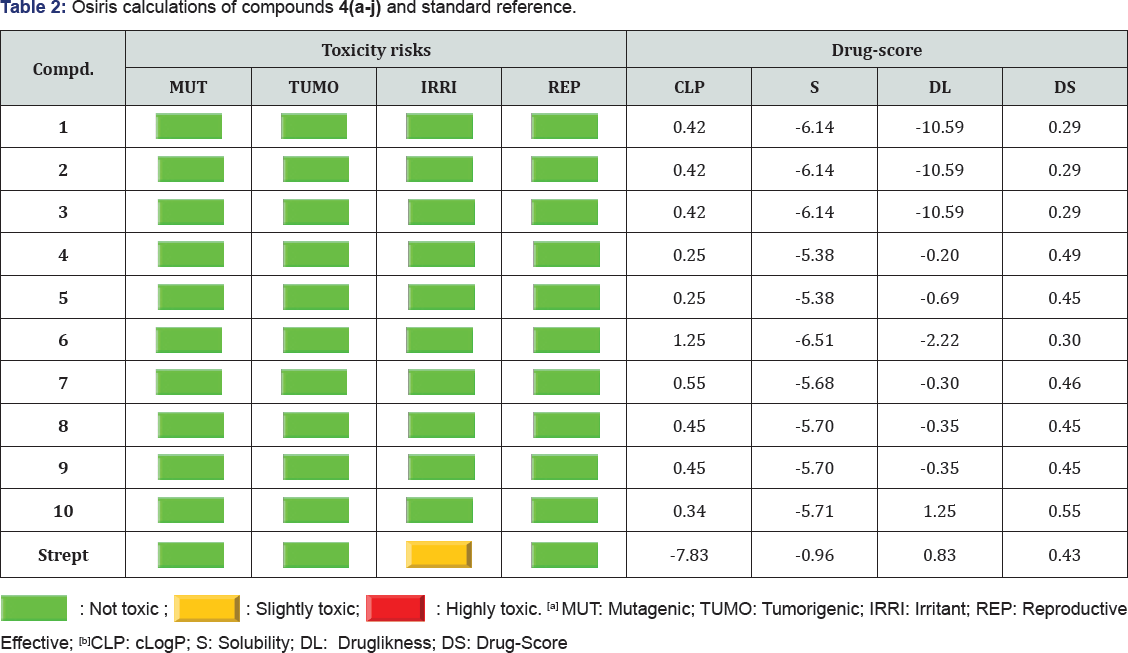
Structure based design is now fairly routine but many potential drugs fail to reach the clinic because of ADME-Tox liabilities. One very important class of enzymes, responsible for many. ADMET problems, is the cytochromes P450. Inhibition of these or production of unwanted metabolites can result in many adverse drug reactions. Of the most important program, Osiris is already available online. With the recent publications of the drug design combination of various pharmacophore sites by using spiro-heterocyclic structure, it is now possible to predict activity and/or inhibition with increasing success in various targets (bacteria/virus or bacteria/fungus or virus/fungus). This is done using a combined electronic/structure docking procedure and an example will be given here. The remarkably well behaved mutagenicity of divers synthetic molecules classified in the data base of CELERON Company of Swiss can be used to quantify the role played by various organic groups in promoting or interfering with the way a drug can associate with DNA.
The results of the present study revealed the following order of bactericidal activity intensities elicited by the annulated pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives: 4-OH > 3-OH > 4-OCH3 > -H > 2-OCH3 > 3,4-OCH3 > 4-NO2 > 3-NO2 > 2-NO2 > 4-Br. For mono-substituted derivatives, the 3-OH and 4-OH groups enhance the antimicrobial activities of annulated pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as the ionization of its OH groups increases and it was found that the activity increased with increasing the number hydroxyl group of the bioactive compounds. The 4-OCH3 substituent and -H (phenyl) alone also increased antimicrobial/ biological activity. However, compounds with two methoxy groups (3,4-OCH3) shows moderate activity due to their steric hinderness. The pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives containing electron withdrawing substituent 4-NO2 and 4-Br shows less biological activities against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
It is found that the negative and positive charges of the nitrogen of CN group and hydrogen of NH group contribute positively in favour of an antibacterial activity, more, and this is in good agreement with the mode of antibacterial action of the compounds bearing (Xδ----Yδ+) pharmacophore site. It was hypothesized that difference in charges between two terminal groups of the same dipolar pharmacophore site (Xδ---Yδ+) may facilitate the inhibition of bacteria, more than viruses. It is further found that the activity decreases with decrease in negative charge of CN group of the common pharmacophore fragment of the series 4(a-j) (HN---CN). The presence of tautomerism phenomena in nitro analogue 1-3 was very indicative (Table 2 and Figure 2).
Molinspiration Calculations

[a] TPSA: Total Polar Surface Area; O/NH: O---HN Interraction, VIOL: Number of Violation; VOL: Volume;
[b] Strept: Streptomycine
CLogP (octanol/water partition coefficient) is calculated by the methodology developed by Molinspiration as a sum of fragment-based contributions and correction factors. The method is very robust and is able to process practically all organic and most organometallic molecules. Molecular Polar Surface Area TPSA is calculated based on the methodology published by Ertl et al. as a sum of fragment contributions. Table 4: Molinspiration calculations of compounds 4(a-j) and standard O- and N- centered polar fragments are considered. PSA has been shown to be a very good descriptor characterizing drug absorption, including intestinal absorption, bioavailability, Caco- 2 permeability and blood-brain barrier penetration. Prediction results of compounds 4(a-j) molecular properties (TPSA, GPCR ligand and ICM) are valued (Tables 3 & 4).
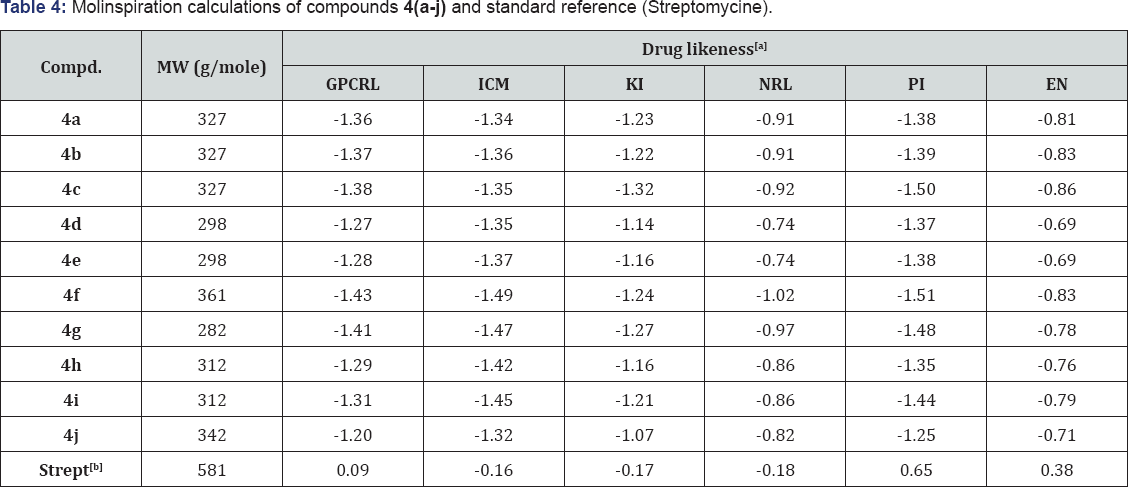
[a] GPCR: GPCR ligand; ICM: Ion Channel Modulator; KI: Kinase Inhibitor; NRL: Nuclear Receptor ligand; PI: Protease Inhibitor; EI: Enzyme Inhibitor.
[b] Strept: Streptomycine
The structural function analysis contributes to design and elucidate the effects of structures and action mechanisms of antibacterial activities of annulated uracil derivatives. The antimicrobial activity results showed some definite and interesting facts about the structure activity relationship (SAR) of synthesized molecules. The dependence of the activity report on structural modifications of the molecule is clear and fascinating. Strain specificity and variation in the activity profile of molecules are also directly recognized to the structural variations in molecules. The important highlights of structure- activity relationship of the synthesised molecules are.
i. Effect of the substituent on phenyl ring: The presence of phenyl ring at C5 position of the pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine (Table 1) compound 4g, without any substitution at ortho, meta and para position, makes the molecule active towards Bacillus cereus, Pseudomonas aureus and E. coli bacterial strains.
ii. Effect of methoxy group: The electron donating substituent like methoxy group at para position (Table 1) compound 4h and meta at compound 4i showed maximum activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia. Substituents of methoxy group at meta, para position (compound 4j) on the phenyl ring of synthesised compounds gives the broad spectrum activity against Bacillus cereus, Klebsiella pneumonia and E. coli.
iii. Effect of hydroxyl group: The electron donating substituent like, hydroxyl group attached to the phenyl ring at the para (Table 3) compound 4d and meta, para position (compound 4e) gives the most potent broad spectrum activity againest Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aureus and E. coli. Compound 4d also showed activity againest Bacillus cereus. Structure activity relationship (SAR) showed that substituent with OH were more active than with OCH3, irrespective of the position of substitution on the benzene ring.
iv. Effect of nitro group: The electron withdrawing nitro group on the phenyl ring at the ortho (Table 3) compound 4c meta (compound 4b) and para (compound 4a) positions make the molecules less active against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria like Pseudomonas aureus, E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia and Bacillus cereus. This may due to its electron withdrawing effect on phenyl ring.
v. Effect of bromo group: The electron withdrawing bromo group attached to the phenyl ring at the para position (Table 3) compound 4f exhibited less activity againest grame positive and grame negative antimicrobial strains. This clearly indicates that the change in position of the bromo group from para to meta and ortho on the phenyl ring preserve its effects against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. Since substituent of bromo group at para position makes the molecule less active againest Staphylococcus aureus.
vi. Effect of heterocyclic ring: Annulated uracil derivatives revealed that the presence of cyano, amino and aromatic heterocycles (both pyrimidine and pyran ring) make these more basic, which increases its penetrating power on bacterial cell wall, because the side groups of the most typical and essential constituents of living cells, DNA and RNA, are based on pyrimidine ring. The fusion of pyrimidine ring having two nitrogen atoms at 1 and 3 with pyran ring enhanced the antimicrobial activity of molecule towards the different Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. Future flexible pharmacophore sites and geometric conformation enables to prepare derivatives for multi-therapeutic annulated uracils with high selectivity.
Conclusion
The antimicrobial screening study revealed significant antimicrobial activity at conc. 20 mg/mL dose level comparable to Streptomycin as standard drug for annulated uracils 4(a-j). The following notable conclusions are drawn by screening the activities of synthesized uracils as: (i) Annulated pyrano uracils were more active with OH than with OCH3, irrespective of the position of substitution on the benzene ring since hydrophobic property is important for the drugs to diffuse through the pathogenic biological system (ii). Annulated uracils containing -H (no substituent) shows moderate biological activity (iii). Compounds with disubstituent group of 3,4-OCH3 exhibit moderate antimicrobial activities (iv). Annulated uracils containing 4-NO2 and 4-Br groups exhibited less activity. Hence, this study may be helpful for the medicinal chemists in understanding antimicrobial activity of annulated uracil products, one with different inter atomic distances (linkers) steric, electronic effects, polar parameters and with different electronic environments (v). The anti-Kinase pharmacophore site (O=C-NH-C=O) should be evaluated in coming step as continuation of these investigations on this series.
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, R.T.M. Nagpur University for providing laboratory facilities. Authors would like to thank ACTELION; the Biopharmaceutical Company of Swiss, for the online molecular properties calculations. Special thanks are due to LokManyaTilak Sc. and Comm. College, Ujjain (M.P) for providing in vitro antimicrobial activity of the synthesised compounds.
References
- V D Piaz, M C Castellana, C Vergelli, M P Giovannoni, A Gavalda, et al. (2002) Synthesis and evaluation of some pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyridazinones and analogues as PDE 5 inhibitors potentially useful as peripheral vasodilator agents. J Enz Inhib Med Chem 17(4): 227-233.
- Z K Sweeney, SF Harris, N N Arora, H H Javanbakht, YY Li, et al. (2008) Design of annulated pyrazoles as inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J Med Chem 51(23): 7449-7458.
- K Takayoshi, W Masai chi, O Makoto, S Kentaro, N Masahiro, et al. (2006) Crystal structure of human ERK2 complexed with a pyrazolo[3, 4-c]pyridazine derivative. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16(1): 55-58.
- M F Brana, M Cacho, M L Garcia, E P Mayoral, B Lopez, et al. (2005) Pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridazines as novel and selective inhibitors of cyclin- dependent kinases. J Med Chem 48(22): 6843-6854.
- A A Fayed, H M Hosni, E M Flefel, A E Amr (2009) Synthesis and pharmacological activities of some new thieno [2,3-d] pyrimidine and pyrimidino pyrazolo thieno pyrimidine derivatives. W J Chem 4:58-65.
- A H F Abd El-Wahab (2002) Activated nitriles in heterocyclic synthesis: Synthesis of new [1]benzopyrano[30,40:5,6]pyrano[2,3-d] pyrimidineand [1] benzopyrano[30,40:5,6]pyrano [3,2-e][1,2,4] triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine derivatives with promising antibacterial activity. Acta Pharm 52: 269-280.
- M El Agrody, M H El Hakim, M S Abd El Latif, A H Fakery, E M El Sayed, et al. (2000) Synthesis of pyrano [2,3-d]pyrimidine and pyrano[3,2-e] [1,2,4]triazolo[2,3-c]pyrimidine derivatives with promising antibacterial activity. Acta Pharm 50(2) :111-120.
- L V G Nargund, Y S R Reddy, R Jose (1991) Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Pyrido [1, 2-a]pyrimidin-4 (1H)—Ones. Indian Drugs. Indian Drugs 29: 45-46.
- E M Grivsky, S Lee, C W Sigel, D S Duch, C A Nichol (1980) Synthesis and antitumor activity of 2,4-diamino-6-(2,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-5- methylpyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine. J Med Chem 23(3): 327-329.
- D Heber, C Heers, U Ravens (1993) Synthesis and positive inotropic activity of several 5-aminopyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines. Part 5: Compounds with positive inotropic activity. Pharmazie 48(7): 509-513.
- Y Sakuma, M Hasegawa, K Kataoka, K Hoshina, N Kadota (1991) 1,10-Phenanthroline Derivatives. WO 91/05785 PCT Int. Appl. 1989 May 2. Chem Abstr 115: 71646.
- L R Bennett, C J Blankely, R W Fleming, R D Smith, D K Tessonam, et al. (1991) Antihypertensive activity of 6-arylpyrido[2,3- d]pyrimidin-7- amine derivatives. J Med Chem 26(3) : 403-411.
- BR Ajmal, D S Rajendra, S S Rupali (2014) Potent in vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities of pyrano[2,3-d] pyrimidine derivatives with quantitative yield. Int J Pharma & Bio Sci 5(1): 422-430.
- A Agarwal, R Ashutosh, N Goyal, PMS Chauhan, S Gupta (2005) Dihydropyrido [2,3- d]pyrimidines as a New Class of Antileishmanial Agents. J Bio-org & Med Chem 13(24) : 6678-6684.
- A R Bhat, A H Shallab, R S Dongrea (2016) Dibutylamine (DBA): A highly efficient catalyst for the synthesis of pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives in aqueous media. J Taib Unv for Sc 10(1): 9-18.
- A Jarrahpour, J Fathi, M Mimouni, T B. Hadda, J Sheikh, et al. (2012) Petra, Osiris and Molinspiration (POM) together as a successful support in drug design: antibacterial activity and biopharmaceutical characterization of some azo Schiff bases. Med Chem Res 21(8):1984- 1990.






























