Formation of Communicative Speech Skills of the future Specialist in the Sphere of Physical Culture and Sport in the Modular Training
Nagovitsyn Roman* and Volkov Pavel
Department of Pedagogical Science, Glazov State Pedagogical Institute, Russiay
Submission: January 29, 2018; Published: February 06, 2018
*Corresponding author: Nagovitsyn Roman, Department of Pedagogical Science, Glazov State Pedagogical Institute, Russia, Email: gto18@mail.ru
How to cite this article: Nagovitsyn Roman, Volkov Pavel. Formation of Communicative Speech Skills of the future Specialist in the Sphere of Physical Culture and Sport in the Modular Training. J Phy Fit Treatment & Sports. 2018; 2(1): 555576 DOI: 10.19080/JPFMTS.2018.02.555576
Abstract
Discusses pedagogical conditions of formation of communicative speech skills of the future specialist in the sphere of physical culture and sport in the modular training. Formation of communicative speech skills of the future expert is ensured through: the competent approach modeling activities of students on the lesson of physical culture, shaping the behavior of future expert, implementation pedagogical technologies. During the research tested longitudinal complex pedagogical conditions, providing formation of communicative speech skills of the future specialist as professional quality. Analysis of results on the formation of communicative speech skills for future professionals confirms the efficacy of use in educational process of Pedagogical University unit training.
Keywords: Communicative speech skills; Modular training; Methods are strictly regulated exercises
Introduction
In school education, a modern physical education lesson requires the GEF to form universal learning activities among learners. Future specialists in the field of physical culture and sports need a high level of proficiency not only in special professional terminology, but also in literary language. Development of communicative, cognitive, regulative, subject, personal qualities of students determines the importance of students' speech training in the specialty of physical culture. However, objective reasons, for example, a small amount of hours for humanitarian disciplines in the university; subjective reasons - an inadequate desire for students to form skills in the direction of the communicative sphere, reflect the quality of training of future specialists. The identified problems allow us to concretize the search for ways to improve the effectiveness of vocational training on the basis of using a methodological arsenal to form and develop the foundations of communicative skills and skills in students. It is assumed that the deficit of the amount of hours for humanitarian disciplines and the low level of motivation to master communication skills among future specialists in the field of physical culture and sports should be leveled, emphasizing the training in exercises with specific speech utterances (algorithm) at each stage of the lesson in physical culture.
Performing skill in speech utterances among students is advisable to implement in the form of modular training. Modular training in the training of a future specialist in the field of physical culture and sports ensures the development of communicative and speech skills in each section of the program material of the academic discipline with an output to the result: the formation of specific competences, mastering of work knowledge, skills, and actions. For each module of the academic discipline, the teacher developed the formulations of communicative and speech skills for students [1]. As a methodological justification for modular training, IV Vladykina et al. consider a systemic approach, the implementation of which, in conjunction with competency, activity, qualimetrical, personality-oriented, culturological and innovative-technological approaches, provides a higher qualitative level of development of professional skills and communicative and speech activity of students in the specialization of physical culture [2].
Senator SYu argues that it is possible to improve the quality of education of students by specializing in physical culture through the combination of various technologies, components and innovative technologies of physical education that are provided with a set of complementary theoretical methods, the results of analysis of domestic and foreign pedagogical theory, practice and experience in the field of physical education [3]. Scientific and methodological support of the process of formation of communicative and speech skills in the future specialist is based on a competent approach. Method of formation of communicative and speech skills: standard and problem situation, conversation, dialogue [4]. Modeling the activities of students in the physical culture lesson and shaping the future specialist's behavior is carried out through the analysis of specific learning situations, role plays, imitative exercises, educating situations.
Forms of control
Pedagogical observation, expert evaluation, rating, selfesteem, mutual evaluation [5]. Formation of communicative and speech skills from a future specialist is ensured through the implementation of pedagogical technologies: reproductive and illustrative technology with methods of activating speech activity and training (the goal is the formation of communicative and speech skills, a tool for modeling the activity of students in a physical training class) [6]. In the practice of organizing and conducting physical education classes, the following methods of training motor activities are used: methods of strictly regulated exercise (learning exercises in parts and learning the exercises without dividing into parts) and partially regulated exercises (game and competition method). In the work of RS Nagovitsyn presented a special educational module "Fundamentals of separation of motor action in parts" in the process of teaching students the physical culture and experimentally proved the effectiveness of its introduction in vocational training.
The author claims that the introduction of the developed methodology for the systematic use of the method of "learning by parts" in the process of teaching students the physical culture will positively affect the increase in the effectiveness of students' passing of practice in the secondary school [7,8]. The method of learning by parts, according to SYu Senator, etc., provides for the initial study of individual parts of individual actions with the subsequent combination of them into a necessary whole. The full implementation of this method largely depends on the understanding of the possibility and necessity of dismemberment of the motor action, as well as on the practical ability to implement it in accordance with the task of training. To understand the whole action is possible only through the knowledge of its constituent motions and the laws of the formation of action. The dismemberment is a characteristic feature of the methods of learning by parts, but the very learning of the part is not an end in itself. It serves only as an initial stage, facilitating the mastery of an integral action. The completion is the mastery of the action as a whole. Without this, the meaning of any training is lost. Ultimately, students must perceive action as a whole from beginning to end. In this cohesion of execution, it should not be the main and secondary.
Learning by parts makes the learning process at each lesson more concrete, and, consequently, motivated, because the successes of students in mastering even one element are satisfying. The application of the method of learning by parts contributes relatively quickly to the restoration of lost skills [9]. This method cannot be replaced with an increase in the level of communicative and speech skills among students, since in the study of coordination-complex actions there is a need for instruction, installation, commenting, disposal, methodological support, correction, analysis [10,11].
Organization and Methods of Research
At the Department of Physical Education and Life Safety of the State Pedagogical Institute, a longitudinal study was conducted using the method of "cross sections" to determine the level of communicative and speech skills among students of the 3rd 2016-2017 school year (n = 28) in the discipline "Theory and Methods of Teaching Physical Education". In the course of the longitudinal study, a set of pedagogical conditions was tested, ensuring the formation of communicative and speech skills in the future specialist as a professional quality:
a) Ensuring continuity in the formation of communicative and speech skills, using a competent approach in modular learning, modeling the activity of students in the physical culture lesson, shaping the future specialist’s behavior, and implementing pedagogical technologies.
b) Purposeful use of standard and problem situations, conversation, dialogue, role-playing games, imitative exercises, educating situations.
c) Motivation of the future specialist to the formation of communicative and speech skills.
d) Construction of the educational process on the basis of modular training, in which the formation of communicative and speech skills is carried out.
Work on the formation of communicative and speech skills among future specialists were determined by the following:
a) Communication of information to students on the formation of subject and meta-subject results in physical culture classes;
b) Observation of the principles of constructing speech statements by students in modeling the activities of students at a physical training lesson;
c) Familiarizing students with standard speech utterances, heuristic questions at each stage of the lesson, training;
d) Demonstration of the possibilities of linguistic means in modeling the activity of students at the physical culture lesson;
e) The formation of communicative and speech skills among students associated with finding language facilities of the language, with the help of which there is the formation of universal learning activities among learners.
The Fund of Evaluation Means determines the level of the formation of communicative and verbal skills:
a) High level: He speaks communicative and speech skills, and is ready to use them in modern techniques and technologies to ensure the quality of the teaching and educational process.
b) Average level: He knows the knowledge, but not enough communicative and speech skills for their implementation in modern techniques and technologies to ensure the quality of the teaching and educational process.
c) Low level: He experiences difficulties in using communicative and speech skills and is not ready to use them in modern techniques and technologies to ensure the quality of the teaching and upbringing process.
Results
The results of the first transverse section for determining the level of communicative and speech skills among students of the 3rd 2016-2017 school year are as follows: a high level was noted in 10% (for p <0.05) of students; the average is 30% (for p <0.05); low - 60% (with p <0.05). The results of indicators of communicative and speech skills among students indicate that they are not sufficiently prepared for physical culture and sports activities at school. The results of the testing were discussed at the meeting of the chair. As a result, a decision was made to implement modular training in the specialization "physical culture". Students began to master the content of the academic discipline in the framework of its division into modules, and the training material for each module promotes the formation of communicative and speech skills among future specialists. In June 2017, a repeated cross-sectional survey was conducted to determine the level of communicative and speech skills among students. The results of the study revealed the following: a high level was observed in 40% (for p <0.01) of students; mean - 50% (for p <0.01); low - 10% (for p <0.01) (Figure 1).
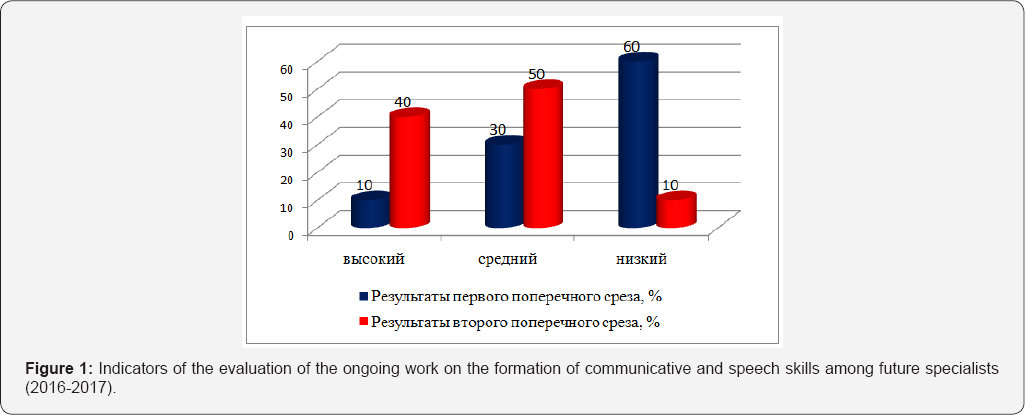
Discussion
The analysis of the level results in the formation of communicative and speech skills in future specialists confirm the effectiveness of modular training in the educational process of a pedagogical university. This conclusion is confirmed by the results of studies by the team of authors EA Rassolova et al. [7]. On the basis of a comparative analysis of the indicators of communicative and speech skills among students in the specialization of physical culture, used in the classroom method of teaching motor actions: learning exercises in parts and learning the exercises without dividing into parts. The effectiveness was 70% (p>0,001). The students who used the methods of training in the classroom: the game and competitive efficiency was 45% (p>0,001). In our opinion, the implementation of modular training in the educational space contributes to the formation of a certain set of standard speech utterances suitable for the performance of the functional duties of the teacher of physical culture for students who are needed in the future profession. On the other hand, modular training is effective also in the implementation of the new generation standards in the teaching and upbringing process in the lessons of physical culture, since the set of specific speech utterances that the student possesses serves to create the basis for universal learning activities among learners.
The methods of strictly regulated exercise are characterized by repeated performance of the action (or its parts) under strict regulation of the form of movements, the magnitude of the load, its growth, alternation with rest, etc. As a result, it becomes possible not only selectively to master individual movements, consistently forming necessary actions from them, but also to use speech utterances (sports terminology) specifically for each motor action. In this aspect, the results of a study by PB Volkova, etc. The authors correlate the methods of strictly regulated exercise with the quality of education in physical education classes. In their opinion, these teaching methods determine a specific educational task: the group and personal characteristics of students, the stage of training, the nature and content of the training material, the duration of the lesson, the local learning conditions, the availability of training tools (equipment, shells) [5,6].
The construction of a pragmatic image of a specialist presupposes the solution of three systemic tasks: ensuring that graduates' qualifications match current and prospective requirements from employers; integration of theoretical and practical skills in the implementation of future professional activities; Practical, modular training of specialists. Modular training reflects the requirement of employers to qualify, the level of knowledge of graduates of the university, because this form of training is practically oriented to the professional qualities of a specialist. In modular education, the evaluation criterion does not dominate within the individual rating of the student; it is aimed at stimulating teamwork, group cohesion. Students are immersed in the educational environment, in the subject of the program, the course, they do not compete with each other, but learn to cooperate, negotiate, and jointly extract the necessary information for professional activities. The obtained results do not exhaust all aspects of the indicated topic and open the prospects for further research of modular education in the field of higher education in pedagogical specialties.
References
- Nagovitsyn RS, Volkov PB, Miroshnichenko AA (2017) Planning of physical load of annual cycle of students’, practicing cyclic kinds of sports, training. Physical education of students 21(3): 126-133.
- Nagovitsyn RS (2014) Conceptual framework of formation of personal physical culture of student based on mobile learning. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture, Russia.
- Nagovitsyn RS, Vladykina IV, Senator SYu (2015) Training program to hit standards of all-russian sports complex «Ready for labour and defence* (GTO) based on mobile learning. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture 1: 13.
- Nagovitsyn RS, Vladykina IV, Volkov PB, Tutolmin AV, Sokolnikova EI (2015) Program management of improvement of physical education of students using mobile methods. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture 4: 10.
- Romanchyshyn O, Briskin Yu, Sydorko O, Ostrovs kyy M, Pityn M (2015) Student learning in Physical education in Russia (problems and development perspectives). Journal of Physical Education and Sport 4: 815-822.
- Volkov PB (2016) Organization of scientific research activities of students in the educational cluster. International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research 2: 38-44.
- Nagovitsyn RS, Rassolova EA, Senator SYu, Torbina II (2016) Web portal design to prepare students for gto tests. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture 1: 13.
- Nagovitsyn RS, Rassolova EA, Sokolnikova EI, Senator SYu, Torbina II (2015) Technology of system development of physical qualities of young people with regard to mobile learning. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture 11: 32.
- Nagovitsyn RS, Tutolmin AV, Volkov PB, Chubukova LV (2017) Organizational climate and individual psychological qualities of the personality of participants in the educational process in the educational cluster "institute-college”. Alma mater 3: 38-44.
- Platonov DN, Platonova LL, Cherkashin IA (2015) Formation of strategy of development of regional system of continuous physical culture education. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture 10: 1.
- Volkov PB (2016) Assessment of the quality of work and training of teachers and students during the reorganization of the educational institution by merger in a scientific-educational cluster. Modern European Researches 5: 124-131.






























