Fatality Rate of Corona Virus: A Study in Medical Geography
Mohamed Nour Eldin Elsabawy
Professor of Medical geography, Minia University, Egypt
Submission: July 15, 2020; Published: August 24, 2020
*Corresponding author: Mohamed Nour Eldin Elsabawy, Professor of Medical geography, Minia University, Egypt
How to cite this article: Mohamed N E E. Fatality Rate of Corona Virus: A Study in Medical Geography. JOJ Wildl Biodivers. 2020: 2(5): 555599
Abstract
This paper aims to identify death or Fatality rates due to the Corona virus epidemic in the world since the beginning of the disease spread in China in December 2019 until April 2020, in the view of medical geography, which interesting in disease ecology, disease diffusion and geographical distribution of infected cases. This study relies on identifying the most countries in the world in cases and rates of death, or fatality rate, and because it is difficult to compare All countries of the world in this rates, so it will suffice for the thirty or thirty five countries that come on the top countries list of the world in these rates and compare them .
Keywords: Pandemic; Covid19; Mortality; Fatality; Medical geography
Methods and Materials
This paper relies on approaches and methods of medical geography, including the Prevalence of disease and Disease pattern, the paper data depends on statistical analysis, quantitative methods, and cartographic representation.
The concept of Fatality rate
The death rate varies from one disease to another, as it reaches 100% in African Trypanosomiasis caused by the Tse Tse fly, and it reaches from 83-90% in Ebola, from 80-90% in AIDS, and from 5-60% in Plague disease, it reaches 50% in Tetanus, 30% in all kinds of Cancer, 26% in Dengue fever, and Typhoid fever has a 10-20% death rate, and Yellow fever is 7.5%. This ratio is 2.5% in the Spanish flu that struck the world in 1918, and this rate in the new Corona virus reached 5.3.
It’s important to know the severity of the disease, how much of the disease is eliminated among those who have it, and if it is assumed that there is a disease, not all of those affected by it have been affected, so this means that the percentage of death is 100% because all the people with the disease perished, and so called the death rate of a disease, and some call it the fatality rate. This percentage is calculated by dividing the number of deaths from a specific disease such as corona, during a specific time period by the number of individuals who were diagnosed with the disease during that period and the result is multiplied by 100 to get Percentage of deceased.
Reasons of differentiations
Some genetic and immunological factors play a role in the tolerance and recovery of some patients with the disease. Individuals whose immunity is strong transforms their pathological condition from positive cases into negative ones. You can see these cases globally and it will be clear to your presentations how some peoples withstand and are treated and fully recovered, so that some of them. It does not need medication and recover without treatment, as it varies from one age group to another. Children and youth can resist the disease, and there are some races that are characterized by innate and instinctive resistance against some diseases compared to others of the other races.
Statistical Analysis
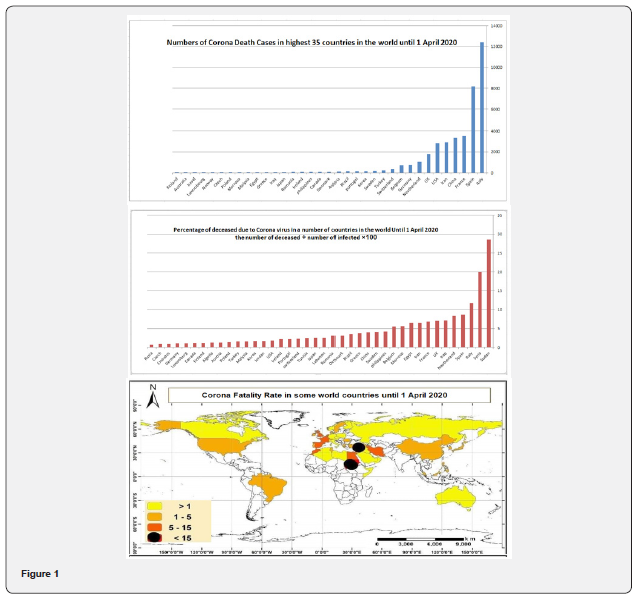
If we look at the world map and the proportion of those who died from Corona’s disease from the proportion of the infected, we will find a great difference between countries, on the one hand, and between the absolute numbers of the deceased, there are countries where the proportion of those who have died is more than 10%, and countries have this percentage less, and the reason for this is due to two main factors. The ability of some peoples to resist, and the second reason is due to the lack of accuracy in recording data and the desire to reduce the numbers of infected people, and the cause of death can be traced back to other causes, so that this does not cause terror or anxiety for the population.
Sudan, where the number of the dead reached 2 and only 7 cases were recorded, and thus comes in the forefront of the world in the percentage of death due to illness, which is 28.6%, and we are certain this is not true, followed by Syria with 20%, then Italy 11.8%, Spain 8.7% and the Netherlands 8.3%, Iraq 7.2%, then the United Kingdom 7.1%, France 6.8%, and Iran 6.5.
Egypt comes in the tenth position with 6.5%, and this percentage is expected to be much lower, due to the fact that this percentage has been calculated on the basis of the cases already registered, although there are tens of hundreds of cases and perhaps more that have not been registered, because the patients themselves do not They know the truth about their infect, and they doesn’t reach the hospital and records only cases that suffer from the true manifestations of the disease, but the deaths are undeniable, especially as they are subject to an examination by the health authorities who want to reach the real numbers and find out the causes of the disease.
The main difficulty in estimating the loss rate here is to ensure the accuracy of the numerator and denominator. If the position is inaccurate and less than the truth, the percentage of death rises, and it indicates high rates that are not true. With the length of the disease, the probability of a person’s death may increase due to other reasons that are not related to the specific disease. Comparing case numbers or virtual mortality rates across countries can be misleading (Figure 1) [1-4].
References
- Charles HH (1987) Epidemiology in medicine, little, Brown and company
- Elsabawy MN (2011) Hepatitis Gender Gap in Egypt: A study in medical geography Elsevier Procedia 19:121-130.
- Rebecca AH Case fatality rate at Encyclopedia Britannica.
- WHO reports December-1 April 2020?






























