Recent Advancements in Anticancer Activities of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Conjugates
Ankush Kumar1, Rohit Bhatia1*
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, ISF College of Pharmacy, GT Road, Ghal Kalan, Moga, 142001, Punjab, India
Submission: March 16, 2022; Published: March 30, 2022
*Corresponding author: Rohit Bhatia, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, ISF College of Pharmacy, GT Road, Ghal Kalan, Moga, 142001, Punjab, India
How to cite this article:Ankush K, Rohit B. Recent Advancements in Anticancer Activities of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Conjugates. JOJ Pub Health. 2022; 6(5): 555699. DOI: 10.19080/JOJPH.2022.06.555699
Abstract
Oxadiazole derivatives have a wide range of pharmacological properties, including antiviral, antibacterial, anticancer, anticonvulsant, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Because of its broad range of biological functions, the oxadiazole ring structure is a popular heterocyclic template for pharmaceutical molecules. This article comprises of 1,2-4 oxadiazole-conjugates with different moieties exhibiting anticancer potential on different cell lines such as MCF-7, DU-145, MDA MB-231, and many others along with Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR). Furthermore, medicinal chemists are always battling to develop selective cytotoxic drugs with the fewest possible adverse effects. This review is intended to stimulate fresh ideas in the search for rational designs of more active and less hazardous oxadiazole medical medicines.
Keywords: 1,2-4 Oxadiazole; Anticancer Activity; Cytotoxicity; Docking
Introduction
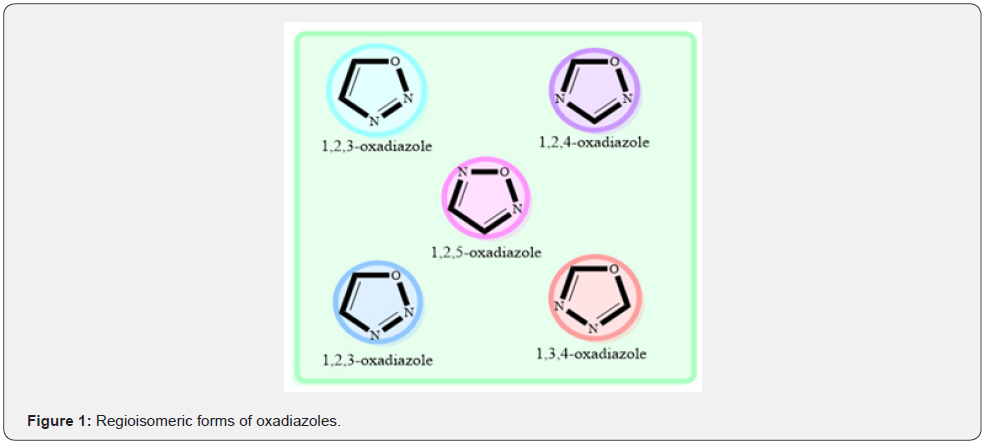
Cancer continues to be a global concern to humanity, posing a threat to both developed and developing countries. Compounds with various heterocyclic moieties have piqued interest in drug development. Oxadiazole is a kind of heterocyclic molecule that has sparked a lot of interest in medicinal chemistry due to their wide spectrum of pharmacological and biological activity [1]. New anti-cancer drugs are being investigated all around the world [2,3]. The majority of new synthetic anti-cancer drugs are heterocyclic derivatives, in which structures having an oxadiazole ring form a class of molecules with very strong cytotoxic potential [4]. Oxadiazoles are heterocyclic compounds with two carbon atoms, two nitrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom which occur in many isomeric forms. Regio isomeric forms of oxadiazoles have been expressed in (Figure 1). The presence of the 1,2,4-oxadiazole ring in a molecule impacts its physicochemical and pharmacokinetic characteristics [5]. The oxadiazole ring is a key component of the pharmacophore since it can interact with ligands [6]. Oxadiazole scaffold is a versatile material that has undergone substantial research in recent years. In certain circumstances, it functions as a flat aromatic linker to ensure that the molecule is oriented correctly [7]. The anti-cancer effects of 1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives appear to be of special relevance, given the ever-increasing prevalence of many forms of cancer [8]. This article comprises 1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives which showed prominent anticancer activity on different cancer cell lines. 1,2,4-oxadiazole is also a privileged scaffold for Anticancer, Antibacterial [9].
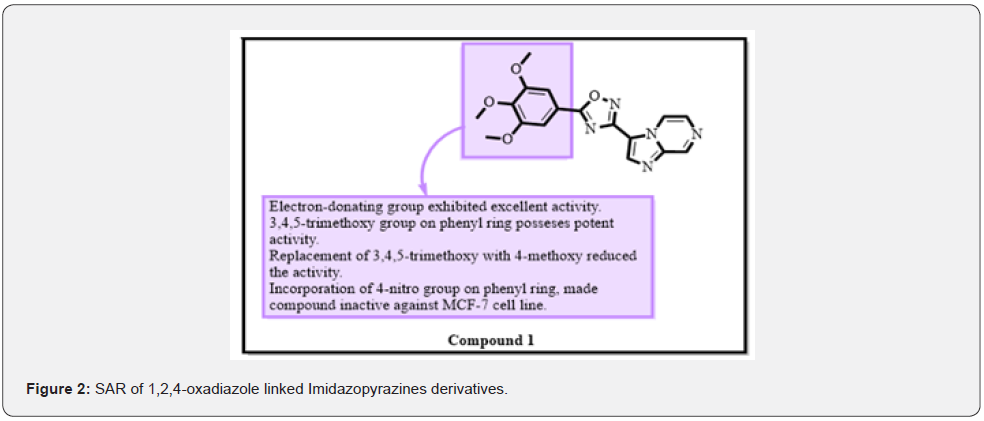
Antimalarial [10]. Anti-inflammatory [11]. Anti-depressive [12]. And Antiviral effect [13,14]. Synthesized 1,2,4-oxadiazole linked Imidazopyridines derivatives and accessed them against MCF-7, A-549, and A375 cell lines. They found that compound 1 was found to be most potent against these three cell lines MCF-7, A-549, and A375 with the cytotoxic activity of 0.68±0.03 μM 1.56±0.061 μM and 0.79±0.033 μM, respectively. MTT assay was carried out to determine In vitro cytotoxicity by taking Adriamycin as a reference. The structure-activity relationship showed that the electron-donating group on the phenyl ring was necessary for potent anticancer activity. Replacement of 3,4,5-trimethoxy group with 4-methoxy reduced the activity. If an electron-withdrawing group such as 4-Cl was incorporated, the activity towards the breast cancer cell line increases (Figure 2). Incorporation of the 4-nitro group on benzyl ring made compound inactive against MCF-7 cell line. By this, activity decreased to 10-fold [14].
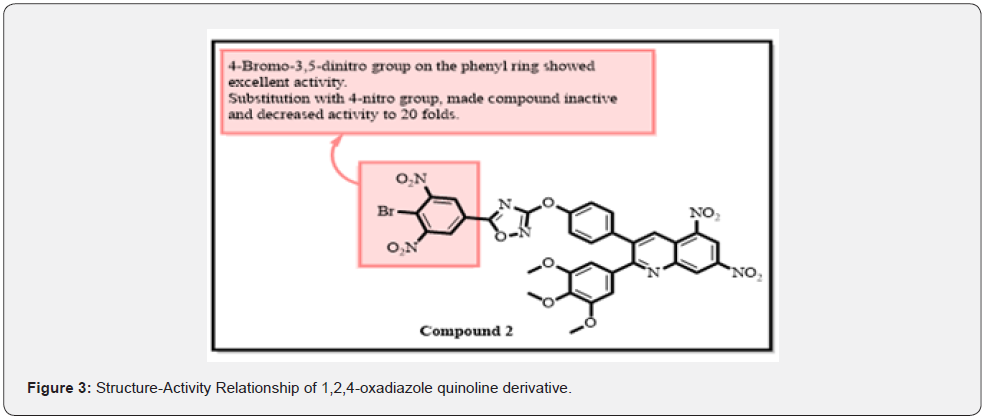
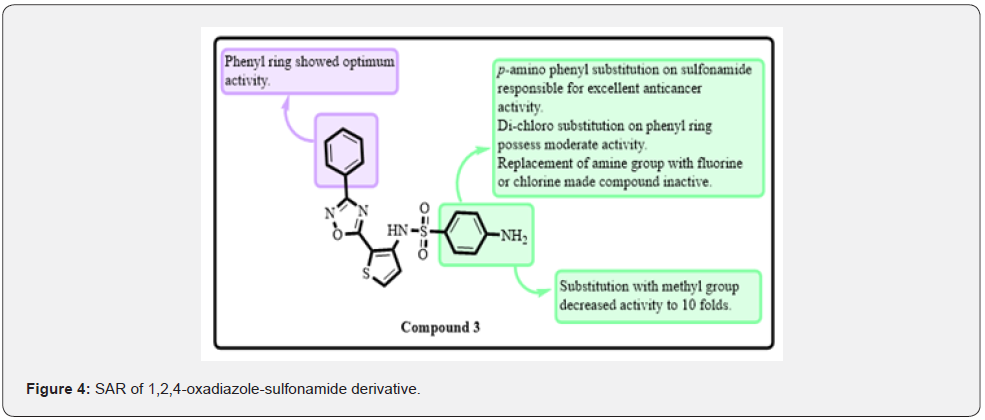
Designed and synthesized a series of 1,2,4-oxadiazole functionalized quinoline derivatives as anticancer agents [15]. The anticancer activity was accessed on MCF-7, A549, DU-145, and MDA MB-231 cell lines through MTT assay. Etoposide was taken as a positive control. Among them, compound 2 was found to be the most active against MCF-7, A549, DU-145, and MDA MB-231 cell lines with IC50 of 0.11 ± 0.04 μM, 0.23 ± 0.011 μM, 0.92 ± 0.087 μM 0.43 ± 0.081 μM, respectively. SAR studies revealed that the 4-Bromo-3,5-dinitro group on the phenyl ring connected with oxadiazole moiety exhibited potent anticancer activity against all cell lines (Figure 3). Substitutions with the 4-nitro group made the compound inactive and decreased activity to 20 folds. Most of the compounds were found to be excellent anticancer agents than reference drug etoposide. As a result, many derivatives might potentially be used as drug lead scaffolds in cancer treatment [15]. Shamsi and co-workers synthesized a series of novel 1,2,4-oxadiazole-sulfonamide derivatives as anticancer agents. Anticancer activity was evaluated on the HCT-116 cancer cell line. They found that compound 3 was most potent against this cell line with an IC50 of 6.0 ± 3 μM. Potency remained the same if the oxadiazole ring was replaced with dichloro substituted pyridyl ring. The most powerful inhibitor was discovered by replacing the p-methyl substitution in the sulphonamide group with the p-amino group while leaving the entire molecule intact. 4-amino substitution exhibited excellent activity. If the amino group was replaced with a methyl group, activity decreased to 10 folds. Phenyl ring with 1,2-4 oxadiazole moiety was necessary for optimum activity. Docking studies were performed on the CAIX active site of protein 3IAI. They found that the SO2NH2 group of compounds 3 formed a hydrogen bond with His64 amino acid. The nitrogen atom of the oxadiazole ring formed a hydrogen bond with Gln92. His64, Gln92, and Ser65. Phenyl linker formed π-π interactions with His94, π-sigma with Val121, π-sulfur with His96, π-alkyl with Val131 and Leu198 (Figure 4). Flow cytometric assays showed that compound 3 mainly causes cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. They look at the levels of ROS in HCT-116 cells after they’ve been treated with compound3. When HCT-116 cells are treated with compound 3, the relative DCF fluorescence increases, indicating an increase in ROS levels in the cells [16].
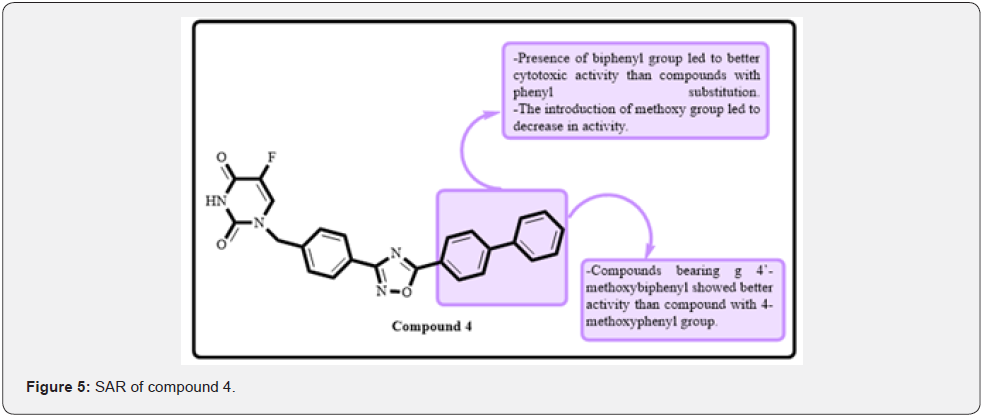
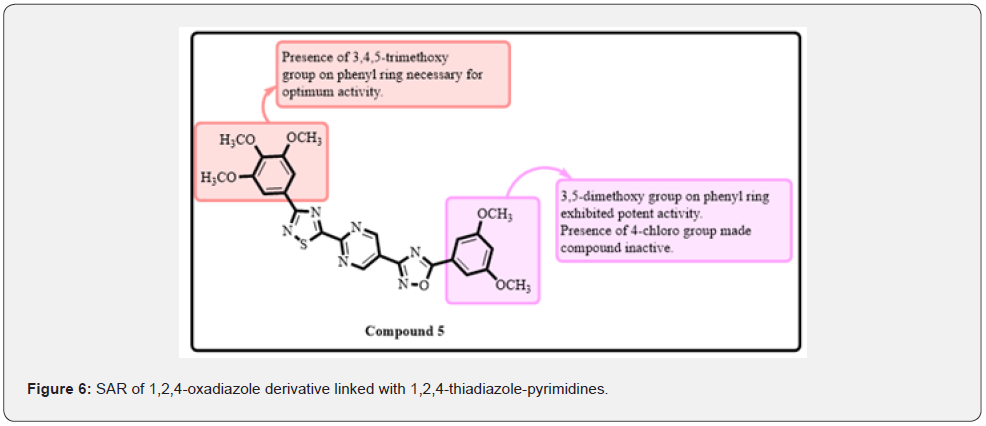
Mansouri and coworkers developed and synthesized a new series of clubbed uracil and 1,2,4-oxadiazole analogues. Melanoma (A-375), fibrosarcoma (HT-1080), breast (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231), and lung cancer (A-549) cell lines were used to investigate the effectiveness of the proposed derivatives. Compounds 4 flound to be most potent against HT-1080 A-549 and MCF-7 cell lines with IC50 of 0.883 μM, 3.123 μM and 1.19. Later, SAR findings revealed that compounds with a biphenyl group had stronger cytotoxic activity than those with a phenyl substitution, whereas those with a methoxy group had lower activity. Compounds with a 4’-methoxybiphenyl group had higher efficacy than those with a 4-methoxyphenyl group. Docking investigations on compound 4 indicated that Asn342, Trp348, Trp348, Arg341, and Ser343 created five hydrogen bond connections with each other. Compound 4 also exhibited Pi-cation, Pi-anion, PI-donor hydrogen bonds, Pi-Pi T shaped interactions, and Pi-alkyl interactions (Figure 5) [4]. Ashok and co-workers have designed and synthesized a series of 1,2,4-oxadiazole linked with 1,2,4-thiadiazole-pyrimidines which were found as anticancer agents. The anticancer activity was evaluated on four cell lines such as MCF-7, A-549, Colo-205, and A2780. MTT assay was performed to evaluate the activity. They found that compound 5 was most active against these cell lines. The IC50 was found to be 0.22±0.078 μM, 0.11±0.051 μM, 0.93±0.043 μM and 0.34±0.056 μM against MCF-7, A-549, Colo-205, and A2780 cell lines, respectively. SAR studies showed that 3,4,5-trimethoxy group on phenyl ring was necessary for optimum activity. 3,5-dimethoxy group on phenyl ring attached with oxadiazole ring exhibited excellent activity (Figure 6). Replacement with a 4-chloro group made the compound inactive [17].
Conclusion
The nucleus of the 1,2,4-oxadiazole and its derivatives appear to be an advantageous framework for the discovery and development of medicines with large bioactivities. Several 1,2,4-oxadiazole-based compounds have been discovered to have considerable value in the synthesis of new therapeutics potential relevant in the treatment of cancer because of the above considerations. According to this review, the anti-cancer potential of 1,2,4-oxadiazole-heterocycle hybrids has been studied in the last 2 years. Furthermore, the hybrids SAR and molecular docking have been reviewed to offer a clear concept for the creation of non-toxic, effective anticancer medicines.
References
- Benassi A, F Doria, V Pirota (2020) Groundbreaking anticancer activity of highly diversified oxadiazole scaffolds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21(22): 8692.
- Cragg GM, PG Grothaus, DJ Newamn (2009) Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chemical reviews 109(7): 3012-3043.
- Pawar SR, SS Jangam, SA Waghmare (2018) Anti-cancer herble drugs: An overview. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 8(4): 48-58.
- El Mansouri, AE (2020) Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking of new uracil analogs-1, 2, 4-oxadiazole hybrids as potential anticancer agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 30(19): 127438.
- Thakkar SS (2017) 1, 2, 4-Triazole and 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole analogues: Synthesis, MO studies, in silico molecular docking studies, antimalarial as DHFR inhibitor and antimicrobial activities. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 25(15): 4064-4075.
- Pace A (2015) Recent advances in the chemistry of 1, 2, 4-oxadiazoles. Advances in Heterocyclic chemistry 116: 85-136.
- Khan I, A Ibrar, N Abbas (2014) Oxadiazoles as privileged motifs for promising anticancer leads: Recent advances and future prospects. Archiv der Pharmazie 347(1): 1-20.
- Zareian B (2016) Synthesis, molecular docking study, and cytotoxic activity of 3, 4-diaryl-5-(4-pyridinyl)-1, 2, 4-oxadiazole. Medicinal Chemistry 12(4): 394-401.
- Othman AA, M Kihel, S Amara (2019) 1, 3, 4-Oxadiazole, 1, 3, 4-thiadiazole and 1, 2, 4-triazole derivatives as potential antibacterial agents. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 12(7): 1660-1675.
- Dos Santos Filho JM (2016) Conjugation of N-acylhydrazone and 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole leads to the identification of active antimalarial agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 24(22): 5693-5701.
- Gobec M (2015) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole analogs of resveratrol. Chemico-Biological Interactions 240: 200-207.
- Ergün Y (2010) Synergistic effect of [1H-[1, 2, 4] Oxadiazole [4, 3-a] quinoxalin-1-one] and antidepressant drugs in the mouse forced swimming test: Possible involvement of serotonergic pathway. European journal of pharmacology 630(1-3): 74-78.
- Al Soud YA, MN Al Dweri, NA Al Masoudi (2004) Synthesis, antitumor and antiviral properties of some 1, 2, 4-triazole derivatives. Il Farmaco 59(10): 775-783.
- Reddy KT, R Sreenivasulu, RR Raju (2019) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole linked imidazopyrazine derivatives as anticancer agents. J Ind Chem Soc 96: 1085-1090.
- Kala P (2020) Design, synthesis, and anticancer evaluation of 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole functionalized quinoline derivatives. Medicinal Chemistry Research 29(1): 136-144.
- Shamsi F (2020) Synthesis and SAR studies of novel 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole-sulfonamide based compounds as potential anticancer agents for colorectal cancer therapy. Bioorganic Chemistry 98: 103754.
- Ashok N, J Madhukar, G Sridhar (2021) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole linked 1, 2, 4-thiadiazole-pyrimidines as anticancer agents. Chemical Data Collections 32: 100653.