Competence Training and Incentives Medical Services Support the Achievement of Nurses’ Performances in General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang
Dr. Frans Salesman1* and Thresia Bayo2
1 Institute of Health Sciences, Citra Husada Mandiri Kupang, Indonesia
2Nusa Cendana University, Kupang-East Nusa, Indonesia
Submission: September 03, 2018; Published: September 12, 2018
*Corresponding author: Dr. Frans Salesman, Institute of Health Sciences, Citra Husada Mandiri Kupang, Indonesia, Tel: +6281337909998; Email: franssalesman@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Dr. Frans S, Thresia B. Competence Training and Incentives Medical Services Support the Achievement of Nurses’ Performances in General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang . JOJ Nurse Health Care. 2018; 9(4): 555766. DOI: 10.19080/JOJNHC.2018.09.555766.
Abstract
Background:Nurse gives professional nursing service to patients according to competence owned. Based on these services in the end of every year, nurses are given incentives for medical services as financial incentive.
Purpose: To analyze the impact of competence training and incentives medical services’ distribution upon the achievement of nurse’s performances in General Hospital of Prof W Z Johannes Kupang.
Material and Method:Observational survey research with cross sectional design. Population. Nurses in General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang Technique. Total sampling technique with number of samples 183 respondents. Inclusive criteria of samples are willing to be interviewed, nurse’s status, permanent offices without limitation from particular working unit or poly in hospital. Independent variable:
a) competence training
b) Incentives for medical services.
c) Dependent variable; Nurse’s performance achievement. Variables are measured by using Lickert scale. Information are recorded through questionnaire. Analyzes using linier regression.
Result: There are impacts of competence training (α=0; ß=0.489) and distribution of incentives for medical services (α=0.012; ß=0.152) upon nurse’s performances achievement in General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang.
Conclusion:The training of nursing service status that could increase competences among nurse with affair incentives for medical services’ distribution simultaneously end up in the increasing of nurse’s performances achievement in a hospital.
Keywords: Training; Competence; Incentives; Management; Performance.
Introduction
Nurse is a person who has competence along with other medical officers, gives professional nursing services to individuals, families, groups, or society whether they are healthy or sick based on knowledge and performance of nursing’s [1]. The application of nursing services in the form of medical aid helps doctors in diagnosing, full filling basic human needs of patients, identifying, preparing and giving medication, and take care all sickness of patient including trauma and medical crisis. All of competences are applied through professional and calm attitude by putting forward the philosophic of medical services that is “serve with a heart that is as clean as white uniform worn, without giving any peculiar service towards any patient from any tribe, religion and class”. A nurse, in doing the duties in hospital, should apply 12 kinds of a nursing service standard for mother and child, eyes, leprosy, orthopedic, infectious diseases, kidney, cancer, heart and artery, lunge and respiration, stroke, neuroscience, and drug addict. All of those standards are done based on procedure operational standard and working charge established by the management of nursing service quality in every hospital [2]. Every nurse is obliged to reach the target of performance every day, and then accumulated every year. Based on that, the nurses get incentives for medical services accordingly with indicator of financial incentive established by the management of the hospital. Accordingly, with the increasing need of quality service, that is not only in the core of medication, but also in additional service to overcome the deficiency of patients’ psychology during inpatients or outpatient process, there is a need of training in order to upgrade the knowledge, attitude, and skill of nursing service. Through Competences Based Training, employees in the organization can improve their knowledge, skills and skills to support achieving the organization’s vision and mission [3]. General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes as a hospital of education and reference of subspecialists should give competence training for its nurses. Education and training of nursing core competence are very much helping the nurses in increasing individual’s ability in doing the nursing practice [4,5]. It applies also to the distribution of incentives for medical services that goes accordingly with the need of management’s need.
In the pre-research on 10th August 2017, 20 nurses in first class units for inpatients are interviewed. It was found that all had not got the chance to have nursing training to upgrade their knowledge and skills in nursing status. It was found out also that 13 of them had not got incentives for medical services as their rights. Researchers also found many complains from patients upon nurses’ performances that did not reach the expectations who were getting inpatient’s services in the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang. This research analyzes the impact of training and distribution of incentives for medical services toward the nursing’ performances achievement in General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
Material and Method
This is an observational survey research with cross sectional design [6]. Population of the survey are nurses in General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang. The technique used is total sampling with 183 samples. Inclusive criteria of samples are willing to be interviewed, nurse’s status, permanent offices without limitation from particular working unit or poly in hospital. Independent variable:
a) Competence Training: Incentives for medical services. Dependent variable; Nurse’s performance achievement.
b) Both Variables are Measured by using Lickert Scale:
Competence Training is measured based on numbers and
types of training according to the nursing service standard in
the hospital; if
c) Incentives for medical services is measured based on the amount of commission given to the nurses on the end of every year according to the position and official period in the hospital. If the money given is less than the position and the official period, the score is 1;
If the money given is more or less enough according to the position and the official period, the score is 2; If the money given is according to the position and the official period, the score is 3; and if the money given is more than the position and the official period, the score is 4. Dependent variable: Nurse’s performance achievement is measured based on Minimum Service Standard established by Indonesian Health Minister’s Regulation Number 43 2016 about Minimum Standard of Health Service in Indonesia [7]. If it is not or less according to the regulation, the score is 1; If it is more or less enough according to the regulation, the score is 2; If it is according to the regulation, the score is 3; If it is more than the regulation, the score is 4. The information gotten from the respondents is recorded through questionnaire. Research period is from February 2018 until March 2018. The basis of the research is the Research Permission of the Director of Postgraduate Program of Nusa Cendana University Number 3218/UN15.8.1/ PP/2017, and Clerence Ethics from the Director of Hospital Prof WZ Yohanes Kupang Number 070/UM.314/III/2018.
Research Ethics
Informed Consent: The interviews are proceeded if there are written agreements from the respondents. Researchers gives agreement notice to be signed by respondents after giving useful explanation about the aim and the use of the research. If the respondent rejects, then there will be no force for the respondent to participate in the research.
Anonymity: Researchers is obliged to keep the confidentiality and privacy of the respondent by not write down the names of the respondents. Researchers only writes the codes of the respondents which only known to the researchers.
Confidentiality: Researchers guarantees the confidentiality of information and data given by respondents, and not using them for any other purposes. Data are analyzed by using Linear Regression. Respondents characteristics are: educational level and official duty period. All variables’ reliabilities are examined.
Result
Respondent Characteristics
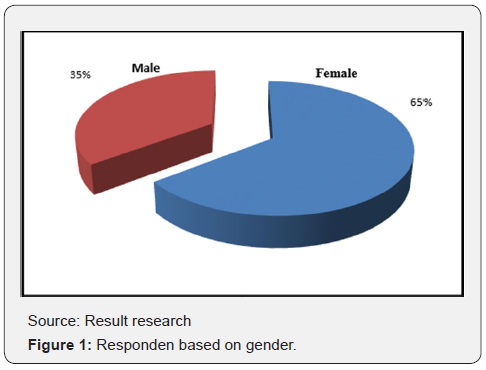
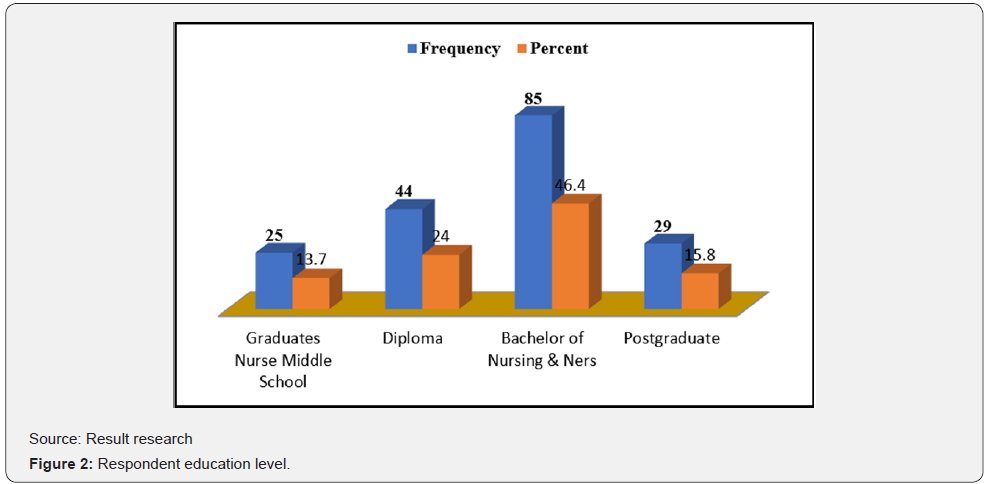
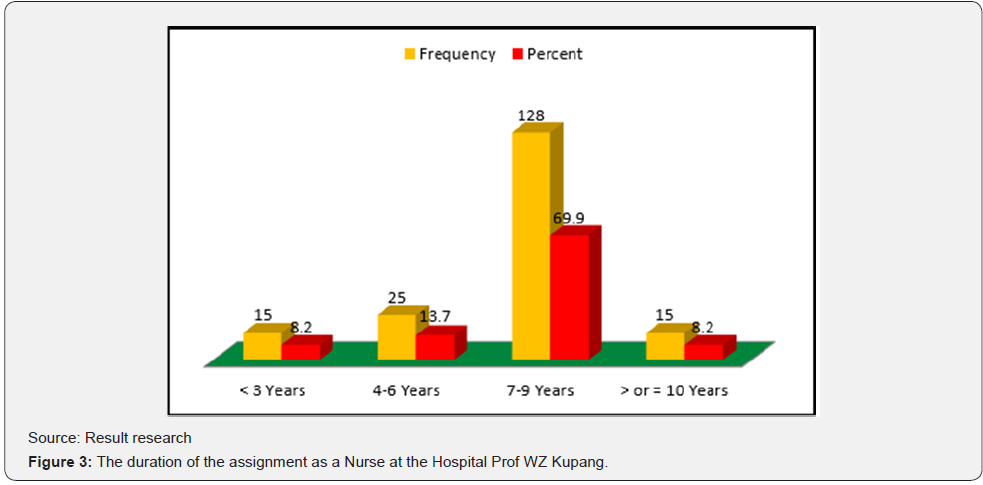
Respondents characteristics analyzed are: Gender, education and official period. Information about gender are shown in Figure 1: informs that 64 respondents (35%) are male and 119 respondents (65%) are female. Respondents’ educational level are shown in Figure 2. Information in Figure 2 explains that 25 respondents (13,70%) graduated from Nursing Medium School, 44 respondents (24%) graduated from diploma, 85 respondents (46%) graduated from Bachelor of Nursing and Profession Nurse, and 29 respondents (15,80%) graduated from Magister of Health/Nursing. Official duration of assignment as a nurse in the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang is shown in Figure 3. Information in Figure 3 explains that 15 respondents (8,20%) duration of assignment<3 years, 25 respondents (13,70%) duration of assignment 4-6 years, 128 respondents (69,90%) duration of assignment 7-9 years, and 15 respondents (8,20%) duration of assignment >or=10 years.
Regression Analyzes
Regression analysis of the influence of competency training and the distribution of medical services to the performance of nurses in hospitals Prof WZ Yohan Kupang is shown in Table 1, below table describes the information that variables of competence training effects the performance achievement (α=0; ß=0.489), so does the variables of incentives for medical services affects performance achievements (α=0.012; ß=0.152). If both are compared from tendency points of impacts toward performance achievements between the two independent variables, then variable of competence training (ß=0.489) is bigger than variable of incentives for medical services (ß=0.152).
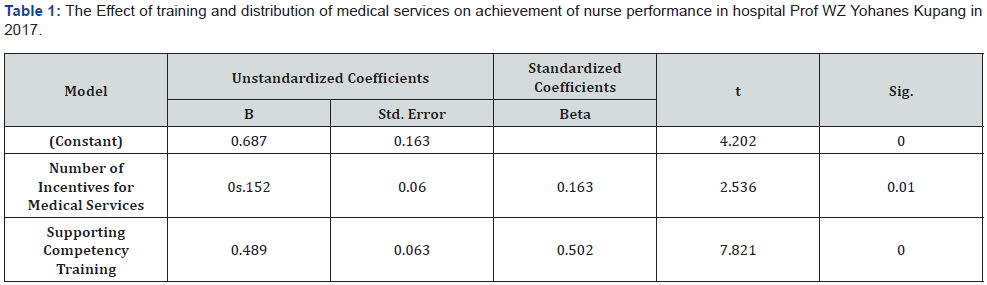
Dependent Variable: Performance achievements
Discussion
Competence Training and Nurse’s Performance
The competence of nursing services as an essential attribute of a nurse in doing nurse’s status to achieve performance targets set by management of hospital. The competence is obtained through formal education. A person is declared to have graduated and received a bachelor of nursing degree and/or nurse should have gone through a set of competency-based curriculum and then passed his knowledge and skills test in a period of learning, but another study states that the majority of new and skilled nursing students bathe patients in bed after they competency training. They have never obtained these skills during formal education at the university [8]. Other studies have found that nurses do not have the competence to manage diarrheal diseases in a professional manner before completing diarrhea handling competency training [9]. The importance of professional nursing services competence to ensure the quality of health services provided by a nurse to patients. To measure the significance of the competence according to the need in work field, a nurse has to follow a structured test to get Registered Nurses as a professional nurse. David McCleland stated that a competence is measured through knowledge, skill, and the ability needed in doing the duties. Competence is believed as key factor of success for everyone in the job [10]. Every nurse, when entering work sphere with several characteristics of aim, missions of health service organization and organization culture that might be different from any other organization, is demanded to always upgrade the quality of knowledge and skill through technical training, at least 20 hours a year, in 12 nursing status standards in hospitals according to the minimum service standard of health sector that is established by the Regulation of Indonesian Ministry of Health [11]. A nurse’s competence is one of inputs in the process of health service reaching the performance target of nursing services. The indicators are: on-time service, respond time, time motion, nursing services according to standard procedure, standard and ethics of services, no mistake in nursing status, numbers of patients nursed in a day, no complains form patients, and patients’ satisfaction. Competence is analogical to “iceberg” on the water, while knowledge and skill as foundation that can carry the upper part. The strength of lower parts needs to be injected with competence training held by internal organization of the hospital or other stakeholders that has interest in nursing services. The analyzes’ result of this research shows that there is impacts of competence training toward performance achievement of nurses in the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupangwith α=0; ß=0.489, which means the more quantities and types of competence training followed by a nurse triggers the increasing of indicators of nursing services performance in the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang. The same thing was found in Private Hospital Class-B in Makasar: that there is a significant impact between the intervention of training with performance achievements through indicators of communication with nursed, hospital’s staffs responds, and communication about drugs and other health information [12]. The importance of communication to convey information to mothers who have infants under five in Northwest Ethiopia. It was found in research at Dabat Health Center that nurses provided sufficient information to mother’s a boat the importance knowledge of giving exclusive breast feeding for children’s health care and to achieve performance targets for the provision of exclusive breast feeding [13]. Submission of information as knowledge new, not only given to mothers, but given by senior nurses as educators to fellow junior nurses a new learning in providing health information in services to mothers of toddlers in other places [14]. The competency themes in this document reflect a need for clinical competence; sound teaching and assessment skills reflective of an adult learning approach; and organizational and communication skills [7].
Incentives for Medical Services
This incentive stimulates nurses to increase their work productivity toward the achievement of performance’s targets established by the Management of the hospitals. Incentives for medical services in the form of financial incentive that is given by the management of the hospital for their health officers usually happens in the end of calendar year. Nevertheless, there is also a non-financial incentive and social incentive that is given by the management of the hospitals for successful officer in the form of promotion, appreciation and acknowledgement for the work’s result. In this research, the content of the variables of incentives for medical services is financial incentive. The result of regression analyzes finds out that there is a significant impact of the distribution of medical services based on index point, position, work duties, and work risk toward performance achievements of the nurses in the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang (α=0.012; ß=0.152). These statistic points mean, the bigger amount of incentives received, the higher performance achievement. Every nurse expects a fair distribution the incentives, as it is found in Lumajang hospital, where most of the respondents expect the components of educational level, position level, competence level, and the level of work risk are used as components for the formulation of the distribution of incentives in inpatient unit of Dr. Haryoto Hospital Lumajang [15]. When the management does not distribute incentives not according to the formula of financial incentive, the work stability of the nurses becomes instable and this will hampered the services given to the patients.
Weakness of the Research
The research’s result where there is an impact of competence training (α=0; ß=.0489) and the distribution of incentives for medical services (α=0.012; ß=0.152) toward the performance achievements of nursing has only internal validity, since the samples are all from the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang. It means that, this research only applicable in the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang. We give permission for any other researchers who wants to use this research as a reference for the next research in other places.
Conclusion
The training of nursing service status increases the competence of nurses along with the fair distribution of incentives for medical services, simultaneously increases performance achievement of the nurses in a hospital. The management leaders of hospitals need to consider these two aspects of this research in order to guarantee the survival of the organization and increase the quality of hospital’s services which focus on the satisfaction of patients.
Acknowledgment
Appreciation for the Director of the General Hospital of Prof WZ Johannes Kupang with staffs, researches’ assistants who had contributed for this research. Appreciation also given to Head of the Body of Nusa Cendana University’s Postgraduate Program. Head of Study Program of Society Health Science, Head of Statistic Bureau of East Nusa Tenggara Province, Head of Health Department of East Nusa Tenggara Province who had provided data, information, and documents used by researchers to finish this writing.
References
- Ministry of Law and Human Rights (2014) Law of The Republic of Indonesia 8 of 2014 About Nursing, p. 1-2.
- Ministry of Health of The Republic of Indonesia (2015) Regulation of The Minister of Health the Republic Indonesia Number 10 of 2015 About Nursing Services Standards In Special Hospitals, pp. 410-423.
- Prabawati I, Meirinawati, Oktariyanda AT (2018) Competency-based training model for human resource management and development in public sector. Journal of Physics Conference Series 953(1): 012157.
- Fordham AJ (2005) Using a competency based approach in nurse education. Nurs Stand 19(31): 41-8.
- Fang qin Wu, Yan ling Wang, Ying, Wu, Ming Guo (2014) Application of nursing core competency standard education in the training of nursing undergraduates. International Journal of Nursing Sciences 1(4): 367- 370.
- World Health Organization (2016) Nurse Educator Core Competencies.
- Solvik E, Struknes S (2018) Training nursing skills: A quantitative study of nursing students’ experiences before and after clinical practice. Nursing Research and Practice.
- Desta KB, Assimamaw TN, Ashenafi DT (2017) Knowledge, practice, and associated factors of home-based management of diarrhea among caregivers of children attending under-five clinic in Fagita Lekoma district, Awi Zone, Amhara regional state, Northwest Ethiopia.
- Gaol LJC (2014) Human Capital. Human Resource Management; Concepts, Theories and Development in Public and Business Organizations.
- Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. (2014) Regulation of the minister of health the republic Indonesia number 43 of 2014, Concerning standard minimal health services.
- Saleh A, Ramly M, Gani UM, Suriyanti (2016) Factors affecting the job satisfaction and performance of nurses private hospitals class b in makassar. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research 5(10).
- Wassie MA, Bayu HN, Tebeje BN, Kasa FS (2017) Knowledge and attitude towards exclusive breast feeding among mothers attending antenatal and immunization clinic at Dabat Health Center, Northwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional institution based study. Nursing Research and Practice.
- Alharbi AH, Almutairi AF, Alhelih EM, Alshehry AS (2017) The learning preferences among nursing students in the king Saud University in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Nursing Research and Practice.
- Sudibyo A (2006) Constructing a formula for remuneration of incentive distribution for nurse’s service based on performance related pay.






























